
THE
Stanley Gibbons Philatelic Handbooks.
SAINT VINCENT
WITH
Notes and Publishers’ Prices.
BY
FRANCIS H. NAPIER
AND
E. D. BACON.
STANLEY GIBBONS, LIMITED,
391, STRAND, LONDON.
1895.
The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Stanley Gibbons Philatelic Handbooks:
Saint Vincent, by Francis H. Napier and E. D. Bacon
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and most
other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no restrictions
whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of
the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at
www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the United States, you'll have
to check the laws of the country where you are located before using this ebook.
Title: The Stanley Gibbons Philatelic Handbooks: Saint Vincent
Author: Francis H. Napier
E. D. Bacon
Release Date: December 14, 2018 [EBook #58472]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK GIBBONS PHILATELIC HANDBOOKS: ST VINCENT ***
Produced by MWS, Adrian Mastronardi, The Philatelic Digital
Library Project at http://www.tpdlp.net and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive/American Libraries.)

THE
Stanley Gibbons Philatelic Handbooks.
SAINT VINCENT
WITH
Notes and Publishers’ Prices.
BY
FRANCIS H. NAPIER
AND
E. D. BACON.
STANLEY GIBBONS, LIMITED,
391, STRAND, LONDON.
1895.

THE
Stanley Gibbons Philatelic Handbooks.
SAINT VINCENT.
WITH
NOTES AND PUBLISHERS’ PRICES.
BY
FRANCIS H. NAPIER
AND
E. D. BACON.
London:
STANLEY GIBBONS, LIMITED,
391, STRAND.
1895.
391, Strand, London.
The large number of collectors, not only in this country, but also on the other side of the Atlantic, who now make the postal issues of the various West Indian Colonies of Great Britain the object of their quest, justifies us in believing that the present volume (the fourth of the series) will be received with as much interest as that which has been evinced for the preceding volumes.
The authors of this Handbook, Lieut. F. H. Napier, R.N., and Mr. E. D. Bacon, have in preparation a Handbook on the Stamps of Barbados, which we hope will be ready for publication in the course of the present year.
The prices quoted will in some cases be found higher than the prices given in our General Catalogue and Price List, but it must be borne in mind that those in these Handbooks are specimens of more than average quality, for it is a fact now generally recognized by all philatelists that a specimen in exceptional condition commands a higher price than that which rules for an average specimen.
We have priced only those varieties which we have in stock in certain quantities, but it must not be concluded from this that all those unpriced are of such rarity or value that we are unable to supply them.
STANLEY GIBBONS, Limited.
May, 1895.

The prehistoric times of Philately may be said to have ceased in 1863, when the publication of the Stamp Collector’s Magazine and the Timbre-Poste commenced. The few and meagre catalogues which preceded them in 1862—such as those of Mount Brown and Dr. Gray in England, Moens in Belgium, and Potiquet in France—can only be looked upon as archaic productions, interesting certainly because of their associations, but of no appreciable utility now-a-days to the student of stamps. It is, however, worthy of remark that the difference between imperforate and perforated stamps was then recognized, as they are distinguished from each other in the catalogues both of Moens and Potiquet; this shows that even at that early date the true philatelic spirit was already abroad.
When studying countries of which the philatelic histories begin prior to 1862 or 1863, we are dependent entirely on public notices emanating from postal authorities, official records, and information derived from the books of firms who manufactured the stamps, or supplied the plates, paper[6] &c. for printing them, sources of knowledge not always easy of access. Luckily for our present purpose, seeing that postage stamps were not adopted in St. Vincent until 1861, we are not so dependent on these official or commercial records, having a great number of philatelic works, such as catalogues and periodicals, to rely upon, all of which we have carefully searched and collated; at the same time we have received great assistance from Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., Limited, the printers of the stamps included under the head of Section I. This Company have been good enough to furnish us with a complete list of every stamp sent out by them to the Island, a copy of which we give in Appendix D, and we acknowledge with thanks our indebtedness to the Managing Director and Secretary, for the valuable material they have so considerately placed at our disposal, which has enabled us to satisfactorily clear up several points that before were more or less obscure. It will also be seen that the list helps in no small degree to form what we hope may be considered a fairly complete history of the stamps of this Island.
Our method of designating and arranging the perforations of the stamps supplied to the Colony by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. from 1861 to 1882 is a novel one, but we think it will remove the difficulty that has hitherto been felt in classifying the perforations, as it has always seemed impossible to assign any limit to the number of so-called compounds, which, if we are to believe some recently-published catalogues, must indeed be infinite, and incapable of any classification whatsoever. For instance, in one of these catalogues, five simple and seven compound perforations are given to the stamps of 1861; to those of 1866 seven simple and five compound; to those of 1869 four[7] simple and five compound; and so on through later issues. On the other hand, another catalogue, also of recent date, is content to make the general statement that the issues up to 1880 are perforated 11½ to 15, simple and compound. This is at first sight an apparently innocent statement, but in reality it opens up an appalling perspective of interminable lists. We think we shall have justly earned the gratitude of the many philatelists who (as far as it is compatible with strict accuracy) desire above all things simplicity of arrangement, in having banished from the lists all mention of these fanciful perforations, whether simple or compound. The fact is that in the St. Vincent stamps printed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., with the exception of one (that is the yellow-green Six Pence of 1862), there are only two simple perforations and one compound, and although this last makes its appearance very frequently, it is always exactly the same in every issue in which it occurs. No doubt the confusion which has arisen has been caused by the too zealous and indiscriminate use of a perforation gauge limited to two centimetres, and applied to single specimens of stamps, which has led true compounds to be confounded with those apparent deviations from the normal gauge arising from irregularities in the spacing of the holes, irregularities existing in both of the two machines used for these stamps by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., but in a very much greater degree in one of them than in the other.
The whole point of our argument lies in this, that to separate perforations, it is only necessary to differentiate between those produced by distinct machines, and that there is no object in collecting the same stamp over and over again merely because the perforation varies within a space of 2 centimetres, if it can be shewn that the stamps[8] were all perforated by one and the same machine. Hitherto it has been the great aim of collectors and writers to try and gather together every variety of perforation that can be found on a stamp of any one particular issue—this quite regardless of the cause from which these varieties arise. Our method obviously removes many difficulties, and greatly simplifies the arrangement of all stamps that have been perforated by machines in which the pins were irregularly spaced. We further claim that our system is based upon strictly scientific lines, and that it is applicable, not only to St. Vincent, but to the other British Colonies whose stamps were printed and perforated by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., although it must be borne in mind that in some of these there were other machines used, besides those we describe for St. Vincent.
As in the Notes we go fully into all details of perforation, it is not now necessary to dwell further upon this point; we only wish to insist on the importance of the subject, as it was the uncertainty hitherto regarding it that first induced us to particularly examine the stamps of St. Vincent, and that now leads us to make public the results of our investigations.
In order to make the list of the varieties of perforation as complete as possible, we have during the last three years examined a very large number of St. Vincent stamps, so many that we think it is highly unlikely there still remains anything to be added to the tables of perforations (Appendices B and C), and this in spite of the gaps that will be seen to exist in them.
The history of the use of distinctive postage stamps in St. Vincent dates from May 1st, 1860, when the Colonial Authorities took over from the Imperial Government the entire management of the Post Office of the Island, which,[9] like the posts of many of the other British West Indies, had up to that date been administered by the Postmaster-General of the United Kingdom. The Local Legislature of the Island thereupon passed an Ordinance, known as the “Post Office Act,” which became law on June 14th, 1860. This Act, amongst other things, provided for the appointment of a Colonial Postmaster, a General Post Office for the Island, rates of postage, and the issue of postage stamps. As many of the clauses of the Ordinance possess a good deal of interest for Philatelists, we give, in Appendix A, a copy of those which, from a collector’s point of view, may be considered the more important ones. After the passing of the Act postage stamps were ordered from England, and, as we shall afterwards see, a supply was despatched to the Island on March 27th, 1861. The stamps were no doubt put into use immediately on their arrival, as a statement in the Blue Book of the Colony for 1861 gives the amount received for postage during that year as £158 16s. 5d., as against £78 5s. 4d. for 1860, and the increase is accounted for by the “Sale of Postage Stamps which were obtained in 1861.” This fixes with certainty the date of the first issue, but when we commenced to study those of the later issues, and attempted to make a proper chronological list, we found there were many discrepancies in the published catalogues we consulted; from them we turned to contemporary notices in the pages of the Timbre-Poste, the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, the Philatelist, the Philatelic Record, and other less celebrated periodicals, in hopes of removing our difficulties. Unfortunately Philately was decidedly under a cloud from the middle to near the end of the seventies, and this is just the time during which a number of issues took place in St. Vincent. The Stamp Collectors Magazine ceased with[10] 1874, the Philatelist, never a good source of original information, stopped in 1876, and after that the Timbre-Poste alone filled the breach until the Philatelic Record made its appearance in 1879. It is with regard to this important subject of dates that Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s list has been so extremely useful, as we have thereby been enabled to check the notices scattered through the pages of the various philatelic works we have mentioned. We therefore believe that the dates of issue given by us will be found to be more accurate than those in any previous publication.
With regard to describing the colours of the stamps, we have met with the usual difficulty of at once satisfying our own opinions, and those of various friends whom we have occasionally questioned as to what they would call the colour of such or such a stamp, and we do not think we have got out of the difficulty either better or worse than other compilers of catalogues usually do, the differences of opinion we have met with, as to the proper names by which to call certain shades, being generally hopelessly irreconcilable. No reference to other works is of much use; for instance, we find the one shilling of 1874 called “dirty rose colour” in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, “dull rose-pink” in the Philatelist, “lilac-rose” in the London Society’s list, “pink” by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., “rose sale” in Moens’ Catalogue, and “lake” in Messrs. Stanley Gibbons & Co.’s price list. It must be confessed that all this is very confusing, and we are afraid that collectors will always find the task of distinguishing between the earlier red shillings of St. Vincent rather a difficult one. Fortunately there are not many cases in this Colony where the identification of a particular stamp depends on the description of its colour[11] alone, as we are generally helped to the desired conclusion either by the watermark or the perforation.
We think that the two plates of autotype illustrations accompanying this work will be found something more than mere embellishments, and will be of real use to our readers as a means of discriminating between genuine and false surcharges, and also of distinguishing the various perforations alluded to in our text.
There are many interesting questions connected with the perforating machines used by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., as well as with the papers, unwatermarked and watermarked, employed by them for the numerous British Colonies to which they supplied stamps; but in this handbook we do not propose to enter into these questions more fully than is absolutely necessary for elucidating our subject. We intend to do so at greater length in a handbook of the stamps of Barbados, now in course of preparation. This country is much more complex than St. Vincent, both in its watermarks and perforations, and a thorough knowledge of the stamps of the latter Colony will prove to be of the greatest assistance when the more difficult subject of Barbados comes to be studied.
The stamps of St. Vincent are remarkable, inasmuch as this is the only British Colony that still continues to print the whole of its stamps from line-engraved plates. This is certainly noteworthy when we bear in mind that since the year 1883 the stamps have been printed by Messrs. De La Rue & Co., whose name is generally associated with surface-printed stamps.
The change of printers, although the same plates have always been employed, marks such a distinct epoch in the history of the stamps, that we have thought it advisable to[12] place those furnished by the two different firms under separate headings, and so break up the Reference List into two parts, under the nomenclature of Sections I. and II.
It will be observed that our lists contain no mention whatever of postal fiscals. Such stamps do not exist in St. Vincent, although M. Moens and other writers have chronicled them. All postmarked specimens that may be met with must have either been passed through the post by inadvertence, or been obliterated by favour.
In concluding these remarks we beg to acknowledge with thanks the kindness of Mr. T. Maycock, Mr. M. Giwelb, and Mr. W. H. Peckitt, who have lent us stamps for illustration, and of Messrs. Whitfield King & Co., who sent us for examination a great number of entire sheets of the De La Rue printings, which have been of the greatest assistance to us in writing the notes to Section II. of this Handbook.
Stamps printed and perforated by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., London, from 1861 to 1881 inclusive.
May 1861.
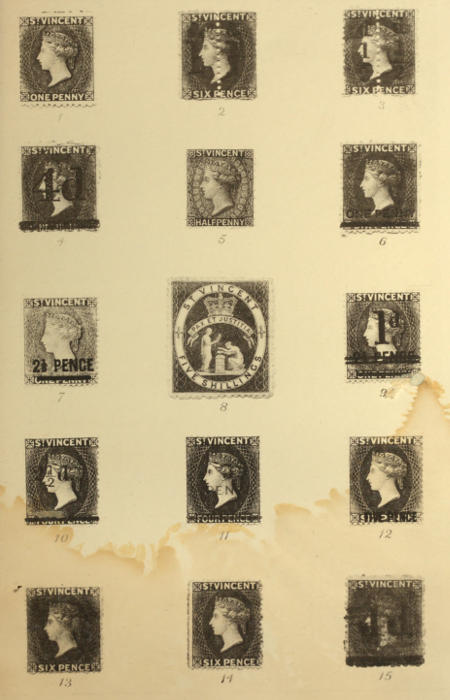
| Type | Shape, upright rectangular—22¼ mm. × 19¼ mm. Diademed head of Queen to left on engine-turned background. Straight labels above and below, with “St. Vincent” and value in words in white block capitals on solid background. |
| Illustration No. 1. | |
| Paper | White wove, inclined to greyish, rather rough, and varying considerably in thickness. |
| Watermark | None. |
| Gum | Yellowish. |
| Perforation | A.[1] |
| Illustrations 16 and 17. |
[1] This is a roughly punctured, slightly irregular perforation, varying from 14 to 15, but generally about 14½. See Note to Section I.
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 1 | 1d., bright rose-red | 5 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| 2 | 6d., blue-green | 12 | 6 | 3 | 0 |
| Variety. Imperforate vertically. | |||||
| 2a | 6d., blue-green | ||||
| Variety. With double perforation horizontally. | |||||
| 3 | 1d., bright rose-red | ||||
| Varieties. Imperforate. | |||||
| 4 | 1d., bright rose-red | ||||
| 5 | 6d., blue-green | ||||
1862.
| Type and Paper | As in Issue 1. |
| Watermark | None. |
| Gum | Yellowish. |
| Perforation | C.[2] |
| Illustrations Nos. 13 and 14. |
[2] This is a clean cut, slightly irregular perforation, generally 15½, sometimes 15, and more rarely 14½. See Note to Issue 2.
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 6 | 6d., yellow-green | 10 | 0 | ||
1863-1866.
| Type and Paper | As in Issue 1. |
| Watermark | None. |
| Gum | Yellowish to yellow-brown. |
| Perforation | [3]B and B × A.[4] |
| Illustrations Nos. 18, 19, and 20. |
[3] This is a clean cut, very irregular perforation, varying from 11 to nearly 13. See Note to Section I.
[4] Throughout this handbook, in describing perforations made by two machines, the first given measurement denotes the horizontal gauge, and the second the vertical.
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| (i.) Perforated B. | |||||
| 7 | 1d., bright rose-red | 5 | 0 | 2 | 6 |
| 8 | 6d., blue-green | 20 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| (ii.) Perforated B × A. | |||||
| 9 | 1d., bright rose-red | ||||
August 1866.
| Type and Paper | As in Issue 1. |
| Watermark | None. |
| Gum | Yellowish, and white. |
| Perforation | A, B, and B × A. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| (i.) Perforated A. | |||||
| 10 | 1s., dark slate-grey | 20 | 0 | ||
| 11 | 1s., greyish-purple | ||||
| (ii.) Perforated B. | |||||
| 12 | 4d., deep bright blue | 17 | 6 | 12 | 6 |
| (iii.) Perforated B × A. | |||||
| 13 | 1s., dark slate-grey | 45 | 0 | 17 | 6 |
| 14 | 1s., greyish-purple | ||||
April 1869.
| Type and Paper | As in Issue 1. |
| Watermark | None. |
| Gum | Yellowish and white. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 15 | 1s., indigo | 65 | 0 | 25 | 0 |
September 1869.
| Type and Paper | As in Issue 1. |
| Watermark | None. |
| Gum | Yellowish. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 16 | 4d., deep bright yellow | 60 | 0 | 35 | 0 |
| 17 | 1s., bright brown | 65 | 0 | 22 | 6 |
June 1871.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper | White wove, varying considerably in thickness. |
| Watermark | A six-pointed Star, measuring 13 mm. from point to point across the Star; generally regular, but sometimes varying a little in the shape of the rays. |
| Gum | Yellowish, and white. |
| Perforation | A and B × A. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| (i.) Perforated A. | |||||
| 18 | 1d., black | 2 | 6 | 0 | 9 |
| 19 | 6d., dull blue-green | ||||
| 20 | 6d., dark blue-green | 20 | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Variety. Imperforate vertically. | |||||
| 21 | 1d., black | ||||
| (ii.) Perforated B × A. | |||||
| 22 | 1d., black | 20 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
June 1872.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper and Watermark | As in Issue 7. |
| Gum | Yellowish to brownish-yellow. |
| Perforation | B and B × A. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| (i.) Perforated B. | |||||
| 23 | 1s., bright rose-red | 17 | 6 | ||
| 24 | 1s., deep rose-red | 17 | 6 | ||
| 25 | 1s., dull red | 17 | 6 | ||
| (ii.) Perforated B × A. | |||||
| 26 | 1s., bright rose-red | ||||
| 27 | 1s., deep rose-red (?) | ||||
| 28 | 1s., dull red (?) | ||||
Early in 1874.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper and Watermark | As in Issue 7. |
| Gum | Yellowish to brownish-yellow. |
| Perforation | B and B × A. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| (i.) Perforated B. | |||||
| 29 | 1s., pale violet-rose | ||||
| (ii.) Perforated B × A. | |||||
| 30 | 1s., pale violet-rose | 16 | 0 | ||
1875.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper and Watermark | As in Issue 8, but the paper is usually strongly toned by the gum. |
| Gum | Yellow-brown. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 31 | 1s., dark claret | 70 | 0 | 17 | 6 |
February 1877.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper and Watermark | As in Issue 7. |
| Gum | Yellowish, and white. |
| Perforation | A, B, and B x A. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| (i.) Perforated A. | |||||
| 32 | 6d., pale yellow-green (October 1878) | 15 | 0 | ||
| (ii.) Perforated B. | |||||
| 33 | 1s., bright vermilion-red (June 1880) | 30 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| (iii.) Perforated B × A. | |||||
| 34 | 6d., pale yellow-green (February 1877) | 15 | 0 | 5 | 6 |
| 35 | 1s., bright vermilion-red ( ” ” ) | 40 | 0 | 12 | 0 |
July 1877.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper and Watermark | As in Issue 7. |
| Gum | Yellow-brown to white. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 36 | 4d., dark deep blue | 40 | 0 | ||
May 1880.
| Type | A provisional stamp of One Penny made locally by surcharging “d./1” twice vertically, in red, on the Six Pence, dark blue-green, of Issue 7, the two halves of this stamp being divided vertically by a line of perforation gauging 12. Illustration No. 2. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 7. |
| Perforation | A, and 12 on one side. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 37 | “1d.,” in red, on right half of 6d., dark blue-green | 70 | 0 | 70 | 0 |
| 38 | “1d.,” in red, on left half of 6d., dark blue-green | 70 | 0 | 70 | 0 |
| Variety. With additional line of the local perforation. | |||||
| 39 | “1d.,” in red, on right half of 6d., dark blue-green | ||||
June 1880.
| Types | As in Issue 1 for 1d. and 6d. |
| New type for 5s. Shape, large upright rectangular—30 mm. × 25½ mm. Royal Crown over white scroll, inscribed “Pax et Justitia,” in small coloured block capitals, below which are allegorical figures, the whole contained in white oval band, 2 mm. in width. The band is inscribed St. Vincent above, and Five Shillings below, in coloured block capitals; and the spandrels and background are composed of engine-turning. Illustration No. 8. | |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 7. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 40 | 1d., pale grey-green | 10 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 41 | 6d., bright yellow-green | 60 | 0 | 12 | 6 |
| 42 | 5s., deep rose-red | £8 | 10 | ||
September 1881.
| Type | A provisional stamp of One Halfpenny, made locally by surcharging “d/½” twice vertically, in red, on the Six Pence, bright yellow-green, of Issue 14, the two halves of this stamp being divided vertically by a line of perforation gauging 12. The figure “1” of the fraction has a curved serif. Illustration No. 3. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 14. |
| Perforation | B, and 12 on one side. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 43 | “½d,” in red, on right half of 6d., bright yellow-green | 30 | 0 | ||
| 44 | “½d.,” in red, on left half of 6d., bright yellow-green | 30 | 0 | ||
| Variety. Figure “1” of fraction has a straight serif. | |||||
| 45 | “½d.,” in red, on half of 6d., bright yellow-green | 80 | 0 | ||
November 1881.
| Type | A provisional stamp of Four Pence, made locally by surcharging “4d.,” in black, on the One Shilling, bright vermilion-red, of Issue 11. The original values are obliterated by black bars printed across the sheet. Illustration No. 4. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 11. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 46 | “4d.,” in black, on 1s., bright vermilion-red. | ||||
December 1881.
| Type | A provisional stamp of One Penny, made locally by surcharging “One Penny,” in black, on the Six Pence, bright yellow-green, of Issue 14. The original values are obliterated by black bars printed across the sheet. Illustration No. 6. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 14 |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 47 | “One Penny,” in black, on 6d., bright yellow-green | 60 | 0 | 60 | 0 |
December 1881.
| Types | As in Issue 1 for 1d. and 4d. New type for ½d. Shape, small upright rectangular—20 mm. × 17 mm. Diademed head of Queen to left on engine-turned background. Straight labels above and below, with St. Vincent and Halfpenny in white block capitals on background of solid colour. Illustration No. 5. |
| Paper and Watermark | As in Issue 7. |
| Gum | White. |
| Perforation | B. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 48 | ½d., orange-yellow | 0 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| 49 | 1d., drab | 1 | 0 | ||
| 50 | 4d., bright ultramarine | 12 | 6 | ||
Stamps printed and perforated by Messrs. De La Rue & Co., London, from 1883 to present time.
January 1883.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper | White wove, smooth, and slightly surfaced. |
| Watermark | A Crown over “C A.” |
| Gum | White, and pale yellowish. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 51 | 1d., drab | 5 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 52 | 4d., bright blue | 15 | 0 | ||
February 1883.
| Type | A new value of Two Pence Halfpenny, made by surcharging “2½ Pence,” in black, on the One Penny, printed in rosy-lake, the original value being obliterated by a bar 14 mm. in length. Illustration No. 7. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 53 | “2½ Pence,” in black, on 1d., rosy-lake | 2 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
October 1883.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 12. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 54 | 4d., dull blue | ||||
| 55 | 6d., bright green | 20 | 0 | ||
| 56 | 1s., orange-vermilion | 15 | 0 | ||
September 1884.
| Types | As in Issues 1 and 18. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 12. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 57 | ½d., dark green | 7 | 6 | 4 | 0 |
| 58 | 4d., ultramarine | 60 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| Variety. Prepared for use, but never issued. | |||||
| 59 | ½d., orange-yellow | ||||
March 1885.
| Type | A provisional stamp of One Penny, made locally by surcharging “1d,” in black, on the 2½d. of Issue 20. The values “2½ Pence” are obliterated by double lines 1 mm. apart, printed across the sheet. Illustration No. 9. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 60 | “1d,” in black, on “2½ Pence” on 1d., rosy-lake | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
April 1885.
| Types | As in Issues 1 and 18. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 61 | ½d., dark green | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 62 | 1d., carmine | 0 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| 63 | 4d., red-brown | 12 | 0 | ||
June 1886.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 64 | 1d., pink | 1 | 0 | ||
| 65 | 1d., rosy-lake | ||||
| 66 | 4d., purple-brown | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| 67 | 4d., lake-brown | 2 | 6 | 2 | 0 |
October 1888.
| Types | As in Issues 1 and 14. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 68 | 6d., dark lilac | 5 | 0 | ||
| 69 | 5s., lake | 10 | 0 | ||
August 1889.
| Type | A stamp of Two Pence Halfpenny, made by surcharging “2½ Pence,” in black, on the One Penny, printed in blue, the original value being obliterated by a bar 14 mm. in length (surcharge of same type as in Issue 20). Illustration No. 7. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 70 | “2½ Pence,” in black, on 1d., milky-blue | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
August 1890.
| Type | A provisional stamp of Two Pence Halfpenny, made locally by surcharging “2½d.,” in black, on the Four Pence, lake-brown, of Issue 25. The original values are obliterated by black bars, printed across the sheet. Illustration No. 10. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 71 | “2½d.,” in black, on 4d., lake-brown | 15 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Variety. Without the fraction line. | |||||
| 72 | “2½d.,” in black, on 4d., lake-brown | ||||
November 1890 to 1891.
| Type | As in Issue 1. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 73 | “2½ Pence,” in black, on 1d., bright blue | 0 | 5 | 0 | 3 |
| 74 | 6d., pale red-lilac | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 75 | 6d., deep red-lilac | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 76 | 1s., vermilion-red | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
November 1892.
| Type | A provisional stamp of Five Pence, made locally by surcharging “5—Pence” (in two lines), in carmine, on the Four Pence, lake-brown, of Issue 25. The original values are obliterated by carmine bars printed across the sheet. Illustration No. 11. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 77 | “5 Pence,” in carmine, on 4d., lake-brown | 8 | 0 | 10 | 0 |
March 1893.
| Types | As in Issue 1 for 4d. The Five Pence is made by printing the Six Pence in a new colour, and surcharging “Five Pence” (in one line), in black, over the original value. Illustration No. 12. |
| Paper, Watermark, and Gum | As in Issue 19. |
| Perforation | 14. |
| Unused. | Used. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s. | d. | s. | d. | ||
| 78 | 4d., canary-yellow | 0 | 8 | 0 | 8 |
| 79 | “Five Pence,” in black, on 6d., dull carmine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 80 | “Five Pence” ” ” carmine-brown | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |

This section of the Reference List comprises all issues printed and perforated by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., London; that is, from the first issue of 1861 until the end of 1881, when the last stamps printed by this firm made their appearance. For about half this time unwatermarked paper was used, and afterwards each stamp was watermarked with a star. We shall consider these two papers, as well as their minor varieties, in later notes, but we must here give a detailed description of the perforations, three simple and one compound, found in the stamps included in Section I. During all this time only two perforating machines were employed, except in 1862, when for one particular stamp, namely, the yellow-green Six Pence, another machine was used. With this exception all the stamps printed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. were perforated by one or the other of the two first-mentioned machines, and it is of these two that we now propose to treat, leaving the description of the perforation of the 1862 Six Pence to the note on Issue 2, as it is altogether an exceptional stamp, and need not be taken into account just at present.
The two machines we have now to consider were both[30] single-line, or guillotine ones; that is, they made but one line of perforation at a single stroke. These two machines, as well as the perforations made by them, we have elected to call “A” and “B,” so that in the Reference List the perforations of the stamps are called “A” or “B,” or “B × A,” instead of being, as is usual in philatelic writings, labelled with a number denoting the number of holes found in a space of 2 centimetres. Further on we shall endeavour to make plain and justify our reasons for so doing.
The method now in use for describing the perforations of stamps succeeded a previous clumsy and inaccurate system of counting the actual number of notches along the top or bottom of a stamp, as well as those down one side, so that the perforation of each stamp was denoted by two numbers. These numbers depended as much on the size of the stamp as on the spacing of the holes, and we suppose the system proved to be unworkable, as we do not think it was ever adopted in a catalogue, although it was certainly the first manner in which philatelic writers ever specified differences of perforation. It was soon abandoned for the well-known method in general use at the present day.
This latter system, invented by Dr. Legrand, was evidently intended by its original contriver to apply to lines of perforation of which the holes were so regularly spaced that all intervals of 2 centimetres in the same line contained the same number of holes, all these holes being exactly the same distance apart. Irregularity in the spacing of the holes does not seem to have been contemplated, but, as the vast majority of machines make holes spaced at regular intervals, this system of taking a gauge of 2 centimetres, applying it to a line of perforations, and counting the holes contained[31] in that space in order to get a number by which that particular perforation may always be identified, works admirably in practice in by far the greater number of cases. St. Vincent is one of those cases in which it entirely fails to satisfy our requirements (that is, in as far as the stamps of Section I. are concerned), and its misuse has led to the recording of such a bewildering number of different perforations, simple and compound, that no one has ever yet been bold enough to give a properly arranged list of them, or to attempt to explain how so many varieties arose. A description of the two perforations will explain all this.
That made by the A machine is well known in many other British Colonies—Antigua, Bahamas, Barbados, Ceylon, Grenada, Natal, Queensland, St. Helena, Trinidad, Turks Islands, Western Australia—that is, in most of the Colonies whose stamps were printed from plates prepared by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., and is one of the best known perforations in the world of Philately. Although its eccentricities are trifling compared with those of its fellow, the B machine, since it was in use in St. Vincent before that one, we take the description of its perforation first.
The gauge in 2 centimetres varies from 14 to 15, this variation arising from a slight, but frequent, irregularity in the spacing of the pins or plungers of the machine. It may be possible by moving a gauge backwards and forwards along a line of perforations to hit off a space of 2 centimetres containing rather more than 15 or fewer than 14 holes, but we have not been able to do so ourselves. With the best of goodwill the limits we have attained are 14 in one direction and 15 in the other, and we rather suspect that the frequent records seen of a gauge of 15½, and sometimes even of 16, in St. Vincent, have all been obtained from[32] the Six Pence of 1862, as that is the perforation with which this stamp (for which the A machine was never used) is most frequently found. The difference of gauge between 14 and 15 can often be found by moving a perforation-gauge a few holes only to the right or left, so it is evident that we can get both extremes on one single side of one particular stamp, and also haply all the measurements which lie between these limits. The variation between 14 and 15 is of course very slight, and since intermediate gauges are those generally found, had we in St. Vincent to deal only with the A machine, we might, with no great degree of inaccuracy, and for the sake of general simplicity, call the perforation of the A machine “14½,” or “14 to 15”; but since it was used so much in conjunction with a far more irregular machine—that is, the one we have called “B”—it is better to treat them both in the same manner, and call the first one “A,” rather than label it with a gauge which, strictly speaking, does not belong to it.
This perforation A, either alone or compounded with B, was in use from the first issue of stamps in 1861 until 1878; after that the B machine was used exclusively up to 1882, when Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. ceased to supply stamps to the Colony.
We must here call attention to a change which took place about 1871 in the character of the perforation made by the A machine. Up to that time the paper was very seldom even slightly pierced by the pins, or any of it removed—i.e., the perforation is what is called blind. A writer in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine of December, 1866, speaking of St. Vincent stamps, thus describes it: “… the stamps … are perforated (if that term be quite accurate) by an instrument fixed in the machine, which leaves a series of[33] indentations … which does not remove a particle of paper except in a very occasional spot, hardly one in a thousand. On severing the stamps by tearing, a rough indented edge is left…” This is quite correct, and we cannot better the description of the work of the A machine given by this old-time philatelist of nearly thirty years since, who collected and studied stamps in a day when perforation-gauges were not. It is only after 1871 that we generally (but not always) find the pins piercing through the sheet and leaving small holes, the paper being thrust aside and turned back by the passage of the pins through it, but little or any of it being removed. We wish to call particular attention to this point; that is, that the holes are small, and that the portion of paper displaced is not clean-cut or punched out. If this be not attended to, these particular examples of the later work of the A machine may be confused with the clean-cut perforations of 1862, which we have yet to consider.
It is to the vagaries of the B machine that we are principally indebted for the extraordinary number of perforations, simple and compound, that have been ascribed to the stamps of St. Vincent, as well as to those of the few other Colonies for which this machine was used. These Colonies are Antigua, Bahamas, Barbados, and Turks Islands. We know of no other instances in which the B machine was used, and in all these it was employed to a very limited extent as compared with its use in St. Vincent. Possibly this limitation was owing to the very unsatisfactory nature of its performance, and to the difficulty of separating the stamps without tearing them.
In examining unsevered blocks perforated by the B machine, the first thing we notice is that the holes cut by it[34] are circular, and of nearly uniform size, and that the pieces of paper are punched out and altogether removed, leaving holes varying from a little less than 1 mm. to a full 1 mm. in diameter, and of which the edges are clean-cut. These holes vary in their spacing to a very great extent, some being separated from edge to edge by a space of 1¼ mm., while between others there is only a thread of paper left. This is not owing to variation in the size of the holes, since measuring from centre to centre we find some holes to be as much as 2¼ mm., and others as little as 1 mm. apart. Besides these extremes all sorts of different measurements are to be found, generally in close proximity to each other, so that it is impossible to get more than a few consecutive holes that measure the same from centre to centre. Under these circumstances, how is it possible to assign in the usual manner any particular gauge to a perforation so erratic? And is it worth while, by the laborious examination of single stamps, to attempt to make a list that we know from the nature of the case must necessarily be interminable? We ourselves are quite content to look on all stamps perforated by the B machine as being of one and the same perforation, and we have so treated them in the Reference List, extending the same system to the perforations of the A machine. At the same time we do not think that any philatelists ought to lay down the law to others perhaps more ardent than themselves in the pursuit of varieties, as to what ought or ought not to be collected, and it is quite open to any such collectors, whenever they find a stamp in these lists said to be “perforated B,” or “perforated A,” to gather together, by what we call the injudicious use of the perforation-gauge, as many examples of the aberrations of the machines as they please, or as their time and purses[35] will permit. We think they will find it in some cases, say in that of the Five Shillings, to be a laborious, an expensive, and above all an unsatisfactory, task.
In order to ascertain the mean gauge of the B machine, the only possible way would be to get a line of perforations representing the whole length of the machine, and measure it. The longest line of perforations we have been able to experiment on is one of 124 mm.; this contains 72 holes, giving a mean gauge of about 11⅔ in the 2 centimetres. In some places in this line nearly 13 holes can be counted in the space of 2 centimetres, in others not more than 11, and all intermediate gauges as well are present in the same line. Indeed one has only to move the perforation-gauge one or perhaps two holes to the right or left to obtain a striking change of gauge. We have seen that the same sort of thing occurs in the perforation done by the A machine, but in a much lesser degree, the variation being only between 14 and 15—here it is from 11 to nearly 13, and is visible at a glance without the aid of the perforation-gauge. The above mean gauge of 11⅔ is very near to the 11½ usually ascribed in catalogues to stamps perforated by the B machine, but even if that be correct as a mean gauge for the whole line, it is very misleading so to call the perforation, as a collector whose solitary specimen might gauge, say 13 x 12½, would naturally suppose that it was a variety differing essentially from those said to gauge 11½. This, as we have seen, it would not be.
As in the case of the A machine, after the B machine had been in use some considerable time (about 1876), its perforations show a change of character, the holes being seldom punched right through; the discs of paper remain in their places, so that when the stamps are severed the[36] edges are very ragged. Otherwise there is no change whatever, the holes, or the marks where they should be, being still circular, and spaced in the same irregular manner.
Besides the two simple perforations A and B, we find one compound when the two machines are used in conjunction for the same sheet. Whenever this compound appears it is invariably the same in all cases; that is, the horizontal lines of perforation are made by the B machine, and the vertical lines by the A machine; or, adopting the philatelic notation now generally accepted, it is “B×A.”
Omitting the Six Pence of 1862, this reduces the possible number of varieties in the perforations of the stamps of Section I. to three in all; and in order to show at a glance how these occur in the different issues, we have arranged them in a table, which will be found under the head of Appendix B.
It will be observed that no one stamp is known with all three varieties of perforation, except the One Penny, bright rose-red, on the unwatermarked paper, and it is not at all certain that all these varieties existed together in any one of the seven different printings that were made of this stamp. Another point we may also note is, that whenever a stamp is to be found with the compound perforation, it also invariably exists with one of the two simple ones, but, with the above exception, never with both.
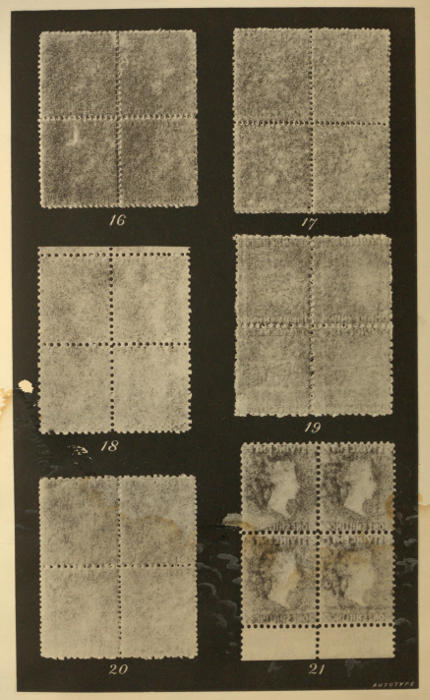
Our second plate of illustrations consists of six groups of four unsevered stamps each. These are intended to illustrate the various perforations of the A and B machines, and as these are more easily studied on the reverse side than on the face of the stamps, it is the backs of the groups we have had reproduced. Nos. 16 and 17 show the work[37] of the A machine at two different periods of its career. No. 16 is a group of four of the One Penny of 1861, when the perforations made by the A machine were blind; and No. 17 is a similar group of the One Penny of 1871, when the pins generally pierced the paper.
These particular groups were selected by us for illustration as showing a very marked contrast between the character of the perforation of 1861 and that of 1871; but as regards the latter, it is not easy to find such long lines of perforations in which all the holes are pierced through, as in the example we show in No. 17. In these two particular instances, if the central lines of perforation be gauged, the vertical line in No. 16 will be found to be 14 at the bottom and 14½ at the top. Its horizontal line is 15 on the left and 14½ on the right. In No. 17 the vertical line is 14½ at the bottom, higher up it is 15, and at the top it is again 14½. The horizontal line of No. 17 gauges 15 throughout its length. It will be noticed that in no one of these four lines do the two extremes of 14 and 15 both appear; but it must not be inferred from this that such is never the case, and we have now before us a group of four of the Six Pence of 1871, in which both gauges of 14 and 15 are present in the same line, and actually overlap each other. This group would not, however, have been so suitable to illustrate the general character of the A perforation in 1871 as the one we selected, since the holes in it are only pierced through in parts of the lines.
Illustrations Nos. 18 and 19 show the work of the B machine. No. 18 is a group of four of the Four Pence of 1866, and No. 19 a group of four of the One Penny of 1880. These groups speak for themselves, both as regards the irregularity in the spacing of the holes, and the different[38] character of the perforation at the two mentioned dates. In No. 18, in the central vertical line, the space separating the second and third holes, counting from the bottom, may be contrasted with that between the eleventh and twelfth in the same line, as this affords a good example of the irregularity of the machine, and a little search will yield many more such examples, both in No. 18 and in No. 19.
No. 20 is a group of four of the Six Pence of 1877, and shows the compound perforation B×A. In this case the later work of both machines appears. We should have liked to have been able to illustrate the compound perforation as it appears in 1866, when the machines made lines of holes as in illustrations No. 16 and No. 18. The only stamp available for this purpose would have been the One Shilling of 1866, but we have been unable to procure a group of four of these for illustration.
No. 21, which shows the De La Rue perforation 12, has been given so as to allow of its comparison with the early work of the B machine, as shown in No. 18, as it approximates to it in gauge, is like it in character, and even faintly imitates its irregularities. We shall revert to this perforation in our notes to the Issues of Section II.
May 1861.
These two values constitute the first issue for St. Vincent. They were printed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., and sent out to the Colony on March 27th, 1861, the consignment consisting of 934 sheets of the One Penny, and 167 sheets[39] of the Six Pence.[5] Both values were printed from plates engraved in taille-douce, each plate consisting of 60 stamps, arranged in six horizontal rows of ten. The paper used was without watermark, either for the stamps themselves or in the margins, and at least two very distinct sets can be made, one on thick and the other on much thinner paper. The texture is rough, and the colour greyish, sometimes slightly toned by the yellowish gum. There can be no reasonable doubt that the perforation of the first consignment was A, for although we have no direct evidence to that effect, any supposition other than this would involve us in such contradictions that our belief on this point amounts to what is practically a certainty.
We have inserted the imperforate varieties in the list, as, although we have not seen a satisfactory used copy of either value, both stamps have always been described in catalogues from the earliest to the present time. They are, for instance, so given in the catalogue of Mons. Alfred Potiquet, published in Paris in December, 1861, and also in the first edition of Mons. J. B. Moens’ Manuel du collectionneur de Timbres-poste, which appeared early in 1862. We think, therefore, that there can be little doubt that both stamps were issued in the imperforate state. The only postmarked specimen that has come under our notice is one of the One Penny, which is in the “Tapling Collection.” This stamp has fair margins on three sides, but is cut close on the right side, so that it cannot be considered of quite unimpeachable authenticity. Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s books state that each lot of stamps sent out to the Island was perforated and gummed, and this applies to the first as well as to all the other consignments,[40] so that the specimens chronicled by early writers must have come from sheets which were sent out imperforate in error. Looking at the date these varieties were first catalogued, they probably came from sheets out of the lot despatched on March 27th, 1861. Some of the later consignments seem also to have contained imperforate sheets, as we have seen an entire one of the Six Pence, which came out of the lot forwarded on June 15th, 1868. Of late years quite a number of the imperforate stamps have turned up, but we do not believe that any of these ever saw the Colony, and in our opinion they stand upon very different ground to the early chronicled varieties.
Altogether there is such an atmosphere of uncertainty surrounding these imperforate varieties that, had it not been for the references to them in the above-mentioned catalogues, we should have been inclined to have excluded them from the lists, and classed them either as proofs or trials for colour.
The variety of the Six Pence, imperforate vertically, is noted from a horizontal pair recently in the collection of Mr. F. de Coppet of New York, and which was sold at the sale of his stamps on December 12th, 1894. The pair was perforated all round, but imperforate between the two stamps.
[5] See chronological list of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s printings, and consignments in Appendix D.
1862.
This very interesting issue consists of one value only—a yellow-green Six Pence—which not only differs in colour from any other stamp of the same denomination on unwatermarked paper, but has a perforation quite peculiar to itself among the stamps of St. Vincent.
Hitherto when it has figured at all in any catalogue it has been mentioned only as a shade of the green stamp of the first issue, and as far as we are aware no hint has ever yet been given that not only is its colour quite distinct from that of any other Six Pence, but its perforation, being unknown in any other stamp of the Colony, clearly points out that it belongs to one particular printing, and that it is important enough to rank by itself as a separate issue.
That it has remained altogether unchronicled up to now is not exactly the case. In the Stamp Collector’s Magazine of August 1863 it is stated “Saint Vincent. The green of the Six Penny is of a different shade to what it used to be.” This is the only chronicle of it which may be called contemporaneous; but in the same periodical of August 1866, in an article entitled “Postage Stamp Paper and Watermarks,” the writer says, “St. Vincent. The pair of values belonging to this Island, of which the green is found in two distinct hues, seem unwatermarked.”
On referring to Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s list of printings we find that at the date, August, 1863, when it was chronicled in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, besides the first consignment of March 27th, 1861, two other printings of the Six Pence value had been made and sent out to the Island. It is quite clear to us, from the marked difference in colour and perforation between this stamp and any other Six Pence, that it constituted a printing by itself, and therefore in order to assign it a date we have to choose between July 22nd, 1862, when 167 sheets, consisting of 10,020 stamps, were printed; and May 28th, 1863, when the number of stamps was 40,080 in 668 sheets. Now there can be no hesitation in saying that the probabilities are enormously in favour of the smaller of these two[42] printings being the yellow-green Six Pence, seeing the scarcity of this stamp even in a used state, the unused stamp ranking as one of the rarest of the St. Vincents. It is quite probable that it had been some time in use before it was noticed by the writer in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine; but, on the other hand, although it was sent out to the Island in July, 1862, it may not have been issued for some little time after that. On the whole we do not think we can be far wrong in dating its issue 1862, rather than in the early part of 1863.
Even if the distinctive colour of this stamp did not make its identification very easy, its peculiar perforation would do so. It is the solitary instance in Section I. in which neither the A nor the B machine was used, but a third machine, which we call “C.” This is hardly the proper place for us to enter into a dissertation on the various perforating machines that were employed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., and used by them for perforating the stamps of the Colonies for which they held contracts; but, at all events, the C perforation is to be found, not only in this one St. Vincent stamp, but also more or less frequently in those of Bahamas, Barbados, Ceylon, Natal, Queensland, St. Helena, St. Lucia, Trinidad, and Western Australia.
Like the A and B machines, the C machine was a guillotine one, and like them its irregularities prevent us from naming it by any particular gauge. It is generally a rather regular 15½, but also frequently 15, and in some instances we have found it to measure only 14½. It is probable that this machine is also responsible for a perforation of 16, said to have been seen in St. Vincent stamps. It can never be mistaken for the perforation A, for not only[43] is its most frequent gauge a higher one than that to which the A machine usually attains, but its pins, or plungers, make clean-cut circular holes, smaller in size, but otherwise just like the early perforations of the B machine, although, from insufficient care and attention being paid to the working of the machine, it is rather difficult to find specimens that show the holes clean cut on all four sides.
This stamp, like those of the preceding issue, is found on both the thin and the thick paper.
We give two illustrations of this stamp, Nos. 13 and 14, which are taken from the only two unused specimens we have ever seen, or heard of. No. 13 gauges 15½ on all four sides; this is the gauge which is most frequently found in stamps perforated by the C machine. No. 14 is perforated 15 at the bottom and right side; the top and left side are too ragged to be measured with accuracy, but they appear to be the usual 15½. The gauge of 14½ (and that of 16, if it exists) must have been present in a very limited portion of the line of pins, as it is very rarely met with.
Between 1863 and 1866.
The two stamps constituting this issue differ in no respect from those of Issue I., except in the perforation, which is now B, or B×A, instead of A. It is not possible to say at what precise date the B perforation first came into use. One thing which is certain is, that it, as well as the compound B×A, was known to philatelists as existing in these two values before December, 1866, at which date both[44] perforations A and B as well as the compound B × A, were described by a writer in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine.
It follows from this that the B perforation must have been used for one or more of the printings made before this date.
Now if we turn to the table of the consignments sent out to the island, we see that there had been in all five printings of both values. The first of these, that of March 27th, 1861, was the first issue, and, as we have said, it was perforated A. The second, that of July 22nd, 1862, was, as far as the Six Pence is concerned, incontestably perforated C, and there therefore only remains the printing of the One Penny of that date, and the three printings of both values of May 28th, 1863, March 1st, 1865, and March 14th, 1866. We think it more than probable that when the B machine was first used both values were perforated by it; and we therefore pass over the second printing of the One Penny, and give 1863 to 1866 as the date which most likely belongs to Issue 3. We are thus able to antedate this issue at least three years, all previous catalogues having given 1869 as the earliest date at which the B perforation made its appearance.
It must not be inferred that after the B machine came into use the A machine was discarded, or even that any printing of either value was altogether perforated by the same machine. The perforation A is much too common in both values for it to be supposed for a moment that the first issue only was so perforated. There were in all seven printings of the One Penny, red, and five of the Six Pence, blue-green, on unwatermarked paper, perforated by one or other of these two machines; and as there is little or[45] nothing to choose in point of rarity between the two perforations A and B in either value, it is to be presumed that once the B machine had come into use both machines were used indiscriminately for both values, as long as they continued to be printed.
We are fortified in our opinion that more than one kind of perforation was used for the same printing, by the impossibility of believing that one whole printing of the One Penny, red, was perforated B × A. This variety is so scarce, that the number of specimens known to us can literally be counted on the fingers of one hand. About three years ago we unearthed two specimens from a dealer’s stock. These were mounted on a card, and endorsed as “very scarce” in the handwriting of the late Mr. E. L. Pemberton. Two other specimens are known to us, and all these four are used. It is not possible to believe that 18,000 of these ever existed, and that is the least number of the One Penny ever printed at one time.
The Six Pence with the compound perforation is not known to us, but we think it is a variety that may possibly exist. The writer in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, in referring to this compound, unfortunately does not specify the denomination of the stamp in which he had “occasionally” noticed it.
As stated in our note to Issue 1, it is quite possible that some of the consignments belonging to this issue, at any rate of the Six Pence, contained a sheet or sheets that missed being perforated.
August 1866.
The plates for these two values were prepared by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., early in July, 1866. They contained 30 stamps, arranged in three horizontal rows of 10, so were just half the size of those used for printing the One Penny and Six Pence values.
On July 28th a consignment of stamps printed from them was sent out to the Colony. This consisted of 500 sheets of each of the values; that is, 15,000 stamps of each denomination.
The stamps must have been immediately put in issue, as they were in use in August. They were chronicled in October, both by the Timbre-Poste and the Stamp Collector’s Magazine. The notice in the latter is as follows: “Within the last month or six weeks the number of St. Vincent stamps has been doubled by the emission of a Four Penny, blue, and Shilling, purple-black.” In the Timbre-Poste the colour of the Shilling is called “pourpre,” but in the same publication of April, 1867, M. Moens calls the colour “ardoise.” There is a further notice touching these stamps in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine of December, 1866, which is worth quoting in extenso, as it is a valuable contribution to our knowledge as regards both the colours and perforations of the stamps: “The newly-issued Four Pence and One Shilling have come over with the late mails in entire sheets. The colour of the former is a clear Prussian-blue, while the[47] latter varies, one sheet we have examined being a purple, while the other is a deep slate without the tinge of red in it, which makes a purple. The normal colour is evidently one which requires great nicety in manipulation, a slight difference in mixing forming the two shades, which are very distinct. Like the Penny and Six Pence already known these stamps are on thin woven paper, without watermark, and perforated. The Four Pence is perforated by a machine which removes a little circular piece of the paper, like that in use for the English stamps, but the holes very much wider apart. The sheets of the Shilling stamps are also perforated by a machine, and show the following remarkable peculiarity in the perforation: the horizontal lines which sever the stamps from the rows above and beneath them are, as in the Four Pence, perforated by a succession of small circular holes cut or punched out, but the vertical lines dividing the stamps from their fellows side by side in the row are perforated (if that term be quite accurate) by an instrument fixed in the machine, which leaves a series of indentations much closer than the holes before alluded to, and which does not remove a particle of paper, except in a very occasional spot, hardly one in a thousand. On severing the stamps by tearing, a rough indented edge is left on each side; a ragged edge caused by the holes being too far apart is left above and below. A similar difference has been remarked by us in the former issues, specimens of each of which, completely perforated by either method, may be found, as also occasionally a copy showing both systems on the same stamp.”
We have already in previous notes given extracts from the above to show that the difference between the A and B perforations was thoroughly understood by the writer, and[48] also that the B perforation and the compound B×A both existed in the One Penny and the Six Pence previous to December 1866. We learn from the same source that the two colours of the One Shilling—what we have called “dark slate-grey” and “greyish-purple”—appeared in the same consignment; and, moreover, that part of this consignment of the One Shilling was perforated A, and part of it B×A, both of which statements are confirmed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s list. We have found the greyish-purple very rare as compared with the other colour.
The One Shilling perforated B×A is certainly much more common than the one with the A perforation, and the greater part of the consignment probably consisted of the compound. No other printings of either of the two values were ever again made in these colours on the unwatermarked paper. The Four Pence is a clear deep blue, and there are practically no shades; but as it has a strong tendency to oxidation, it is to be found in all sorts of deteriorated colours up to nearly black. Out of the 15,000 printed, a great number must have found their way into dealers’ stocks, as it is quite as common unused as used. It continued in use for some years after it had been superseded by a Four Pence of a different colour. The Philatelist of February, 1873, that is three years after the issue of the Four Pence, yellow, says, “The colour of the Four Penny would seem to have reverted to its original hue, our specimens just received by the last mail being a full blue, but unwatermarked as far as we can distinguish.” Were it not for the information we have been fortunate enough to obtain from Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., this might lead us to believe that another printing of the Four Pence, blue, had been made about the end of 1872; but we know that this was not the case, as[49] only one printing of it was ever made, and the stamps alluded to must have been some of the old stock that were being used up. The One Shilling is given in the London Philatelic Society’s Catalogue as perforated 11½ on all four sides. We have not met with this variety, and do not believe in its existence. If the specimen from which the description was taken is one in the “Tapling Collection,” as seems probable, the particular stamp proves, after examination, to be merely an oxidised copy of the One Shilling, indigo, of the following issue.
April 1869.
On February 27th, 1869, Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. sent out a consignment of 300 sheets (9,000 stamps) of the One Shilling. Their records note no difference between the colour of this stamp and that of the One Shilling of the last issue—they call them both “purple,” although the difference between them is really very great. We think the colour of the new stamp, which is very deep, is best described as “indigo.” The Stamp Collector’s Magazine, which chronicled it in July, 1869, calls it “dark muddy-blue”; the Timbre-Poste of a month earlier, “bleu-sale”; but the colour really does not matter much, as there is no other stamp with which it can be confounded. If any shades of it exist they are certainly very slight, and probably due more to oxidation than to any other cause. It only exists with the B perforation.
We do not know exactly the month of its issue, but since[50] it was sent out late in February, and first chronicled in June, it most likely came into use some time in April.
It is a much rarer stamp than the One Shilling of Issue 4, especially unused, but this is what we might expect to find when we consider that only 9,000 of it were printed, as against 15,000 of the first One Shilling.
September 1869.
On August 13th, 1869, a consignment of stamps of two values—Four Pence and One Shilling—was sent out to the Colony by the printers, the colour of the Four Pence being altered from blue to yellow, and that of the One Shilling from indigo to brown. The consignment consisted of 300 sheets—9000 stamps—of each value.
The One Shilling was the first of these to be chronicled in the philatelic periodicals. It was noticed in Le Timbrophile of September 30th, 1869, and in the Philatelist and the Timbre-Poste of November, but the Stamp Collector’s Magazine did not announce its appearance until the December number of that year. It is therefore certain that the issue of the One Shilling, brown, took place in September, and most probably the Four Pence, yellow, was issued at the same time, although the latter was not chronicled until November 30th, when it was noticed by Le Timbrophile, the other three above-mentioned periodicals not chronicling it until January, 1870.
The Philatelist, speaking of the change of colour, says of the new Four Pence, yellow: “It is now in full[51] service, and proves to be of a very deep rich yellow. The emissions of this Island, for some time two only, now amount to a respectable figure, there being the slate, indigo, and brown Shilling; a dark and light green Sixpenny; the blue and the new yellow Fourpenny; and the Penny in slightly varying shades of red. In addition are varieties of perforation, one being pin-pricked, one fully perforated, and some anomalously presenting both methods in the same stamp. Such emissions as these must shut up all Pendragonites, and puzzle the patronizers of Lallier’s and other exclusive albums.” Here is additional evidence, were such required, of the attention paid in those days by certain writers and collectors to those minutiæ of stamp collecting, which in the aggregate make up what is now understood by the term “Philately.”
Like all the preceding issues these two stamps are on unwatermarked paper, varying from thick to thin, and are perforated B, with gum from yellowish to almost white. The colours of each are nearly uniform, slight shades only being found, the darker shades of the brown Shilling being generally due to oxidation. Only this one printing was ever made in these colours, and as this was limited to 9,000 stamps of each value, it need not be a matter of surprise that they are both fairly rare in the unused state.
The One Shilling is described in Stanley Gibbons’ Monthly Journal for December, 1891, as found perforated 11 by 15½. We have examined the particular specimen by the kindness of the owner, and the stamp turns out to be an unmistakable oxidized copy of the vermilion-red Shilling of Issue 11.
This was the last issue of stamps for St. Vincent to be printed on the unwatermarked paper.
June 1871.
With this issue a radical change of paper took place, and the new paper, which was watermarked with a star, continued to be exclusively used as long as Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. supplied stamps to the Colony. It varies very much in thickness; the thinnest variety is about the same thickness as the thinnest of the unwatermarked paper, but the thickest sometimes approaches card. This is especially noticeable in certain issues, in which the thick paper predominates, and we will refer to this subject in subsequent notes.
The star of the watermark is a six-pointed one, measuring 13 mm. from point to point across the star, and the watermarks in the sheet are so spaced that when the plate has been printed in register each star falls exactly on the centre of a stamp. The lateral distance between the stars from centre to centre is 20⅓ mm., and the vertical 24 mm.; these measurements of course correspond with those of a St. Vincent stamp, plus one margin each way. All the stars in the sheet are disposed with two opposite rays in a vertical line—that is when the stamps are printed in the normal position with regard to the paper. Personally we have not much sympathy with the collection or cataloguing of inverted or reversed watermarks, which we think tends to the undue lengthening out and complicating of lists, to no useful purpose whatever, but we may as well mention[53] that the star watermark is to be found sideways on all the St. Vincent stamps printed on this paper. Of course when in this position two opposite rays are in a horizontal instead of in a vertical line. This peculiarity of position in the watermark is not confined to St. Vincent stamps only, among those of the Colonies for which Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. used the same paper, as in 1874 it was noticed by philatelists in the stamps of Antigua. A correspondence about the watermarks of these stamps took place early in that year in the pages of the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, and at about the same time the subject was discussed at a meeting of the Philatelic Society, London. Those who are curious in these matters will find all the particulars given in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, vol. xii., where it appears from the letters printed that an idea prevailed that, as concerned the stamps of Antigua, the paper with the star sideways denoted a later issue. The explanation given by the then President of the London Society was that the change in the position of the watermark was due to “the stars being turned when cleaning the plates, or when they became worn.” This was rather far-fetched, not to say grotesque, nor did it succeed in satisfying all the correspondents of the Stamp Collector’s Magazine. The true solution of the question is, that as the paper was sufficiently large to admit of the plate being printed on it in either position, the printer was quite indifferent as to how the paper was placed, and were it not that this particular watermark is a symmetrical figure we should doubtless occasionally find it inverted, as well as sideways. A variety of the One Penny, with one point of the star up, was indeed chronicled with “inverted” watermark in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine, vol. xii., p. 95, by the same writer who noticed the[54] two different positions of the stars we have just alluded to. The design of the watermark was, however, such that it made no difference which end of the sheet was put first into the press, and it passes our comprehension to know how an inverted watermark could therefore be distinguished.
Although all the stars in St. Vincent stamps are of the same size, owing to the “bits” being hand-made they vary a little in shape, and we have seen faulty ones having one or more rays with the points broken or twisted out of their proper direction. Besides this there are two rather distinct varieties in the shape of the star. These exist side by side in the same sheet. In the star more usually found all the six rays are of similar size; in the other variety the two opposite rays in the vertical line are narrower at the base than the other four, so that they are thinner throughout their length, and end in a more acute angle. This last variety of star is in shape almost exactly like the larger stars found in the paper used by the same firm for printing the stamps of South Australia and certain other Colonies.
In the thicker varieties of paper it is sometimes very difficult to see the watermark. This is especially the case when the specimens are unused and have the gum intact. The change in the colour of the One Penny from red to black marked that stamp at once, so that we find its advent recorded in the Stamp Collector’s Magazine of September 1871, and in the Philatelist and Timbre-Poste of the following month, the last-named periodical being the only one to mention the watermark or perforation, which last was given as 14½. We learn from the list of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. that the consignment was sent out on March 28th, 1871, and consisted of 300 sheets (18,000 stamps) of One Penny, black, and a like number of Six Pence, green;[55] and, since the One Penny was chronicled in September, we may assume that the issue took place some time in June. There can be little doubt that the Six Pence was issued with the One Penny, although it was unnoticed at the time by philatelists, probably because the colour was unchanged, and the watermark, owing to the thickness of the paper, not readily seen. It was not until September, 1872, that it was chronicled by M. Moens in the Timbre-Poste, which is the only record of it we can find in any of the philatelic periodicals.
The One Penny, black, is found with two varieties of perforation—A and B × A. It continued in use from the date of its issue, in 1871, until the colour was changed in 1880. Nine printings of it were made, and the last consignment was sent out on August 28th, 1878, making in all the large total of 6000 sheets, or 360,000 stamps. The great majority of these must have been perforated A, since the compound B × A is very much less common, and is even rather scarce unused. We do not know in which particular printing this last variety of perforation occurred. We have the authority of the Timbre-Poste that some at least of the first consignment were perforated A, and the sample stamp attached to the entry in the books of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., referring to the despatch of the last consignment in 1878, is also perforated A. In the absence of further information we have, however, catalogued both the two varieties of perforation as belonging to Issue 7.
The Six Pence, green, of which only three printings were made, is always perforated A. It is generally in a blue-green colour, identical with that of the Six Pence, blue-green, of previous issues on unwatermarked paper.[56] It is sometimes, but rarely, met with of a dull green hue, rather pale in shade, and nearer a yellow-green than is the ordinary colour. We have only found one unused specimen of this stamp, nor have we seen many used ones, so we are still a little doubtful whether it is an original colour or not.
There is a rather mystifying chronicle of another green Six Pence in the Timbre-Poste of January, 1876, which was copied by the Philatelist, and which we think it as well to refer to here. M. Moens appears to have overlooked the fact that he had already, in 1872, mentioned the Six Pence, green, with Star watermark—“Le 6p. vert arrive avec étoile en filagramme et piqué 15”; and in January 1876 records it again as “6p. vert foncé piqué 15.” At this time no printing of the Six Pence had taken place since March 1875, so what M. Moens saw could not have been a new variety, and was probably only a specimen, rather darker than usual, of the same stamp he had already chronicled in 1872.
A horizontal pair of the One Penny, black, with no perforation between the stamps, was sold at the sale of Mr. M. P. Castle’s collection of British and Colonial stamps, on May 2nd, 1889, the pair being described erroneously in the catalogue as imperforate horizontally. M. Moens, in his Catalogue Prix Courant, gives the same stamp as existing imperforate, but not having been able to verify it we have omitted it from our list.
June 1872.
We now come to a series of issues of the One Shilling, which present a good deal of difficulty to collectors, because of the number of colours and shades they contain, all rather closely resembling each other. They are not easy to describe in print, so as to be properly understood, owing chiefly to the great divergence of opinion on the subject of the names of colours, when these are closely allied.
On April 13th, 1872, Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. despatched 9000 stamps in 300 sheets of the One Shilling value printed in a colour they call in their books “pink,” but this is a description we put out of court at once, especially as the sample stamp in the firm’s books is a rose-red one.
In addition to the sample stamp, Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. possess an imperforate proof sheet of the stamp in the same colour, but upon unwatermarked paper. This sheet is inscribed on the margin “Patterns for colour. Postage Pink, small quantity of Drop carmine-lake about ½ oz. for 300 sheets.” The technical name of the colour appears consequently to be “carmine-lake.”
The first chronicle of the issue was in the American Journal of Philately of August, 1872, which was quoted by the Timbre-Poste of September. The Philatelical Journal of September says that they have accidentally omitted to chronicle it in August. We give June as the probable date of issue.
As regards the colour of the stamp, the Philatelist of October, when chronicling its issue, says that “the colour is precisely that of the rose penny,” but in the following month it adds to this statement that other specimens have been seen, “all deeper in hue than the penny ones of the same colour.” This, as far as it goes, agrees exactly with our own experience, which is that there are specimens in shades of bright rose-red, all of which may be found in the bright rose-red One Penny of Issues 1 and 3, but that there are others in a deeper rose-red of a slightly different colour, never seen in the One Penny, and due to something more than mere depth of shade. Besides these two colours we find a third, which we have called “dull red,” differing from both of them, and in which a faint tinge of yellow is sometimes to be seen, as if it were turning somewhat towards vermilion. There was only one printing made of this One Shilling, rose-red or dull red, but we have already seen in the case of the One Shilling of Issue 4 that more than one colour may exist in the same printing, from causes connected with the mixing of the ink. The paper of this issue is sometimes found more or less toned by the action of the gum, which seems always to be yellow, and never white; this affects the appearance of some specimens, and adds considerably to the difficulty of limiting the number of colours even to three.
By far the greater number of the stamps of this issue are perforated B. We have seen very few indeed perforated B × A, and all these have been bright rose-red in colour. The only periodical which in chronicling the stamp gave the perforation was the Philatelical Journal, which says that it is “perf. circ. 14½ to 15½” which we would call A; but in 1872 compound perforations were ignored, and the usual[59] plan was to measure only the long side of a stamp, so this record of the perforation probably corresponds to our B × A, as the stamp does not exist perforated A alone, so far as we have been able to discover. The sample stamp kept by the printers is perforated B.
This One Shilling is a very scarce stamp in the unused state.
Early in 1874.
We learn from the books of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. that on July 28th, 1873, they sent out to the colony a consignment of 300 sheets—9000 stamps—of a One Shilling which they call “pink,” as they did the rose-red One Shilling of the 1872 printing. Fortunately the sample stamp attached to their book is there to show us what it was they sent out, and we find it to be a violet-rose stamp perforated, as are most of this issue, B × A. In few other cases in St. Vincent have the records of the firm been of more use to us, as the stamp remained unchronicled by the periodicals until quite the end of 1874, and their various descriptions of its colour are extremely misleading.
At the same time, it seems almost impossible that had it been issued at once on its arrival in the island, its existence should have been unsuspected by all philatelic writers for a period of more than a year, as it was not until September, 1874, that the first chronicle of it was made in the Timbre-Poste, where M. Moens calls its colour “rose-sale”; and we are therefore inclined to[60] believe that its issue was delayed for at least some months, perhaps until the early part of 1874.
Its colour is a pale violet-rose, always of uniform shade, but, as the stamp has a strong tendency to oxidation, some very dark specimens may be found in which the colour has greatly deteriorated.
Like the One Shilling of the preceding issue, it is found perforated B and B × A. It is scarce unused, and we have seen very few specimens perforated B, all of which have been used ones.
1875.
This One Shilling was printed and sent out to the Colony on March 27th, 1875. The consignment consisted of the same number of stamps as those of the last two issues. It is not clear in what month its actual issue took place. It was not chronicled until the Timbre-Poste noticed it in January 1876, where the colour is called “lie-de-vin foncé.” In their books the printers still adhered to the term “pink,” but although no sample stamp of this printing was preserved, we can be quite certain that it consisted of 300 sheets of One Shilling, dark claret, as both the other two printings of “pink” Shillings have been accounted for.
In colour it is a rich dark claret, with very slight shades, and even most of these are due to the deep toning of the paper, as the gum used is always the darkest to be found in St. Vincent stamps, and the paper is invariably more or less deeply stained. The perforation is always B.
Although no more of this issue were printed than of the One Shilling, rose-red, or the One Shilling, pale violet-rose, it is rather more common unused than either of those two stamps.
February 1877.
The two values in changed colours were sent out to St. Vincent by the printers on December 30th, 1876, the consignment consisting of 300 sheets of each value; that is, 18,000 stamps of the Six Pence value and 9,000 of the One Shilling. They were both chronicled by the Timbre-Poste of April, 1877, and must have been issued some time in February. The Six Pence remained current until the middle of 1880, and the One Shilling as long as Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. supplied stamps to St. Vincent. Besides the printing of the two values in December, 1876, one other printing of the Six Pence and two of the One Shilling were made. The second printing of each value was sent out on August 28th, 1878, and the third printing of the One Shilling on May 13th, 1880. All these printings consisted of 300 sheets each, so that the total printed of the Six Pence of this issue amounted to 36,000, and that of the One Shilling to 27,000 stamps. In the printers’ books sample stamps are attached to all the entries referring to these printings, with the exception of the second lot of the One Shilling. The samples of the first printing are perforated B × A in both values; in that of 1878, the second printing of the Six Pence is perforated A, and the One Shilling of the 1880 printing is perforated B.
We have seen from the case of the One Shilling of Issue 4 that more than one variety of perforation (and even of colour) may exist in the same printing, nor is it to be expected that in such cases samples of each variety would be preserved by the printers, since differences of perforation are more appreciated in philatelic than in printing circles. There is, however, a circumstance connected with the perforation of the vermilion Shilling which leads us to believe that the stamps of all these printings were perforated only as shown in the sample stamps of each consignment. We know that in 1881 the third printing of the vermilion Shilling was utilized for making a provisional stamp of Four Pence, and that all these provisionals are perforated B only. We therefore think it probable that all of the One Shilling value perforated B × A belong to the first printing, and all perforated B to the second and third, more especially as the stamp perforated B is much the commoner of the two varieties. We have extended this theory to the Six Pence as well, and in the Reference List we give in brackets after each variety the probable date of issue of the different perforations.
One thing that is remarkable about the colours of both these stamps is that there are no appreciable shades of either, the colours being maintained unchanged in all the printings of each value, although in the books of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. the colour of the first two printings of the One Shilling is called “scarlet,” and that of the third “bright red.”
In the unused state the Six Pence is very much rarer perforated A than with the compound, but the converse is the case with the One Shilling, in which B × A is by far[63] the rarer perforation. The paper of the stamps of this issue varies a great deal in thickness, but this is more pronounced in the Six Pence than in the One Shilling, as the former value is met with on what can only be described as thin card.
Both values, as well as the One Penny and Six Pence of Issue 7, and other stamps current during the later years the stamps of Issue 11 were in use, are not uncommonly found with a curious obliteration of an upright oval, pointed at the top and bottom, and divided across the centre by a double line. The upper part contains the letters “G.B.,” and the lower “40 c.” The cancellation made its appearance upon these three stamps about the end of 1878, or early in 1879, and was first thought to be a surcharge. The credit of its explanation is due to the editor of the Foreign Stamp Collectors’ Journal, who made enquiries at the Post-office, and who stated in the numbers of that journal for December, 1879, and July, 1880, that “in addition to the ordinary mail steamers from the West Indies, letters are conveyed to England by the French Packets running intermediately. These letters are stamped as above; the G.B. signifying ‘Grande Bretagne,’ and the 40 C., the amount payable to the French Post-office for their services.” “The stamp ceased to be employed for its original purpose some time ago, but is now used instead of the ordinary cancellation stamp, which is worn out.” Its use as an obliterating stamp must have been continued at least up to some time in 1882, as we have frequently seen it on the Halfpenny orange of Issue 18, a stamp which was not issued until December, 1881.
July 1877.
A consignment of 200 sheets—6,000 stamps—of the Four Pence value, printed in very dark deep blue, was sent out to St. Vincent on May 29th, 1877. In the absence of any evidence to the contrary, we have no reason to doubt the stamp was immediately put in issue, and that it was first used in July of the same year, but had it not been for the record in the books of the printers, we should have had a good deal of difficulty in assigning a date to it. Most of the principal catalogues, including the London Society’s list and the current edition of M. Moens’ Catalogue Prix-Courant, give 1876 as the date of issue, but the stamp is not catalogued in the 1877 edition of the last mentioned work. The solitary chronicle of it we can find in philatelic literature is in the Timbre-Poste of May, 1878, where we find it recorded in the following terms: “Réapparition du 4 pence, en bleu foncé, mais avec étoile en filagramme.”
We think it far more likely that the fact of the stamp being on watermarked paper should have escaped the notice of M. Moens, than that its issue should have been delayed for nearly a year after its arrival in the Colony. The one printing of the Four Pence yellow had been a small one; it consisted of only 9,000 stamps, as compared with 15,000 of the Four Pence blue, on unwatermarked paper, issued in 1866. We do not know for what reasons the postal authorities had changed the colour of this value from blue to yellow, but they could not have been very important ones, as the blue Four Pence of Issue 4 was, as we have seen,[65] undoubtedly still allowed to be used in 1873—that is, about four years after the introduction of the Four Pence, yellow, so it is evident that the use of the two stamps was concurrent for some time at least. It is stated in the London Society’s West Indian Catalogue that the Four Pence value became “disused,” but this cannot have been the case, as we have the evidence of postmarked specimens of the yellow Four Pence that it was in use in July, 1876, and we know that a fresh supply of the value was sent out in 1877. There is therefore every reason to believe that although the Four Pence, deep blue, of the issue now under consideration had probably been seen by M. Moens when first issued, he mistook it for the old blue Four Pence that was still being occasionally used, and it was not until 1878 that he discovered the difference in the paper, and chronicled the watermarked stamp in the Timbre-Poste. There is every excuse to be made for this temporary omission, as the great majority of the issue is printed on the very thick variety of paper which approaches thin card, and it is a matter of great difficulty to detect the watermark in this paper, even when it is known to be there.
There was only one very small printing, 6,000 stamps, made of this Four Pence, and so it is naturally very much rarer than either of the two stamps of the same denomination previously issued. In addition to this, its rarity unused is even out of all proportion to the smallness of the printing, and we may be certain that since it was unchronicled in the philatelic publications of the day it was not put into stock by the dealers, and that the unused specimens we occasionally find have been preserved by accident rather than by design.
It is always perforated B, and the colour, which would[66] alone distinguish it from the Four Pence of Issue 4, shews no shades, except those due to oxidation, to which it has a certain tendency.
May 1880.
This is the first of a very interesting and important series of four provisional stamps that were made in St. Vincent, in 1880 and 1881, to supply a temporary want of certain values. From information received from Mr. Frank W. Griffith, late Acting Colonial Postmaster, and already published in the West Indian Catalogue of the London Society, we know the date of issue of the provisional One Penny was May, 1880, and that the number of stamps issued amounted to 1,800. Reference to Messrs. Perkins, Bacon and Co.’s list of consignments shows that the last printing of the black One Penny had been sent out in August, 1878, and it is evident that another supply of the value had already been ordered, but not received when this provisional was made, as the new One Penny, printed in grey-green, was only despatched from London on May 13th, 1880.
The stamp used for surcharging was the dark blue-green Six Pence of Issue 7, perforated A, a remainder being in hand, probably from the last printing of March, 1875.
In those days surcharged stamps, especially in British Colonies, were not so common as unfortunately they have subsequently become, and were much appreciated by philatelists, as may be seen by the tone of the writer who chronicled the provisional One Penny in the Philatelic Record of July, 1880. “A very curious provisional stamp,[67] forming a fit pendant to the makeshift 1d. employed in Barbadoes in 1878, has been used recently, but may by this time have become obsolete. The postal authorities of St. Vincent have treated their 6d. value in the same way as the Barbadians did their 5s. stamp—perforating it down the centre, and surcharging each side with 1d. in red, the numeral being 8 mm. in length.” The writer then goes on to say that the central line of perforation is clean cut, and gauges 12, which is quite correct, and records a fact worth bearing in mind when examining doubtful specimens, as the forgers have found the perforation much more difficult to imitate than the surcharge. Unfortunately our illustration of this stamp, No. 2, is not as clear as we could have wished, owing to the red and green colours not lending themselves readily to photography—so we give the measurements of the surcharge, which are as follows: Height of figure, 8¾ mm.; width of figure, 1½ mm.; length of foot of figure, 3½ mm.; height of “d,” 3 mm.; extreme width of “d,” 2 mm.; space between “d” and figure, 1½ mm.; space between figures on right and left halves of the same stamp, 8½ mm. The figure “1” has a straight serif. These details will help to protect collectors against at least the more ordinary forgeries, but the gauge of the perforation and its regular clean-cut circular holes are really the crucial tests, as some of the surcharges are heavily printed, and are difficult to measure with accuracy. A description of the forgeries known to us would be of little use. They all fail in the perforation, most of them in the dimensions of the surcharge, and one rather dangerous one we recently discovered has the figures on the two halves of the stamps wrongly spaced. The one most likely to be met with is the least dangerous, as it has a large cross stroke to the top of the figure, instead of a serif,[68] besides being wrong in many other particulars. This forgery is evidently copied from the illustration in a well-known catalogue, and not from the stamp itself.
This provisional One Penny has always been a rare stamp, especially unused, or in pairs; none of the issue seems to have found its way into dealers’ stocks, but to have been all used up for legitimate postal purposes, so that a great part of it must have been destroyed, and only a small proportion of the original 1,800 saved for philatelic purposes.
June 1880.
On May 13th, 1880, Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. sent out 1000 sheets (60,000 stamps) of the One Penny, printed in pale grey-green, 300 sheets (18,000 stamps) of the Six Pence, printed in bright yellow-green, and 100 sheets (2,000 stamps) of a new value—Five Shillings, printed in deep rose-red. In this consignment was included the third and last printing of the One Shilling bright vermilion-red. All the three first mentioned values were perforated B only, this we know because no other variety of perforation exists in any of these stamps, the issue of which was in all three cases confined to this one printing. We think this is a very good reason for believing that the printing of the One Shilling that was made at the same time was like them perforated B only, and that at this date the use of the A machine had been discontinued for ever, as far as the stamps of St. Vincent are concerned.
The printings of both the One Penny and the Six Pence were small ones. The former value must have been used up quickly, as a new supply was ordered in the next year; we may, therefore, expect this stamp to become much scarcer than any of the same value that preceded it, and of which such a large quantity were printed.
The Six Pence was the last of that value to be printed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., and it remained current for more than three years, until October, 1883, when it was succeeded by a stamp printed by Messrs. De La Rue & Co. About a fifth part of the printing was used in 1881 for making provisional stamps of the One Penny and Halfpenny values.
It is rather a scarce stamp, even in a used state, and is decidedly rare unused, it being one of the St. Vincent stamps the dealers appear to have neglected.
The Five Shillings value is a striking stamp, both in its size and design, which is very artistic, and it is altogether a fine example of the line-engraved work of its makers, Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. The central portion of the design portrays the Arms of the Government of St. Vincent, and represents “Justice pouring out a libation to Peace,” which illustrates the motto of the Colony, Pax et Justitia—“Peace and Justice”—given on the scroll above the Arms. The plate contained twenty stamps, arranged in four horizontal rows of five, and the same star paper was used for printing the issue as for the other stamps of smaller dimensions; the consequence of this being that each stamp is watermarked with at least more than one star. There seems to have been very little demand for the stamp for postal purposes in the Island, and genuinely postmarked specimens are now of great rarity. Used Five Shillings[70] stamps have always been eagerly sought for by philatelists, who for many years declined to have anything to do with unused specimens, as they looked upon the stamps as fiscals only. This belief seems to have arisen from the way they were chronicled in the Philatelic Record of August, 1880, which said—“The 5s. fiscal stamp has lately been used for postal purposes.” The Timbre-Poste, in announcing the stamp, quoted from the Philatelic Record, and so the error came to be perpetuated, until the true character of the stamp was explained in the London Society’s West Indian Catalogue, published in 1891. In that work will be found an official notification, dated 15th September, 1882, in which it is called “the existing five shilling postage stamp,” and in which it is directed to be “over-stamped Fifty Pounds—Revenue,” and “used as a Revenue stamp of that value.” Its use as a Revenue stamp was not confined to this high denomination, as it exists with “Revenue” only on it, and fiscals with this surcharge are fairly common. We are of opinion that the great majority of the 2,000 stamps printed were so treated, and that only a very small number were ever used for postage, or escaped the fiscal surcharge. This readily accounts for the great rarity the stamp has acquired of recent years, and this rarity cannot, we think, but increase still further in the future.
The official notification quoted above contains a clause which “directs that the present six penny postage stamps may be cut diagonally in half—each half to be over-stamped 3d. Revenue, and be used as a revenue stamp of that value.” It was further used, with the surcharge “Revenue,” as a fiscal Sixpence. This fiscal use of the Six Pence, bright yellow-green, of Issue 14, is an additional reason for its now being so rare in an unused state.
September 1881.
The necessity for a Halfpenny value arose from the Colony of St. Vincent having joined the Postal Union on September 1st, 1881, and, pending the arrival of the stamps ordered from England, this provisional was made in the Island by dividing the Six Pence of the last issue by a vertical line of perforation through the centre, and surcharging each half stamp “½d.” in red, the additional perforation being the same as that of the provisional One Penny of Issue 13.
It was thus chronicled in the Philatelic Record of October, 1881: “St. Vincent, proud apparently of her provisional One Penny, which has eluded the grasp of so many collectors, has provided herself with a Halfpenny makeshift, which is as like it as possible. The current Sixpenny stamp has been perforated down the centre, and each half surcharged ½d. in red. We have only, as yet, seen a single specimen, but there may be almost as many varieties as there are stamps to the sheet.” This surmise of the writer, fortunately for collectors, turned out to be incorrect, as there are practically no varieties on the sheet, except one in which the serif of the figure “1” of the fraction is straight, instead of being curved as in the other figures on the sheet. Beyond this there are no varieties of the surcharge, save in very slight differences in the position of the fraction line, due to the surcharge being type set. Our illustration No. 3 shows the variety with the “1” with straight serif on the right half of the Six Pence. It will also be observed that this surcharge is on a slightly higher level than its[72] neighbour on the left half of the same stamp. It may also be noted that the surcharges were not always printed fairly in register with the sheet, so that each one fell exactly in the centre of a half stamp, as we have seen a used specimen of a right half stamp, which shows portions of a second surcharge down the line of perforation on the right side of the stamp.
A variety of this stamp, with the fraction line of the surcharge omitted, is reported to us from the United States, but not having been able to verify for ourselves whether the surcharge is genuine or not, we have omitted it from our Reference List.
There were twelve sheets (1,440 stamps) of these provisionals printed, but not many were issued for use, and we believe they were withdrawn from issue before the arrival of the new Halfpenny value in December. It is an excessively rare stamp used, and at the date of its issue and for some considerable time afterwards it was unattainable unused. We believe this was owing to an official order to the effect that neither stamp collectors nor dealers were to be supplied with it. Whether this order was eventually rescinded, or fell into abeyance in the course of time, we do not know; but one thing is certain—that philatelic persistence triumphed in the end, and that the unused remainder of the issue found its way at last into the hands of philatelists, so that now it is not at all a rare stamp in the unused state. For this reason, and because the unused Six Pence itself is so difficult to find, the forgers have not been so busy with it as with its predecessor, the provisional One Penny; but forgeries of it do exist, and for the satisfaction of our readers, we give the dimensions of the surcharge. The extreme length from the top of the letter “d” to the bottom of the[73] numeral “2” is 16½ mm.; the height of the letter “d” is 4 mm.; the space between the “d” and the figure “1” is 2 mm.; the height of the figure 1 is 4 mm.; the space between the figures “1” and “2” is 2½ mm.; the height of the figure “2” is 4 mm.; and finally, the width of the letter “d,” without measuring the foot, is 2¼ mm. These measurements all vary a little according as the surcharge is lightly or heavily impressed.
November 1881.
Four Pence being one of the Postal Union rates, the stamps of that value remaining in hand from the issue of July, 1877, were soon used up, and in November, 1881, the new lot of the Four Pence value not having yet come out from England, 21 sheets (630 stamps) of the vermilion-red shilling perforated B were surcharged in the Island with a large “4d.” in black, and issued as provisionals. The original values were obliterated by black bars, 2 mm. wide, printed across the sheet. The Philatelic Record of December, 1881, says: “St. Vincent.—Since this Colony joined the Postal Union there has, of course, been a demand for Four Penny stamps. Those used hitherto have been blue, like the issue of 1866, and not yellow, like those of 1869. They were not remainders of the 1866 issue, but stamps reprinted in a brighter shade of blue, and perforated in the rough way which has lately distinguished the stamps of St. Vincent. By the mail delivered here on the 13th inst. we have received letters franked by a provisional Four Penny adhesive, formed by surcharging the current scarlet Shilling[74] 4d., and obliterating the original value by means of a bar.”
We now see how deep was the mystery enshrouding the Four Pence on star paper of Issue 12, when the editor of the leading English philatelic periodical had been ignorant of its existence up to this time, and even then failed to perceive any difference, except in the perforation, between it and the Four Pence of 1866.
The provisional Four Pence has always been a very rare stamp; and it is probably much scarcer than it is generally credited to be, as it has been a favourite with the forgers of all nations, who have in some instances been able to produce articles that pass current as genuine even in circles believing themselves to be well-informed. We refrain, for several reasons, from giving the measurements of the surcharge. First, because, owing to the “4d.” being generally deeply indented in the paper, it is not at all easy to measure it with accuracy; and also because, as regards dimensions, there is a very dangerous forgery frequently met with, which is not to be detected by any amount of measurement, however carefully done, and which can only be distinguished by careful comparison. Particular attention must be paid to the shape of the different angles of the figure “4,” and especially to the contour of the top of that figure, and to the way in which the slanting stroke joins the horizontal and the vertical ones. The forgery alluded to fails in these particulars, but it is like the genuine in this—that it is heavily printed, although not quite so deeply indented as the genuine is sometimes found.
Our illustration, No. 15, represents a well-known forgery of British manufacture, which has been kindly lent to us for the purpose by a gentleman to whom it was presented[75] by the artist himself as a specimen of his skill. This is a much easier forgery to detect than the one we have just been speaking about, as it is generally accompanied by a forged postmark, and is altogether too smoothly printed. Its measurements are also incorrect, the foot of the figure “4” being fully ½ mm. too long. There are a good many specimens of this latter forgery in circulation.
Another point to which we direct attention is, that in the genuine stamps the black bar across the sheet begins on the left exactly flush with the left of the figure “4” of the left hand stamp of the row, and ends exactly under the right edge of the tail of the letter “d” of the right hand stamp. It follows from this, that when the surcharges have been printed in register with the sheet, the three stamps of the left hand vertical column and the corresponding three on the right have the words of value only partly obliterated, the bar under the “4d.” only reaching part of the way across the label containing the original value.
December 1881.
This provisional, which was also surcharged in the Island, was probably issued on the 1st of the month. It was chronicled in the Philatelic Record of January, 1882, and the editor of that periodical notes a specimen postmarked “2nd December 1881.”
The issue consisted of 27 sheets (1,620 stamps) of the Six Pence, bright yellow-green, of Issue 14, surcharged “One Penny” in block capitals. The length of the surcharge is 18 mm., and the height of the letters 2 mm. The[76] original values are obliterated by black bars on the sheet, placed exactly the same as those described in our note to Issue 16, but only 1 mm. in width instead of 2 mm.
It is not nearly such a scarce stamp as the provisional Four Pence, or the One Penny of Issue 13; but it is rarer than the Halfpenny of Issue 15, except when this last is in the used state.
A number of the provisional One Penny of this issue came over unused to English dealers after the stamp had been withdrawn from use, just as in the case of the provisional Halfpenny. Used specimens were at first very scarce, but to remedy this deficiency a certain number of these unused stamps were reshipped to an agent in St. Vincent, and came back through the post in instalments during the course of 1883 and 1884, whenever their owner had a demand for used specimens. This explains the late dates seen on some of these stamps. At the present time there is nothing to choose in point of rarity between used and unused specimens.
There are a good many foreign-made forgeries of this surcharged One Penny, but all we have seen have been very poor attempts, and none of them have ever been made on the right stamp, the one usually selected for forging being the pale yellow-green Six Pence of Issue 11.
We think this is the proper place to note a curious stamp that has just reached our publishers from the United States. It is the left half of a bright yellow-green Six Pence of Issue 14, which stamp has been divided in half by a vertical line of perforation gauging 12. This half stamp is surcharged “D/1” in red, and is postmarked, apparently over the surcharge. The extreme height of the surcharge is 8½ mm.; the height of the figure “1” is 5 mm., and its[77] width ¾ mm.; the height of the letter “D” is 2¾ mm., and its width 2¼ mm. The figure “1” has a long serif, slanting downwards, and a foot like that of a Roman figure “I.”
We do not like to hazard an opinion as to what this stamp may be, but we think it right to place its existence on record, as the perforation which has divided the stamp has been, in our opinion, done by the same official machine that performed the same operation, not only on the postal provisionals of 1880 and 1881, but also on the fiscals that were made in 1882 by dividing diagonally this same Six Pence of Issue 14, and surcharging each half “3d. Revenue.” It was expressly forbidden in St. Vincent to make use of postage stamps for fiscal purposes, unless they had been overprinted “Revenue”; this stamp, if genuine, cannot therefore have been intended for anything but postage. It may have been experimentally prepared in December 1881, when a provisional One Penny was required, and rejected in favour of the one actually issued; but farther than this we cannot go. We are sorry that this interesting stranger has reached us too late for illustration.
December 1881.
The consignment of these three stamps, which was sent out on November 16th, 1881, consisted of 1000 sheets (60,000 stamps) of the Halfpenny, 1000 sheets (60,000 stamps) of the One Penny, and 500 sheets (15,000 stamps) of the Four Pence. All three values were issued in December,[78] and the three provisionals which had temporarily supplied their places were at once withdrawn from use, if indeed this had not already taken place in the case of the provisional Halfpenny.
The plate for the Halfpenny value, like those of the One Penny and Six Pence, consisted of 60 stamps arranged in 6 horizontal rows of 10. Like the other current values, it was printed on the star-watermarked paper.
The lateral distance between the stamps is 19 mm. from centre to centre, and the vertical 21½ mm. These dimensions being smaller by 1⅓ mm. one way, and 2½ mm. the other, than those of the spaces between the stars in the paper, it follows that these last are distributed among the stamps in less than the proportion of one star to each, so it is very seldom that we find the watermark properly centred on any single specimen.
The colour of this Halfpenny varies a good deal in depth of shade, and, like that of most St. Vincent stamps, it has a strong tendency to oxidation. This colour was called “primrose” by the printers. Although only one printing was ever made of it, this was a large one, and it is a very common stamp either unused or used.
We have called the colour of the One Penny “drab,” but it is not a very easy one to define, although our term is more likely to be understood by our readers than that of the printers, which is “chemical black.” For some reason or other it is a very much scarcer stamp unused than the Halfpenny, in spite of there having been printed an equal number of both. We suppose that this must be through the dealers having omitted to put it in stock in any great quantity, and from a number of the sheets having been overprinted “Revenue” for fiscal purposes.
Possibly for the same reasons the Four Pence is also a rare stamp unused, and even used specimens are getting scarce. Only 15,000 of these were printed, and they must have been quickly used up, as a new issue of the value was required within a year.
The three stamps of this issue are only known perforated B; they were the last to be printed for the Colony by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.
In a letter in Stanley Gibbons Monthly Journal for December, 1891, the One Penny drab, with star watermark, is said to exist perforated 14, but the reputed owner has since informed us that this is a mistake.
With the end of 1881 the printing of the stamps of St. Vincent by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co. ceased, and on February 25th, 1882, that firm delivered up the various plates of stamps to the Crown Agents of the Colony in London. These plates were afterwards handed over by them to Messrs. De La Rue & Co., and this firm has since printed all the further supplies of stamps ordered by the Colony, using Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s plates for that purpose.
We give the dates of the various issues comprised in Section II. as accurately as it is in our power to do, but, as we do not enjoy for the stamps of this section the same advantages as we did for those printed by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., we are now obliged for our information to fall back entirely upon the philatelic periodicals, the authorities we have chiefly relied upon being the Philatelic Record and the Timbre-Poste.
With the change of contractors alterations took place in the paper, colours, and perforation of the stamps—printers’ accessories that naturally differ with each individual firm. At the time Messrs. De La Rue & Co. took over the contract they had, in the case of stamps of the size of the majority of those of St. Vincent, ceased using their well-known paper watermarked with a crown and “C.C.,” and had substituted in its place a paper with watermarks of a crown over the letters “C.A.”—these[81] initials standing for “Crown Agents.” This paper is milled or surfaced, medium in thickness, and varies but slightly in both of these two respects. It was specially made for the electrotype plates used by Messrs. De La Rue & Co. in the surface-printing process they employ for most of the current British Colonial stamps. The entire sheet measures 21¼ inches in height by 11 inches in width, or 54 centimetres by 28 centimetres, approximately. In order to correspond with the stamps on these electrotype plates, the watermarks in the sheet are grouped in four panes of sixty, and those in each pane are arranged in ten horizontal rows of six, with a line in watermark enclosing each pane. The two upper panes are separated from the two lower ones by a space of an inch, and this interval is watermarked with the words “Crown Agents,” in a straight line in double-lined block capitals 12 mm. in height. The two panes on the right are separated from the two on the left by a narrow unwatermarked space of 6 mm. There is no marginal watermark at either the top or bottom of the sheet, but at each side the words “Crown Agents for the Colonies” are watermarked in a straight line of double-lined block capitals 7 mm. in height, the words on the left reading upwards, and those on the right reading downwards.
From these particulars it will be seen how ill-adapted this paper is for plates of the size of those of the St. Vincent stamps. The consequence is that the watermarks, “Crown C.A.,” are irregularly distributed over the sheets of all the different values, never being in proper register with the stamps, but more so in the cases of the Halfpenny and the Five Shillings, on account of the sizes of these two values being so very different from that of the De La Rue stamps for which the watermarks are spaced.
We have seen that the plates of the Halfpenny, One Penny, and Sixpence contained sixty stamps, in six horizontal rows of ten, and that of the Five Shillings twenty stamps, in four horizontal rows of five. The “Crown C.A.” paper was, therefore, quite large enough to be divided horizontally, so as to take three impressions of any of these plates. The result of this division of the sheet is that the impression of the plate that happens to be printed on the middle portion has one row of stamps, either partly or wholly, watermarked with as much of the inscription, “Crown Agents,” as the length of the plate will permit; and specimens of all the above values, as well as of the two issues of the One Penny surcharged “2½ Pence,” and the Six Pence surcharged “Five Pence,” by Messrs. De La Rue & Co. are found so watermarked. The plates of the Four Pence and One Shilling, which only contained thirty stamps in three horizontal rows of ten, admitted of the paper being so cut that the words “Crown Agents” are only found watermarked in the margins of the sheets of these two values.
The sheets printed from Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s plates were even less adapted to the perforating machines used by Messrs. De La Rue & Co. for stamps of their own design printed on “Crown C.A.” paper, than, as we have seen, were the Perkins-Bacon plates to that paper. These machines, to which we give the name of “comb,” perforate the top and two sides of every stamp in an entire horizontal row at each descent of the pins. The second descent of the pins, therefore, perforates the bottom of the stamps in the first row and at the same time the top and two sides of the stamps of the second row. This process is continued through the sheet until the bottom of it is reached, when the last descent of the pins perforates the bottom of the lowest row of stamps,[83] and at the same time continues the vertical lines of perforation into the bottom margin of the sheet. If the sheet has been put to the machine in an inverted position, it is the top margin we find perforated vertically. The machines are, however, so constructed that in the centre of the long line of pins two of the vertical lines of the “comb” are placed much closer together than the rest, in order to perforate each side of the narrow central space separating the panes of stamps—vide our description of the paper watermarked “Crown C.A.” This arrangement of the pins makes the machine utterly useless for perforating a row of more than six stamps placed close together. In consequence of this, the stamps of St. Vincent, and those of other Colonies for which Messrs. De La Rue & Co. use the old plates of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., have to be perforated by a different make of machine to that they usually employ for colonial stamps.
For the stamps of St. Vincent three varieties of perforating machines have been used by Messrs. De La Rue & Co. First, a comb-machine of the gauge of 14, similar to the one they employ for perforating the current One Penny &c. of Great Britain, in which the horizontal line of pins is long enough, without the interposition of two vertical lines placed close together, to perforate a row of ten or more stamps; second, a single-line or guillotine-machine with 12 holes in a space of 2 centimetres; and third, a similarly constructed machine to the second, but with a gauge of 14.
In order to distinguish between the perforations of the guillotine-machine gauging 14 and those of the comb-machine which also gauges 14, it is necessary to have either a block of at least four stamps, or a vertical strip with the top and bottom margins of the sheet attached. By examining the[84] points where the lines of perforation intersect each other, or noticing whether both margins of the sheet have been perforated through or not, it is possible to decide the nature of the machine. If, at the point where a vertical and a horizontal line of perforation intersect, there is one hole common to both lines, this hole being of the usual size, or if either the top or bottom margin of the sheet is imperforate, then the perforation must have been done by the comb-machine. On the other hand, if the lines of perforation cross each other so that there is no one hole common to both lines, or if there appears to be such a one that it has evidently been made larger by the passage of a second pin, or if the top and bottom margins of the sheet are both perforated through, then we may be equally certain that the perforation has been performed by the guillotine-machine.
The comb-machine perforating 14 is far more regular in the spacing of the pins than the guillotine-machine of the same gauge. If a long line of perforation of the latter be examined, it will be found that here and there the holes are not in line, and also that there is a slightly wider distance between certain of them, although the gauge of the perforation does not perceptibly vary from 14.
The guillotine-machine gauging 12 is more irregular still in the spacing of the pins, as an examination of our illustration No. 21 will show. For instance, the tenth hole from the bottom is further from the ninth than it is from the eleventh, and the second and third holes from the top, and also others, will be seen to be more or less out of line. The gauge also varies; for if two centimetres be taken up the central line, commencing with the fifteenth hole from the bottom, that space will be found to contain eleven holes,[85] plus the distance between the eleventh and twelfth, which is equivalent to a gauge of 11¾.
For some reason Messrs. De La Rue & Co. do not appear to have made much use of the comb-machine for the stamps of St. Vincent; it may be because their machines were in constant requirement for British stamps. The One Penny, and “2½ Pence” on 1d., rosy-lake, two of the first three values printed by them, were perforated by this comb-machine; but with the exception of one or two other stamps that we shall specify in our notes to the various issues, the remainder, including all the stamps now current in the Island, have been perforated by one or other of the guillotine-machines.
We have not thought proper in our Reference List to make any distinction between the two machines gauging 14, nor have we catalogued stamps showing part of the words “Crown Agents” in the watermark, as we feel that had we done so we should have been adding a fresh terror to stamp collecting, already over-burdened by the weight of “varieties.”
The gum on all the stamps of Section II. is usually white, but sometimes varies to a pale yellow.
The colours of the stamps are for the most part brighter than those used by Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co., and the combination of the line-engraved plates with the colours, paper, and perforations of Messrs. De La Rue & Co. produce certainly some of the finest stamps that have ever been printed.
January 1883.
These two stamps, the first to be printed for the Colony by Messrs. De La Rue & Co., were chronicled in the Philatelic Record of February, 1883, so we may safely put down the date of issue as January. The colours of both values were unchanged, and, allowing for the difference of appearance in Messrs. De La Rue & Co.’s stamps, caused by the whiteness and surfacing of the paper, there is hardly any change to be noticed even in their shades. The One Penny is perforated 14, the machine used having been the “comb.” The Four Pence is also perforated 14, but not having been able to examine a block, or even a pair of these stamps, we are unable to say which of the two machines was used. In all probability it was the guillotine-machine.
February 1883.
Although a surcharged, this is by no means a provisional stamp, since it was made to obviate the necessity of making a plate for the new value of Two Pence Halfpenny required for the Postal Union rate, and, with a change of colour of the One Penny value on which the surcharge is printed, it has remained current ever since its issue in February, 1883.
It was chronicled in the Philatelic Record of March, 1883, and is dated February in the last edition of M. Moens’[87] Catalogue. The surcharge is printed in black, in block figures and capitals 3 mm. in height, and the extreme length of the whole surcharge is 16 mm. A bar, 1 mm. in width, and 14 mm. in length, is printed at a distance of 1 mm. below the “2½ Pence,” and the surcharges are so printed on the sheet that these black bars fall more or less exactly on the lower labels of the stamps, and obliterate the original values. Like the stamps of the last issue, the sheets were perforated 14 by the comb-machine.
We have been shewn some specimens of the One Penny rosy-lake, which their owners fondly imagined were stamps that had escaped the surcharge “2½ Pence.” This is not so, as the One Penny stamp was afterwards issued in exactly the same colour as the surcharged variety we are now considering: vide Issue 25.
October 1883.
In the Philatelic Record of November, 1883, the editor chronicles the two higher values of this issue, on the authority of Dr. Viner, but they were not noticed in the Timbre-Poste until January, 1884. We have every belief that the Four Pence, dull blue, was issued with the two other values, but we can find no contemporary record of it. It is called “bleu terne” and dated 1883 in the First Supplement (published July 1884), to the 6th Edition of M. Moens’ Catalogue. This settles the question as to its colour at least, for although M. Moens’ in the current edition of his Catalogue has dropped the term “bleu terne,” and substituted[88] for it two colours, “outremer” and “bleu foncé,” we cannot help thinking that in this instance he has followed the lead of the London Society’s West Indian Catalogue, which employs precisely these terms in describing the colour of the blue Four Pence perforated 12, ignoring the dull blue stamp altogether. The stamps so described in the London Society’s list certainly belong to a later printing, and we believe them to have been non-existent in July, 1884, when M. Moens issued the First Supplement to the 6th Edition of his Catalogue. The colour of the Four Pence of this issue is a dull dirty blue, inclined to grey-blue, and cannot possibly be mistaken for any of the shades of the Four Pence of the next issue. It is a very rare stamp, particularly unused. All the stamps of this issue are perforated 12 by the guillotine-machine described in our note to Section II.
September 1884.
In the Philatelic Record of March, 1884, will be found an account of a spurious provisional Halfpenny, for which the Deutsche Philatelisten Zeitung seems to have been responsible. The stamp is described as the Six Pence, green, divided vertically, and each half surcharged in black “Halfpenny.” In the June number of the Philatelic Record the editor says: “The result of enquiries made of the Postmaster of St. Vincent is that no such stamp has been issued. There are still large supplies of the small ½d., orange, on hand, which is attested by the fact that the watermark of this stamp has not yet been altered to C.A. and Crown.” The new[89] Halfpenny printed in green, and perforated 12, was afterwards chronicled in the October number of the same journal.
We believe it was at this time that the third and last printing of a blue Four Pence was made by Messrs. De La Rue & Co., and that this is the ultramarine, or dark blue stamp, that is dated by the London Society as having been issued at the end of 1883. Both the stamps of this issue are perforated 12, and this is the last instance in which a machine of this gauge was used for St. Vincent stamps.
The variety of the Halfpenny printed in orange-yellow, but otherwise identical in all other respects with the green Halfpenny of this issue, has been known to us for some two years. A specimen of it was found by our publishers in a collection they had purchased, and at least two others are known, one of which has recently (January, 1895) been advertised for sale. All these are unused, and are printed on “Crown C.A.” paper, gummed, and perforated 12. We have catalogued this stamp as a variety “prepared for use, but never issued,” and, although it would be indiscreet to repeat here all the gossip we have heard on the subject, this fairly represents the case, as far as the evidence that has reached us can be trusted. One thing is at least certain, and that is, none of these yellow Halfpennies ever reached the Island officially.
March 1885.
This provisional stamp was made in the Island by surcharging “1d.” in black on the Two Pence Halfpenny of Issue 20, the surcharged value of that stamp being obliterated by two black bars printed across the sheet. The[90] numeral “1” is 8½ mm. in height, and 1½ mm. in width; it has usually a straight serif, and a foot 3½ mm. long; the letter “d” is 4 mm. in height, and its extreme width is 3 mm. The bars that obliterate the original surcharge “2½ Pence” are each ½ mm. wide, and there is a space of ¾ mm. between them; between the upper of these two bars and the foot of the figure “1” there is a space of 3¼ mm. The top of the “d” is about level with that of the figure “1,” but the position of the letter varies, and it is sometimes a little higher or a little lower than the numeral. Between the “1” and the “d” there is a space of 1½ mm. The only variety of the surcharge that we have found is a stamp which has the serif of the numeral “1” sloping upwards. There appear to be no other varieties of surcharge on the sheet, unless we reckon as such the slightly varying positions of the letter “d” or a type of the figure “1” which has the right hand projection of the foot broken off.
This provisional One Penny was chronicled in the Philatelic Record of April, 1885, and there can be no doubt it was issued in March. Its perforation is of course the same as that of the Two Pence Halfpenny of Issue 20.
April 1885.
The One Penny and Four Pence of this issue were chronicled in the Philatelic Record of May, 1885, and these two at least were issued in April. There is no such certainty with regard to the Halfpenny, dark green, perforated 14, as[91] this is another St. Vincent stamp that altogether escaped being noticed in the periodicals. The earliest record of it we can find is in Mr. Gilbert E. Lockyer’s Colonial Stamps, published in April, 1887. In this work it is grouped with other values as having been issued in “1885-86.” This is a little vague, but we do not suppose that Mr. Lockyer had any more precise information about the date of issue than we ourselves have now. Taking into consideration that the Halfpenny, dark green, perforated 12, of Issue 22, September, 1884, is rather a rare stamp either unused or used, we are inclined to assign to it as short a life as possible, and we believe that the Halfpenny perforated 14 must have been sent out by Messrs. De La Rue & Co. in April, 1885, rather than in June, 1886, with the new printings of the One Penny and Four Pence.
The colour of the Halfpenny is dark green, varying in shade, and it does not differ in this respect from the Halfpenny of Issue 22. The impression is sometimes rather blurred, or woolly, and when this is the case the letters of the inscription appear narrower, and have badly defined edges.
We have called the colour of the One Penny, “carmine,” and that of the Four Pence “red-brown.” In the Philatelic Record of May, 1885, they were called “bright-rose” and “reddish-chocolate,” but in July, 1886, the editor of that periodical, says, “… we think it better to explain that the colour of the One Penny of 1885, when compared with the more recent issue, must be rather termed ‘vermilion-red’ than ‘bright-rose.’”
The Four Pence is rather scarce even used, and unused it is decidedly rare.
All the stamps of this issue are perforated 14 by the guillotine-machine, and the Halfpenny is one of the values that still remain in issue in the Island.
June 1886.
The change in colour of the two values of this issue was first chronicled in the Philatelic Record of July, 1886, where they were spoken of as “recent arrivals,” and their colours described as follows: “The present colour of the One Penny is a decided pink, and it is printed in water-colour; while the Four Pence is a very dark puce-brown.” For the One Penny we have adopted the term “pink,” but prefer “purple-brown” to “puce-brown” for the Four Pence. Besides the usual pink shades of the One Penny we have found that stamp in a colour identical with some of the specimens of the rosy-lake One Penny, which, surcharged “2½ Pence,” appeared in 1883. We have given this stamp a separate number in the Reference List, as, had we been content to include it as a shade of “pink,” it might in time have come to be considered as an error of Issue 20, without surcharge, which it certainly is not. There must have been a great number of printings of the One Penny made since 1886, as the stamp is still current. They are now coming over, in 1895, in shades undistinguishable from the carmine stamp of Issue 24.
If there are any shades of the purple-brown Four Pence they are very slight. It is by no means so scarce a stamp as the red-brown Four Pence of the last issue, but it is not nearly as common as any of the shades of the lake-brown[93] Four Pence, and we think there could only have been one printing of it. The Four Pence, lake-brown, is certainly the result of later printings, but we cannot say for certain when the first of these was made; the earliest date we have found on one is October 2nd, 1886.
All the stamps of this issue are perforated 14 by the guillotine-machine.
October 1888.
The Six Pence, dark lilac, was first chronicled by the Timbre-Poste of November, 1888, although by some oversight M. Moens in the current edition of his Catalogue has dated it December, with the Five Shillings lake. These two stamps were probably sent out together, and issued in October, 1888.
The Six Pence is a dark lilac, more inclined towards blue than red. We are certain that this, and not the red-lilac, was the first printing, as the specimen in the “Tapling Collection,” which came over at the time, is dark lilac.
We have recently seen two unused specimens of the Five Shillings, watermarked Crown C.A., which in colour are almost identical with the Five Shillings of Messrs. Perkins, Bacon & Co.’s printing (Issue 14). An examination of the stamps showed that they had no gum, and that the paper was very white and without surface, clearly showing that the stamps had been tampered with. We have no hesitation in condemning these varieties, as being only the ordinary lake stamps with the colour changed.
All the stamps of this issue are perforated 14; the Four Pence and Five Shillings are done with the guillotine-machine,[94] but the Six Pence is one of the later instances in which the comb-machine was used.
The Five Shillings, lake, is still current.
August 1889.
The issue of this stamp must have taken place in August, 1889, as it was chronicled in the September number of the Philatelic Record of that year. The editor seems to have been rather confused in his ideas about St. Vincent stamps, as in April, in noting the change of colour of the Six Pence from green to lilac, which had taken place six months previously, he surmised that the Six Pence of the former colour had been used up for making provisionals, and he now speaks of the “2½ Pence” on One Penny, lake, as having been issued in 1882, whereas it was not issued until 1883.
The surcharge “2½ Pence” does not call for any remarks, as it is identical with that of the same value of Issue 20. The stamp remained current until August, 1890, when the supply seems to have become exhausted, owing possibly to large purchases for philatelic purposes, and it became necessary to make a provisional, pending the arrival of a fresh supply from the printers in England.
It was perforated 14, and is the last stamp in St. Vincent for which Messrs. De La Rue & Co. used the comb-machine. Its colour is a pale milky-blue, not unlike that of one of the Six Pence values of St. Helena, and a few slight shades are to be found.
August 1890.
As we have said in our note to the foregoing issue, this provisional was made locally, during a temporary dearth of the De La Rue surcharged Two Pence Halfpenny, by surcharging “2½d.” in black on the Four Pence, lake-brown, of Issue 26, the original values being obliterated by black bars printed across the sheet. These bars are 1 mm. in width, and do not extend right across the sheet, but only reach to within 2 mm. of the frames of the right and left hand stamps in the rows. The total length of the surcharge, including the period after “d.,” is 10½ mm. The height of the large figure “2” is 4 mm.; its width is 2½ mm., and it has a curved foot. The small figure “1” is rather more than 2 mm. in height, and the small figure “2” is the same. The “d” is 4 mm. in height by 2 mm. in width, and is followed by rather a large full stop placed within 1 mm. of it. The surcharges are printed from type, and a good many minor varieties are to be found, of which the principal is one in which the fraction line is omitted. Other varieties consist of the large figure “2” with a break in the body just above the foot; small figure “2” with a break in the curve of the head; small figure “1” with differently shaped serifs; and fraction lines of varying lengths in different positions; but none of these varieties are of any great importance.
We take the date of issue from the list of provisional stamps furnished by Mr. Frank W. Griffith, late acting Colonial Postmaster of the island, published in the London Society’s West Indian Catalogue.
November 1890 to 1891.
In this issue we have grouped together the stamps printed subsequent to the issue of the provisional “2½d.” on Four Pence, lake-brown, up to the end of 1891, but for none of which can we give more precise dates. All these stamps are perforated 14 by the guillotine-machine.
The Two Pence Halfpenny differs from the previous printing of the same value in the colour of the stamp, which is now in varying shades of bright blue, instead of in milky-blue as before. When in sheets, or blocks, it can also be distinguished from its predecessor by the perforation having been done by the guillotine-machine, whereas the Two Pence Halfpenny of Issue 27 was perforated by the comb-machine. Its issue was chronicled in the Timbre-Poste of January 1891, in the following terms: “Le 2½ pence, surcharge noire sur le 1 penny, est imprimé en blue vif. Ce timbre vient de nous parvenir ainsi en remplacement de celui, même valeur, dont la surcharge avait été appliquée sur le 4 p. lie de vin.” From dated specimens we have seen, we infer that the issue took place in November, 1890, or even before that date.
We are altogether in the dark as to when the first printing of the red-lilac Six Pence took place. Although this stamp in both its shades of pale and deep red-lilac differs materially from the dark lilac stamp of Issue 26, we can find no chronicle of it anywhere; but we do not think we are far out in[97] dating it at the early part of 1891. In describing the Six Pence of Issue 26, we said that the lilac colour of that stamp inclined more towards blue than red. In both shades of the Six Pence we are now considering the red predominates over the blue, so that the colour almost approaches lake. It is necessary to be quite clear on this point, as there seems to have been only one printing of the dark lilac Six Pence, and it is bound, sooner or later, to become a much rarer stamp than the red-lilac one, which has already had a currency of four years.
There is much the same difficulty with regard to the date of issue of the One Shilling, vermilion-red. This stamp differs both in colour and perforation from the orange-vermilion Shilling of Issue 21, which was perforated 12, but it was unnoticed by philatelists until Mr. Gilbert Lockyer called attention to its existence, in a letter in Stanley Gibbons’ Monthly Journal of December, 1891. In this letter Mr. Lockyer states that Mr. E. Hawkins possesses a specimen, but there can be little doubt that the stamp had been at least some months in issue before this mention of it.
All the stamps of this issue are still current.
November 1892.
The earliest chronicle of this provisional is in Stanley Gibbons’ Monthly Journal for November, 1892, which is the actual date of issue. The stamp was made locally, pending the arrival of a supply from the printers, by surcharging the Four Pence, lake-brown, with “5—Pence,” in thin block capitals, in two lines, and obliterating the original values by[98] bars printed across the sheet. The colour of the surcharge is carmine, inclined to lake. The editor of the Philatelic Record evidently looked with great suspicion on the necessity for this provisional, as when chronicling it he made this remark: “It is said that the issue only lasted an hour, after which the price outside rose to shillings in place of pence.” The dimensions of the surcharge are as follows: The figure “5” is 4 mm. in height, and 2¾ mm. in width; the word “Pence” measures 12 mm. × 2¼ mm. The width of the bar is 1 mm., and this bar extends right across the sheet, and terminates exactly at the outer frame of the right and left-hand stamps of each row. The space between the bar and the word “Pence” is 5½ mm., and that between the same word and the figure “5” is 1¾ mm. At a distance of 20 mm. above the bar there is a row of small ornaments, two to each stamp, so grouped in pairs that they fall exactly on the stars in the two top corners of each stamp—that is, when the surcharges are in exact register with the sheet. It is not easy to say what these ornaments are, or why they have been introduced. They measure about 2 mm. each way, and are very faintly printed. As far as we can make out they are printer’s type ornaments of a somewhat uncommon pattern, and the illustration here given is from an enlarged drawing of one of them.

The whole surcharge—values, bars, and ornaments—is evidently done from a cliché, and there are no varieties on the sheet. In the one now before us, the third stamp from the left on the bottom row has the first “E” of “Pence” double printed,[99] with a space of about ½ mm. between the two impressions. We cannot say whether this is a variety existing on every sheet, or whether it is peculiar to this one only.
March 1893.
These values were issued in March, 1893, and are perforated 14 by the guillotine machine. The Four Pence is the old design, but with the colour once more changed to canary-yellow. For the Five Pence Messrs. De La Rue & Co. printed the current Six Pence in a new colour, and surcharged each stamp, over the original value, with the words “FIVE PENCE” in a straight line of block capitals, measuring 13½ mm. × 2¾ mm. There are two very distinct colours of this stamp—dull carmine and carmine-brown. They were both in existence in November, 1893, at which date they were chronicled in Stanley Gibbons’ Monthly Journal.
The stamps of this issue are still current.
SAINT VINCENT.
An Act to authorise the appointment of a Colonial Post-Master for the Colony of Saint Vincent, and to transfer to the Executive Government of the said Colony the control over the Post Office therein, heretofore exercised by Her Majesty’s Post-Master-General.
Whereas it hath become necessary to provide for the appointment of a Colonial Post-Master, and to transfer to the Executive Government of the Island of Saint Vincent and its Dependencies, the authorities, power, and control, over the Post Office Establishment of the said Island, heretofore exercised by Her Majesty’s Post-Master General.
Be it therefore enacted by the Governor, Council, and Assembly of the said Island of Saint Vincent and its Dependencies, as follows; that is to say—
1. Immediately on the passing of this Act, and so from time to time as often as a vacancy shall occur in the said Office, there shall be appointed by the officer for the time being administering the Government of the said Island of St. Vincent, by Commission under his hand and the Public Seal of the Colony a fit and proper person to be Colonial Post-Master of the said Government, &c., &c., &c., &c.
5. There shall be one General Post Office provided by the Executive Government, in the Town of Kingstown, where all Letters, Newspapers, Books, Pamphlets, and other Papers, which shall arrive in this Colony from any place out of the same (unless excepted or exempted by any Act of the Imperial Parliament, or by this Act) shall be brought[101] and received, and whence the same shall be delivered to the persons to whom addressed, and where all Letters, Newspapers, Books, Pamphlets, and other Papers (except such as are excepted or exempted as aforesaid) shall be posted and received for transmission to any place out of this Colony, and whence the same shall be despatched to all places out of this Colony; and such General Post Office shall be in such part of the Government Buildings, in the said Town of Kingstown, as the Governor, with the consent of the Executive Council shall, from time to time, fix and direct; and the hours of attendance at such Post Office shall be governed and regulated by and according to the Rules to be made, as hereinafter provided for the governance of the Post Office Establishment of this Colony.
11. The Postage on all Letters, posted in this Colony for transmission to any place out of the same, shall be paid by the sender on delivering the same at the Post Office in money, until stamps shall be provided, under the provisions of this Act. Provided always, that Letters written on stamped paper, or enclosed in stamped covers, or having a stamp affixed thereto (the stamp, in every such case, being of the value or amount in this Act expressed, and specially provided for the purpose, under the authority of this Act) shall if within the limitation of weight fixed by or under the authority of any Statute of the Imperial Parliament in that behalf, and if the stamp have not been used before, pass by the Post free, subject only as to such Letters as shall not be sent to the United Kingdom, to such Postage as the same shall or may be liable to, on arrival at their places of destination, under the Laws of such places respectively.
12. And whereas, under arrangements entered into by Her Majesty’s Post-Master-General, one rate, or the sum of one penny, is to be paid to and received by the Local Government on every single Letter coming from the United Kingdom, and received in this Colony from or through Her[102] Majesty’s General Post Office; and a like rate, or one penny, on every single Letter collected in, and sent from this Colony, to the United Kingdom, through the said General Post Office, and a double rate on every Double Letter, and so in proportion, according to the rate or scale governing the Postage on Letters sent by the General Post Office from the United Kingdom to these Colonies, or from these Colonies to the United Kingdom. Be it therefore enacted—That the Colonial-Post-Master shall keep an account, and shall collect and receive, on behalf of the Local Government, such Rates and Postage as aforesaid, as shall be payable for all such Letters as aforesaid.
13. On every Letter arriving in this Colony, by Her Majesty’s General Post, from any place beyond the limits of the Colony, except from or passing through the United Kingdom; and on every Letter posted in this Colony for transmission to any place beyond the limits of the same, except to or through the United Kingdom, there shall be charged, and paid to Her Majesty, for the use of this Colony, Postage by weight, according to the following Scale, that is to say—
Not exceeding half-an-ounce—One rate of one penny.
Exceeding half-an-ounce, but not exceeding one ounce—Two rates, or two pence.
Exceeding one ounce, but not exceeding two ounces—Four rates, or four pence.
Exceeding two ounces, but not exceeding three ounces—Six rates, or sixpence.
And so on in progression, an additional two rates being charged for every additional ounce or fraction of an ounce.
16. (Provides for Registration of Letters and Book Packets, at rate of one shilling each.)
17. It shall be lawful for the Governor to cause to be provided, at the Public expense, proper and sufficient Postage Stamps and Dies, or other Implements for expressing and[103] denoting the Rates or Duties of Postage for this Colony; and such Dies, Stamps, and Implements, shall be kept in such custody, and such Stamps shall be made or impressed from such Dies or other Implements, and sold in such manner as the Governor, with the consent of the Executive Council, shall from time to time direct by writing under his hand.
Act passed June 14th, 1860.
Note.—Another Act was passed on September 10th, 1863, which raised the postage on letters despatched to foreign countries, with the exception of those going to or through the United Kingdom, from one penny to two pence the half ounce, and so on in proportion. The charge of one penny on letters coming to St. Vincent through the Imperial Post Office was at the same time abolished.
| Number of Issue. |
Date of Issue. | Wmk. | Denomination and Colour. | Perforation. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | May 1861 | None. | 1d., bright rose-red | A. | ||
| 6d., blue-green | A. | |||||
| 2 | 1862 | None. | 6d., yellow-green | C. | ||
| 3 | 1863-1866 | None. | 1d., bright rose-red | B. | B×A. | |
| 6d., blue-green | B. | |||||
| 4 | August 1866 | None. | 4d., deep bright blue | B. | ||
| 1s., dark slate-grey | A. | B×A. | ||||
| 1s., greyish-purple | A. | B×A. | ||||
| 5 | April 1869 | None. | 1s., indigo | B. | ||
| 6 | October 1869 | None. | 4d., deep bright yellow | B. | ||
| 1s., bright brown | B. | |||||
| 7 | June 1871 | Star. | 1d., black | A. | B×A. | |
| 6d., dull blue-green | A. | |||||
| 6d., dark blue-green | A.[6] | |||||
| 8 | June 1872 | Star. | 1s., bright rose-red | B. | B×A. | |
| 1s., deep rose-red | B. | ? | ||||
| 1s., dull red | B. | ? | ||||
| 9 | Early in 1874 | Star. | 1s., pale violet-rose | B. | B×A. | |
| 10 | 1875 | Star. | 1s., dark claret | B. | ||
| 11 | February 1877 | Star. | 6d., pale yellow-green | A. | B×A. | |
| 1s., bright vermilion-red | B.[7] | B×A. | ||||
| 12 | July 1877 | Star. | 4d., dark deep blue | B. | ||
| 14 | June 1880 | Star. | 1d., pale grey-green | B. | ||
| 6d., bright yellow-green | B.[8] | |||||
| 5s., deep rose-red | B. | |||||
| 18 | December 1881 | Star. | ½d., orange-yellow | B. | ||
| 1d., drab | B. | |||||
| 4d., bright ultramarine | B. | |||||
[6] This stamp was used for making the provisional One Penny of Issue 13.
[7] This stamp was used for making the provisional Four Pence of Issue 16.
[8] This stamp was used for making the provisional Halfpenny of Issue 15, and the provisional One Penny of Issue 17.
| No. of Issue. |
Date of Issue. | Watermark. | Denomination and Colour. | Perf. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | January 1883 | Crown “CA.” | 1d., drab | 14* | |
| ” | 4d., bright blue | 14† | |||
| 20 | February 1883 | ” | “2½ Pence” on 1d., rosy-lake[9] | 14* | |
| 21 | October 1883 | ” | 4d., dull blue | 12 | |
| ” | 6d., bright green | 12 | |||
| ” | 1s., orange-vermilion | 12 | |||
| 22 | September 1884 | ” | ½d., dark green | 12 | |
| ” | ½ d., orange-yellow (variety, never issued) | 12 | |||
| ” | 4d., ultramarine | 12 | |||
| 24 | April 1885 | ” | ½d., dark green | 14† | |
| ” | 1d., carmine | 14† | |||
| ” | 4d., red-brown | 14† | |||
| 25 | June 1886 | ” | 1d., pink | 14† | |
| ” | 1d., rosy-lake | 14† | |||
| ” | 4d., purple-brown | 14† | |||
| ” | 4d., lake-brown[10] | 14† | |||
| 26 | October 1888 | ” | 6d., dark lilac | 14* | |
| ” | 5s., lake | 14† | |||
| 27 | August 1889 | ” | “2½ Pence” on 1d., milky-blue | 14* | |
| 29 | Nov. 1890-91 | ” | “2½ Pence” on 1d., bright blue | 14† | |
| ” | 6d., pale red-lilac | 14† | |||
| ” | 6d., deep red-lilac | 14† | |||
| ” | 1s., vermilion-red | 14† | |||
| 31 | March 1893 | ” | 4d., canary-yellow | 14† | |
| “Five Pence” on 6d., dull carmine | 14† | ||||
| “Five Pence” on 6d., carmine-brown | 14† | ||||
* Comb-machine. † Guillotine-machine.
[9] This stamp was used for making the provisional One Penny of Issue 23.
[10] This stamp was used for making the provisional Two Pence Halfpenny of Issue 28, and the provisional Five Pence of Issue 30.
| Date of Despatch. | Denomination and Colour. | Quantity. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| March 27th, 1861 | 1d., red | 934 | sheets, | 56,040 | stamps. |
| 6d., green | 167 | ” | 10,020 | ” | |
| July 22nd, 1862 | 1d., red | 467 | ” | 28,020 | ” |
| 6d., green | 167 | ” | 10,020 | ” | |
| May 28th, 1863 | 1d., red | 467 | ” | 28,020 | ” |
| 6d., green | 668 | ” | 40,080 | ” | |
| March 1st, 1865 | 1d., red | 467 | ” | 28,020 | ” |
| 6d., green | 167 | ” | 10,020 | ” | |
| March 14th, 1866 | 1d., red | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” |
| 6d., green | 500 | ” | 30,000 | ” | |
| July 28th, 1866 | 4d., blue | 500 | ” | 15,000 | ” |
| 1s., purple | 500 | ” | 15,000 | ” | |
| June 15th, 1868 | 1d., red | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” |
| 6d., green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” | |
| February 27th, 1869 | 1s., purple | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” |
| August 13th, 1869 | 4d., yellow | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” |
| 1s., brown | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” | |
| February 14th, 1870 | 1d., red | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” |
| March 28th, 1871 | 1d., black | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” |
| 6d., green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” | |
| January 5th, 1872 | 1d., black | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” |
| April 13th, 1872 | 1s., pink | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” |
| October 28th, 1872 | 1d., black | 600 | ” | 36,000 | ” |
| July 28th, 1873 | 1d., black | 600 | ” | 36,000 | ” |
| 6d., green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” | |
| 1s., pink | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” | |
| August 15th, 1874 | 1d., black | 600 | ” | 36,000 | ” |
| March 27th, 1875 | 1d., black | 600 | ” | 36,000 | ” |
| 6d., green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” | |
| 1s., pink | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” | |
| February 28th, 1876 | 1d., black | 1000 | ” | 60,000 | ” |
| December 30th, 1876 | 6d., light green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” |
| 1s., scarlet | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” | |
| May 29th, 1877 | 1d., black | 1000 | ” | 60,000 | ” |
| 4d., dark blue | 200 | ” | 6,000 | ” | |
| August 28th, 1878 | 1d., black | 1000 | ” | 60,000 | ” |
| 6d., light green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” | |
| 1s., scarlet | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” | |
| May 13th, 1880 | 1d., pale green | 1000 | ” | 60,000 | ” |
| 6d., green | 300 | ” | 18,000 | ” | |
| 1s., bright red | 300 | ” | 9,000 | ” | |
| 5s., pink | 100 | ” | 2,000 | ” | |
| November 16th, 1881 | ½d., light orange | 1000 | ” | 60,000 | ” |
| 1d., slate | 1000 | ” | 60,000 | ” | |
| 4d., light blue | 500 | ” | 15,000 | ” | |
Note.—The colours in the above list are those given in the printers’ books. The list will be found of the greatest assistance to philatelists in helping them to determine the relative rarity of the stamps of Section I. It must, however, be borne in mind that at least two other factors enter into this problem. These are the number of stamps that were surcharged “Revenue” for fiscal purposes, and also the number of unused stamps that were stocked by the dealers at the time of their issue. Take for instance the Four Pence of 1866 and the Four Pence of 1877, of which the numbers printed were 15,000 and 6,000 respectively. Theoretically speaking, the latter should be 2½ times as rare as the former, but in reality it is much more so. The earlier one was stocked by the dealers, and is no rarer unused than used. The later stamp unused is at least ten times as rare as the first Four Pence in the same state, although the relative rarity of the two stamps when used is, roughly speaking, in proportion to the quantity printed of each.

End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Stanley Gibbons Philatelic
Handbooks: Saint Vincent, by Francis H. Napier and E. D. Bacon
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK GIBBONS PHILATELIC HANDBOOKS: ST VINCENT ***
***** This file should be named 58472-h.htm or 58472-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/5/8/4/7/58472/
Produced by MWS, Adrian Mastronardi, The Philatelic Digital
Library Project at http://www.tpdlp.net and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive/American Libraries.)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions will
be renamed.
Creating the works from print editions not protected by U.S. copyright
law means that no one owns a United States copyright in these works,
so the Foundation (and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United
States without permission and without paying copyright
royalties. Special rules, set forth in the General Terms of Use part
of this license, apply to copying and distributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works to protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm
concept and trademark. Project Gutenberg is a registered trademark,
and may not be used if you charge for the eBooks, unless you receive
specific permission. If you do not charge anything for copies of this
eBook, complying with the rules is very easy. You may use this eBook
for nearly any purpose such as creation of derivative works, reports,
performances and research. They may be modified and printed and given
away--you may do practically ANYTHING in the United States with eBooks
not protected by U.S. copyright law. Redistribution is subject to the
trademark license, especially commercial redistribution.
START: FULL LICENSE
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full
Project Gutenberg-tm License available with this file or online at
www.gutenberg.org/license.
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or
destroy all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your
possession. If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a
Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound
by the terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the
person or entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph
1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this
agreement and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the
Foundation" or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection
of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual
works in the collection are in the public domain in the United
States. If an individual work is unprotected by copyright law in the
United States and you are located in the United States, we do not
claim a right to prevent you from copying, distributing, performing,
displaying or creating derivative works based on the work as long as
all references to Project Gutenberg are removed. Of course, we hope
that you will support the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting
free access to electronic works by freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm
works in compliance with the terms of this agreement for keeping the
Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with the work. You can easily
comply with the terms of this agreement by keeping this work in the
same format with its attached full Project Gutenberg-tm License when
you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are
in a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States,
check the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this
agreement before downloading, copying, displaying, performing,
distributing or creating derivative works based on this work or any
other Project Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no
representations concerning the copyright status of any work in any
country outside the United States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other
immediate access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear
prominently whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work
on which the phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed,
performed, viewed, copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere in the United States and
most other parts of the world at no cost and with almost no
restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it
under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this
eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org. If you are not located in the
United States, you'll have to check the laws of the country where you
are located before using this ebook.
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is
derived from texts not protected by U.S. copyright law (does not
contain a notice indicating that it is posted with permission of the
copyright holder), the work can be copied and distributed to anyone in
the United States without paying any fees or charges. If you are
redistributing or providing access to a work with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the work, you must comply
either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 or
obtain permission for the use of the work and the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any
additional terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms
will be linked to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works
posted with the permission of the copyright holder found at the
beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including
any word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access
to or distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format
other than "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official
version posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site
(www.gutenberg.org), you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense
to the user, provide a copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means
of obtaining a copy upon request, of the work in its original "Plain
Vanilla ASCII" or other form. Any alternate format must include the
full Project Gutenberg-tm License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
provided that
* You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is owed
to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he has
agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments must be paid
within 60 days following each date on which you prepare (or are
legally required to prepare) your periodic tax returns. Royalty
payments should be clearly marked as such and sent to the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the address specified in
Section 4, "Information about donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation."
* You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or destroy all
copies of the works possessed in a physical medium and discontinue
all use of and all access to other copies of Project Gutenberg-tm
works.
* You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of
any money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days of
receipt of the work.
* You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work or group of works on different terms than
are set forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing
from both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and The
Project Gutenberg Trademark LLC, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm
trademark. Contact the Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
works not protected by U.S. copyright law in creating the Project
Gutenberg-tm collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may
contain "Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate
or corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other
intellectual property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or
other medium, a computer virus, or computer codes that damage or
cannot be read by your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium
with your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you
with the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in
lieu of a refund. If you received the work electronically, the person
or entity providing it to you may choose to give you a second
opportunity to receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If
the second copy is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing
without further opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS', WITH NO
OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT
LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of
damages. If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement
violates the law of the state applicable to this agreement, the
agreement shall be interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or
limitation permitted by the applicable state law. The invalidity or
unenforceability of any provision of this agreement shall not void the
remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in
accordance with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the
production, promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works, harmless from all liability, costs and expenses,
including legal fees, that arise directly or indirectly from any of
the following which you do or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this
or any Project Gutenberg-tm work, (b) alteration, modification, or
additions or deletions to any Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any
Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of
computers including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It
exists because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations
from people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future
generations. To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation and how your efforts and donations can help, see
Sections 3 and 4 and the Foundation information page at
www.gutenberg.org
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent permitted by
U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is in Fairbanks, Alaska, with the
mailing address: PO Box 750175, Fairbanks, AK 99775, but its
volunteers and employees are scattered throughout numerous
locations. Its business office is located at 809 North 1500 West, Salt
Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887. Email contact links and up to
date contact information can be found at the Foundation's web site and
official page at www.gutenberg.org/contact
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
[email protected]
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To SEND
DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any particular
state visit www.gutenberg.org/donate
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations. To
donate, please visit: www.gutenberg.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works.
Professor Michael S. Hart was the originator of the Project
Gutenberg-tm concept of a library of electronic works that could be
freely shared with anyone. For forty years, he produced and
distributed Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of
volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as not protected by copyright in
the U.S. unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not
necessarily keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper
edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search
facility: www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.