The footnotes follow the text.
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Palestine, by Claude Reignier Conder This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license Title: Palestine Author: Claude Reignier Conder Release Date: August 28, 2013 [EBook #43588] Language: English Character set encoding: UTF-8 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK PALESTINE *** Produced by Heiko Evermann, Chuck and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This book was created from images of public domain material made available by the University of Toronto Libraries (http://link.library.utoronto.ca/booksonline/).)
| Every attempt has been made to replicate the original as printed. The footnotes follow the text. |
| Some images have been moved out of paragraphs for easier reading. |
| (etext transcriber's note) |
| In certain versions of this etext, in certain browsers,
clicking on this symbol |

The World’s Great Explorers
and Explorations.
Edited by J. Scott Keltie, Librarian, Royal Geographical Society; H. J. Mackinder, M.A., Reader in Geography at the University of Oxford; and E. G. Ravenstein, F.R.G.S.
A PICTORIAL MAP OF JERUSALEM AND THE HOLY LAND, FOR THE
USE OF PILGRIMS.
(From a MS. of the 13th Century in the Burgundian Library at
Brussels.)
Frontispiece.
BY
MAJOR C. R. CONDER, D.C.L., R.E.
LEADER OF THE PALESTINE EXPLORING
EXPEDITION.
NEW YORK
DODD, MEAD & COMPANY
Publishers
THE Editors of the present series having done me the honour to ask me briefly to relate the story of Palestine Exploration, and especially of the expeditions which I commanded; and having stipulated that the book should contain not only an account of the more interesting results of that work, but also something of the personal adventures of those employed, I have endeavoured to record what seems of most interest in both respects.
Many things here said will be found at greater length in previous works which I have written, scattered through several volumes amid more special subjects. I hope, however, that the reader will discover also a good deal that is not noticed in those volumes; for the sources of information concerning ancient Palestine are constantly increasing; and, among others, I may mention, that the series of Palestine Pilgrim Texts, edited by Sir Charles Wilson, has added greatly to our knowledge, and has enabled me to understand many things which were previously doubtful.
The full story of the dangers and difficulties through which the work was brought to a successful conclusion cannot be given in these pages, and no one recognises more than I do the imperfections which—as in all human work—have caused it here and there to fall short of the ideal which we set before us. What can, however, be claimed for Palestine exploration is, that the ideal was always as high as modern scientific demands require. The explorations were conducted without reference to preconceived theory, or to any consideration other than the discovery of facts. The conclusions which different minds may draw from the facts must inevitably differ, but the facts will always remain as a scientific basis on which the study of Palestine in all ages must be henceforth founded.
I fear that even now, after so much has been written, the facts are not always well known—certainly they have often been misrepresented. It is my desire, as far as possible, in these pages to summarise those facts which seem most important, while giving a sketch of the mode of research whereby they were brought to light.
C. R. C.
Note.—The maps illustrating this volume have been revised by Major Conder, who is more especially responsible for those of the Kingdom of Jerusalem and of Modern Palestine. The geological sketch-map embodies Major Conder’s researches, as also the important explorations of Dr. K. Diener in the Lebanon.—Ed.
| CHAP. | PAGE | |
| INTRODUCTORY CHAPTER | 1 | |
| I. | EXPLORATIONS IN JUDEA | 22 |
| II. | THE SURVEY OF SAMARIA | 59 |
| III. | RESEARCHES IN GALILEE | 83 |
| IV. | THE SURVEY OF MOAB | 134 |
| V. | EXPLORATIONS IN GILEAD | 171 |
| VI. | NORTHERN SYRIA | 190 |
| VII. | THE RESULTS OF EXPLORATION | 214 |
| ———— | ||
| APPENDICES:— | ||
| NOTE ON JERUSALEM EXCAVATION | 247 | |
| INDEX OF OLD TESTAMENT SITES IDENTIFIED IN PALESTINE | 252 | |
| INDEX OF NEW TESTAMENT SITES IDENTIFIED IN PALESTINE | 262 | |
| INDEX | 267 | |
| FULL-PAGE ILLUSTRATIONS. | ||
| 1. | A Pictorial Map of Jerusalem and the Holy Land for the use of Pilgrims (from a MS. of the 13th Century in the Burgundian Library at Brussels) | Frontispiece |
| 2. | The Plain of Jericho, as seen from Ai | to face page 35 |
| 3. | The Dead Sea (view S.E. of Taiyibeh) | " 43 |
| 4. | Alphabets of Western Asia | " 173 |
| 5. | Jebel Sannin (Lebanon) | " 192 |
| ILLUSTRATIONS IN TEXT. | ||
| Portrait of Dr. Robinson (from a photograph) | page 16 | |
| Portrait of Sir C. Wilson (from a photograph by Maull & Fox) | " 17 | |
| Portrait of Sir C. Warren (from a photograph) | " 18 | |
| Desert of Beersheba | " 53 | |
| Kurn Sartaba | " 68 | |
| The Jordan Valley (’Esh el Ghurab) | " 73 | |
| A Camp in the Jordan Valley | " 80 | |
| Mount Tabor | " 86 | |
| Carmel | " 88 | |
| Nain | " 93 | |
| The Sea of Galilee | " 99 | |
| Krak des Chevaliers (Kala’t el Hosn) | " 108 | |
| Moab Mountains from the Plain of Shittim | " 142 | |
| A Dolmen west of Heshbon | " 144 | |
| View of Dead Sea from Mount Nebo | " 158 | |
| Hittites from Abu Simbel | " 198 | |
| Hamath Stone, No. 1 | " 200 | |
| MAPS (Printed in Colours). | ||
| I. | General Map of Palestine | facing page 1 |
| II. | Physical Map of Palestine | at end |
| III. | Geological Map of Palestine | " |
| IV. | Palestine as divided among the Twelve Tribes | " |
| V. | Palestine | " |
| VI. | The Kingdom of Jerusalem, showing the Fiefs, about 1187 A.D. | " |
| VII. | Modern Palestine, showing the Turkish Provinces | " |
| MAPS IN TEXT. | ||
| Palestine and Syria according to Ptolemy, c. 100 A.D. | page 2 | |
| A Section of Peutinger’s Table | " 4 | |
| Marin Sanuto’s Map of the Holy Land, 1321 | " 12 | |
| The Holy Land, from the Atlas of Ortelius, c. 1591 | " 14 | |
THE long narrow strip of country on the east shore of the Mediterranean, which in a manner was the centre of the ancient world, has in all ages been a land of pilgrimage. For five hundred miles it stretches from the deserts of Sinai to the rugged Taurus, and its width, shut in between the Syrian deserts and the sea, is rarely more than fifty miles. It can never be quite the same to us as other lands, bound up as it is with our earliest memories, with the Bible and the story of the faith; and it is to the credit of our native land that we have been the first to gather that complete account of the country, of its ancient remains, and of its present inhabitants, which (if we except India) does not exist in equal exactness for any other Eastern land.
The oldest explorer of Palestine—if we do not reckon Abraham—was the brave King Thothmes III., who marched his armies throughout its whole length on his way towards Euphrates. Many are the pilgrims and conquerors who have followed the same great highways along which he went. When, in the early Christian ages, the land became sacred to Europe, the patient pilgrims of Italy, and even of Gaul, journeyed along the shores of Asia Minor, and sometimes were able to reach the Holy City, and to bring back to their homes some account of the country; while in later ages the pilgrims came not singly, but in hosts continually increasing, and finally as crusaders, colonists, and traders.
![]()
PALESTINE AND PART OF SYRIA ACCORDING TO PTOLEMY, c.
100 A.D.
The literature of Palestine exploration begins, therefore, with the establishment of Christianity. Before that date we have very little outside the Bible except in the works of Josephus, whose descriptions, though at times unreliable as regards measurement, are invaluable as the accounts of an eye-witness of the state of the country before the destruction of Jerusalem by Titus. We have scattered notes in the Talmud, in Pliny, in Ptolemy,[1] in Strabo, and in other classic works, which have been collected by the care of Reland and of later writers; but it was only when the Holy Land became a land of pilgrimage for Christians that itineraries and detailed accounts of its towns and holy places began to be penned.
The Bordeaux pilgrim[2] actually visited Jerusalem while Constantine’s basilica was being built over the supposed site of the Holy Sepulchre, and in Palestine his brief record of stations and distances is expanded into notes on the places which he found most revered by Syrian Christians. In the same reign, Eusebius, the historian of the Church, constructed an Onomasticon, which answered roughly to the modern geographical gazetteer. His aim—and that of Jerome, who rather later rendered this work from Greek into Latin, adding notes of his own—was to identify as far as possible the places mentioned in the Old and New Testaments with places existing in the country as known to themselves. This work is both scholarly and honest in intention, but the traditions on which Eusebius and Jerome relied have not in all cases proved to be reconcilable with the Biblical requirements as studied by modern science. The Onomasticon is, however, of great importance as regards the topography of Palestine in the fourth century, and has often led to the recovery of yet more ancient sites, which might otherwise have been lost. Jerome had an intimate personal knowledge, not only of the country round Jerusalem and Bethlehem, where he lived so long, but also of the whole of Western Palestine. Places east of Jordan are noticed in the Onomasticon, but that region was less perfectly known to the Christian co-authors of this work. In the fourth century the Roman roads were marked by milestones, and thus the distances given by Eusebius and Jerome are actual, and not computed distances. Measurement on the Survey map, which shows these milestones whereever they remain by the roadside, proves that for the most part the Onomasticon distances are very correct, and the sites of places so described can, as a rule, be recovered with little difficulty.
![]()
A SECTION OF PEUTINGER’S TABLE.
The Peutinger Tables, representing the Roman map of Palestine about 393 A.D., give us also the distances along these roads; but the knowledge of the map-maker as to the region east of Jordan was most imperfect, and the map, which presents no latitudes or longitudes, is much distorted. To the same century belongs Jerome’s elegant letter on the travels of his pious friend Paula, which is, however, but a slight sketch, more remarkable for its eloquence and fanciful illustration of Scripture than for topographical description.[3]
A short tract—very valuable, however, to the student of Jerusalem topography—was penned by Eucherius in the fifth century; and in the sixth we have the account by Theodorus (or Theodosius) of the Holy Land in the days of Justinian.[4] The eulogistic record by Procopius of the buildings of Justinian also gives accounts and references to the names of his monasteries and churches in Palestine, which are of considerable use.[5] In the same reign also (about 530 A.D.) Antoninus Martyr[6] set forth from Piacenza, and journeyed to Constantinople, Cyprus, Syria, and Palestine. He even crossed the Jordan and went through the Sinaitic desert to Egypt. Like the Bordeaux pilgrim, Antoninus was a firm believer in the apocryphal Gospels, which already began to be held in high estimation. The former pilgrim repeats stories from the Gospel of the Hebrews; the latter, in addition, refers to the Gospel of the Infancy; but, in spite of the superstitious tone of the narrative of Antoninus, his itinerary is valuable, because it covers the whole region west of Jordan, and contains notes of contemporary custom and belief which are of great antiquarian interest.
The conquest of Palestine by Omar did not by any means lead to the closing of the country to Christians. One of the best known and most detailed accounts of the Holy Land written up to that time was taken down from the lips of the French Bishop Arculphus[7] by Adamnan, Bishop of Iona, about 680 A.D., in the monastery of Hy. It appears that Arculph was in Palestine during the reign of Mu’awîyeh, the first independent Khalif of Syria ruling in Damascus, and the same policy of toleration and peace which was inaugurated by this ruler enabled St. Willibald in 722 A.D.[8] to journey through the whole length of the land. These writers are concerned chiefly in description of the holy places, which increased in number and in celebrity from century to century. Arculphus constantly interrupts his narrative with pious legends, much resembling those of the modern Roman Catholic guide-books to Palestine, though some of the sites which were correctly identified by these early Christian pilgrims were transferred by the Latin priests of the twelfth century to impossible localities, where they are still in some cases shown to Latins, while the older tradition survives among the Greek Christians. We often encounter an interesting note in these pilgrim diaries, such as Arculphus’ description of the pine-wood north of Hebron, now represented by but a few scattered trees. St. Willibald seems to have been regarded as a harmless hermit, who, when once the object of his journey was understood, was allowed by the “Commander of the Faithful” to travel in peace throughout the land.
In the reign of Charlemagne good political relations existed between that monarch and the Khalif of Baghdad, Harûn er Rashîd. The keys of Jerusalem were presented to the Western monarch, who founded a hospice for the Latins in that city. About half a century later, at the time when Baghdad was at the height of its glory as a centre of literature and civilisation, Bernard, called the Wise,[9] with two other monks, one Italian, the other Spanish, visited the Holy Land from Egypt, and they were able to obtain permits which were respected by the local governors.
The rise of the Fatemites in Egypt altered materially the status of the Christians in Syria. We have no known Christian account of Palestine between the ninth and twelfth centuries. Hakem, the mad Khalif of Egypt, destroyed the Christian churches in Jerusalem in 1010 A.D., and the country seems to have been then closed to pilgrims.
During this period, however, we have at least two important works, namely, that of El Mukaddasi (about 985 A.D.), and the journey of Nasir i Khusrau in 1047 A.D.[10] El Mukaddasi (“the man of Jerusalem”) was so named from his native town, his real name being Shems ed Dîn. He describes the whole of Syria, its towns and holy places (or Moslem sanctuaries), its climate, religion, commerce, manners and customs, and local marvellous sights. The legends are no less wonderful than those of his monkish predecessors, but his notes are often of great historical interest, and he is the earliest writer as yet known who plainly ascribes the building of the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem to its real author, the Khalif ’Abd el Melek. It is remarkable that he speaks of the Syrian Moslems as living in constant terror of the Greek pirates, who descended on the coasts and made slaves of the inhabitants, whom they carried off to Constantinople. The Christians were still, he says, numerous in Jerusalem, and “unmannerly in public places.” The power of the Khalifs was indeed at this time greatly shaken by the schisms of Islam, and the Greek galleys invaded the ports, which had to be closed by iron chains. The Samaritans appear to have flourished at this time as well as the Jews, and the Samaritan Chronicle, which commences in the twelfth century, speaks of this sect as very widely spread even earlier, in the sixth and seventh centuries A.D.
Abu Muin Nâsir, son of Khusrau, was born near Balkh, and journeyed through Media and Armenia by Palestine to Cairo, thence to Mecca and Basrah, and back through Persia to Merv and Balkh, the whole time spent being seven years. He gives good general accounts of Jerusalem, Hebron, and other places, though his description does not materially add to our information.
The rise of the Seljuks boded little good to Syria. Melek Shah in 1073 A.D. conquered Damascus, and by the end of the century Jerusalem groaned under the Turkish tyranny. It was at this time—just before the conquest of the Holy City, which had been wrested from the Turks by the Egyptians—that Foucher of Chartres began his chronicle of the first Crusade, which contains useful topographical notes. The great history of the Latin Kingdom by William of Tyre is full of interesting information as to the condition of the country under its Norman rulers (1182-85 A.D.), and to this we must add the Chronicles of Raymond d’Agiles and Albert of Aix, which belong to the time of the first Crusade.[11]
Two other early works of the Crusading period are of special value. Sæwulf[12] visited the Holy Land in 1102 A.D., before the building of most of the Norman castles and cathedrals; and the Russian Abbot Daniel, whose account has only recently been translated into English,[13] is believed to have arrived as early as 1106 A.D. From Ephesus he went to Patmos and Cyprus, and thence to Jerusalem and all over Western Palestine. His account is one of the fullest that we possess for the earliest Crusading period. In the middle of the twelfth century we have the topographical account by Fetellus,[14] which refers to places not generally described; and rather later we have the valuable descriptions by Theodoricus and John of Wirzburg,[15] while only two years before Saladin’s conquest of Jerusalem, John Phocas[16] wrote a shorter account in Greek upon silk, which is interesting as the work of a Greek ecclesiastic at a time when the Latins were the dominant sect. The names of monasteries in the Jordan Valley, otherwise unnoticed, are recoverable in his account.
Much interesting topographical information of this period is to be found in the Cartulary of the Holy Sepulchre,[17] which gives striking evidence of the rapidly increasing possessions of the Latin Church, due to the gifts and legacies of kings and barons. The cartularies of the great orders and the laws contained in the Assizes of Jerusalem are equally important to an understanding of Palestine under the rule of its feudal monarchs. It is possible to reconstruct the map of the country at this period in a very complete manner from such material.[18]
The Jews were not encouraged in Syria by the Normans. Benjamin of Tudela, however, made his famous journey from Saragossa in 1160, and returned in 1173 after visiting Palestine, Persia, Sinai, and Egypt; he was interested in the “lost tribes,” whom the mediæval Jews recognised in the Jewish kingdom of the Khozars in the Caucasus, and his account of Palestine is a valuable set-off to those of the Christian visitors.[19] We have pilgrimages by Rabbis in later centuries, viz., Rabbi Bar Simson in 1210 A.D., Rabbi Isaac Chelo of Aragon in 1334, and others of the fifteenth, sixteenth, and seventeenth centuries.[20] These refer chiefly to the holy cities of the Jews, especially to Tiberias and Safed in Galilee, and record visits to the tombs of celebrated Rabbis, many of which are still preserved, and some yet visited by the Jews of Palestine. Several important points regarding early Christian and Talmudic topography are cleared up by these works.
One of the favourite accounts of the Holy City and of Palestine at the time of its conquest by Saladin was written by an unknown author, and was reproduced in the thirteenth century in the Chronicle of Ernoul.[21] There are many manuscripts of this, as of earlier works, which were preserved in the monasteries of Europe, and recopied by students who seem to have had little idea of the importance of preserving the original purity of their text. Some of the versions are mere abstracts, some are supplemented by paraphrases from Scripture. The original work known as the Citez de Jherusalem was evidently penned by one who had long lived in the Holy City, and knew every street, church, and monastery. He gives us the Frankish names for the streets, and the topography is easily traced in the modern city. There are perhaps few towns which are better known than Jerusalem in the latter part of the twelfth century A.D., and the varying manuscripts throw an interesting light on the way in which errors and variations crept into a popular work before the invention of printing.
The vivid and spirited chronicle of the campaigns of Richard Lion-Heart by Geoffrey de Vinsauf (1189-1192 A.D.) informs us of the condition of the maritime region, and describes a part of Palestine which few have visited, between Haifa and Jaffa, as well as the region east of Ascalon and as far south as the border of Egypt. The topography of this chronicle I studied on the ground with great care in 1873-75. The charming pages of Joinville, though of great interest as describing the unfortunate Crusade of St. Louis in 1256 A.D., contain much less of geographical value than the preceding.[22]
In the fourteenth century men’s minds were often occupied with schemes for the recovery of the Holy Places. Marino Sanuto, a Venetian noble, who is said to have travelled in the East, wrote an elaborate work on the subject, which he presented to Pope John in 1321. The greater part is taken up with his views as to the military steps necessary for an expedition against the Saracens, but a very full gazetteer of Palestine, with a map, is also introduced into the work. Some have doubted whether Marino Sanuto ever visited Palestine. His information is, however, very correct on the whole, and his account of roads, springs, and other features appears to be founded on reliable observation.
During the transition period of the struggle between Christendom and Islam, Palestine had narrowly escaped the horrors of a Mongol invasion. Mangu Khan, to whom St. Louis had sent the mild and pious William de Rubruquis at his distant capital of Karakorum (in Mongolia) in 1253, was defeated by the Egyptian Sultan Kelaun, successor of the terrible Bibars, in 1280, and had already been defeated in 1276 by Bibars himself near La Chamelle (now Homs) in Northern Syria. A very interesting letter has lately been published by Mr. Basevi Sanders from Sir Joseph de Cancy in Palestine to Edward the First in England,[23] written in 1281, and describing the later defeat near Le Lagon (the Lake of Homs), which saved the country from the cruelty from which other lands were then suffering. The Mameluk Sultans ruled in Palestine down to 1516 A.D., when the Turkish Selim overthrew their power at Aleppo, since which time Palestine has been a Turkish province. During the three centuries of Mameluk rule there are many descriptions, Christian and Moslem, of the country, and the well-known Travels of Sir John Mandeville are among the earliest. He was a contemporary of Marino Sanuto, and although those portions of the work (with which he consoled his rheumatic old age) that refer to more distant lands are made up from various sources, going back to the fables of Pliny and Solinus, still the account of Palestine itself appears to be original, and contains passages (such as that which relates to the fair held near Banias) which show special knowledge of the country. In 1432 Sir Bertrandon de la Brocquiere, with other knights, made an adventurous journey through the whole length of the country, and through Northern Syria and Asia Minor to Constantinople.[24] To the same period belongs John Poloner’s description, which shows us how tenaciously the Latin monks held to their possessions in the Holy Land.[25]
![]()
THE HOLY LAND, FROM THE ATLAS OF ORTELIUS, c. 1591.
In the fifteenth century we have Moslem accounts by Kemâl ed Dîn and Mejr ed Dîn, which are of value in tracing the architectural history of Jerusalem. Mejr ed Dîn was Kady of the city, and his topographical account, though brief, is minutely detailed.[26] Among other Christian travellers of this century, Felix Fabri (1483-84), a Dominican monk, has left one of the best accounts. But how little these later Christian pilgrims contributed to enlarging our exact knowledge of Palestine may be judged of from such a map as that contributed by Christian Schrot to the Atlas of Ortelius, a map very decidedly inferior to that supplied more than two centuries earlier by Marino Sanuto.
Of travellers who visited Palestine during the early Turkish period, the first in importance is the shrewd and moderate Maundrell (1697 A.D.).[27] He was chaplain of the English factory at Aleppo, which dated back to the time of Elizabeth, and the account of his travels shows that it was more difficult to traverse Palestine in his days than to penetrate into Eastern Mongolia in the days of Rubruquis and Marco Polo. Among the tyrannical chiefs of various small districts who robbed and annoyed him was Sheikh Shibleh near Jenin, whose tomb is now a sacred shrine on the hill above Kefr Kud. Of this holy man he records that “he eased us in a very courteous manner of some of our coats, which now (the heat both of the climate and season increasing upon us) began to grow not only superfluous but burdensome.”
In these early days travelling was perilous, and, as a rule, only possible in disguise. In 1803 the journey of Seetzen was specially valuable, and the travels of the celebrated Burckhardt followed soon after in 1809-16. Both these explorers died in the East before their self-allotted tasks were complete. In 1816 Buckingham (still remembered by the elder generation as a gallant explorer) visited Palestine, and in 1817 Irby and Mangles made an adventurous journey in the country east of the Jordan. Their account is still valuable for this region. From that time forward the accounts of personal visits to the country become too numerous to be here recorded. The names of Bartlett, Wilson, Töbler, Thomson, Lynch, De Saulcy, Van de Velde, Williams, and Porter are among the better known of those who preceded or were contemporary with the celebrated Robinson.
![]()

PORTRAIT OF DR. EDWARD ROBINSON (Born 1794, Died
1863).
But it was only in 1838 that really scientific exploration of Palestine began with the journey of the famous American (Dr. Robinson), whose works long continued to be the standard authority on Palestine geography, and whose bold and original researches have been so fully confirmed by the excavations and explorations of the last twenty years.
![]()

PORTRAIT OF SIR CHARLES WILSON.
From a Photograph by
Maull & Fox, Piccadilly.
To this same period, preceding actual surveys, belongs the work of De Vogüé, whose monographs on the Temple, the Dome of the Rock, the churches of Palestine, and his splendid volume of plates for Northern Syrian architecture, together with his collection and decipherment of various early inscriptions in the country, give him the highest rank as an Orientalist. With his name must be coupled that of Waddington, who first attempted to form a corpus of Greek texts from inscriptions found in Palestine, while the standard authority on Phœnician and Hebrew texts is the recently published corpus of Semitic inscriptions by Renan.
Sir C. W. Wilson’s survey of Jerusalem and travels in Palestine in 1864-66, and his subsequent exploration of the Sinaitic desert in 1867, roused public attention to the neglected state of Palestine geography, leading to the execution for the Palestine Exploration Fund of the wonderful excavations by Sir C. Warren at Jerusalem. These excavations round the walls of the old Temple area, carried out in the teeth of fanatic and political obstruction, have enabled us to replace the weary controversies of half a century ago by the actual results of measurement and scientific exploration. Sir Charles Wilson’s already published survey of the Holy City, his reconnaissances throughout the length of the Palestine watershed, preceding his Sinai Expedition, his survey of the Sea of Galilee, and his exact determination of the level of the Dead Sea, 1292 feet below the Mediterranean, were the first efforts of modern science to supply really valuable statistics concerning Palestine itself. The shafts and tunnels of Sir Charles Warren were the first serious attempts of the engineer to place our knowledge of Jerusalem on an equal footing with that which had been in like manner attained at Nineveh and Babylon some twenty years before.
It was by the advice of these experienced explorers that the survey of Palestine from Dan to Beersheba, and from the Jordan to the Great Sea, was undertaken, a work which commenced in 1872, was completed in the field in 1877, but not fully published till 1882. It is with this work that the present volume is chiefly concerned, since it was my good fortune to conduct the parties almost from the first, and to carry out the publication of the maps and memoirs. It had first been intended that Captain Stewart, R.E., should have commanded the party, but that officer was unfortunate in falling ill almost at once on reaching the field of work; and it was through the kindness of the late Major Anderson, R.E., the comrade of Sir Charles Wilson in Palestine, that my name was brought forward as one who had been deeply interested in the work of previous explorers, and who desired to act as Captain Stewart’s assistant. By the sudden illness of that officer, the non-commissioned officers were left in Palestine without a military superior; and as my military education at Chatham had just been completed, I was fortunate in being selected, at the age of not quite twenty-four years, to the command of the Survey Expedition.
Since the completion of the survey of Western Palestine, the survey of Moab, Gilead, and Bashan has been commenced. In 1881 I set out in charge of a small party, hoping to finish this new enterprise in about three years’ time. But alas! I found much change in Syria during the interval of my absence. The suspicions of the Sultan were aroused; the Turkish Government refused to believe in the genuineness of our desire to obtain antiquarian knowledge. Political intrigues were rife, and after struggling against these difficulties for fifteen months, after surveying secretly about five hundred square miles of the most interesting country east of the Dead Sea, and after vainly attempting to obtain the consent of the Sultan to further work, it became necessary to recall the party in the same year in which the researches of Mr. Rassam in Chaldea were suspended and a general veto placed on all systematic exploration.
Since that year, however, a little work has been done from time to time by residents in communication with the Home Society. Herr Schumacher, a young German colonist, has made some excellent maps of parts of Bashan, and Dr. Hull has explored the geology of the district south of the Dead Sea, while further discoveries have even been made in Jerusalem by Herr Konrad Schick, who has recovered part of the second wall and one of the important pools (the Piscina Interior) in the north-east corner of the city.
The most interesting result of Herr Schumacher’s journeys have been the discovery of the sites of Hippos and Kokaba east of the Sea of Galilee, and of dolmen centres like those which I found in Moab.
The task with which I am charged is, however, to give a general account of the exploration of Palestine conducted by the parties under my command; and taking the subject roughly in the order of date of survey, I hope to show that not only in a geographical sense, but also as a contribution to the true understanding of the ancient history of the East, our labours were not in vain, and our method was such as to give exhaustive results.
In concluding this introductory sketch, I should wish to point out that the Palestine of 1889 is not the Palestine which I entered in 1872. Partly on account of the work of the Palestine Exploration Fund, partly because of political changes, the number of travellers has enormously increased. In 1873 it was possible to visit villages where the face of a Frank had never been seen, but now even the Arabs beyond Jordan are often brought in contact with Europeans. Such a chance of studying the archaic manners of the peasantry and the natural condition of the nomadic Arabs as we enjoyed cannot now recur. For six years I lived entirely among the peasantry, but since then war, cruel taxation, and the rapacity of usurers has broken up and ruined the peasant society as it existed fifteen years ago. In 1882 I saw only too plainly the change that had come over the land. The Palestine of the early years of the Survey hardly now exists. The country is a Levantine land, where Western fabrics, Western ideas, and even Western languages, meet the traveller at every point. In the present pages I have attempted to give some idea of the country as it was in the last years of its truly Oriental condition, with a peasantry as yet hardly quite tamed by the Turk, and regions as yet hardly traversed by the European explorer.
NEARLY every tourist in Palestine lands at Jaffa, and thence travels to Jerusalem. The open roadstead, the yellow dunes, the distant shadowy mountains, the brown town on its hillock, the palms, the orange-gardens and the picturesque crowd are familiar to very many of my readers. So are the paths over the plain, the mud villages and cactus hedges, the great minaret tower of Ramleh, and the rough mountains, with scattered copses of mastic and oak, with stone hamlets and terraced olive groves, through which lies the way to the Holy City.
When first I traversed this road in July 1872, it was less frequented than it is now. The long rows of Jewish cottages which first meet the eye on reaching the plateau west of the city were not then built, and Mr. Cook’s signboard was not fixed to the ancient walls of Jerusalem. The increase of the population by the arrival of 15,000 European Jews had not commenced, and what has now been gained in prosperity has been lost in picturesque antiquity of appearance. Jerusalem was then still an Oriental, but has now become what is known as a Levantine town.
The winters of 1873, of 1874, and of 1881 I spent within the walls, and many other visits were necessary from time to time; but our work lay in the country, and it was only here and there that we were able to add new details to the exhaustive and scientific records of Sir Charles Wilson and Sir Charles Warren in Jerusalem itself. My first impression was one of disappointment. The city is small, the hills are stony, barren, and shapeless. One seemed always to be traversing bylanes, so narrow were the steep streets, which afterwards became so familiar. But Jerusalem is a city which to the student becomes more interesting the longer he explores the remains of a past stretching back through the proud days of the Crusading kingdom to the glories of the Arab Khalifate, to the quaint superstitions of the Byzantines, to the greatness of the Herodians, to the earlier civilisation of the Hebrews. Relics still remain of the works of every age, from the time when David first fixed his throne on Sion; and even after fifteen years of exploration a great discovery remained to be made in the finding of the only Hebrew inscription, as yet known in Western Palestine, which dates back to the times of the kings of Judah.
Space will not allow of a complete account of Jerusalem, which may be found in the publications of the Palestine Exploration Fund.[28] Few scenes in the East remain more distinctly printed on the memory than do those connected with life in Jerusalem. The motley crowd in its lanes, where every race of Europe and of Western Asia meets; the gloomy churches; the beauty of the Arab chapel of the Rock; the strange fanaticism of the Greek festival of the Holy Fire; the dervish processions issuing from the old Temple area; the pathetic wailing at the Temple wall; the Jewish Passover; the horns blown at the feast of Tabernacles; Russian, Armenian, Greek, and Georgian pilgrims; the Christ crucified by Franciscan monks in the gilded chapel of Calvary; the poor whose feet are washed by a crowned bishop—all remain in the memory with the mighty ramparts of the city as seen by Christ and His disciples, and the blue goggles of the tourist from the West. No other town presents such an epitome of history, or gathers a crowd so representative of East and West.
There are only two discoveries to which I propose to refer, as being the most important since the closing of Sir Charles Warren’s mines. These are the discovery of the Temple rampart and that of the Siloam inscription. The extent of the Temple area, as rebuilt by Herod the Great, was defined by the excavations which Sir Charles Warren carried down to the rock foundations, in some parts by mines 70 to 100 feet deep,[29] but in no part did he find the ancient walls rising above the level of the inner court. The north-west corner of the area is occupied by barracks, standing on the cliff which was once crowned by the citadel of Antonia; and outside this cliff is the rock-cut trench, converted later into a covered double pool, which the Christians of the fourth century regarded as Bethesda. From this pool a narrow lofty tunnel leads southwards through the cliff. It is an ancient aqueduct, which was stopped up by the building of the Temple wall. Sir Charles Warren explored it with great difficulty on a raft on the sewage with which it was filled; but in 1873 was cleared out by the city authorities, and I was able to explore it at leisure. At the very end, through a hole in the floor, it was possible to reach a chamber over this rocky passage, built against the Temple wall and lighted by a window which looks into the north-west part of the Temple court. The east wall of the chamber is the ancient wall built by Herod, and here I found the same great drafted stones which occur in the foundations. I also found that the wall was adorned outside above the ground-level by projecting buttresses, just like those of the enclosure at Hebron, to be mentioned immediately. We are thus able to picture the appearance of the great ramparts of Herod’s Temple enclosure, with such buttresses running round the walls and capped by a boldly corbelled cornice, presenting the same simple and massive appearance which may still be seen in the smaller enclosure round the tombs of the Patriarchs at Hebron.
The discovery of the Siloam inscription was an instance of the accidental manner in which important monuments are often recovered; yet, as in other cases, it was due to the education which the native population receives from the scientific explorer. Had the importance of such discoveries not been impressed on the minds of natives, it is possible that the Jewish boy who, falling down in the water of the narrow aqueduct, first observed the only known relic of the writing of his ancestors in King Hezekiah’s days, would not have been conscious how valuable a discovery he had made on a spot visited by more than one eager explorer who passed unconscious by the silent text.
On the east side of Jerusalem runs the deep Kedron gorge; under the Temple walls on its western slope a rock chamber contains the one spring of Jerusalem, known as the Virgin’s Fountain to Christians, and as the “Mother of Steps” to Moslems, because of the stairs which lead down into the vault from the present surface of the valley, as raised by the accumulated rubbish of twenty-five centuries of stormy history. This spring, with its intermittent rush of waters welling up under the steps, is the En Rogel of the Old Testament, and I believe the Bethesda or “House of the Stream,” the troubling of whose waters is mentioned in the fourth Gospel. From the back of the rock chamber a passage, also rock-cut, and scarcely large enough in places for a grown man to squeeze through, runs south under the Ophel hill for about a third of a mile, to the reservoir which is the undisputed site of the ancient Pool of Siloam. The course of the channel is serpentine, and the farther end near the Pool of Siloam enlarges into a passage of considerable height. Down this channel the waters of the spring rush to the pool whenever the sudden flow takes place. In autumn there is an interval of several days; in winter the sudden flow takes place sometimes twice in a day. A natural syphon from an underground basin accounts for this flow, as also for that of the “Sabbatic river” in North Syria. When it occurs, the narrow parts of the passage are filled to the roof with water.
This passage was explored by Dr. Robinson, Sir Charles Wilson, Sir Charles Warren, and others, but the inscription on the rock close to the mouth of the tunnel was not seen, being then under water. When it was found in 1880 by a boy who entered from the Siloam end of the passage, it was almost obliterated by the deposit of lime crystals on the letters. Professor Sayce, then in Palestine, made a copy, and was able to find out the general meaning of the text. In 1881 Dr. Guthe, a German explorer, cleaned the text with a weak acid solution, and I was then able, with the aid of Lieutenant Mantell, R.E., to take a proper “squeeze.” It was a work of labour and requiring patience, for on two occasions we sat for three or four hours cramped up in the water in order to obtain a perfect copy of every letter, and afterwards to verify these copies by examining each letter with the candle placed so as to throw the light from right, left, top and bottom. Only by such labour can reliable copies be made. We were rewarded by sending home the first accurate copy published in Europe, and were able to settle many disputed points raised by the imperfect copy of the text before it was cleaned. An excellent cast was afterwards made.
The contents of the text, which now ranks as one of the most valuable found in the East, are not of historic importance. The six lines of beautifully chiselled letters record only the making of the tunnel, which seems to have been regarded as a triumph of Hebrew engineering skill. It was begun from both ends, and the workmen heard the sound of the picks of the other party in the bowels of the hill, and called to their fellows. Thus guided, they advanced and broke through; the two tunnels proving to be only a few feet out of line. No date, no royal name, or other means of ascertaining the age of the text exist; yet our knowledge is enough to fix very closely, from the forms of the letters, the century in which it must have been written. It is probably to this tunnel that the Bible refers in noting the water-works of King Hezekiah (2 Chron. xxxii. 30); and the text shows us that monumental writing was in use among the Hebrews about 700 B.C. The differences between these Hebrew letters and those used by the Phœnicians of the same age also show us that writing must have been familiar to the inhabitants of Jerusalem for many centuries before the time when this text was engraved; and it thus becomes the first monumental proof of the early civilisation of the Hebrews which has been drawn from their own records on the rock.
Being aware of the contents of the text, we determined to re-explore and survey the whole length of the tunnel, in order to see if any other texts could be found, and to discover if possible the exact place where the two parties of workmen met, on that day 2580 years before, when they heard each others’ voices through the rock. Followed by Lieutenant Mantell and Mr. G. Armstrong, I crawled over the mud and sharp pebbles for the whole distance, dragging with us a chain, and taking compass angles, which were entered in a wet note-book by the light of a candle often put out by the water. We also suffered from the bites of the leeches and from the want of air; but our chief danger was the sudden rise of the water, which might have caught us in that narrow part of the passage, where, crawling flat, we were hardly able to squeeze through and to keep our lights burning. We noted, however, two shafts to which we might retire if the water rose, and which were perhaps made in order to allow the workmen to stand upright at times and rest. It is almost impossible to suppose that the narrowest parts were excavated by grown men; at all events, they must have been narrower in the shoulders than the explorers; but I believe that boys were probably employed. In this narrow part no inscription could have been cut, nor did we find any tablets on the rock in other parts like that already noticed. On the first occasion, after five hours, we reached the Virgin’s Pool safely; but we found a second visit necessary, and in order to make the danger less, we determined to pass down the tunnel from the spring, where I stationed a servant to warn us if the water began to rise. Hardly had we got a hundred yards down the passage when we heard his shouts, and at once began to canter on all fours to the spring chamber over the pebbles and mud. We had crossed the pool with the water only up to our knees, but when we again reached it from the tunnel at the back, it was well up to the arm-pits; and hardly were we safe on the landing of the steps, when we heard the water gurgling in the tunnel, and knew that it must in the narrow part be full to the roof. In a short time the flow subsided, and we were able to go back safely, knowing that it would not rise again that day. We were astonished, however, on emerging at Siloam, to find the stars shining, for we had again spent five hours in the dark, with the mud, stones, and leeches, and considered ourselves lucky in escaping an attack of fever, which generally follows such exposure to wet and cold in Palestine. We were rewarded by finding the place where the two parties, working from either end of the tunnel, met nearly half-way.
From the fourth century to the present day the sites of Calvary and of the Holy Sepulchre have been shown within the precincts of the Crusading cathedral, standing where Constantine’s basilica was raised. The discovery of part of the “second wall” in 1886 shows pretty clearly that the line which—guided by the rock-levels—I drew in 1878, nearly coinciding with Dr. Robinson’s line, is correct, and that the traditional site was thus in the time of our Lord within the city walls. For the last half century this view has been very generally held, but there was no agreement as to the true site. I was enabled, however, through the help of Dr. Chaplin, the resident physician, to investigate the ancient Jewish tradition, still extant among the older resident Jews, which places the site of the “House of Stoning” or place of execution at the remarkable knoll just outside the Damascus gate, north of the city. There are several reasons, which I have detailed in other publications, for thinking that this hillock is the probable site of Calvary. When General Gordon was residing at Jerusalem, he adopted this idea very strongly, and it has thus become familiar to many in England.[30] The bare and stony swell breaks down on the south side into a precipice, over which, according to the Talmud, those doomed to be stoned were thrown, and on the summit they were afterwards crucified, according to the same account. The hillock stands conspicuous in a sort of natural amphitheatre, being thus fitted for a spectacle seen by great multitudes. The neighbourhood has always apparently been regarded as of evil omen, and a Moslem writer says that men may not pass over the plateau beside it at night for fear of evil spirits. Close to this same spot, also, the earliest Christian tradition pointed out the scene of the stoning of Stephen.
When first I reached Palestine in 1872, the Survey party were at work at Shechem, thirty miles north of Jerusalem. Sergeant Black and Sergeant Armstrong, whose names should be specially recorded among those who worked at the survey, because they were longest employed, and because their ability was conspicuous in framing a plan of operations suited to the peculiar requirements, had made good progress, with the aid of Mr. C. F. Tyrwhitt Drake, left in charge when Captain Stewart came home ill. They had carried the work from Jaffa to Jerusalem, and thence along the mountains to Shechem, in six months, and the hill country of Benjamin, which I afterwards examined, was thus surveyed before I reached Palestine. This part of Judea, though presenting immense difficulties to the surveyor, which had been overcome by patience and toil, did not yield much of great interest beyond Mr. Tyrwhitt Drake’s discovery of a Jewish tomb-inscription, and the identification of several lost Hebrew cities. The site of Bethel, famous as it is in Bible history, is only that of a small village, on a ridge which, even for Judea, is remarkably barren and rocky. Here truly the wanderer who dreamed of angels could find nought save a stone for his pillow; but the long vista of the Jericho plain, seen over the peaks and ridges of the desert of Judah, might even now, by some modern Lot, be likened to the “garden of the Lord,” so green do its pastures look in spring, set in the stony ring of barren hills.
Not far thence we one day crossed the great gorge of Michmash, where was the fortress of the Philistines that Jonathan assaulted. We were able to lead our horses down from ledge to ledge, following the strata, to the bottom of the valley on its south side; but on the north towered the cliff of Bozez (“the shining”), which the Hebrew hero scaled. Here no horse could find a footing, and climbing up to visit the hermit’s caves, I was able to judge the effort which would be necessary to scale the whole height and then to fight at the top. No doubt the garrison must have regarded Jonathan’s feat as practically impossible.
The ridge on which Jerusalem stands, 2500 feet above the Mediterranean, runs southwards, gradually rising to 3000 feet in the neighbourhood of Hebron, where the open valley of vineyards forms one of the heads of the great Beersheba watercourse. This difficult region was surveyed in the autumn of 1874, and many ancient sites and ruins were discovered. We were not, however, at that time able to enter the Hebron Sanctuary, which had never been fully explored, and which is one of the most interesting places in Palestine. In 1882, however, I accompanied the Princes Albert Victor and George of Wales, who, under the guidance of Sir Charles Wilson, explored this zealously-guarded mosque, of which I then made the only complete plan in existence. The Haram (or “Sanctuary”) at Hebron is an oblong enclosure, repeating that of the Temple of Jerusalem on a smaller scale. It is not mentioned by early writers, yet there can be little doubt that it must be the work of Herod the Great, or of one of his immediate successors. It already existed in 333 A.D., and the walls are so exactly like those of the Jerusalem Haram, that they cannot be supposed the work of the Byzantine emperors.
The ramparts enclose a mediæval church and a courtyard, built over an ancient rock-cut cave, which in all ages has been regarded as the sepulchre purchased by Abraham from the sons of Heth, where Sarah first is said to have been buried, and afterwards Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob, Rebecca and Leah. Six cenotaphs, like Moslem tombs, covered with rich embroidered cloths, stand in the enclosure—two inside the church (now a mosque), two in chapels beside the porch of the same, and two in buildings against the opposite rampart walls. It is not however supposed, even by Moslems, that these are the real tombs; they only mark supposed sites of tombs beneath the floor. These lower tombs, which Benjamin of Tudela, the Jewish traveller of the twelfth century, claims to have seen, are now inaccessible, and it is impossible to say how far his account can be trusted.[31] In the floor of the mosque there are two entrances closed by flagstones, which are said to lead down by steps into the rock-cut cave. No Moslem would dare to enter this sacred cavern, where, as they say, Isaac would await and slay them, while Jewish legends tell that Eliezer of Damascus stands at the door to watch the repose of Abraham asleep in the arms of Sarah. There is, however, a hole in the floor which pierces the roof of a square chamber, lighted by a silver lamp suspended from the mouth of the hole.
Into this well-mouth we thrust our heads, and the lamp was lowered almost to the floor. Here I saw clearly that in one wall of the chamber a small square door exists, just like those of rock-cut tombs all through Palestine. There is thus probably a real tomb under the mosque, and the chamber is apparently an outer porch to this tomb. The floor was covered to some depth with sheets of paper, evidently the accumulations of many years. These papers are petitions to Abraham, which the pious Moslems drop through the hole, and thus leave lying at the door of his sepulchre.
Another opportunity of so thoroughly exploring this interesting site may not speedily occur; and so long as the mosque remains a mosque, it is doubtful if any one will succeed in entering the tomb itself, though it might perhaps be reached by the stairs said to exist on the south side of the building, if permission could be obtained to force up the flagstones.[32]
As regards the identity of this sepulchre with that of the Patriarchs, all that can be said is that tradition is unvarying on the subject, and the site nowise improbable; but the Hebrews never appear to have embalmed the dead, and if any inscriptions existed (inscriptions of early date on Hebrew tombs being almost unknown), they would probably belong to a very recent period.
In an account like the present it is difficult to follow either a geographical or a chronological order. The geography of Palestine is, however, very generally understood, and the regions next to each other are here mentioned in order. The Survey was extended from a central band along the watershed, the reason being that the plains could only be visited, with due regard to the health and comfort of the party, in the spring and early summer, while the mountains were our refuge in the great heats of August and September, and in the sickly autumn, when the climate of the lower regions becomes almost pestilential. Only once was this system disregarded, and the result was an outbreak of virulent fever in the camp, which threatened for a time to put an end to the expedition.
East of the Hebron and of the Jerusalem hills stretches the desert of Judah, a plateau broken by ridges and ravines reaching to the tall cliffs which rise from the shores of the Dead Sea. Beyond this desert the plains of Jericho, through which the Jordan flows, stretch along the north shores of the sea, and are about 1000 feet lower than the surface of the Mediterranean. On the west of the Judean mountains there are foot-hills (the region called Shephelah in the Bible), and west of these again the broad plains of Sharon and of Philistia extend to the sandhills of the Mediterranean coast, which presents no natural harbour south of Mount Carmel.
The Judean desert I surveyed with a very small party in the early spring of 1875. The Jericho plains we unfortunately visited too soon in December 1873. The Shephelah and the plain of Philistia were completed in the spring of 1875 without any difficulty, save a small part near Beersheba, which was finished in 1877. Beersheba itself was visited in the autumn of 1874. These regions were all more or less wild, and inhabited by nomadic Arabs, so that the adventures of the party were more numerous than when our work lay near the civilised centres and among the settled villagers. The four regions above mentioned may be briefly mentioned in order.
The Judean desert is without exception the wildest and most desolate district in Syria. It seems hardly possible that man or beast can find a living in such a land. Yet, as David found pasture for those “few poor sheep in the wilderness,” so do the desert Arabs find food for their goats among the rocks. It is none the less a desert indeed, riven by narrow ravines leading to deep gorges, and rising between the stony gullies into narrow ridges of dark brown limestone, capped with gleaming white chalk, full of cone-like hillocks and fantastic peaks. Here sitting on the edge of the great cliffs, which drop down a sheer height of some two thousand feet to the rock-strewn shore, gazing on the shining waters of that salt blue lake, watching the ibex herds scudding silently over the plateau, the tawny partridges running in the valley, hearing the clear note of the black grackle as it soars among the rocks where the hyrax (or coney) is hiding, I have felt the sense of true solitude such as is rarely known elsewhere. There is no stirring of the grass by the breeze, no rustling of leaves, no murmur of water, no sound of life save the grackle’s note or the jackal’s cry, re-echoed from the rocks. The sun beats down from a cloudless sky; the white glare of the chalk, the smooth face of the sea, are broad stretches of colour unbroken by variety, save where the tamarisk with its feathery leaves makes a dark line among the boulders of the torrent course. Here really out of the world the solitary hermits sate in the rocky cells which were their tombs; here in the awful prison of the Marsaba monastery men are still buried, as it were, alive, without future, without hope, without employment, with no comradeship save that of equally embittered lives. The chance traveller alone connects them with the world. The grackles, to whom, on the wing, they toss the dried currants, the jackals, who gather beneath the precipice for the daily dole of bread, these are almost the only living things they see. Many are monks disgraced by crime, and what wonder, too, that some are maniacs or idiots? Few sadder scenes can be witnessed than that of a mass sung in the chapel of Marsaba, where John of Damascus (once the minister of a Moslem Khalif) sleeps in the odour of sanctity.
I think it is General Gordon who has somewhere said that for a man to understand the world he should for a time leave the life of busy cities and think out his thoughts alone in the wilderness. Often have I thought that could the critic leave his comfortable study and dwell for a time in this desert of Judah, under the starry sky at night and the hot glare of the sun by day, in a land which men once thought to have been burned by fire, cursed, and sown with salt, and in the great stillness of a world almost without life, he would be able better to understand what Hebrew poets, prophets, and historians have written, and we should perhaps not see Solomon in the garb of a German Grand Duke, or Isaiah in the robes of an University Don.
The north part of this desert is inhabited by scattered groups of the Taamireh tribe, the southern part by the Jahalin Arabs. The Taamireh, or “cultivators,” are not true Arabs, but villagers who have taken to desert life. They wear turbans, and resemble the villagers in type more closely than the Bedu. The Jahalin, whose name means “those ignorant of the Moslem faith,” are a wild and degraded tribe, the poorer being almost naked, while the chiefs have an evil name. I went into this desert without either guide or interpreter, and the party depended throughout on such knowledge of Arabic as I possessed in communicating with natives. I was not then aware how exact are the border divisions between nomadic tribes, and was surprised to find the Taamireh chief one day very unwilling to follow me. As we returned home the reason became evident. We had crossed the boundary valley into Jahalin country, and a number of wild half-clad figures sprang up from behind the rocks on the hillside armed with ancient matchlocks. The Sheikh’s influence was enough to prevent their robbing me, but they guarded us for some distance to the border valley, only asking how soon I was going to cover the land with vineyards. They believe that the Franks control the rain, and that they once grew vines in the desert. It is perhaps a dim memory of the days when the Crusaders had sugar-mills at Engedi, on the shores of the Dead Sea, as mentioned in the chronicles of the twelfth century, of which mills the ruins are still to be seen.
At Engedi the Taamireh left us, and a few days later I rode with my scribe to the camp of the Jahalin, where we sat down and made ourselves guests of the chief. The Arabs were at first surly, but soon came to see that money was to be earned, and finally asked us to recommend their country to tourists. To those who choose to venture into this wild corner, there is an attraction in the wonderful fortress of Masada, on the shores of the Dead Sea, one of the most remarkable places in Palestine, and one which has been little visited.
Masada (now called Sebbeh) was the stronghold built by Herod the Great which held out against the Romans after the terrible destruction of Jerusalem by Titus in 70 A.D. A people less determined than the Romans might well have been content to leave the surviving Jewish zealots in so remote and inaccessible a fortress. But not so the Romans. After the death of Bassus the procurator, his successor, Flavius Silva, in the spring of 74 A.D., gathered his forces against this last refuge of the fanatical robbers called Sicarii or Zealots, who were enemies alike of Jews and Romans. The difficulty of the task was immense. Water had to be brought by Jewish captives from a distance of eleven miles: the nearest supplies of corn were twenty miles away; and only in spring could an army have endured the great heats in the valleys, 1200 feet below sea-level. The fortress is a lozenge-shaped plateau, with precipices 1500 feet high all round; walls and towers, now in ruins, surrounded it on all sides; and while on the east a narrow path called the “Serpent” wound up the cliffs, the only vulnerable point was on the west, where a chalky undercliff 1000 feet high lies against the rocky walls. Opposite this undercliff Silva placed his camp on a low hill, and round the fortress he drew a wall like that which Titus had built round Jerusalem, with small posts at intervals, and a second larger camp on the east. The Romans then piled a great mound 300 feet high on the top of the undercliff, and built a wall on the mound, from the top of which they fought in a siege-tower plated with iron, and battered the fortress wall with a ram.
The besieged were not in want of food or water. There were rain-water tanks, and corn was grown on the plateau. It is even said that the stores of wine, oil, pulse, and dates laid in by Herod a hundred years before were still edible, because of the dryness of the desert air. Within the ramparts was Herod’s old palace, towards the north-west part of the plateau, and until the walls fell to the battering-ram the courage of the Zealots was unabated. Even then they made an inner stockade of beams and earth, and still continued their fierce fight for freedom when this was in flames.
But when the dawn of the Passover came, the Romans put on their armour and shot out their bridges from the siege-tower, yet met with no resistance, and heard no sound save that of the flames in the burning palace: “A terrible solitude,” says Josephus, “on every side, with a fire in the place as well as perfect silence.” In the night 960 persons had been slain; first the women and children by their own husbands and fathers, then the men each by his neighbour. Only one old woman with five children hidden in a cavern had escaped.
Such was the wonderful history of the fortress which we explored and planned. From the plateau one looks down on the Roman wall which crosses the plain and runs up the hills to south and north. One can see Silva’s camp and the guard-towers almost as he left them 1800 years ago. The Roman mound, the wall upon it, the ruins of Herod’s palace and of the fortress walls, the towers on the cliff-side to the north, the empty tanks, the narrow “serpent” path, all attest the truth of Josephus’ account (VII. Wars, viii., ix.), and remain as silent witnesses of one of the most desperate struggles perhaps ever carried to success by Roman determination, and of one of the most fanatical resistances in history. On the east is the gleaming Sea of Salt; the dark precipices of Moab rise beyond, and the strong towers of Crusading Kerak. On all sides are brown precipices and tawny slopes of marl, torrent beds strewn with boulders, and utterly barren shores. There has been nothing to efface the evidence of the tragedy, nor was Masada ever again held as a fortress. Yet even here the hermits found their way, and built a little chapel from the stones of Herod’s house; while in a cave—perhaps the one in which the poor Jewish matron hid—I discovered on the dark walls a single word, Kuriakos, flanked by crosses and written in mediæval letters—evidence of some peaceful anchorite’s last rest among the ghosts of the Zealots.
The survey of this wilderness was completed in ten days, and the party, having no food for beast or man, were forced to march to Hebron in one of the great spring storms. Sleet and hail, a biting wind, and a rocky road made this one of our most toilsome journeys, and when, half frozen, we reached the fanatical town, we were greeted only with curses, and owed shelter, food, clothing, and fire to the hospitality of a Jewish family in the despised suburb to the north of the Haram.
The desert of Judah was no doubt as much a desert in David’s time as it is now. Here he wandered with his brigand companions as a “partridge on the mountains.” Here he may have learned that the coney makes its dwelling in the hard rock. Here, in earlier days, he tended the sheep, descending from Bethlehem, as the village shepherds of the present day still come down, by virtue of a compact with the lawless nomads, and just as Nabal’s sheep came down from the highlands under agreement with the wild followers of the outlaw born to be a king. I do not know any part of the Old Testament more instinct with life than are the early chapters of Samuel which recount the wanderings of David. His life should only be written by one who has followed those wanderings on the spot, and the critic who would embue himself with a right understanding of that ancient chronicle should first with his own eyes gaze on the “rocks of the wild goats” and the “junipers” of the desert.
North of the Dead Sea, the wide plain of Jericho lies beneath the wilderness where the Jordan Valley broadens between the Moab mountains and the western precipices. This region we first entered in the November of 1873, and pushed the survey rapidly over the plain. Our camp was by the clear spring of “Elisha’s Fountain,” well known to tourists; and here, emerging from the glaring chalk hills and barren precipices of Marsaba, we enjoyed greatly the greenness of the plain, the song of the bulbuls in the thorn trees, and the murmur of the stream. Unfortunately, this very greenness was a sign of deadly climate, especially in the autumn months. No sooner had the first thunderstorm swept over us, turning the Brook of Cherith (as it is traditionally called) into a torrent ten feet deep or more, than fever suddenly attacked the party, then numbering five Europeans and fifteen natives. Even the Nuseir Arabs, who were our guides, lay round the tents shaking with ague; and for a time the life of my companion, Mr. Tyrwhitt Drake, was in danger. In fact, though his zeal and fortitude prevented his leaving the work, he never really recovered from this terrible Jericho typhoid, and the hardships of the following spring, which we again passed in the Jordan Valley, proved too much for his shaken health. It is only after the soil in such malarious regions has been purified by a winter’s rain that it is safe to remain, even for a night, in the low ground or near water; and the premature visit to Jericho threatened at one time to bring our small party entirely to a standstill.
The region round Jericho is well known. The tall cliff burrowed with hermit’s caves, and supposed to be the place where Christ fasted forty days in the desert; the flat marshy valley sprinkled with alkali plants and with lotus trees and feathery tamarisks; the eastern mountain ridge which we afterwards explored; the strange white peak of Kurn Sartaba on the north; the oily Dead Sea on the south, must have been seen by many who may read these lines. In clear weather in spring, the snowy dome of Hermon can be seen from near the mud village of Jericho, marking the north end of the Jordan Valley; but the Lake of Tiberias is hidden even from the higher ground near the plain.
In this Jericho region also new discoveries were made. A solitary tamarisk marks the site where, at least in early Christian times, it was believed that the Gilgal camp was set up by Joshua. The surveyors verified the existence of the name, even now known to the Jericho peasants. Here also we copied the curious mediæval frescoes, which still remained on the ruined walls of two monasteries, and several hermit caves. In the twelfth century there were many monasteries in the desert and round Jericho, and the memory of the monks has not died out. The Bedu point to a curious chalk hill called the “Raven’s Nest” as the “place where the Lord Jesus ascended;” and in studying the mediæval accounts of Palestine, I found that this very place, although the top is below sea-level, was pointed out to Crusading pilgrims as “the exceeding high mountain” whence, as we read in the Gospel, Christ surveyed the kingdoms of the world. This is but one instance out of many in which the teaching of the monks and hermits still lingers among the Moslem population in many parts of Palestine.
In England a fresco of the twelfth century is to us a rare and ancient thing. In Palestine, so far back are we carried by history, that Crusading remains rank among the latest. But the explorer has no right to confine himself to any one period. His duty is to bring home everything he can find, and without such exhaustive work the sifting out of the most valuable and most ancient results cannot with safety be undertaken. I spent several days in the hermits’ caves and in the ruined monasteries, copying such frescoes as were distinguishable, and reading the various titles above them. In the middle of the Jericho plain lies Kusr Hajlah, then a Crusading ruin with frescoes bearing the names of Sylvester Pope of Rome, Sophronius of Jerusalem, and John Eleemon. By the character of the writing I was able to fix these paintings as twelfth-century work. When in 1881 I revisited the spot, I found that not a single trace remained of any one of the pictures. Russian monks from Marsaba had settled there, and had rebuilt the monastery. Every fresco had been scraped from the walls, in order, they said, that new and better might replace them. Judging from the existing paintings at Marsaba, it is hardly to be expected that much advance will be made on the quaint style of the figures which represented the Last Supper, or the Apostles robed by angels in resurrection garments of white. I think rather that the monks suspected that the frescoes were of Latin origin; yet, in destroying them, they had obliterated the names of two of the most famous Greek Patriarchs of Jerusalem; but then they also destroyed the representation of Sylvester Pope of Rome. This single instance shows that the systematic exploration of Palestine was undertaken none too soon.
Not only in monasteries and hermits’ caves were these pictures painted. On the north side of the Kelt ravine (the traditional Brook Cherith) there is a ruined monastery of St. John of Choseboth. Here I copied many texts and pictures; and outside the gate there is a wall of rock eighty feet in length, once covered with very large figures, like those which I have seen on the outer walls of Italian churches. The weather had long since destroyed them, but at Mar Marrina, near Tripoli, I afterwards found another cliff cemented and painted in like style. In this case the Greeks had come after the Latins, and instead of scraping off the old work, had begun to paint over it huge figures of the throned Christ and of the Mother of God, beneath which—as though on a palimpsest—I was able to copy a set of pictures representing the miracles performed by some Latin saint or abbot.[33]
Such are the remains preserved by the dryness of the desert air in the vicinity of Jericho. We must now cross to the west side of the watershed, where the country presents a very different aspect. Looking down from the heights of the Judean mountains, you see beneath a strip of low hills, covered in some places with brushwood, but full of villages, and with olive yards along the valley courses and round the stone or mud houses of the hamlets, so many of which preserve the old names of the Book of Joshua. Beyond these foot-hills is the broad plain, here and there rising into sandy downs, but, as a rule, brown in autumn with rich ploughlands, and yellow in summer with ripening grain. In spring the delicate tinge of green, the wide stretches of pink flush from the phlox blossoms, and the great variety of flowers and flowering shrubs, present a strong contrast to the grimness of the desert.
The Shephelah or foot-hills form a district full of interesting sites, and of ruins from the twelfth century A.D. back to the times of Hebrew dominion. Here our discoveries were numerous and important, but I will only refer to two periods of special interest—the time of the Jewish revolt under Judas Maccabæus, and the time of the first establishment of the Crusading kingdom in Jerusalem.
The history of the heroic brothers who recovered the religious freedom of the Jews by revolting from the Greek kings of Antioch in the second century B.C., is as easy to follow in detail on the ground as is that of David’s wanderings. I have already devoted a short volume to the subject,[34] and have tried to show how the attacks on Jerusalem were made successively by the Greek armies along the roads from the north-west, the west, and the south; how Judas met the foe on each occasion at the top of the narrow passes; how he hurled them back, as Joshua did the Canaanites on the same battle-fields; and how not even the elephants dismayed him. The native town of Judas, Modin—now called Medyeh—is a little village in the foot-hills, where, however, the reported tomb of the Maccabee and his family turned out to be merely a Byzantine monument. The scene of the death of Judas, while he was defending a fourth mountain pass leading from Shechem to Jerusalem, was not known; but we have, I think, been able to identify this important battle-field, where for a time the hopes of the national party seemed for ever to have been crushed.
It is an instructive fact that so long as the Greeks strove to prevail by arms, the puritan movement was never stamped out. When at length the native princes were allowed to reign and to coin money in the native tongue, they became in a few generations as Greek as the Greeks themselves, and finally as hateful to the extreme party of the orthodox as any Greek oppressor.
At the border between the foot-hills and the Philistine plains three Norman castles were built to protect the kingdom of Godfrey and Baldwin against their Egyptian enemies. A little later (in 1153 A.D.) Ascalon was taken, and long remained the great Christian bulwark on the south. Still later, when Richard Lion-Heart was striving to prop up the Latin kingdom, ruined even more by vice and degeneracy than by the fierce attacks of Saladin, the English conqueror spent many months in this region. I had with me in Palestine the chronicle of his expedition, written by Geoffrey de Vinsauf, which is one of the most vivid monographs of the age. It was thus possible to trace every point in his travels; and very few places remain, among the many mentioned in the Philistine plains, which cannot be found on the Survey map. The lists of property of the canons of the Holy Sepulchre, and other documents of like kind, were compared, and thus what is to us an early chapter of our history could be worked out on the spot in Palestine. The difficulties and dangers of Richard’s army, how they were troubled by the wind, rain, and hail, which blew down the tents and spoiled the biscuit and the bacon, how the flies, “which flew about like sparks of fire, and were called cincenelles” (mosquitoes), stung the Englishmen till they looked like lepers, and how they suffered from fever and fatigue, we could well understand; and even of the attacks of Saracens we had some experience when one day a party of Bedu on the war-path, mistaking us for their enemies, charged down upon us with flying cloaks and lances fifteen feet in length quivering like reeds.
The walls of Ascalon, so often built, and which Richard raised again from the foundations, we surveyed with difficulty, clambering over the fallen masses of the towers, all of which are mentioned by name in the chronicle—such as the Maiden’s Tower, the Admiral’s, the Bedouin’s, and the Bloody Tower, and Tower of Shields. Yet farther south we explored the little fortress of Darum, which Richard rebuilt, with many others, as garrisons against the Moslems. North of Jaffa, in the Sharon plain, we found the oak wood through which the English in 1191 A.D. marched down from Acre, sorely harassed by the rain of arrows on their armour. Every river and every tower mentioned on that toilsome march are now identified, and the fort of Habacuc, where fell the brave knight Renier of Marun, who was, I believe, an ancestor.
Yet earlier scenes belong to this region, which was the theatre of Samson’s exploits. In the low hills, Zoreah and Eshtaol and the valley of Sorek were already known, but to these we added the site of the rock Etam, where the strong man hid in a cave, which we explored. The tracing of this topography gave us, however, experience of the great caution which the explorer must exercise in sifting the evidence of natives. It had been supposed that the memory of Samson’s history still survived among the peasants of Zoreah. Certainly they all were able to repeat a garbled version of the story, and this excited the greater interest because such tales are extremely rare in occurrence among the villagers, though the Arabs have a fancy for wonderful legends, as we afterwards found in Moab. I was anxious to ascertain if the Samson legend was a truly ancient one, but soon discovered that it was quite modern. The village lands had recently been purchased by a Christian Sheikh from Bethlehem, and it was from him that his tenants learned the Bible story, which they were unable to repeat without converting all the characters into good Moslems and wicked Christians.
In these same foot-hills lies the site of the celebrated Cave of Adullam, on the side of the Valley of Elah, the scene of David’s meeting with Goliah. It was first discovered by M. Clermont Ganneau, whose views were fully borne out by our researches. The cave itself is a small one, blackened by the smoke of many fires, and scooped in the side of a low hill, on which are remains of a former town or village. Beneath the slope is a wide valley, which was full of corn; and the spot is marked by a group of ancient terebinths, like those which gave the name Elah, or “terebinth,” to this important Wâdy. There are other caverns opposite to the Adullam hill, and these are used as stables, while in the cave itself we found a poor family actually living. The name is now corrupted to the form ’Aidelmîa, but the position fully agrees with the Bible accounts, and with the distance from Eleutheropolis (now Beit Jibrîn) noted by Eusebius.
The Philistine plain from Jaffa to Gaza is one of the best corn districts in Palestine. It grows steadily wider to the south, and sweeps round the base of the Hebron hills to Beersheba. The celebrated cities of the Philistine lords are now, with the exception of Gaza, no longer important places. Ekron and Ashdod are villages with a few cactus hedges; Ascalon lies in ruins by the sea; Gath is so much forgotten that its name has disappeared, and the site is still not quite certain. Gaza is, however, a large place, with some trade, and with extensive olive groves. Along this whole coast the sand from the high dunes, which, as seen from the hills, form a yellow wall between the ploughlands and the sea, is always steadily encroaching. It has covered up a great part of the gardens within the walls of Ascalon, and has swept over the little port of Majuma, west of Gaza; but beyond the line of its advance the soil is everywhere fertile, and the villages are numerous.
The Philistine plain seems never to have been long held by the Hebrews. Joshua, Samuel, or Simon the Hasmonean may have conquered its cities, as Richard Lion-Heart afterwards did, but the Egyptian power in Syria in all ages has been first felt in this plain. The natives indeed, in dress and appearance, are more like the peasantry of Egypt than they are like the sturdy villagers of the other parts of Palestine. In times of trouble this region is now much exposed to the attacks of the southern Arabs. Egyptian records show us that the Philistine plain was long held by the Pharaohs, and we have a representation of the siege of Ascalon by Rameses II. In Hezekiah’s reign we learn, from the cuneiform records, that each of the Philistine towns had its own king, and these princes allied themselves with Sennacherib against Jerusalem.
These facts agree with the account of David’s struggles with the Philistines, and give the reason why Israel did not enter Palestine “by the way of the Philistines,” as probably at that time the plain was actually garrisoned by Egyptians.
It is clear from monumental accounts that there was a Semitic population in Philistia at a very early period, but it is not certain that the Philistine race was of this stock. We have Egyptian portraits of Philistines—a beardless people wearing a peculiar sort of cap or tiara. Many scholars believe that the Philistines were of the same stock with the Hittites (who were a Mongolian people), and this may account for the curious fact that the Assyrians speak of the Philistine town of Ashdod as a “city of the Hittites.” In Philistia the name of the Hittites is also probably still preserved in the villages of Hatta and Kefr Hatta. Among the peasantry there are several legends of the Fenish king and his daughter, of his garden, and of the place where she used to spin. I think it is probable that the Fenish was a Philistine, rather than a Phœnician, legendary monarch.
The town of Gaza, standing on a mound above its olive groves, surrounded by the crumbling traces of its former walls, contains several good mosques, one of which is the fine Crusading Church of St. John. Near Gaza, on the south, is a mound called Tell ’Ajjûl, “hillock of the calf,” from a legend of a phantom calf said to have been here seen by a benighted peasant. At this place was discovered a fine statue of Jupiter, 15 feet high, which now stands at the entrance of the Constantinople Museum, where I drew it in 1882. This discovery reminds us that Palestine had also its age of classic paganism, when statues like those of Roman temples were erected. We have, indeed, an account of the temples of Gaza, which existed as late as the fifth century, when the Christians overthrew them and built a church. Venus had here a statue, much adored by the women, and the Cretan Jupiter was known under the name Marnas, which is thought to mean “our lord.” It is probably the statue of Marnas himself that has now been discovered, one of the very few statues of any importance as yet found in Palestine.
The Philistine plain merges on the south in the plateau called Negeb, or “dry,” in the Old Testament. This is the scene of Isaac’s wanderings as described in Genesis, where lie Gerar the city of Abimelech, and Rehoboth and Beersheba. The region was visited late in 1874, when it was at its driest, the spring herbage being all long since burnt up. The Beersheba plains consist of a soft white marl, rising in low ridges, and not unlike some parts of the Veldt or open grazing-land of Bechuanaland, in South Africa. The Negeb still supports a considerable nomad population, and their flocks and herds are numerous. On the east it sinks to the Judean desert, and on the south descends by bold steps to the Wilderness of Sinai. The view from the spurs of the Judean hills near Dhaherîyeh (identified with Debir) is very extensive, ridge beyond ridge of rolling down stretching to the high points on the horizon which mark the passes by which ascents lead from the south.
This region, though generally without water on the surface, possesses several groups of deep and abundant wells, where the herdsmen gather to water the flocks. Among the most renowned are the Beersheba wells, of which there are three, each a round shaft lined with masonry; one is dry. The principal supply is from the largest well, 12 feet 3 inches in diameter, and 38 feet deep to the water in autumn. The smaller dry well is 5 feet in diameter and 40 feet deep. Round these wells, which have no parapet, rude stone troughs are placed, into which the water, drawn up in skin bags, is poured. The water-drawing, to the sounds of Arab shepherd songs, is one of the most picturesque of sights. It used to be thought that the masonry was very ancient, but it only extends to a depth of 28 feet in the largest well, and on one of the stones I found the words, “505 ... Allah Muhammad,” showing apparently that the stonework was at least renewed in the fourteenth century A.D.
Any student who desires really to be able to judge of the social life of the Hebrew Patriarchs should visit the plains of Beersheba. It was here, we are told, that Isaac passed his life. Here Abraham settled after long wanderings through the length of Palestine. Here Jacob was born, and hence he descended into Egypt. It is very notable that Palestine appears in Genesis as a country already full of cities, and in which land could only be obtained by the Hebrew immigrants by purchase from landowners already settled—the Hivites of Shechem and the Hittites of Hebron. In the pastoral plains of Beersheba, however, the wanderers ranged undisturbed even by the Philistines of Gerar. So it is to the present day. The Jordan Valley, to which Lot is related to have taken his flocks, the desert of Judah, where David fed his sheep, the plains near Dothan, and the pastures of Beersheba, are still the grazing-lands of Palestine, where nomadic shepherds range, while the higher lands are held by a settled population. Although we have no monumental records sufficiently early to compare with the narrative of Genesis, we find that the country presented the same aspect when the conquering Pharaohs of the eighteenth and nineteenth dynasties invaded it. There were then regions held by the nomads, and other regions full of fortresses and open towns.
In the history of the Patriarchs we find described a mode of life just like that of the modern Arab. The great chief or Emir dwelt in his tent among his followers, led them out to war, and allied himself to the neighbouring townsmen, with whose families, however, he scorned to intermarry. The sons of the Emir and his daughters (like Leah and Rachel) tended the flocks and herds, and strove at the wells, where countless beasts awaited their turn. The relation which the Hebrew chiefs bore to the distant paternal tribe beyond the Euphrates reminds us how Syrian Arabs still trace their descent from distant families, with the same tribal name, far off in the Nejed. The stone memorial is still raised by the Bedawi, as Jacob reared his stone of Bethel; and the covenant is still sealed by the eating of bread. Still, too, the Arab hunter brings back savoury venison to the camp, like Esau; and by the wells of Beersheba you look northwards to the same low hills which were before Isaac’s eyes when he went forth to pray in the open field—as the Arab still prays outside his camp—and “beheld the camels coming.” In the early morning, by the light of the rising sun, I have seen the camels, preceded by their giant shadows, coming in troops to the wells, guided by the shepherd-boys, whose music is the same rude pipe on which the ancient shepherds played. I have seen, too, the dark gipsy-like girls, with elf locks, blue robes, and tattooed faces, who tend the sheep as Rachel and Leah (still children) tended those of Laban before they were old enough to be restricted to the women’s side of the curtain, and to follow their mothers to the well.
The visit to Beersheba was not without its adventures. This was the only occasion on which a thief—of many who tried but were discovered by our terriers—succeeded in making his way into the tents. He took with him all our food, and we had to depend on the wild sand-grouse and plovers for our dinner. It was during the fast of Ramadan that this journey was undertaken, and the Moslem guides suffered greatly in consequence; for fasting among the Moslems in Ramadan is a very serious matter, and especially so among the primitive villagers of Judea. Not a scrap of food, not a drop of water, not a whiff of tobacco will then pass the lips of the strict Moslem between sunrise and sundown. I have seen the wrath of the spectators roused when an old man of eighty washed his mouth with water on a day of scorching east wind. We had gone down to explore an underground tank in Hebron, and as he stooped to the water we heard a voice shouting, “Ah! Hamzeh, God sees you!” and the unfortunate elder rose at once in confusion. When the sun sets, a cry goes up throughout the town or village—a shout from the men and a shrill tremulous note from the women—for then it is lawful to break the trying fast. Even children are induced by pious parents to keep Ramadan, and some zealots will continue fasting for ten days beyond the prescribed time. The Moslem year being lunar, and thus never the same year by year in relation to the seasons, it is especially at those times when Ramadan falls in September that this privation is most felt.
Not that I would lead the reader to suppose that all Moslems are thus strict in religious duty. In Islam there is as much scepticism, indifference, outright rejection of religious belief as in Christendom; and history reveals that this has always been so since Islam became a religion.
Among the antiquities of the Beersheba desert there are several rude buildings of undressed chert blocks, which may be almost of any age. It was, however, in the early centuries of Christianity that this region was apparently most fully inhabited.
The hermits who, like Hilarion, came from Egypt and settled in the Holy Land, soon gathered disciples round them; and even against their will monasteries rose by their cells, and a village round the monastery. Pious pilgrims like Antoninus, not content with seeing Palestine, ventured far into the deserts, and down to the miraculous tomb of St. Catherine in Sinai. Thus, in the fourth century, Jerome found the land full of monks and nuns, even in the wilderness; and stories which may have been told to the Arabs by these eremites still linger among them. We have early Christian accounts of Pagan rites among the natives of the Negeb, who still in the seventh century were worshipping Venus at Elusa, and the stone menhirs on Mount Sinai. There is no part of Syria in which the anchorites’ cells are not found, though in modern times they are only represented by the Jericho hermits—Abyssinians and Georgians, who, I believe, only retire to the wilderness during Lent.
Glancing back over this sketch of exploration in Judea, I only note one place of primary interest which has not been mentioned, namely, Bethlehem. It is, however, familiar to every tourist, and nothing new was added by the surveyors to what was already known concerning this city, except that the crests which Crusading knights drew upon the pillars of Constantine’s great basilica were carefully copied.
Bethlehem is a long white town on a ridge, with terraced olive groves. The population is chiefly Christian, and thrives on the manufacture of carved mother-of-pearl shells, and objects made from the bituminous shale of the desert, which pilgrims purchase. The peculiar (and probably very ancient) head-dress of the women, adorned with rows of silver coins, has often been represented in illustrated works.
The main antiquity of the place is the great basilica of Constantine, with its thirteenth-century mosaics and wooden roof. Beneath the choir is the traditional site of the “manger,” which has been constantly shown in the same place for nearly eighteen centuries. The church itself is one of the oldest in the world; and Justin Martyr, in the second century, mentions the cave. Origen also says that “there is shown in Bethlehem the cave where He was born, and the manger in the cave” (Against Celsus, I. li.), so that the Bethlehem cave-stable is noticed earlier than any other site connected with New Testament history. It is the only sacred place, as far as I know, which is mentioned before the establishment of Christianity by Constantine, yet it is remarkable that Jerome found it no longer in possession of the Christians. “Bethlehem,” he says, “is now overshadowed by the grove of Tammuz, who is Adonis; and in the cave where Christ wailed as a babe the paramour of Venus now is mourned.”
MY first experiences of Palestine survey were from the camp at Nâblus,[35] the ancient Shechem. The method which we then employed was very little varied throughout the whole period of our labours. The camp, consisting of three or four tents, was pitched in some convenient central position by a town or village. Thence we were able to ride eight or ten miles all round, and first visited a few of the highest hill-tops, where, when the observations with the theodolites were complete, we built great cairns of stone. The survey was trigonometrical, depending on two bases, one near Ramleh, east of Jaffa, the other in the plain of Esdraelon, north of Jenin. In 1881 I measured a third base on the Moab plateau, south of Heshbon. All these were connected by triangulation, the stations being from five to fifteen miles apart. The heights of these stations were also fixed by theodolite angles, and thus the elevations above the sea of every great mountain from Dan to Beersheba, and of those east of Jordan between the Jabbok and the Arnon, are known within a limit of four or five feet at least.
The triangles having been calculated in camp, the surveyors separated, and each with his prismatic compass worked in the detail of roads, valley beds, villages, ruins, towers, and all that is usually shown on maps of this scale by Ordnance surveyors. He took the aneroid heights of all important points, which I regard as reliable within ten or twenty feet. He was invariably accompanied by a local guide, who gave the names of the various features shown. The surveyor was never responsible for the spelling of these names. A native scribe was employed to catalogue them in Arabic letters, and thus the errors which might have been caused by the difficulty of distinguishing the sounds of Arab letters were avoided. Without such precaution it would have been impossible to make any scientific comparison with the Hebrew names of the Old Testament.
This work being complete and penned in, we were ready to move the camp. There are parts of the map which I executed to assist my staff, but, as a rule, when the triangulation was complete, I was free to spend much of my time in exploring the important sites within reach, of which I made special surveys on a larger scale.
The explorer is, however, not his own master until he becomes practically acquainted with the language of the natives; and although I had learned French in France and Italian in Italy, the acquisition of a Semitic tongue was only so far rendered easy, that no one who has learned one foreign language grammatically and idiomatically is likely to be content with any other kind of knowledge of other tongues. At the same time, those who have had the advantage of studying foreign languages on the spot know how much easier and more agreeable it is to learn them, as a child learns his mother tongue, first by practice, afterwards by the rules of the grammarian. In the East, the spoken dialects, such as those of Arabic and Turkish, differ greatly from the literary languages. In speaking, simplicity and brevity take the place of the high-flown and artificial refinements of the modern grammarian. The vernacular grammar is simplicity itself compared with the literary style, which only schoolmasters or pedants affect in everyday speech. Nor, indeed, is such indifference to strict grammar unknown even in our own land, though in a less degree, in spoken as compared with written phrase.
At first there was only time to obtain a very superficial smattering, for everyday uses, of the Fellah dialect, which is archaic and rude as compared with the Nahu or “correct” language; but it appeared to me absolutely necessary, not only to understand the Arabic alphabet, but also to become acquainted with the elements at least of grammatical structure; and for this I found leisure during the winters, and the summer holiday of 1873, when a native teacher could be obtained from Damascus. When once the unfamiliar principles of Semitic grammar are understood in one language of the small group (including Hebrew, Arabic, and the Aramean dialects), the student should be able to learn other tongues of the group by the aid of books; but my first lessons in Hebrew I owe to the kind interest of a friend since dead, who devoted time to my education in Jerusalem itself. So unlike in structure are these tongues to either Aryan or Turanian languages, that the idiom is at first hard to catch; and I doubt if any European, until he has lived in the East some time, is ever likely correctly to pronounce the gutturals of the Arabic, unless he is gifted with an ear much more sensitive than usual.
After many years’ study of the native dialect, it appears to me that its further investigation would be of great value to scholars. There can be no doubt that ordinary conversation of the peasantry preserves archaisms of sound, of idiom, and of expression which recall rather the Aramaic spoken in Palestine in the days of Christ than the pure Arabic of southern Arabia. The Syrian dialect (which is much less degraded than Egyptian) is acknowledged, even in dictionaries, to have its peculiarities. The Lebanon servants in my employ were almost unable to understand the speech of the Beni Sakhr Arabs in the Moab desert. The dialect of the towns differs, again, especially in pronunciation, from that of the peasants. The convenient auxiliaries used in daily speech are not recognised in standard grammars, and not a few familiar words of the Fellah dialect I have been unable to discover in the standard dictionaries of Lane and Freytag.[36] The Hebrew goran, “a threshing floor,” and moreg, “a threshing-sledge,” are still words used by the peasants, as is the Assyrian sada, for a “mountain,” and many other ancient words which a good Hebrew scholar will recognise. The peasantry, in short, are not, properly speaking, Arabs, but descendants, in part at least, of the old population to which the Phœnicians belonged, mingled with colonists imported by the Assyrians from Aram, and with the Nabathean and Arab tribes from the south-east. To one acquainted with such a race, the narratives of Genesis and Samuel must always read as though falling from the lips of a modern Syrian, speaking with the same terse vigorous idiom in which his fathers wrote. The Fellahin have been called “modern Canaanites,” and if by this is meant descendants of the Semitic race which the Egyptians found in Palestine before the time of the Hebrew conquest under Joshua—akin to those whose language is represented by the Moabite Stone, and the Phœnician texts from the north coast—the term seems justified by what is known; but, as we shall see a little later, there has always been another population in Syria side by side with the Semitic, of which a few traces are yet discoverable not far north of Shechem.
Ancient Shechem stood very nearly on the same site occupied by the large stone town of Nâblus, in the well-watered gorge, full of gardens of mulberry and walnut, with vineyards and olive-yards and fig trees, above which rise the barren slopes, of Ebal on the north and Gerizim on the south. About one and a half miles to the east, where the vale opens into the small plain of Moreh, is the undisputed site of Jacob’s Well; and north of this, at the foot of Ebal, the little village of Askar, among its cactus hedges, preserves the site of Sychar, mentioned in the fourth Gospel, below which is the tomb of Joseph.
It is curious that Josephus believed Joseph to have been buried at Hebron, for the Book of Joshua places his tomb at Shechem. The monument now shown is an ordinary Syrian tomb in an open-air enclosure by a little ruined mosque. The peculiar feature consists in two pedestals with shallow cups in their tops, placed one at the head, the other at the foot of the grave. I have been told that both Jews and Samaritans offer burnt-offerings at this shrine on these pillar altars, the offerings consisting of shawls, silks, and such fabrics. The same practice is observed by Jews annually at the tomb of the celebrated Simeon Bar Jochai at Meirûn, in Upper Galilee. The substitution of fabrics for animal sacrifices recalls the paper figures which the Chinese burn, representing the various sacrifices, animal or human, which in earlier ages were burned at tombs.
Shechem has long been a place of special interest, because it is the last refuge of the few survivors of the old Samaritan sect, which, according to their own records, once inhabited every part of Galilee and Samaria, and whose synagogues down to quite recent times existed in Damascus and Alexandria. Although almost every traveller visits their synagogue at Nâblus, it is very difficult to become intimately acquainted with this proud and reserved people; and there are very few persons living who have really seen the oldest of the manuscripts of the Pentateuch which they possess. Scholars, it is true, no longer attach the exaggerated value to this document which it was thought to possess when first attention was called to its existence, and before science was able to show its comparatively modern date, as indicated by the character in which it is written. Yet this venerable roll is perhaps the oldest copy of the Bible in the world, and until it has been read by a competent scholar, it is impossible to say what light it may throw on the study of the Pentateuch.
The Samaritans, according to the latest accounts which I have been able to obtain, number about 160 persons. I had opportunities not only of visiting their synagogue, but of holding a long conversation with the high priest, and questioning him concerning their traditions and literature. They claim to know not only the real tombs of Joseph and Joshua, and of the sons and grandsons of Aaron, sites which are now identified, but also the burial-places of all the sons of Jacob, of which tombs many are also revered by Moslems; but the reliability of such traditions is not very certain. The Samaritan chronicles are not traceable beyond the Middle Ages; but one of these (to be distinguished from their “Book of Joshua,” with its wild legends of Alexander the Great) is a very sober work, to which successive high priests are said to have added brief notes of the chief events of their age.[37] Of this chronicle I made careful study, and found that, as regards its geography at least, it is possible to obtain a very clear idea, and many interesting notices are included of places otherwise very little known in all parts of Palestine. This practice of extending a historic journal from time to time is worthy the attention of students of other ancient literatures; and although the chronicle only claims to have been started by Eleazar ben Amran in 1149 A.D., it has been carried down to 1859 by successive authors. This chronicle presents, as above noted, a great contrast to their “Book of Joshua,” which is full of Samaritan folk-lore tales, and consists of two parts, one penned in 1362 A.D., and the second in 1513 A.D. Of their copies of the Pentateuch, kept in the Synagogue, the oldest of those usually shown dates only from 1456 A.D.; the date of the oldest of all, called “Abishuah’s Roll,” is not yet known, but it is certainly very ancient, the ink being much faded and the parchment decayed. The fact that a Samaritan text of the sixth century is built into a tower near the Synagogue, and preserves letters of the peculiar character employed by this people, seems to show that not impossibly Abishuah’s Roll may be as old as the sixth or seventh century of our era.
The Samaritans are a fine race, above the average of Orientals in stature, and possessing a beauty of feature and complexion very like the best type of south European Jews. Even in the peculiar crinkle of the hair they resemble the Jews, and there can, to my mind, be no doubt that they are more closely allied by blood to their great rivals than they are to any other Oriental people. It is impossible here to inquire into the details of their history, which are very generally known, but the inquiries made by us at various times agree with former researches in indicating that, in many particulars, the pietists of Nâblus have preserved the letter of their law in more primitive degree than have even the Karaites or other puritan Jewish sects which discard Talmudic teaching. So great is their terror of defilement, that they will not even close the eyes of their dead, and employ Moslems to prepare them for burial. In this extreme observance they resemble the Falashas or Abyssinian Jewish converts, who even take the sick out of their houses before death. One very curious custom is observed when, on the eighth day, the Samaritan boys are circumcised. An ancient hymn is sung, which includes a prayer for a certain Roman soldier named German, because he connived at circumcision when forbidden by the Romans, and refused to accept any reward for so doing, asking only to be remembered in their prayers; which desire has been respected for perhaps sixteen hundred years.
Shechem, the home of the Samaritans, has often, from the twelfth century to the present day, been confounded with the city of Samaria, five miles farther to the north-west; but at the latter site there are, I believe, no Samaritans living. The peasant population of Palestine in this central district differs somewhat, however, from that of either Galilee or Judea. It was here that we found the peculiar head-dress which recalls the “round tires like the moon” that roused the Hebrew prophet’s wrath (Isa. iii. 18). These horse-shoe head-dresses, made up of large silver coins laid overlapping, are worn only by married women, often with a crimson head-veil. Some of the little terra-cotta statues of Ashtoreth which are found in Cyprus and in Phœnicia, representing a naked goddess, have just the same crescent-shaped bonnet, and it was perhaps originally connected with the worship of this deity, and therefore hateful to the servant of Jehovah.
The site of Samaria is that of a considerable town, upon an isolated hill, with springs in the valley and olives climbing the terraced slopes. On the summit a colonnade, probably of the age of Herod the Great, runs round a long quadrangle, enclosing the site of the temple built in honour of Augustus by Herodian servility; and on one side are the ruins of the great Crusading Church of St. John, in the crypt of which was shown his tomb. It was believed in the Middle Ages that the head of the Baptist was here preserved. St. John had apparently two heads, since another was shown in Damascus.
There is no doubt that the tomb in question is an ancient Hebrew sepulchre. Perhaps it may be that of the “Kings of Israel.” At least eleven bodies could have been here interred, and there were only thirteen Kings of Israel between Omri and the fall of Samaria.[38] An ancient stone door once closed this tomb, carved in panels like other doors of tombs in Palestine belonging to an early age. One which was found farther south was adorned with the heads of lions and bulls, like those found in Phœnician sarcophagi. The date of these monuments is uncertain. In Lycia, Sir Charles Fellows found doors sculptured with exactly the same ornamental details, which may be as old at least as 500 B.C.
East of Shechem, and to the south, there are mountains more rugged than any south of Galilee. The border of Samaria, which divided it from Judea, ran through these mountains, following the line of the principal valley bed. It had never been laid down with any attempt at exactness before the Survey, but now that the position of the border towns is correctly fixed, it becomes possible to trace it throughout. The Judean outpost on the north-east was the extraordinary conical mountain called Sartaba, which rises from the Jordan Valley. This little-visited peak was thoroughly explored. On the summit a square foundation was discovered, surrounded by an oval rampart. The cone has been artificially cut in places, and is some 270 feet high. The remains may be those of the fourteenth-century fortress, but the site has a much earlier history.
On their return from exile the Jews were accustomed to fix the first day of each month by actual observation of the new moon, and according to the Mishna, the announcement was made throughout the Holy Land by means of bonfires on the mountains. One of these bonfire stations was Sartaba, and it is not impossible that the remains of extensive ash-deposits observed on the mountain were traces of such beacons. The practice was open to mistake, for the Jews assert that the Samaritans used to light fires on neighbouring heights with the malicious intention of confusing the Jewish calendar, and making the Passover feast to fall on the wrong day. Whether we are to credit the statement that this chain of beacons extended even to Mesopotamia is doubtful, but the Jews certainly long kept up intercourse with their brethren in Babylonia.
On the south of Shechem rises the great rounded top of Gerizim, whence the eye ranges from Gilead to the Mediterranean, and on the north to dusky Carmel and snowy Hermon. On the south side of the mountain is Kefr Hâris, where, according to the Samaritans, Joshua was buried—a tradition nowise discordant with the statements of the Old Testament, and which can be traced back at least to the fourth century. Here also the peasants show the tomb of his father, Nun. On the mountain-side, near the summit, the Passover is still eaten, and here, as the Samaritans say, once stood their temple. There are no remains of any great building, but a sacred slab of rock, in which is one of those curious “cup hollows” so frequently found in connection with prehistoric monuments. On the west, the Sharon plain extends beyond the olive groves of the foot-hills to the dark ruined ramparts of Cæsarea—a region which was surveyed in the spring of 1873, and many interesting ruins were then explored. It is one of the most lawless parts of the country, and was then but little cultivated. Scattered oak woods, sandy dunes, marshes, and boggy streams occupy great part of its extent; and on the north is the Crocodile River, still the dwelling of these monsters, who are not found in other streams, but lie in the muddy river under the papyrus or amid the reeds as comfortably as in the Nile.
The crocodiles of this region are mentioned by many writers, from Pliny downwards. A curious story was told in the thirteenth century, according to which they were imported from Egypt by a lord of Cæsarea, in order that his brother might become their victim. The brothers went to bathe in the river, but the wicked lord went in first and was eaten, while his innocent brother escaped.
This part of the plain of Sharon and the west side of the Esdraelon plain are the only places in Palestine, so far as I have been able to ascertain, where Turkoman encampments are found. In Northern Syria the Turkoman camps are more numerous. I have visited their tents in the plains near Kadesh on Orontes, and in the oak-dotted vale where the Eleutherus rises. To the casual visitor they seem to be Bedu, and indeed those in the Sharon plain have almost forgotten their original language. We know historically that a horde of the followers of Ghazan Khan in 1295 A.D., consisting, it is said, of 18,000 tents, came down to Damascus and settled on the coasts of Palestine. Probably the existing Turkoman tribes are the last relics of this horde; but in this mixture of Tartars with the Semitic race of Syria we see still surviving a condition of population as old as the days of Abraham. It is now the general opinion of competent scholars that the non-Semitic population which the Egyptians in the sixteenth century B.C. found in Syria—more especially in the north—was a Mongolic race. The monuments show that in feature they were Mongolian and that they wore the Tartar pigtail, and the names of their chiefs and towns tell the same tale. The Turkomans are degraded representatives of a kindred race. The Turkish masters of Palestine hold now the same position which the Hittite princes held in the days of Abraham and Solomon as over-lords in a country whose inhabitants were mainly of another race.
The greater part of the Jordan Valley lies within the boundaries of Samaria, and it was for this reason that Galilean Jews travelling to Jerusalem crossed the Jordan and journeyed down the left bank to Jericho, where they crossed again without having approached the country of heresy. As regards the western borders of Samaria, there is less certainty perhaps, but such information as we possess seems to show that the limits of this province must be extended to the sea-shore.[39] Indeed, had it been otherwise, the journey from Galilee along the coast would always have been preferable to that along the east side of the Jordan Valley. It must be confessed that the Samaritans possessed some of the best land in Palestine.
Since the greater part of the Jordan Valley thus belonged to Samaria, the exploration of the valley may be here noticed. The survey of the plains of Jericho has been recorded in the preceding chapter. From Jericho in the early spring of 1874 the party proceeded northwards, and by April, in spite of very bad weather, the work was finished within a few miles of the Sea of Galilee.
The total length of the valley is about a hundred miles from the Sea of Galilee to the Dead Sea. The level of the latter Sir Charles Wilson has determined as 1292 feet below the Mediterranean. The former, as determined by the line of levels which, under a grant from the British Association, I commenced in 1875, and which was completed in 1877, is 682 feet below the same datum. Thus the average fall of the river is 600 feet in a hundred miles, but the upper part of the course is the more rapid, falling about 400 feet in fifty miles. The width is pretty constant along the whole course, the evaporation counterbalancing the additional flow of the Jabbok and other affluents. The volume of water brought down by the Jordan, and evaporated during the summer months in the Dead Sea, makes a difference of fifteen feet between the summer and winter surface of that sea over an area of about 400 square miles. The flow is greatest when the snows on Hermon begin to melt, about the time of Passover, when “Jordan overfloweth its banks all the time of harvest;” for harvest in this deep valley is much earlier than even in the Sharon plains. The river flows in a narrow bed between banks of marl, and the Zor, or depressed channel on either side, averages about a mile across, flanked by white cliffs and steep slopes fifty feet high. In high flood this channel is at times all under water, and the river becomes about a mile wide, but soon sinks within its natural borders. The Zor is filled with brushwood of tamarisk, agnus-castus, and other vegetation, and in places the river is hidden between the bushes and cane beds. Near the fords it is seen as a brown swirling stream with a rapid current. In the upper part of its course there are numerous fords and small rapids. No less than forty crossing places, nearly all of which were previously unknown, were marked by the surveyors.
![]()

THE JORDAN VALLEY (ESH EL GHURAB).
The most interesting discovery in connection with the river was that of the ford called ’Abârah. The name was found in one place only, and does not recur in the ten thousand names collected during the survey. It was applied by the Arabs to one of the chief fords leading over to Bashan, in the vicinity of Bethshean, where the road from Galilee comes down the tributary valley of Jezreel. ’Abârah means “ferry” or “crossing,” and there is no doubt that it is the same word which occurs in Beth Abârah, “the house of the crossing,” mentioned (John i. 28) as a place where John preached, and where, according to the usual opinion, Christ was Himself baptized.
The traditional site of the Baptism, from the fourth century down to the present day, lies much farther south, at the ford east of Jericho, where Israel crossed from Moab to Gilgal; but the distance from this spot to Cana of Galilee is so great, that it is impossible to reconcile this tradition with the New Testament account. Nor is there anything in that account which points to this southern site. The visit yearly paid by Greek pilgrims to the traditional spot, near Justinian’s old monastery of St. John on Jordan, has often been described. In the sixth century Antoninus speaks of the vast crowd which used there to assemble at the Feast of Epiphany, when it was believed that Jordan yearly rolled itself back and stood still till the baptisms were ended. “And all the men of Alexandria who have ships, with their crews, holding baskets full of spices and balsams, at the hour when the priest blesses the water, before they begin to baptize, throw those baskets into the river, and take thence holy water, with which they sprinkle their ships before they leave port for a voyage.”
It must be confessed that these offerings to the Jordan savour of paganism rather than of Christianity. Sennacherib, before he crossed the river-mouths at the Persian Gulf, threw gold and silver fishes into the water. Alexander the Great, in like manner, according to Arrian, offered a golden goblet to the Indus. In Etruria the Lake of Ciliegeto was found full of bronze ex votos, with coins and other objects, thrown by pious visitors into the water, and other instances are known in India. Nor is this a solitary example in which the practices of Byzantine Christians in Palestine are intimately connected with the older pagan rites of the country.
There is, as before said, no strong reason for accepting this traditional site for Bethabara. Some of the earliest MSS. of the Gospel read Bethania for Bethabara; but Origen disputed this reading, and Bethania is probably the later form of the Hebrew word Bashan. Bethabara is found at least in the Codex Ephraemi (C2), and Origen says that nearly all copies of the Gospel in his time had this reading. It would seem then probable that the scene is to be laid, not in the lower, but in the upper part of the Jordan Valley, where the highway from Galilee crosses over to Bashan, where, gay with flowers and carpeted with grass, the plain, dotted with stunted palms, extends between the basalt heights crowned by the Crusading Castle of Beauvoir and the long slopes round Pella, the home of the early Ebionites, who fled from the destruction of Jerusalem, and formed a quiet Christian community in the wilderness where John had baptized.
Few more beautiful scenes can be desired than that which the Jordan Valley presents in spring, when the grass has grown long, and the eye looks down from the hill on the wide stretches of varied colour which fields of wild-flowers present. The pale pink of the phlox, of the wild geranium and cistus, the yellow of the St. John’s wort and of the marigold, the deep red of the pheasant’s-eye and anemone, the lavender of the wild stock are mingled with white and purple clover, white garlic and purple salvia, snapdragons, star-daisies, and the earlier narcissus. The retem, or white broom—the juniper of Scripture—is then in blossom; the long wreaths of vapour cling to the stony mountains of Gilead, and hide its oak glades and firs. The stork pilgrims have come from the south, bringing the spring-time, and rest their weary wings by the marshy brooks round Bethshean, where the chorus of frogs day and night invites their own destruction.
But towards the south the saltness of the soil is too great for such vegetation. For five or six miles north of the Dead Sea the marl flats support only the low bushes of the alkali plant. Even half-way up the valley there are salt springs and tracts of barren salt marl; and one of our camps in the narrow gorge called Wâdy Mâleh (“the Valley of Salt”) was placed beside a hot sulphurous spring too brackish to drink. For several days we experienced much discomfort in this volcanic ravine, and had to fetch water from a considerable distance. These traces of volcanic action occur from north to south on both sides of the Jordan Valley. Beds of lava and basalt occur both west and east of the Sea of Galilee, and again east of the Dead Sea. Hot springs are found on either shore of that sea, and again at the famous Baths of Gadara, and at those of Hammath near Tiberias. Even in times long after the great fault had rent this mighty gorge from north to south, tearing asunder the sandstone beds, and bending down the chalk strata on the west, forming the chain of lakes between Hermon and the Arabah of which the Dead Sea and Sea of Galilee are the last relics, and of which we traced the raised beaches far up the valley—long after all these convulsions, fiery streams of lava flowed over the plains of Bashan, and reached the shores of Tiberias, and covered the cliffs to the west with black volcanic rocks, which form rolling downs of treeless land. Nor was this energy spent even in late historic times, when the great earthquake of 1837 overthrew the town of Safed, and raised the temperature of the hot springs in the valley.
Among the curious delusions which seem destined again and again to recover from the ridicule cast upon them by practical knowledge is the famous fallacy of a Jordan Valley Canal. Leaving aside the question of an expenditure to which that of the Panama Canal cannot compare, the theorists who have proposed this wild scheme do not seem to reflect that the whole volume of the Jordan never suffices permanently to alter the Dead Sea level. The canal then must let in much more water than the river. If it were possible to fill this valley to sea-level—as no doubt it may once have been filled by Nature herself—not only would the crops of the inhabitants be overwhelmed, with the villages of Jericho and Delhemiyeh and the town of Tiberias, but the sea so formed would extend to a breadth of from ten to twenty miles, covering all the villages and corn-lands of the valley of Jezreel. It is almost incredible that this chimera should have received serious support from influential and monied believers in the unlimited powers of modern engineering. A very simple calculation shows that were the sea admitted by such a canal as was proposed in 1883, it might pour into the valley, but could never make headway against the enormous power of evaporation in this burning gulf. Even on the higher plateau near Damascus the rushing stream of the Abana is unable to penetrate far into the desert, and sinks in the marshes of the Birket ’Ateibeh.[40]
The exploration of the valley was one of the most trying periods of the Survey. At first a constant downpour of rain, with clouds scudding along below sea-level, and storms of snow and hail interrupting the observations from the hill stations, delayed our progress. Afterwards the want of fresh water at Wâdy Mâleh proved very trying; then the marshy land round Bethshean brought fever into the camp; lastly, the intense heat obliged us to work in the very early hours of dawning light, and nearly cost me a sunstroke.
There was also great difficulty in obtaining supplies and transport. Our party was by this time so well organised that no time, as a rule, was lost in changing camp. But in the valley we waited day after day in the wet, suffering some of us from rheumatism, and unable to move the sodden and heavy tents. Our first camp was at Wâdy Fusail, near the site of the ancient Phasaelis; and here we found it almost impossible to get any of the Bedu to stay with us. The reason, true or not, which they gave for avoiding the place was, that it is haunted by a ghoul,—that evil and corpse-eating demon whose haunts are shown all over Syria. More than once, while exploring a dark cavern or descending a rock-cut tunnel, we have heard the frightened guide shouting outside, and found him astonished to see us emerge in safety from the ghoul’s den. The ghoul lives also in the great dolmens and in hermits’ caves; but though I have felt on one occasion, in a tunnel where it was necessary to crawl flat, the frightened bats creeping in my hair, I have never been privileged to see or hear a ghoul.
The Wâdy Fusail ghoul, however, was the cause of much delay, and when at last we induced the Arabs to come by daylight with camels, we found that they never used saddles, and their camels were, indeed, almost untrained and very small. We missed the sturdy beasts used by the peasantry, and had very great difficulty in loading the desert dromedaries at all.
It was a pleasure, in the times when the party was well provided with transport, to watch the expedition on the march. The horsemen, on trusty Arab ponies, never sick or sorry, never baffled by the stoniest bridle-path, came first, with our breed of white terriers, which were hardly recognised as dogs by the natives, and which often, night after night, saved us from the depredations of determined horse-thieves. Behind the horsemen came our own baggage-mules, carrying all that was needful for the first founding of the new camp; behind these, again, the camels with heavy stores swung slowly along, while the Maronites, on their donkeys, the Bedu guides on horses and dromedaries, formed a picturesque straggling band, which, as reviewed from a low hill, sometimes extended over half a mile of road. It is pleasant to reflect that, in the years we worked together, there was no dissension, no desertion, and no grumbling in the camp. We suffered together in seasons of sickness, but we stuck together as long as health lasted, and till the work, was done.
One of the most picturesque incidents of the Survey was a night-raid which occurred at Sulem (the ancient Shunem), where, with Sergeant Black, I was for a few days at a detached camp. At this time the difficulties of transport obliged us to separate from the rest of the party, and to remain without meat, and with very little other food, for three days. In the darkness, after a fatiguing day’s work, we were roused by the shouts of the villagers, and hastily loading our shot-guns, we turned out to witness a skirmish with the Bedu. Whether the raid was intended to capture our horses or to drive off cattle from the village was uncertain; but the dogs discovered a robber just about to cut the halters, and the hillside was for some time illumined by the flashes from the old matchlocks of the villagers, while the war-song of the retreating Arabs faded in the distance. Failing to surprise, the raiders quickly gave up their enterprise, but drove off a stray cow in the darkness. With such night-attacks we became more familiar afterwards in the wilder parts of the Moabite deserts.
The hardships of this campaign cost us dear. They were severe for the strongest, and for my comrade, Mr. Tyrwhitt Drake, they were fatal. As already stated, the terrible Jericho fever had undermined his strength; and though he was successfully nursed through that attack, I have always regretted that he would not hear advice, tendered with the most friendly intention, that he should leave Palestine at least for a time. During the months we spent in the valley he suffered constantly from ague, asthma, and the terrible fever sores, from which no member of the party escaped. Finally, he was almost unable to ride, and when we reached the higher lands, rest was absolutely necessary. I left him with anxious foreboding; and as he wished during my absence in England to make a tour in Northern Syria, I wrote to friends at Damascus, begging them not to let him travel alone. Hardly, however, had he reached Jerusalem when the fever again seized him, and his grave is now marked by a simple monument in the Protestant cemetery on Sion. There can be no doubt that he fell a victim to his own earnest desire to continue his work after his powers of endurance were exhausted.
The share which he took in Palestine exploration has been fully acknowledged in more than one publication. In many respects he was peculiarly fitted for an explorer’s work. Of tall and commanding appearance, with a grave and reserved manner, such as most impresses the Oriental, with a kindliness for man and beast, which made the natives who had long served him much attached to his person, with a power of silent endurance, which made him scorn to utter a single complaint in the midst of trial and suffering constantly endured—especially in frequent attacks of asthma, Mr. Drake was a pattern of that class of Englishmen of whom we are proudest. Had he lived, his name would have been widely known as a bold and trained explorer. I have heard a French traveller, after talking with him, exclaim, “If we had such men among the youths of France, it would be better for our country.” I am happy to be able to reflect that, during those three years of constant intimacy, in the trying isolation of our camp-life, we never fell out; that our last hand-shake was that of comrades who had suffered and worked with single purpose; and that he trusted me to represent at home, at its proper value, the share which he had contributed to our common work.
THE third province of Western Palestine is divided into two regions—Upper and Lower Galilee. Lower Galilee was surveyed in 1872 and 1875. Upper Galilee was completed in 1877 under the direction of my companion, Lieutenant Kitchener, R.E., who joined the party in the autumn of 1875. During this year, when the field party was engaged in Upper Galilee, I was employed in London in charge of the drawing of the map, executed by Ordnance Survey draughtsmen, and writing the Memoirs of the country already surveyed, consisting of five-sixths of the total area. Upper Galilee, however, I visited in 1873, and again in 1882, and have thus had occasion to explore almost every important site within its limits.
The boundaries of Lower Galilee include the great plain of Esdraelon and the Nazareth hills, with the smaller plains to the north and east, which stretch to the mountains of Naphtali. No part of Palestine is fuller of interesting sites, and several important discoveries were here made, including a synagogue in ruins on Mount Carmel, and the probable remains of the city of Megiddo.
Before the survey was made, Megiddo—one of the most important places in Palestine—was supposed to be identical with the Roman city of Legio. The reason which induced Dr. Robinson to make this suggestion seems to have been that Megiddo is several times mentioned in the Old Testament with Taanach, a ruined town near Legio. In other passages, however, Megiddo is noticed with Bethshean and Ibleam, places east of the great plain, so that the argument has no great force. There is only one place in Palestine where a name at all like that of Megiddo exists, namely, at the large ruin of Mujedd’a, a well-watered site at the foot of Mount Gilboa, just where the valley of Jezreel opens into the Jordan plain south-west of Bethshean.
Megiddo appears as an important place very early in history. Thothmes III. here fought a great battle against the allied Canaanites on his way to Damascus, and has left us a catalogue of his spoils, which gives a most vivid picture of Canaanite civilisation. Chariots of silver and gold, precious stones, bronze armour, Phœnician arms, gold and silver currency, statues and tables of precious metal, ivory, and cedar, are mentioned as Canaanite trophies, with wine, incense, corn, sycamore wood, goats and oxen, mulberries, figs, and “green wood of their fair forests,”—perhaps referring to the oaks of Mount Tabor. Such, according to the Egyptian monuments, were the products of Palestine in the sixteenth century B.C., before the Hebrew invasion under Joshua.
About two centuries later, an Egyptian traveller records how he came down from the shores of the Sea of Galilee to the “fords of Jordan” and to the “passage of Megiddo.” In the Bible we find Megiddo to be the place where Josiah awaited Necho, the Egyptian king, then on his way to Carchemish, on the Euphrates. In every case this point appears to have been that where Egyptian invaders fought for the passage of Jordan on their way to Assyria. There is little now to be seen at Mujedd’a beyond a mound such as marks the site of many another famous city, but the spot is one well fitted for a great town, on account of the fine supply of water from the springs below.[41] The site has a further interest, because from Megiddo was named the Har-Mageddon, or “Mountain of Megiddo,” better known as Armageddon (Rev. xvi. 16)—the author of the Apocalypse evidently referring to the old battle-field of Canaan, which is also noticed in the Book of Zechariah (xii. 11), in connection with the mourning of Hadadrimmon.
Above Megiddo on the west are the barren ridges of Gilboa, where Saul fell in battle, and between this and the Carmel range is the V-shaped corn plain of Esdraelon. In the north-east corner of this plain is the volcanic cone of Nebi Dhahy, and beyond this, on the north, the mole-hill form of Tabor. Nebi Dhahy is named from a little white saint-house on its summit, sacred to a Moslem hero, whose bones are said to have been carried hither from the Kishon by his dog. Probably he is to be connected with Dhahya el Kelbi (Dhahya of the Dog), who was converted before the Battle of the Ditch, according to Moslem chronicles. It is curious that sacred dogs occur more than once in Palestine folk-tales, for the dog is an unclean beast to the Moslem, while, on the other hand, to the Persians it was amongst the most sacred of animals. The Tyrian Hercules was accompanied by a dog, and a sculpture which perhaps represents this group is still to be seen on the rocks not far from Tyre.
Mount Tabor is one of the few places in Western Palestine where the oak grows as a forest tree in abundance. There is an oak wood also west of Nazareth, and an open forest of scattered oak trees in the Sharon plain, but east of Jordan it is found in Mount Gilead in greater luxuriance. In the glades of Tabor it is said that the fallow-deer still lingers, but we never came across one of them. On Carmel, on the other hand, the roebuck is still hunted, and this species—the existence of which in Palestine was quite unknown before—we found to bear the name Yahmûr, which occurs in the Bible as the Hebrew word for a species of deer. I afterwards found that the Yahmûr was known to the Arabs east of Jordan, no doubt as a denizen of the oak woods of Mount Gilead.
Tabor has been pointed out from the time when the heretical “Gospel of the Hebrews” was penned as the site of the Transfiguration. There are ruins of a great Crusading Church on its summit, dedicated to this event; but the New Testament clearly points to some part of Hermon as the site intended. This is not the only instance in which traditions, dating back even earlier than the fourth century A.D., are in conflict with the plain reading of the Bible narratives.
The chain of Carmel, a region little visited by tourists, presents one of the most picturesque districts in Galilee. At one time it seems to have been fully populated, and traces of vineyards were discovered in many places. The main ridge runs for fifteen miles, and rises at the highest point 1700 feet above the Mediterranean. The north slopes are steep, and in parts precipitous, but on the south-west long spurs run out towards the sea. A dense brushwood of oak, mastic, and arbutus covers the greater part of the chain; and of the former villages, only two are now inhabited by Druze families from the north. The generally accepted view places the scene of Elijah’s sacrifice on the highest part of the crest, still called “the place of burning,” but the tradition represented by a large monastery above the promontory which juts into the Mediterranean, points to the opposite end of the ridge.
The most interesting discoveries on Carmel were made in 1872, including the ruins of a small Jewish synagogue and a tomb with a Hebrew inscription. Inscribed tombs in Palestine are almost unknown, three of the five as yet discovered being found by my party. That near Ain Sinia (the ancient Jeshanah), found by Mr. Tyrwhitt Drake, has been already noticed. The text is probably of about the first century B.C., and includes the name of “Moses bar Eleazar ... the priest.” A second was in the Jordan Valley; the third, on the south side of Carmel, records the name of Eleazar bar Azariah. The forms of the letters are ancient and peculiar; the name recalls that of a very celebrated Rabbi who died in Galilee in 135 A.D. There are many gravestones and inscribed sarcophagi in early square Hebrew characters, both at Jerusalem and at Jaffa, but no such archaic text has elsewhere been found on a rock-cut tomb. The letters are rudely cut over the tomb-door, and were originally painted red to increase their distinctness.
A very unpleasant adventure occurred to me in connection with the exploration of the group of tombs where this inscription was found. As before said, the region was lawless. I have been stalked by the “club-bearing” brigand Arabs in the plains to the west, and in many of the tombs we found skulls of recent date, often with marks of violence. The rock cemetery near Umm ez Zeinât, to which I now refer, was remarkable, because the tomb-doors were roughly closed with piled-up stones. I did not pay much attention to this, or to a skeleton which I found in one tomb, but I retreated somewhat rapidly from another when, striking a light, I found myself kneeling in a large chamber, and surrounded with quite fresh corpses of both sexes. As Moslems are buried east and west, with the face to Mecca, whereas these bodies lay in various directions on the floor, it seemed probable that they were those of murdered persons, or of the victims of some epidemic disease.
The Galilean synagogues are among the most interesting ruins in Palestine. They were known before the Survey, many having being visited, and even excavated, by Sir Charles Wilson. The Carmel example was the only one added to the list, and was much less perfect than some examples in Upper Galilee. Synagogues are indeed mentioned in the New Testament, but in Palestine they seem to have become important chiefly after the destruction of the Temple at Jerusalem. Synagogues are noted in one of the Psalms (lxxiv. 8) in the English version, but the Hebrew word in this passage (properly “meeting-places”) is not the same usually applied to the buildings of a later age in the Talmud. The architectural style of the synagogues is a curious imitation of Roman architecture of the Antonine period, and it is to this age that Jewish tradition refers the building of the Galilean synagogues. It appears to me very doubtful if any one of these structures was in existence in the time of Christ. The Hebrew text which occurs on the gateway of the Kefr Bir’im synagogue is ascribed by competent authority (from the forms of the letters) to the second or third century of our era. The text runs in a single line under the semi-classic mouldings of the lintel stone, consisting, as read by Renan, of the words, “Peace be to this place, and upon all the places of God. Joseph the Levite, the son of Levi, put up this lintel. A blessing rest upon his work.”
It is easy for those who think only of the destruction of Jerusalem by Titus and of the persecution of the Jews by Christian emperors to forget how peaceful and prosperous was the life of the Galilean Rabbis in the second century under the tolerant Antonines. After the fatal revolt of Bar Cochebas, the Sanhedrim sat for a while at Jamnia in Philistia, but gradually the centre was shifted to Galilee, and soon Tiberias became the central focus of Judaism in Palestine. It was here that the Mishna was written, and many are the famous teachers of the Talmud whose graves were made in the Galilean mountains or on the shores of Gennesareth. To this period of toleration it is therefore natural to attribute the execution of works as ambitious as are the synagogues still standing in ruins.
One of the most curious facts connected with these buildings is the frequent representation of animal forms. In one case I copied two well-designed lions flanking a vase, and on Carmel a rude repetition of the same design occurs. In other instances rams’ heads and a hare are represented in relief; yet there was perhaps no period when the commands of the Law, which forbade the representation of the likeness of any living thing, were more rigorously observed. In Moslem art, also, it has always been considered impious to carve the figures of beasts and birds; yet I have found on the walls of towns and castles representations of lions clearly due to Moslem sculptors. In this case there is less difficulty, because the newly converted Mongols and Turks very probably rebelled against such restrictions, having long been accustomed to the use of heraldic crests; but it is hard to reconcile the ornamentation of the synagogues with the letter of the Law, so strictly enforced by the Rabbis.
The synagogues are long buildings, divided into walks by rows of pillars, and having generally the entrance doors on the south; perhaps because, as we learn from Rabbinical writers, the north side was considered unlucky. At the doorway end of the building are generally found two double columns, fitted to give extra support. It was suggested to me by a gentleman, whose name unfortunately escapes my memory, that these pillars must have been intended to carry the gallery for the women; for it was a custom in Israel, even when the Temple was still standing, to separate the sexes, the women being placed in an upper balcony, where they could not be seen by the men, just as we find the mosques of the present day to be arranged, or as the great church of St. Sophia at Constantinople is built with spacious galleries for women.
Perhaps the best-known spot in Galilee is the brow of the hill above Nazareth, whence the traveller commands a view of the greater part of the province. On the north is the high rough chain where Safed stands; on the east, the plain where the Crusading kingdom was crushed by Saladin; on the south, Tabor and Gilboa, and Ebal blue in the distance; on the west, the dark outline of bushy Carmel, the round bay, and the city of St. Jean d’Acre; in the nearer mid-distance, the great plain of Issachar and the oak woods of Zebulon. On every side the memory of great battles rises to the mind. By the springs of Kishon, under Tabor, Barak defeated the iron chariots of Canaan, which sank in the boggy stream; farther south, the Philistines defeated Saul; up the valley of Jezreel came Jehu, driving furiously to Jezreel; and farther down the two battles of Megiddo were fought. Round Acre the traces of Napoleon’s siege-works may still be seen; and it was at the battle of Tabor that the simple-minded Junot won his fame, driving the Turks into the same swamps in which the forces of Sisera perished. Near Seffurieh, on the north, the Christian host gathered when it went forth to meet the Moslems coming up from Tiberias on the fatal day of the battle of Hattin. There is no region in Syria where great hosts have so frequently met in great and decisive combats.
When first we look at the map of a country, it is hard to realise how few are the points where armies can meet; but the student of history and of geography knows well that simple physical causes, ever present, so narrow the lines of advance that famous battles constantly recur in the same places—whether at some mountain pass, by the fords of some considerable river, or beside the springs on which an army depends for water. Thus not only have the battle-fields of Palestine proved to be the same in all ages, but, even with our somewhat changed methods and new tactics, it is certain that future battles, if they take place in Syria, must be on the same fields, by Tabor at Megiddo, or farther north, where the main road crosses the Euphrates, at the old battle-field of Carchemish.
There are other memories which this famous view calls up to the mind. The little town of Nain, where the widow’s son was brought out to meet the Saviour and His followers; the long road from Shunem to the wilds of Carmel, pursued by the mother who went to seek Elisha; the paths leading to Cana and to Bethabarah; the many chapels which recall episodes in the life of the Christ. These spots have all become sacred within the last nineteen centuries, and their associations mingle strangely with those of battle and disaster; but Galilee always holds a different place in our minds from any other part of Palestine, because it is the cradle of Christianity and the chief scene of the Gospel narratives.
Of Nazareth itself there is little to be said. It was always a secluded and unimportant place, and probably at the present day is larger and more important than even when it was the see of a Latin bishop. The cave-cisterns, which have been traditionally regarded for many centuries as the “Holy House,” of which part was carried by angels to Loretto, are enclosed in a modern church on the foundations of a Byzantine chapel, converted later into a Crusading cathedral. The Greek church farther north, over the spring head, is the reputed site of the Annunciation, according to the Eastern belief. Another Christian sect was busy, when I first visited Nazareth, in consecrating a round table of rock, which seemed to be newly hewn, but which was to be revered as the Mensa Christi, where Jesus had once sat with His disciples. Such sites have little claim to attention, since no hint is to be found in the Gospels of their locality or preservation. Nor are the mediæval legends connected with the “Leap of our Lord,” at the cliff where the road runs up to Nazareth from the great plain, of interest, save to the student of the curious Crusading chronicles. Antoninus, the pious pilgrim of the time of Justinian, says that “in this city the beauty of the Hebrew women is so great that no more beautiful women are found among the Hebrews, and this, they say, was granted them by the Blessed Mary, who they say was their mother.” The same is said in our own times of the Christian women of the town, and of those in Bethlehem also. Certainly their type of beauty is very superior to that of the peasant women of Moslem villages. The Nazareth girls are more Italian than Arab in feature, and often very comely; but there are many ways of explaining this besides the theory of Crusading ancestry. We must not forget that in Syria mixed types, half Aryan, have long existed, due to Greek, or Italian, or Frankish forefathers, and the blue eyes sometimes seen in Syria may be due to yet later admixture of European blood. More weight is, I think, to be given to such facts than to a comparison with blue and green eyes in the faded pictures at Karnak, which represent the Canaanites. The fairness of the Nazareth women is denied by Père Lievin’s orthodox guide-book, and by the Franciscan fathers—mainly Italians—who have monasteries at Nazareth and at Bethlehem.
North of Nazareth lie the two sites which have at various times been regarded as representing Cana of Galilee. It is curious that Robinson, usually so careful, has confused them together. The one is the Christian village of Kefr Kenna, which was certainly regarded, before the Crusaders arrived, as the true site. Thus Antoninus places it three miles from Sepphoris, which can only apply to Kefr Kenna. The other site is the ruin of Kânah, four miles farther north. The distances given by writers of the twelfth century show most clearly that this was the supposed site in Crusading times. Robinson has twisted the earlier traditions, making them to apply to the more distant ruin; but the reader can measure the distances on the map for himself. This is not the only case in which the views of the Frankish monks of the Latin kingdom differed from the earlier traditions of the Eastern Church, but it is hard to say which is in this case the more reliable, though the opinion of most writers is in favour of Kefr Kenna.[42]
The Buttauf plain is for the most part arable land, well cultivated, but towards the north there is a pestilent swamp surrounded by reeds—whence the name Kânah, from the “canes.” Camping on the borders of this unhealthy morass, we suffered from the inevitable fever, as well as from the most notable mosquitoes in Palestine. The delay at this spot was, however, unavoidable, since the line of levels had to be carried across this plain from the Mediterranean to the Sea of Galilee, and accurate levelling is not rapidly completed in any country. Here also we examined, more closely than our predecessors, one of the smaller synagogues, and I was interested to find that its dimensions were multiples of a cubit of sixteen inches, as are also many dimensions of the Jerusalem Temple. The researches of the great Jewish writer Maimonides point to this length for the Jewish unit of measurement, which was not the same as the Egyptian cubit of about twenty-one inches—a question which is of no little importance in the study of Jewish antiquities.
On the east side of the Buttauf plain, not far north of the curious cromlech now shown as the scene of “Feeding the Multitude,” rises the dark crag of the “Horns of Hattin”—a place celebrated for its connection with the great battle in which Saladin defeated the forces of Christendom. The story of that battle, of the fatal dissensions among the Christians, and their lack of strategical skill, their vacillation and rashness, forms one of the most remarkable incidents in mediæval history. The unhappy King Guy of Lusignan had lain with his hosts by the fountains of Sepphoris for many months, awaiting the attack which it was foreseen would follow the loss of the Castle of Banias and the defeat of the Grand Master of the Templars near Tiberias. Whether through evil fortune or because of hidden designs, the Templars seem always to have been responsible for the great failures of the Latin kingdom. Raymond of Tripoli gave good and disinterested advice, for though his lady was besieged in Tiberias, he was willing to lose all, seeing that the only chance of victory lay in the choice of a battle-field close to the springs of Sepphoris. “Between this place and Tiberias,” he said, “there is not a drop of water. We shall all die of thirst before we get there.” But the Templars prevailed, and on the night of the 1st of July 1187, in the hottest season of the year, the army moved out over a plain which, east of Kefr Kenna, is entirely waterless.
The Saracens had, therefore, the advantage, for there were several springs behind their position. The Arab and Kurdish horsemen harassed the heavy-armed knights and set fire to the dry grass and stubble, which, in 1875, I saw in flames sweeping over this plain and destroying great part of a village by our camp. There was no water for the Franks, but a hot sun, with clouds of dust, smoke, and flames. The issue of the day was not long doubtful, and the army melted away as the deserters threw down their arms and begged for water from their enemies. Only 150 knights gathered round the royal standard on the rocky Horns of Hattin, and here the chiefs and princes of the kingdom were taken alive. The Holy Cross was lost, and with it went the Latin kingdom. Only Raymond, with Balian of Ibelin and his followers, were able to fight their way from the scene of this great disaster, and thus escaped to Tyre.
Renaud of Chatillon, the proud and treacherous lord of Kerak—his great castle by the Dead Sea—whose misdeeds were among the chief causes of the destruction of Crusading power, was the only prisoner whom Saladin slew, having first offered him his life if he would become a Moslem. Iced sherbet was ordered for King Guy in the conqueror’s tent, and the King handed the cup to Renaud. “Thou hast given him drink, not I,” said Saladin, and so pronounced the doom of a foe more feared by Islam than any other Christian in the kingdom; for he had sailed with his men almost to Mecca, and threatened the very centre of Mohammedan faith.
From the neighbourhood of Hattin the eye glances over nearly the whole of the Sea of Galilee, and the scene, which is unlike any other in Palestine, is not easily forgotten. Yet familiar though it is from many descriptions and pictures, it is difficult to bring to the mind of those who have not seen it. The scenery has not the wild and barren grandeur of the Dead Sea precipices, nor has it the rich wooded beauty of English lakes. It is quiet and simple in both outline and colour, and the finest effects depend on the passing shadow of the thunderstorm or the long shades of the sunset. The first view is generally from the top of the steep slope above Tiberias, with the flat plateau of the Hauran above the cliffs to the east, and the peak of the “Hill of Bashan” in the far distance. On the north-east are the volcanic cones of the Jaulân; on the north-west a long slope rises to the Safed ridge. The shore is here indented with tiny bays and strewn with black basalt stones. The cliffs of Wady Hamâm above Magdala, and those south of Tiberias on the west shore, extending to Kerak (Taricheæ) at the Jordan outlet, are among the boldest features of the scene. The lake itself is pear-shaped, twelve miles long and eight at its broadest measurement, east and west. The placid waves reflect the water-worn gullies of the eastern cliffs, save when tossed by the gusts that sweep down Wady Hamâm before the heavy thunder-showers which are here frequent in autumn.
The shores of the Sea of Galilee had been surveyed and thoroughly explored by Sir Charles Wilson before the Survey reached this region, and no important discovery was added to his exhaustive account. The sites of several important places, such as Magdala, Chorazin, Tiberias, Taricheæ, and Sinnabris, with Gamala on the east, are certainly fixed. Hippos (now Susieh) may now be added to these, with Hammath and Rakkath.[43]
The three sites on the shore of the lake which are most discussed represent three conditions of our knowledge of ancient Palestine topography. Bethsaida is practically unknown. Capernaum is the subject of controversy, and Chorazin is certain. In the latter case the name survives at Kerâzeh; in the other two the modern ruins do not preserve in recognisable form the Hebrew titles.
As regards Bethsaida, a city of that name existed at the mouth where the Jordan entered the lake; and the point which struck me most on visiting the ground was that this spot cannot be supposed to be the same at which the river now opens into the Sea of Galilee. Most rivers, and especially those like the Jordan, which flow through soft soil, have within historic times lengthened themselves by the formation of deltas at their mouths. There is a Jordan delta in the Dead Sea very distinctly marked, and the north shore of the Sea of Galilee must also have been widened by Jordan river deposits. Since the time of Ptolemy the Nile Delta has grown considerably, and since the days of Sennacherib the Euphrates has become nearly one hundred miles longer. For this reason Bethsaida Julias must be sought somewhere, as placed by Robinson, near Et Tell.
As regards Capernaum, Sir Charles Wilson has clearly shown that the site of Tell Hûm has been regarded by all the pilgrims, from the fourth century downwards, as representing the celebrated city of the Gospels. Yet, as we have had occasion to remark on previous pages, Christian tradition is not invariably a safe guide; and, after reading all the chief discussions of the question, and visiting all the sites, it seems to me impossible to fix on Tell Hûm as being the place intended by Josephus or by the Evangelists. I think, rather, that Robinson’s view is correct, and that the ruin of Minieh not only represents Capernaum, but preserves the contemptuous Jewish appellation for that town, “The city of the Minai” or “heretics”—a term by which the Christians were intended. Within the limits of this volume it is, however, impossible to detail the reasons which have led me to this view, and which I have fully explained in previous works.
A very curious legend may be noticed in connection with the Sea of Galilee. According to some Jewish and Moslem writers, the Messiah is first to appear in the future, rising from the waters of the lake. This idea appears to be of Persian origin. At all events, it is found in very early Persian literature, and it is not recognisable in the Bible. In one of the Yashts or hymns of the Zendavesta, we read of the lake in the far east, out of which Saoshyant, the Zoroastrian Messiah, will rise in the last days. Such recurrence of Persian legends is not uncommon, both in the Talmud and in the Korân, which borrowed largely from the Zoroastrian literature.
Before entering Upper Galilee there is one famous site which should be described, and which is very rarely visited, namely, the mountain fortress of Gotapata, which Josephus, the celebrated historian, defended against Vespasian and Titus for forty-seven days during the revolt in Galilee before the fall of Jerusalem. The ruin stands on a high spur in the mountains, north of the Buttauf plain, surrounded by deep valleys and rugged ridges clothed with brushwood. I reached the spot by a bridle-path from the north-wes in the autumn of 1875, and found that the various features agreed very closely with Josephus’ description, although an exaggeration, pardonable in one who wrote at a distance and many years later, seems to have crept into his account both of the place and of the events. He speaks of giddy precipices where only rugged slopes can be found, and one would certainly have expected the site to have been larger. The hill, over half a mile to the north, where Vespasian camped, is, however, easily recognised, and the statement that the city was only approachable on this side agrees with fact.
The Roman energy is well shown by the nature of the mountain up which they dragged their heavy battering-rams and the iron casings for their siege towers. The rocky knoll of the fortress of Gotapata is now bare of ruins, but there are foundations of a tower on the north, where Josephus built his wall, and cisterns (some still holding water), recalling the straits of the besieged during the summer, due to the absence of any supply save that from rain-water.
No soldier reading Josephus’ account can fail to see that it was penned by one who had experienced war, and in whose memory certain awful incidents were for ever imprinted. He remembers the terrible fire from the catapults, the gleam of the Roman spears in the sunlight, the darts of the Arab and Syrian auxiliary archers, the thud “which the dead bodies made when they were dashed against the wall” (III. Wars, vii. 23). He delights in recalling his own stratagems and inventions, and has no scruple in telling how he feared and despaired. Banks were raised in due form by the Romans, and screens of raw hide by the defenders to catch the stones and arrows. The spies sent by Josephus crept out in the dusk among the woods towards the west, covered with sheep-skins, so as to be taken when seen for straying beasts. At one time the Jewish general meant to desert his post, but he was overcome by the entreaties of the poor peasants, who wept and kissed his feet. The heavy armour of the Romans proved a disadvantage against the sudden attacks of the Jews, who sallied out even as far as their camp. The silent valleys re-echoed the cries of the women and of the combatants. “Nor was there anything of terror wanting.” When, on the fortieth day of the siege, the trumpets of the legions sounded a general assault, the enemy were met with streams of boiling oil, which flowed inside the armour, and made the scaling ladders slippery, Josephus held out yet another week, and Gotapata was finally surprised at night by Titus himself. The caves, in one of which Josephus hid, are still to be seen in the rock, recalling his curious account of many hairbreadth escapes; for those who sought refuge in the caves cast lots to kill each other, and the lot left Josephus and one other to the last. These two alone surrendered to Nicanor, a Roman friend of the historian’s, and but for the throw of a die (if we may trust his account) we should never have possessed that stirring story of the wars against Rome which Josephus lived to write, and should have depended solely on the curt and cynical chronicles of the Jew-hating Tacitus.
The survey of Upper Galilee was interrupted in the autumn of 1875 by an attack on the party at Safed. This was our only serious collision with natives, and it was due to the fanatical intolerance of the Algerine Moslems, who formed a foreign colony in the town, and held the unfortunate Jewish population in daily terror.
Our relations with natives of all creeds and races had always been excellent, and so remained afterwards. A little rigour was occasionally necessary when my men were pelted with stones, or when the muleteers in camp fought with knives; but our actions were always legal, and a Turkish policeman attached to the party was employed to take offenders before the local magistrates. There were no complaints against any of the party; and indeed, as we spent money, employed labour, and bought provisions at a good price, the Survey was always popular in Palestine. But at Safed a Christian was then rarely seen, and fanaticism always lives longest in the mountains. It is possible that some imprudent speech of the dragoman may have enraged the Emir who attacked us. Certainly a pistol belonging to our party was stolen, and was the immediate cause of the quarrel; but I never expected it to become serious until the furious Algerine attacked me with a knife. Few readers will blame me for knocking him down, and breaking his tooth; but the result was an attack by his followers with stones, and swords, and aged guns. Several shots were fired at us, but no one was hit. They, however, broke my head badly with a club, and I was defended by Lieutenant Kitchener, while I lay for a few moments stunned. I fear that I broke the head of the clubman afterwards even worse, but the party was never out of hand. We were armed with shot-guns and pistols, but we never fired a shot, and defended our tents without bloodshed until the police arrived. The enraged Algerines threatened to kill us during the night, but we kept watch with our guns loaded with ball-cartridge, hastily made up, and only in the morning did we march off the field in good order. The worst hurt was that of my groom, who was an old soldier. His head was laid open with a sword-cut, and had to be sewn up; but he accompanied us for several years after; and except a cook and a scribe little accustomed to such scenes, none of the natives in our party showed any signs of fear in face of the howling mob.
When the Emir was afterwards tried and sentenced to eighteen months’ hard labour, he was asked how the quarrel began. He said that he was taking an evening walk when we set upon him and beat him. It was represented to him by the Kadi that this was scarcely credible, as we were only fifteen in all, in a city where he had hundreds of retainers; and to this he had no answer. It was to his own furious temper that he owed the punishment inflicted for breaking the peace with law-abiding explorers working by express permission of the Sultan.
The negotiations which followed this riot were extremely tedious, and interfered with our progress. In addition to this, I had caught a serious attack of fever in the Buttauf marshes, and at one time the whole expedition was down with fever in the Carmel Monastery, except Sergeant Armstrong, who nursed us all. My health was so much shaken that I was unfit for further field work for several years, and, indeed, was not expected by the doctors to live through the attack of fever, aggravated by the injuries to my head.
The Turks at first did nothing, for the Emir was a relation of the venerable and respected Abd-el-Kader, whose acquaintance I was happy to have made, though this was unknown to his cousin. Afterwards they dispatched a commission, which adjudicated in our absence, and only inflicted nominal punishment; finally, my representations at home, backed by the Foreign Office, led to a proper inquiry, with the result that several of our assailants underwent terms of imprisonment, including the Emir, Aly Agha. The Palestine Exploration Fund Committee were paid the sum of £270 for our broken heads.
The mountains of Upper Galilee rise to a height of 4000 feet above the Mediterranean at Meirûn, the Jewish town where a wild torchlight dance of Jews occurs yearly round the tomb of Bar Jochai, the Cabbalist—a ceremony which I regret never to have witnessed or to have seen fully described. The ridges of these mountains are crowned by several important castles, which defended the kingdom of Jerusalem against the Sultans of Damascus. Toron (now Tibnin) was built as early as 1107 A.D., and Belfort (now Kal’at esh Shukif) in or before 1179 A.D. The great castle above the Jordan springs at Banias was held from 1130 to 1165, and after its loss the line was protected along the Jordan side of Galilee by Chateau Neuf, now Hunin, and Belvoir (Kaukab el Hawa), south of the Sea of Galilee, with another strong fort, built in 1178 A.D., at the Jordan bridge south of the Huleh Lake. This place William of Tyre calls “the Ford of Jacob,” and its modern name is Kasr’Atra, near the “Bridge of Jacob’s Daughters.” The chain of castles ran through Gilead to Kerak, and thence south to Montreal, which was built in 1115, and thence to Ahamant and Taphilah; while on the south-west of the kingdom there were many other forts, such as Blancheward, Chateau Ernuald, the Castle of the Baths, Darum (near Gaza), Ibelin, Gibilin, and Mirabel, all of which are marked on the map. Another similar line of strongholds also protected the county of Tripoli against the Sultan of Aleppo, including Mont Pelerin at Tripoli, Chastel Blanc, Krak des Chevaliers, Mont Ferrand, Margat, and Saone, in Northern Syria. In Galilee other castles were also built in the thirteenth century by the Teutonic Order, who owned much property between Acre and the Sea of Galilee, acquired by treaty with the Saracens. Among these later castles Safed was one, and Chateau du Roi (Malia), with Chateau Judin farther west. The large castle of Montfort (el Kurein) is also not noticed before 1229 A.D.
![]()
KRAK DES CHEVALIERS (KALA’T EL HOSN).
M. E. Rey, the French explorer, who has specially studied Crusading castles, points out a difference between those built by the Templars and those built by the Hospitallers, for most of these strongholds belonged to the great military orders, and very few were held by the King. The Templars had eighteen castles in all, including Chateau Pelerin (now Athlit), built in 1291 A.D. south of Carmel, and Tortosa. The Hospitallers in the twelfth century had only five great castles, Margat, Krak des Chevaliers, Chateau Rouge, Gibelin and Beauvoir. The Templar castles contain polygonal chapels, like the Templum Domini or Dome of the Rock, whence the Order was named, while the chapels in castles of the Hospitallers are of the usual form, with nave and aisles. The latter builders also did not generally make a donjon tower as an inner citadel, but often had a double line of ramparts with several important towers, as at Krak des Chevaliers, one of the finest and best preserved of the castles, which I visited in 1881, or that at Banias, which I explored in the following year. Krak quite recalls the Norman castles of our own country, or the early French castles, as it towers above the hamlet on the rugged slope. In its courtyard the whole population of that hamlet might have taken refuge in time of war. The proud humility of the Hospitallers is brought to mind by the text carved in Gothic letters by the door of the chapel in the inner court—
There is, however, another text on the outer wall at Krak in ornamental Arabic characters and in another style. “In the name of God, merciful and gracious, the rebuilding of this most favoured castle was ordered in the reign of our master the Sultan Melek edh Dhaher, the wise, the just, champion of the holy war, the pious, the defender of frontiers, the victorious, the pillar of the land and of the faith, the father of victory, Bibars.” And such indeed was the history of nearly all these castles, which Bibars took, and afterwards restored and held. The name of that famous champion of Islam, Melek edh Dhaher, “the victorious king,” is even now not forgotten by the peasantry of Palestine.
From the mountains of Upper Galilee you look down to the narrow shore-line of the coast of Phœnicia. In the later Jewish times the Holy Land was only reckoned to extend along the shore as far as Ecdippa (ez Zib), north of Acre. From that point it passed over the spurs along a line which I have traced in detail from the names of places mentioned in the Talmud, leaving a broad strip of country reckoned as Phœnician. It is very remarkable that immediately beyond this line we begin to meet with carvings on the rocks representing human beings. One of these near Tyre I copied in 1881, and another which I have not seen is reported to exist near Kanah. It cannot be accidental that no such sculptures have been found within the borders of the Holy Land, whereas they occur in Northern Syria near Merash, and in Assyria and Asia Minor. The explanation is, I believe, to be found in the Hebrew law which forbade the representation of living things.
If any carved idols of the Canaanites existed on the rocks in Palestine, they were probably destroyed at some period or other by the pious Hebrews or Jews. The distinction is, however, one of race, for the Arab hates carved images as much as did the Jew, while the Turanian Canaanites were fond of such arts, just as the Turanians of other parts of Western Asia were the first to adorn temples and houses with sculpture and painting.
The moment we cross the border into Phœnicia, we also find Phœnician inscriptions, though not of very great age. At Umm el Amed, Renan discovered three texts, of which the longest is a dedication to Baal Shemim, “That I may be remembered and my name good beneath the feet of my Lord Baal of the Heavens for ever.” The ruins among which these texts were found include a city (probably the Biblical Hammon) and a temple. Here I found sculptured sarcophagi and altars still lying on the hill side, where the French explorers left them, and the foundations and pillars of a Phœnician temple.
The exploration of Tyre itself was conducted in 1874, in 1877, and in 1881. The famous city is still a fair-sized town, having a few modern houses with tiled roofs. The population is reckoned at about 5000 souls, half at least being Metâwileh or Persian schismatics—some of the most fanatical Moslems in Syria. It was by these new colonists that the town was raised from its ruins in the eighteenth century.
The old Phœnician capital stood on reefs or islands in the sea, which together formed an area of about 200 acres. It had two ports, the Sidonian on the north and the Egyptian on the south, each about twelve acres in extent, or half the area of the port at Sidon. It is a curious fact that until 1881 recent explorers have spoken of the Egyptian harbour as no longer existing. With Lieutenant Mantell’s assistance, I was able to recover the site of this harbour, but the exploration had to be conducted in a novel manner by swimming. There are reefs, which seem to have been regarded as unconnected with any artificial structure, about 200 yards from the rocky shore of the island. On reaching these, we found that the rock had been carefully levelled, and in some places was still covered with remains of cement and concrete. We know that the Phœnicians used concrete at Carthage, and there was probably at one time a wall on this reef, which was thrown down when the harbour, like that of Acre, was filled up with stones, and thus rendered useless. We were able with some little trouble, walking naked in the sun over the sharp rocks, to discover the entrance to the harbour at its west end, and I can only suppose that no one had previously done more than look at the reefs from the shore.
Another important discovery, which may yet lead to more valuable finds, was the recovery of the probable site of the old cemetery on the island, which may, I believe, exist under the present Moslem graveyard. We squeezed through a narrow fissure in the rocks on the shore, and found ourselves in a Phœnician tomb of the peculiar character found at both Tyre and Sidon—a chamber at the bottom of a deep shaft from the surface. Unfortunately this tomb has been rifled, and the sarcophagus which it once held now lies on the ground outside the shaft. There may be other tombs not far off of the same kind which remain to be discovered, but excavation in a modern cemetery would present considerable difficulties.
Tyre was already a city on an island in the sea in the fourteenth century B.C., as we learn from an Egyptian papyrus of that date. Enumerating the coast towns of Beirût, Sidon, and Sarepta, the Egyptian traveller adds, “They are nigh to another city on the sea. Tyre, the double port, is its name; water is carried to it in boats; it is richer in fish than in sands.” The reference to the want of water is of interest, for this has always been the weakness of Tyre, which was somewhat later supplied by an aqueduct from the fine springs on the shore at Ras el Ain. The joining of the island to the mainland appears to have been first effected when Alexander the Great besieged the city and made a causeway to it from the shore, which causeway is now broadened by the constant drifting of the sands. The so-called “spring of Tyre” on the causeway is fed, I believe, by the ancient aqueduct, which we carefully traced. The work seems in great part to be probably Roman, but I found that in one part “false arches,” like those in Etruscan and early Greek vaults, occur in this aqueduct, which can only be attributed to the Phœnicians. The aqueduct probably existed in the time of Shalmanezer IV., for the inhabitants in 724 B.C. dug cisterns when the water-supply from the land was cut off.
Although Tyre is perhaps more celebrated than any other Phœnician city, it is from Sidon that the finest Phœnician remains as yet found have been recovered, including the celebrated sarcophagus of Esmunazar—the date of which is still disputed within several centuries—and the recent large find of sarcophagi and art objects which remain in the Constantinople Museum, unpublished and only very vaguely described. These remains are not older, apparently, than the Greek period, or in some cases, perhaps, of the Persian age. It is sincerely to be hoped that good accounts of them will be soon forthcoming.
It is still very doubtful what we mean when speaking of Phœnicians. The alphabet and the language of the Phœnician monuments are Semitic, and are traced perhaps as early as the time of Solomon. The representation of the Fenekhu or Phœnicians on Egyptian pictures of the time of Thothmes III. also presents us with a Semitic type of bearded aquiline profile. These Semitic people were certainly the Phœnicians known to the Greeks, and there is no good reason for doubting the statement of Herodotus that they were emigrants from the Persian Gulf.
There are, however, many things in Phœnician antiquity which are not easily explained by the aid of Semitic studies. Thus, for instance, the gods Tammuz and Nergal were adored in Phœnicia. Even Gesenius is unable to give a Semitic derivation for these names, and they are very well known to be Akkadian words, meaning “The spirit of the rising sun” and “The great lord.” Both these deities were adored in Chaldea, and their presence in Phœnicia indicates a population of like character to the Akkadian on the shores of Palestine. Nor is this the only indication of the kind. The Hebrew language itself contains foreign words of the same derivation, including a good many of what are known as “culture words,” relating to architecture, agriculture, and settled life, indicating the influence of that settled non-Semitic population which the Hebrews found dwelling in walled cities and tilling the land when they invaded Canaan.
It is not possible here to enlarge on this subject, though it is one of very great interest. No scholar who has carefully studied the early Phœnician seals and cylinders can fail to observe how like they are to the art of Mesopotamia, not only in general character, but in subject and in the details of symbolism. Rude monosyllabic words constantly meet the eye in Phœnician nomenclature, in the names of gods and in short inscriptions on seals, which it is very difficult to explain as Semitic. The conclusion at which it seems to me we must arrive is, that in Phœnicia, as in other parts of Syria, there was from a very early period a mixed population. The traders and rulers of the cities were of a race akin to the Hebrews, and spoke a language which is only a Hebrew dialect; but there must have been also an old element of population existing perhaps, in this case, chiefly among the lower class, which was quite distinct, and which belonged to that ancient and wide-spread “Turanian” race to which the Medes, the Akkadians, and the Hittites also belonged. It was from this race originally that the Phœnicians acquired their knowledge of metal-work, of seal-engraving, of sculpture; and I believe that it was from the syllabaries and older hieroglyphics of the Hittites that they developed their great invention, the alphabet, which they bequeathed as a practical benefit to all engaged in commerce and literature throughout the world; for it is from the Phœnician alphabet that every other alphabet of Europe or of Asia has sprung.
The number of Phœnician gems with carved emblems, and of small Phœnician pottery figures of the gods which fill our museums contrasts in a very remarkable way with the absence of such remains in Palestine proper. The only places where such pottery figures have been found in the south are at Gaza and at Gezer, as far as I can ascertain. The Jerusalem seals, generally speaking, have only an engraved name, though a few, said to be Hebrew, have emblems like those of Phœnicia. There is no apparent reason why these pottery images and other idols should exist undiscovered in Palestine, for collectors are just as eager in the south as in the north of Syria, and the tombs have been rifled equally in all parts. In the Palestine tombs glass tear-bottles are found, and coins occasionally occur; but the pottery statuettes are absent. The explanation seems to be that there was a difference of religion between the Hebrews and their neighbours; that the Phœnicians, like the Chaldeans or Egyptians, believed in the efficacy of such figures, symbolic of their many gods, while the Hebrews were forbidden by the Law to make any such image. The same sort of conclusion may, as we shall see in a later chapter, be drawn from the absence of rude stone monuments in Palestine, such monuments being very abundant in parts of Syria not reached by the zeal of Hezekiah and of Josiah.
The course of our investigation now carries us into the extreme north-east corner of the Holy Land, to Banias, under the slopes of Hermon, where the Jordan springs forth a full-grown stream, joining the Hasbâny river, which geographically, but not historically, is the true head-water. The fastnesses of this lofty mountain, which forms a conspicuous background to many a view in Galilee, in Samaria, and even in Judea, have always formed a remote and isolated region. It was here that the men of Dan, according to the Book of Judges, came to Laish, “unto a people that were quiet and secure, and smote them with the edge of the sword, and burned the city with fire; and there was no deliverer because it was far from Sidon, and they had no business with any man” (Judges xviii. 27, 28); and in later ages this mountain was the cradle of the Druze religion, which at one time had its missionaries in Afghanistan and in India, as well as in Persia, Arabia, and Egypt.
The Druze race inhabiting Hermon, and now existing in great numbers in the Hauran, to which some of the chief families have migrated from the Lebanon since the establishment of Christian rule in that province, represents one of the finest elements of population in Syria.
Tall, stalwart men, and women with features more delicate than any of the Arab or Fellahah females, seem to belong to a Persian rather than a Semitic race, although the language of their literature and of daily life is Arabic.[44] It is not hard to become acquainted with Druzes of every class, but to penetrate beneath the surface which they present to those of other creeds is far more difficult, and our knowledge of their creed is derived, not from any communications made by themselves, but from the capture of their sacred books; although even these probably only reveal the outer aspect of their belief, with one exception.
The Druzes have long been regarded with great interest in Europe, their bravery and ability having won for them a well-deserved fame. To me they were the most interesting people in Syria next to the Samaritans, and what I observed of the manners of their leaders (under very favourable circumstances in 1873 and 1882) fully agreed with the expectations raised by what I had read. But, on the other hand, a sort of mystery has been conceived by some enthusiasts to surround them, which disappears when the student compares them with other historic sects. They have been represented as if they were Oriental disciples of Mde. Blavatsky, or mystics claiming secrets of a supernatural nature. Those who know them well and have been long familiar with them hold a very different opinion, and regard them as a very practical and politic people, who may yet play a part in the history of the Levant, and who, but for their dissensions, would have become the dominant power in Syria, instead of the Turks. I have had more than one Druze servant, but they do not prove satisfactory in that character, being very independent and averse to regular habits. Their religion allows them to acquiesce in the creed of the dominant people, wherever they may be; thus to a Christian they present the Christian aspect of their system, and their Moslem beliefs to a Moslem. It seems, however, established that they have no rites, ceremonies, or prayers of their own, and that the gatherings in their remote chapels or khalwehs are mainly for political and social purposes.
The accounts of the beauty of their horses, the richness of their dress, the silver ornaments of saddles, bridles, swords, and guns, I did not find to be exaggerated; but the curious horned head-dress, worn under the veil by the women till quite recent times, I have never seen in use, though such a horn, made of silver filagree-work, was once shown to me. It is a curious and interesting fact that this head-dress was also worn by tribes in Central Asia, on the Oxus, near the Caspian; and this indication agrees with others to be mentioned shortly in indicating that the original Druzes were probably emigrants from Persia, or from some region perhaps farther east.
The Druzes are perhaps best described as Moslem Gnostics, and the best key to their rambling and concrete dogmas is found in a study of Gnostic systems. They are schismatics, whose chief distinguishing tenet is a belief that the mad Khalif Hakem, in the eleventh century, was the final incarnation of the power of God. The appearance of this heresy in Egypt was due to the fact that the Fatemite Khalifs in that country were of the Ismailiyeh sect, which was of Persian origin. Other sects of similar character were independently established in Syria (the Metâwileh, the Anseiriyeh, and the Ismailiyeh), among which the Druzes probably gained many recruits.
When the Moslems conquered the Persian dominions, they came in contact with several religions and with numerous philosophies. The Zoroastrian established faith, the Christianity of Nestorians and Sabians, the Judaism of the great Chaldean schools, were firmly rooted in the land; and in addition to these the Manichean system, which was, in fact, a combination of the preceding with Buddhist scepticism, had spread on all sides, even as far as Turkestan. Moslem mystic and philosophic sects very quickly developed under these influences, and the Sufis represent the adoption of Buddhist ideas by professing Moslems.
The philosophic sects held the opinion—which is also a Buddhist view—that the religion of the masses can never be the same as that of leading minds. The Ismailiyeh and other Moslem societies put this belief into practice, teaching to their disciples a series of dogmas in which they had no personal belief. Thus, while they professed to explain a series of incarnations of the Natek and the Asas, who were in the future to appear on earth as Ismail and Muhammad, in secret initiation they taught the more advanced student to discard all belief in either Korân, or Gospel, or incarnation, and to believe only in two natures (“the uprising one” and “the abode”), which together were, they said, the only realities in the universe. This doctrine is closely similar to that of the Syrian and Persian Gnostics, and to the final initiation of Eleusinian and other mysteries, as we learn from many detailed accounts. This simple basis enables us to thread the labyrinth of absurd allegories which the various sects wove round their concealed disbelief. These were, as a rule, politic dogmas, framed to bring into the organisation men from every existing creed, and apparently to reconcile systems which, in the eyes of the initiated, were all equally untrue.
The dogmas generally cited as tenets of the Druze religion are those taught to the lowest and uninitiated class. They are known through the seizure of sacred books by the Maronites in 1837, during Ibrahim Pasha’s wars, and again by the French in 1860. The great Orientalist De Sacy at the earlier period was able to study at leisure the manuscripts in the National Library at Paris, and Dr. Wortabet added to his results after 1860.
There is no reason here to give the details of this fantastic system. The Druze doctrines as to Christ, like those in the Korân, are clearly of Gnostic origin. Their teaching of a paradise for the pious dead in China, whence also Hakem is to return at the last day, and their dogma of transmigration of souls, were no doubt learned from Bactrian Buddhists or from Manicheans. We have already seen that more than one link connects them with the Manichean and Buddhist Mongols of Turkestan, though in appearance they approach nearer to Persians and Parsees. They have celibates among them, and hermits who retire to distant khalwehs, sleeping on mats, with pillows of stone, eating dry bread, and dressed in wool, with a girdle like that of monks or of the Dervish orders; but they are also commonly said to celebrate annual orgies, like those of Gnostics, of Greek pagans, or of the Sakti sects in India. They have secret emblems whereby they recognise each other, one of which is the fig, which was also a Manichean emblem, according to Cyril of Jerusalem. By none of these tenets or customs are they very clearly distinguished from Anseiriyeh or Ismailiyeh heretics, the divinity of Hakem being their true point of schism.
There is, however, in existence a work, said to be that of Hamza, the original Druze teacher, which admits us within the veil of initiation. It is called the “Hidden Destruction,” and it abolishes both Tawil and Tenzil, or open and secret dogma as to the Korân. It reduces the Moslem prayer—the Fetwa—to a cabalistic myth of planets and zodiac. It abolishes prayer, sacrifice, tithes, fasting, pilgrimage, the holy war, and even submission; and for these seven cardinal doctrines of Islam it substitutes seven new laws, which represent truth according to Druze philosophy.
1st, The confession of truth, save when such confession may endanger the safety of the initiate, when silence is allowed. Thus, too, the Buddhist is taught not to interfere with the common beliefs of other men.
2d, The duty of mutual help and assistance.
3d, The concealed renunciation of every form of creed or dogma.
4th, A separation from those who live in error.
5th, The unity of “the Power” in all ages.
6th, Contentment with His will.
7th, Resignation to inevitable fate.
This then, I believe, is the true system of Druze initiation. The fantastic dogmas are but the husk of which this is the kernel. There is no real mysticism in the system, but simply a concealed scepticism which renounces even the most negative of religions—that of Muhammad. The inquirer who expects to discover a secret supernaturalism among these philosophers deceives himself, and would by them be regarded with contempt.
In the present chapter we have thus had occasion to refer to four developments of Moslem religion existing in Syria side by side with the Sunnee faith (the Metâwileh, the Ismailiyeh, the Anseiriyeh, and the Druze), and I may perhaps be pardoned a few words in addition on a question which of late has excited interest in England, namely, the comparative vitality of Christian and Moslem religion in lands where both exist together.
On this matter the views of the tourist visitor, however well stored his mind may be with knowledge obtained from books, have little permanent value. Nor will conversations, carried on by aid of a dragoman, with respectable Moslem doctors, or with peasants, really enable the new-comer to form a true opinion. Islam is not what it appears to be to the stranger, and Moslems do not, and indeed cannot, give to such a visitor a comprehensive view of their creed. It is necessary to live for many years in a Moslem country, and in daily contact with Moslems of all classes, in order really to know what they and their religion are like; and such contact will not lead the impartial observer to form a very high estimate of the practical results of Moslem teaching.
In the first place, Islam can only be regarded as a general term, like Christendom. There are in Islam as many antagonisms, as much indifference and disbelief, as many sects mutually hateful, as much discord and contention over abstract dogmas, as are to be found in the West. A general reconciliation and union is as impossible in the one case as in the other. But if we are to judge Christianity and Islam by their declared moral standards, Islam must stand second. It is, moreover, the most negative of faiths, distinguished by what it denies, not by what it maintains. The enthusiasm for Moslem religion which some writers express is but the natural reaction from that ignorant prejudice against the “wickedness of the false prophet” which used to mark our entire want of knowledge of Moslem belief; but this enthusiasm is also the result of imperfect knowledge, and it dies off as the student of Moslem life becomes more intimate with actual society in the East.
It is true that Islam spreads with rapid strides in countries where the Arabs are strong and where Christian teachers are weak. The conquered are forced to adopt the creed of the conqueror, but the conversion is not superior to the orthodoxy of Spain under the Inquisition; and the propaganda is the same as that of the persecuting days of mediæval Christianity. It is surely no mark of advanced religious culture that uniformity should be due to terror of the sword.
Islam does (as far as I have been able to observe) absolutely nothing for the education and raising up of the ignorant and of the poor. The religion of the so-called Moslem peasant is the paganism of the days before Islam was preached. He swears by Muhammad, but his real gods are the buried saints, whose power to punish him by misfortune he dreads. He lives in fear of the Jân, of the Ghouls, of the Kerâd or “goblins;” he prays to the holy tree; he believes in magic and in witches. No attempt is made to educate him. He cannot read or write; he has no doctor save the charitable European who may chance to pass by. So long as he proclaims his belief in God and the Prophet, no one troubles himself as to his fate. The dark places are full of cruelty, and the morality of the peasant is generally not better than that of the African savage.[45] The visitor, charmed by the natural dignity and courtesy of Oriental manners, does not see more than the surface, and it is not till one incident after another reveals the truth, that it can be recognised that Islam has done nothing to raise the poor. In the cities usually visited the traveller finds mosques filled with decent congregations. In the villages there are no mosques at all. Many peasants cannot repeat the simple Moslem prayer. They can do nothing more than light a lamp to the Nebi when child or husband are sick. They dwell in an imaginary atmosphere of marvels, like that in which the Zulu or the Hindu peasant passes a lifetime of superstitious fear. We have nothing like it, save perhaps as a survival in the wilder mountain districts of Britain, where witches are still feared. The pious doctors and fanatic Imams of Islam have done nothing to compare to the home-missions of England. This is not only the case in Syria; it applies equally to the whole Moslem world.
Among the upper class, too, there are many differences of belief and of life. The mosque students and doctors represent, as a rule, orthodoxy of the most conservative type. Yet even among these some survival of the philosophy of the early Baghdad schools may exist, some tinge of the influence of Plato and of Aristotle, which led captive for a while the intellect of Islam. Among these, again, the passionate mysticism of the Sufis represents an emotional condition not unknown in the West. The Sufi gives up the riddle of existence to seek the final union with God, which is the aim of his life. But side by side with these are men professing Islam, yet breaking its laws, soldiers and diplomatists who have seen the world unknown to the dweller in mosques or to the literary professor; men also who drink wine and who neglect prayer; other men who take bribes and grind the faces of the poor; pitiful ambitions gained by crooked means; white turbans covering hypocrisy, and successful humbugs decked with stars.
There is, however, one phase of Moslem life which has no exact counterpart in the West—a power which is often unsuspected but very great, namely, that of the Dervish orders. The visitor who sees the miserable mendicant in the street, who hears the frantic howls of those performing the zikr, or watches the stately dance of the Mawlawîyeh, little suspects the power which underlies these outward appearances, and little understands the reason for that reverence which is shown, even by Turkish officials, for the Dervish beggar. Miserable and ignorant as is the fanatic who thrusts a sword through his arm, or devours scorpions, charms snakes, treads on the sick babe laid before him, or bathes in charcoal embers, he yet belongs to a wide-spread secret organisation, and has sworn away his private judgment and liberty of action, devoting himself to fulfil the will of one man, the distant head of his order. A letter from such a chief will secure the active help of innumerable associates scattered far and wide, in Turkey, in Egypt, and yet farther afield. The power which Gnostics, Assassins, Templars, and other secret orders used to wield is still wielded in a certain measure by the Dervish leaders: we have only a faint reflex of such a system among Masons. Yet it cannot be said that the Dervish orders have done much for Islam: rather have they served to secure the aims and ambitions of chiefs who, regarded by their ignorant followers as possessed of marvellous powers, are yet perhaps in reality as sceptical as the Druze initiates. By pretensions to spiritual knowledge and power they attract the poor candidate who stands naked at the door begging for admission to the order. By jugglery and sensational acts they captivate the imagination of the mob. But they are careful only to admit to their real counsels those of whose intelligence and trustworthiness they have had long experience. The Dervishes may lead the populace in religious war, but chiefly when certain very practical aims are seen by their leaders to be thereby attainable.
Such considerations, though they have led us far away from Galilee, will perhaps be allowed as the results of practical acquaintance with Islam, gained by six years of life in Moslem lands, and may be useful in face of the somewhat superficial estimates of Moslem religious life which so often appear before the public as the results of a trip to the more frequented towns of the Levant and the talk of dragomans and renegade Turks. I know only one point in which Islam has real advantage over Christianity, namely, in its direct condemnation of drink. Even Islam is unable entirely to stamp out this curse; but when we contrast the sobriety of Palestine with the drink traffic forced on natives of South Africa by an English-speaking race, whose Government draws a revenue from the excise, we find that there is one great lesson to be learned in the East, and one great evil which the voice of Muhammad has always proclaimed as such. In all other respects—the position of women, the condition of education among the poor, the sympathy of the upper class with the ignorant, the love of truth, and of freedom, and of justice—the lands where Islam is established can never be compared with those where Christianity is purest.
These reflections have been raised by the remembrance of days spent in crossing over Hermon, from Banias to Hasbeya, on the road to Damascus, or in the investigation of the ruined towns and temples on the mountain, or in toiling to the summit, 9200 feet above the sea, where the Survey party once spent the night, and took observations of the stars for latitude. It is one of the wildest and most picturesque parts of Syria. The lower slopes are of the sandstone which underlies the Lebanon and appears on the Moab hills. Above is the hard fossiliferous limestone, which is a base-bed in Western Palestine. Near the Druze villages great cascades of bright green foliage deck the mountain slopes, where the vineyards, already famous in Hebrew times, run terrace above terrace. Clumps of pines, low thickets of oak and mastic, and hedges of wild rose rise towards the snowy dome, where the Syrian bears are hiding, and whence sometimes they venture down to eat the grapes. The costumes of the Druzes, the white veils, through which one eye only of the Druze damsels is seen, and the brightly-coloured dress of the men, are equally picturesque; as are, too, the solitary khalwehs or meeting-places perched on cliffs remote from other habitations.
The scenery round Banias is also of remarkable beauty. It is well known to tourists, who generally visit it at its best. Here by the Mound of Dan is the fine clump of oaks, a familiar resting-place, near which is the tomb of Sheikh Merzûk, who is said to have been a dog. To the west the path crosses four rushing brooks, which join the cascades of Banias to form the Jordan, breaking over stony channels in a plain strewn everywhere with blocks of black basalt, covered at times with orange-coloured lichens.
It was here that I discovered a group of dolmens in 1882, which had previously been overlooked amid the many natural boulders, and which are no doubt connected with the old worship of the region. Farther east the town itself still preserves its great Norman wall in parts, and the rush of the Jordan, shooting down in a foaming torrent between thickets of low shrubs, with forest trees in groups here and there, and a few poplars, is that of an Alpine river rather than of a Syrian stream. High up on the east the ruins of the great castle, which was the bulwark of Christendom against Damascus, cover a long spur on the side of Hermon. The great cave of Pan, whence Banias takes its name, has now fallen in, so that the full effect, which probably was to be remarked when Josephus wrote, is lost; for the sudden bursting of the river out of the cavern must have been very striking. A little Moslem chapel is built on the debris, and dedicated naturally to El Khudr, the mysterious “green one,” who drank the water of life, and who represents the vivifying power of moisture in Moslem folk-lore. On the rocks, still half legible, are the Greek inscriptions of the days of Agrippa, one dedicating an altar to the nymphs, another recording the name of Agrippa as archon of the year, a third speaking of the priest of the god Pan. The name of Pan at this place is perhaps older than the Greek age, and of Canaanite origin, since the word as a Turanian term, meaning a “spirit,” is found in many languages of the group to which the Hittite tongue belonged. Looking southwards over the flat Jordan plain, you see the marshy Huleh lake shining amid its papyrus swamps. On the east are the fantastic cones of the Jaulan volcanoes, on the west the bushy range of Naphtali, on the north the rugged ridges of Hermon. The black camps of the Arabs are dotted over the plain, their brown cattle wander beside the streams, and the women in dark flowing robes are churning butter in goatskin bags beside the “houses of hair.”
Hermon appears in all ages to have been a sacred mountain and a religious centre. The name is thought by some to mean a “sanctuary,” but by Gesenius to mean a “mountain spur.” The old Amorite name was Shenir, of uncertain meaning, and the Sidonians called it Sirion, which is probably a Turanian word meaning “white” or “snowy.” Long after the calves of Dan had been overthrown, and before the calf became an emblem in the Druze khalwehs on the same mountain, the Romans covered its slopes with little temples. These have been, for the most part, visited and described. Sir Charles Warren made careful plans of the best-preserved examples, and nearly all of them I have explored on different occasions. At Rukhleh, on the north-west slope, there are remains of such a temple, which has been pulled to pieces apparently to make a church. The Roman eagle, which one traveller in his enthusiasm has called Hittite, is here carved in bold relief, as also at Baalbek, and in the curious temples of the Anseireh mountains; and a great head of the sun-god is sculptured on another stone. Here, too, occur Greek inscriptions; one recording the adorning of the temple gates with silver, another mentioning the Epiarch of Abila. Farther north, at Abila itself, the ground is strewn with Greek funerary texts, and the rocks burrowed with tombs, one of which has rude busts in low relief over the entrance, such as we also found over Roman tombs in Gilead.
On the top of the mountain itself there are some very curious remains. A sort of peak has here been surrounded by an oval of cut stones carefully laid, within which we found a quantity of ashes, apparently belonging to some beacon or sacrificial fire once lighted on the spot. Close to this circle is a cave hewn in the rock, measuring fifteen feet by twenty-four, with a roof supported by a rocky pillar. Three steps lead down into the cave, and the rock above has been levelled, perhaps as the floor of a building. There is no historic account of the object with which this curious cave was cut high up on the snowy summit, remote from all inhabited spots. The Druze hermits are said to retire to Hermon, but their place of retreat was shown to me farther down the side of the mountain. The names of Antar and Nimrod are connected with various buildings on Hermon, and the remains on the top are called “Castle of the Youths” by the shepherds. It is said that a Greek inscription lies near the circle round the highest peak. This I was unable to discover. The rock of the peak has been cut so as to form a sunken trench with a round shaft—perhaps for water—beside it. The object of these cuttings is, however, obscure.
By passing the night on the summit, I was able to witness two of the most interesting scenes imaginable—the sunrise over the plains of Damascus and the sunset in the sea. These I have fully described in another work, but, as there is no other point from which such a general view of Palestine can be gained, I may be allowed to repeat in part what I saw. We ascended the mountain on the 9th of September, at which time it was quite free from snow. Indeed, we could not even find snow to melt for cooking, and had thus great difficulty in getting water.
Beneath us, apparently quite near, lay the calm Sea of Galilee, showing a light green among its dusky cliffs. Tabor and the Horns of Hattin appeared to the right, and the chain of the Safed mountains as far as the Ladder of Tyre. The gorge of the Litany River was clear, with Belfort on its northern slope, and Tyre itself with its harbours. Carmel formed the extreme distance on this side, about eighty miles away.
On the east the Syrian desert stretched unbroken towards the Euphrates, and the white houses and minarets of Damascus were set in a deep border of green from the surrounding gardens. Farther to the south-east, as on a map, we looked down into the craters of the Jaulan volcanoes, which seemed no larger than the hollow cones of the ant-bear. Over the great brown Bashan plains, so full of ruined Roman cities, of endless Greek inscriptions, of Nabathean texts scrawled on the rocks, and of dolmen groups yet older, we saw the great columns of the whirlwinds slowly stalking in the autumn heat. The Druze villages were at our feet, and a green valley with a gleaming stream.
On the west the long ridges of the Southern Lebanon reached out to the great level of the Mediterranean, with dark shadows in the deep ravines. On the north is Sannin, with its cedar clumps, and grey rocky walls, and valleys fringed with pines. The glorious flush of the Eastern sunset bathed all this scene for a few moments, and then, while still in sunshine ourselves, the steel-blue shadow crept over all the lower world. The great conical shadow of Hermon crept out eastwards and swallowed up Damascus, and stretching yet farther for seventy miles over the desert, stood out against the thick haze on the sky itself.
When the dawn rose, we again stood on the peak, where perhaps the old sun-worshippers used to await the great orb, which here rises from the desert horizon. Often in other places have I seen the first white streak and the glory of the aurora behind mountain ranges; but here, as the red globe appears in the mists over a boundless plain, the great shadow of Hermon stretches far across the dim Mediterranean—a sight not often seen by those who watch the dawn. Wherever a single peak stands out alone, such a shadow may be seen from the summit. In Teneriffe it stretches over the Atlantic, and the watchers on other mountains have seen it; but in Palestine there is nowhere else such a sight or so glorious a panorama, because nowhere else does a solitary mountain stand up twice the height of the surrounding hills. The great peak of Monte Viso, rising above the Italian snowy ranges, has a finer outline, but Hermon is unlike any mountain with which I am acquainted. It appears as the centre of every view in northern Palestine, and its snowy dome is seen from the plains near Jaffa, and from the valley of Jericho; while on the north its outline is equally impressive from the plains of Cœle-Syria, or from the heights of Lebanon. It is this scone which rises in the mind of Hebrew poets in many ages, and which inspires the Song of Songs: “Look from the top of Amana, from the top of Shenir, even Hermon, from the lions’ dens, and from the mountains of the leopards.”
THE survey of Western Palestine was happily complete in 1877, and the map was out in the following year; but the Memoirs were still not half published when, in 1881, I was again given command of a party instructed to carry the work east of Jordan. The adventures of the fifteen months which followed were far more exciting than any encountered west of the river. Even in 1877, when it was thought that some trouble might arise, the condition of affairs was really favourable, as the Turkish Government was very cordial, and all the dangerous characters were drafted out of the country to the war, leaving only peaceful elders, women, and boys. But in 1881-82 there was great excitement preceding the Alexandria massacres and the expectation of a Moslem Messiah in the year 1300 of the Hegira. In addition to this, our relations with Turkey had altered. The new Sultan refused to prolong our firman or to allow any exploration. The British Government served me with a notice that any expedition I might undertake was at my own risk, and that they would not be responsible for the consequences. We had, therefore, no support on which to rely, and were yet expected to work in the wildest districts, against the will of the Government of the country, and in a time of religious and popular excitement, finally culminating in massacre.
Arriving at Beirût in March 1881, before the assistants and the stores had left England, I determined to fill out the time by a journey through Northern Syria, in company with Lieutenant Mantell, R.E. The object of the excursion, which, by hard riding, was carried through in eighteen days, was to search for the lost city of Kadesh on Orontes. On our way through Baalbek we made the discovery of a Greek inscription painted in red in a chamber behind the north apse of the church built by Theodosius in the great enclosure. It appears to me to be as old as the time of the building of this church, and had not, I believe, been previously noticed.
Our farthest point was the ancient and picturesque town of Homs, whence we returned by the valley of the Eleutherus to Tripoli, and down the Phœnician coast. The full account of this journey I have already given (“Heth and Moab,” chaps. i. and ii.). The impression left on my mind was that few parts of the East would now better repay scientific exploration than Northern Syria. Excavations at Carchemish are urgently needed. Rock-tablets and large ruins exist in the Northern Lebanon, as yet very imperfectly explored. Round Homs there are great mounds awaiting the spade, which probably contain Hittite and other remains of the highest interest. Even the remains existing above-ground are as yet little known, though De Vogüé has done much for the Byzantine ruins of this region.
Kadesh on Orontes was the Hittite capital attacked by Rameses II., and an Egyptian picture represents it as a walled town surrounded by the river. Its discovery, which rewarded our labour, gave an instance of the necessity of keeping the mind open in archæological research, and of avoiding preconceived theory. South of Homs is a great lake, which, in the fourteenth century, was known as the Lake of Kadesh. A mound in this lake was thought likely to be the site of the city. We found, however, that the lake was artificial, being formed by a Roman dam across the river. This agrees with the statement of a Rabbinical writer, who says that the lake was made by Diocletian as a reservoir for the supply of Homs, the ancient Emesa; and an aqueduct still leads from the dam to this city. The lake, then, did not exist in the days of Rameses II.
Camping for the night a few miles south of this lake, I, as usual, inquired for the names of towns, ruins, &c., in the district, and to my surprise the name Kades was among them. We therefore altered our plan, and turned aside to explore the place pointed out under this name. We found it to be the site of an important town on the Orontes, about five miles south of the lake, and it was afterwards discovered that previous travellers had recovered the name, though it had escaped the map-makers. Standing on the great mound, and observing how the Orontes washes it on the east, while a tributary stream flows on the west and joins the river immediately to the north, no doubt remained possible that the name survived at a site exactly fulfilling the requirements of the Egyptian account. Excavations at the recovered Hittite capital might lead to very important discoveries, if thoroughly carried out.
I was much interested also to find a considerable Turkoman population in these plains; for the border between Turkic and Arab populations is generally placed much farther north. This mingling of Turanian and Semitic peoples round the old Hittite capital represents, in our own times, just the same racial condition which we gather to have existed in the time of Rameses II.
It has come to be generally recognised that the Kheta or Hittites were a Mongolic people, speaking what is called an “agglutinative” language, which was, I believe, akin to the Turkic dialects.[46] They were thus related to that ancient race of Chaldea and Media which, through the labours of Sir Henry Rawlinson and of Dr. Oppert, and their disciples of the second generation, has been so wonderfully demonstrated to have produced the existing population of Central Asia and of the Turkish hordes which spread over Asia Minor. The hieroglyphics found at Hamath, a day’s journey north of Emesa, are the same characters now known in many parts of Asia Minor, and of which examples occur even in Nineveh and at Babylon.
Our troubles were all before us. The Wâli of Syria caused us to be privately told that he must forbid any exploration under the old firman. The Druzes were in rebellion, and the Hauran, which I had intended first to enter, was surrounded by a cordon which we could not pass. Moving southwards, I found the Belka governor, who lives at Nâblus, equally firm. The word had been sent all over Syria. Moreover, the great Arab tribes of the Belka were at war, and the Adwân had just killed a chief of the Beni Sakhr. I soon found that we were watched by spies, and, moreover, that the Turkish power east of Jordan had been so much strengthened since the time when Sir Charles Warren visited Moab, that it was very hard to find an Arab chief independent of the Turks with whom to treat. I felt that the lives and safety of my party rested on my decision, and that while subscribers at home were eager for results, the question of putting my followers in peril rested on my shoulders.
There was another consideration which also weighed with me. Imprudent action and an open breach with the Government of the country might not only endanger our safety and entirely stop our work, but it might also close the doors for many years on Palestine explorers.
After patient waiting, however, during several months, which were fully employed in visiting places of interest only imperfectly described before, fortune at length favoured us for a while. The quarrels of the Arabs were settled, and I found at last a sturdy Arab chief of the old school, regarded by the Turks as a rebel, but powerful and respected over a large area east of Jordan, and willing to escort us. I was thus able to carry out the wishes of those at home and to start the Eastern Survey. It was not difficult, by leaving the greater part of my camp standing west of Jerusalem, to give the Turkish spies the slip. A regular treaty with Goblan, the aged Adwân chief, was signed. With Lieutenant Mantell I crossed Jordan, and finding that no active steps were taken by the Government, I sent for the rest of the expedition. For two anxious months we laboured at very high pressure; and after measuring our base-line and connecting our triangulation with that west of the river, we worked over five hundred square miles in detail.
I had quite hoped that, though not recognised, we might be tolerated in the country, and I believe we might have worked still longer—for I doubt if the Turks at all knew where we were gone—but that there was an adverse influence of some kind at work. Whether it was the jealousy of the Beni Sakhr, or whether some political counter-current existed, I was unable to find out. The Beni Sakhr had certainly seemed friendly. We had already subsidised them, and they expected us soon to work in their country, and to pay them handsomely for escort. No means that I could think of was neglected to interest all who could help in our peaceful and rapid progress. Yet suddenly the whole plan was spoilt by the extraordinary action of the Beni Sakhr chiefs. I am not aware that they are conspicuous for devotion to Turkish interests, though certainly they hated Goblân, with whom they had a blood-feud and whose life they sought. Whatever their reason, they went out of their way to draw attention to our presence. The Haj, conducted by the famous Kurdish Pasha, Muhammad Said of Damascus, was on its way through Moab to Mecca. To this Pasha they pointed out that English captains were measuring the land, and he only did his duty when he at once ordered us to be stopped, and telegraphed to Damascus, whence the news was sent to the Sultan. The governor of the Belka was reprimanded, and he in turn came down on the governor of Es Salt. Yet even after this we were able to extend the work over a considerable area, and only recrossed Jordan in time to escape from the winter storms or from being cut off by the flooding of the river. It was in the same year that Mr. Rassam’s researches in Mesopotamia were stopped, and no important or extensive explorations have since that date been possible in the Turkish dominions.
We could not blame the Turks for their action. They had every reason to be jealous and suspicious at a time when the war in Egypt was brewing, when Cyprus had been handed over and Tunis annexed, and when Russian political emissaries were, I believe, actually exploring Northern Syria. It was not likely that the Sultan or his advisers would discriminate closely between antiquarian work and political intrigue, especially as our explorations were not likely to put much money in the treasury. It had been my wish to go to Constantinople, and to place the matter fully before the Sultan, before attempting to begin the work; but when I was instructed to go to the capital, after our irregular proceedings had been peremptorily stopped, it was with a bad grace that I was forced to ask for regular authorisation, which, though promised, has not yet been granted.
In spite of all difficulties, a substantial bit of work was done—about an eighth of the total proposed—and we came back from the desert with our hands full of valuable results. I believe that but for the Beni Sakhr, or their unknown instigators, we might, through Turkish good-nature, have been allowed to work for some time longer. As it was, I revisited Moab and Gilead next year, through the kindness of our Royal Princes, and thus have seen nearly all the country east of Jordan except Bashan, on which I have only looked from a distance. Finally, we left Syria on a steamer crowded with refugees from the Alexandrian massacres; and Lieutenant Mantell and I had hardly been six weeks in England when we were ordered to Egypt on active service.
Since that date I have been in two campaigns, serving on the staff at Tell-el-Kebir, and laying down the west border of the Transvaal in South Africa; yet I can look back on no more anxious time than the weeks we spent in surveying Moab. Surrounded with lawless Arabs: roused almost every night, at times, by the attacks of thieves bent on stealing the horses on which we so much reckoned; having nothing on which to trust but the unproved loyalty of our old guide, Sheikh Goblan, whose life was in constant danger from his blood-foes on the south, and his liberty from the Turks, who had often tried to catch him, on the north; placed in opposition to the Turkish Government and disowned by the British,—we felt that a disaster might any day occur which might endanger the lives of brave comrades who had ventured to follow, but who certainly were alive to the perils of our position. I write these lines not to exaggerate those dangers, for Goblan was trusty and our relations with the Arabs were excellent, but to show how difficult it was to carry through even that small portion of the great task which we completed, and how utterly impossible it was to do any more.
The stoppage of the work was a great disappointment to us all; but I can only feel thankful that no accident marred our success, and that the sum banked in Syria to pay ransom in case of our being imprisoned, like Dr. Tristram in Kerak, or kidnapped by the wild Anazeh to the east, who could have brought many armed horsemen against our little band of fifteen, was never called into use.
![]()
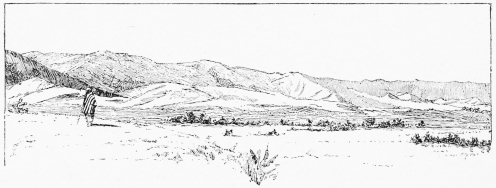
MOAB MOUNTAINS FROM THE PLAIN OF SHITTIM.
Crossing the Jordan, and traversing the plain of Shittim, we ascended the great sandstone spurs to camp by the Brook of Heshbon. Thence we afterwards went south, camping in the wild ravine of Wâdy Jideid, inside the curious Hadânieh circle, and again farther south, near the brink of the gorge of Callirrhoe. A rapid countermarch, which put the Turks at fault, took us thence northwards to Rabbath Ammon in Gilead.
The most remarkable feature of our work was the systematic examination of the rude stone monuments, of which we catalogued some seven hundred in all. They were known to exist east of Jordan, but it was not, I think, expected that they would prove more numerous in this region than anywhere else except in Tunis; and the contrast with their absence in Western Palestine is very remarkable.[47]
Rude stone monuments are found in many parts of Asia, in Europe, and in North Africa. They occur from Norway to Tunis, and from India to Ireland, and they still present many curious problems to the antiquarian. These questions have been complicated by the utilitarian suggestions of writers, who ignore the folk-lore which is so closely interwoven with the history of these remains. It appears, I think, clear, first, that the rude stone monuments are of very high antiquity, having probably been erected in most, if not in all cases, by the early Turanians, who in Asia, North Africa, and Europe preceded the Aryans and the Semites, and who are called by modern students Iberians even in our own islands; and, secondly, that no study of these remains can be considered complete which ignores the beliefs concerning them surviving among the peasant populations of the regions where they occur.
Rude stone monuments are known in Arabia, and have been found near Lake Van and in Persia, in the Crimea and east of the Black Sea. They occur in Greece, in Cyprus, and in Phœnicia. There is, therefore, no reason for surprise at their discovery in Galilee, in Bashan, Gilead, and Moab. The only curious fact is their absence in Samaria and in Judea. There are some peculiarities, such as the occurrence of orientated avenues, of talyots or bilithons, of single stones outside circles, and of ring-marks on rocks, familiar in our own land, but not as yet noted in Syria. I confine my remarks, therefore, to the Syrian remains, including Menhirs, or erect stones, whether single or in groups, circles or alignments; Dolmens, or monuments with a flat stone table; Stone Circles, Disc Stones, and Cup-hollows, all of which are exemplified in Moab.
It is clear that a stone may be placed on end for more than one purpose, though that purpose is generally monumental. Some enormous stones near ’Ammân, I believe, marked boundaries. Standing-stones have also been used to record events, like the Moabite Stone or the modern gravestone. Stones and stone pillars, or even cairns and heaps, have been used as memorials of a visit to some shrine, and are still so used. Other erect stones in Greece, in Chaldea, in Phœnicia, and in India are idols and lingams, worshipped as containing a spirit. In every case the explorer must consider the most probable reason for the erection of the stone. In Greece such stones—afterwards sculptured as terminal figures—marked boundaries, or were sacred emblems. Such boundary-stones occur also in Babylonia, and sacred stones are also mentioned in Chaldean temples. Jacob and Saul and other Hebrew heroes erected such memorials, and the pagan Arabs bedaubed them with blood, and offered to them their babes and daughters, and swore by them as sacred emblems.
In some cases burial at the foot of such a stone may possibly mark a human sacrifice, as, for instance, at Place Farm, in Wiltshire, where a skeleton was found by a menhir in the centre of a circle; but no sepulchral remains are found by or under the majority of these monuments. In all countries where they occur they are remarkable for a rounded or pointed top, which resembles that of later obelisks. In India the lingam stones are worshipped, and peasants rub against them. In some rural districts maidens lean against them, expecting to see a future husband. Marriages were often celebrated by such stones. The Greystone, by the Tweed, witnessed marriages, where bride and bridegroom joined hands through a hole in the stone. Oaths were sworn at these stones in France to a late date; and the oath of Woden was sworn by men who joined hands through the stone. In Sardinia great stones with holes occur at the tombs called Giants’ Graves, and also form the entrance to a circle called cuisses de femme. I have never found such holed stones in Syria, but a pair occur in Cyprus, which I think, from their size, not likely to have belonged, as some suppose, to an oil-press.
These standing-stones were often anointed with oil, with blood, or with milk. Libations of milk were poured through a stone in the Western Isles. Alexander anointed with oil the pillar on the grave of Achilles, as Jacob anointed the stone of Bethel, or as the Arabs smeared their ansâb with blood. The lingam stones in India are still anointed with ghee, and stone circles are splashed with blood. In Aberdeenshire water was believed to spring from a hollow in the top of a sacred stone; in Brittany the menhirs were believed to go to the river to drink. Such monuments are also wishing-stones, such as Dhu esh Sher’a, a black stone at Petra, or the Hajr el Mena (“stone of desire”), which we found in Moab. To some prayers for rain have been offered. Breton menhirs, and others in India and in Somersetshire, are said to represent wedding-parties turned to stone; others in the Khassia Hills are adored as ancestors by tribes which burn the dead. The stones of Allât, ’Azzi, and Hobal at Taif—still shown—were once adored as deities by Arabs, as were those of Asaf, and Naila, and Khalisah near Mecca.
Such instances out of many which have been collected show that the idea of a “Holy Stone” is no theorist’s dream. Those who see in these monuments only gravestones or boundary-marks have not fully studied the facts of the case.
One curious feature of such stones I have not seen noticed. In Gilead I found a fallen menhir with a hollow artificially made in the side, as though to put something into the stone. At Kit’s Cotty-house I found similar holes in the side stones. At Stonehenge I found them in some instances even larger. No doubt many other cases are known.[48] The holes are not water-worn, but have been rubbed as though by fingers or arms thrust constantly into the stone. They are not lewis holes, and they were made after the stones were erected. Probably they were enlarged, like the hole in the pillar at the Church of St. Sophia in Constantinople, by countless visitors putting their fingers into the same hole.
The great alignments of Brittany and of Dartmoor are well known, though the reason for their erection is doubtful. In Moab I found one place where such a collection of standing-stones exists. It is called El Mareighât, “the smeared things,” and stands on the plateau north of the great valley of Callirrhoe. There is a rude circle of menhirs at the site, with a trilithon or dolmen on one side. It surrounds a knoll on which is a group of menhirs, the tallest being six feet high. To the east is a large menhir, which has been hewn to a rounded head and grooved horizontally, and between this and the circle is an alignment consisting of several rows of shorter menhirs, running north and south. The hills close by are covered with fine specimens of dolmens, many of which I measured.
It is impossible to regard this monument as sepulchral. The stones stand, like many in India and elsewhere, on the bare rock. The circle resembles many found in other lands; and the wild tribes of Western India still sacrifice a cock at such circles, smearing the stones with its blood; while the Khonds adore the sun in similar circles, the tallest menhir being on the east. In Mecca, the Kaabah was once surrounded by seven such stones, which also were smeared with blood. I believe the Mareighât circle to be an ancient temple, and the dolmen which faces the central group on the west to be probably an altar facing the sun rising behind the stones, while the alignments appear to consist of memorial stones erected by visitors to the shrine—just as the Moslem pilgrim still erects his stone mesh-hed or “memorial” in the neighbourhood of any shrine.
What has been said of erected stones or menhirs equally applies to what are called dolmens in France, or cromlechs in England, namely, stone tables raised on other stones. Such monuments also may have been erected for many purposes—as huts, as tombs, and as altars. Any hasty generalisation will certainly fail to account for every case. Unfortunately, the great authority of the late Mr. Fergusson, and his wide acquaintance with such subjects, have led recent writers to neglect many important facts not mentioned in his works, and to speak of dolmens as ancient tombs with a degree of dogmatism which shows that their own researches have not been very widely extended. After examining seven hundred examples of these monuments in Moab and Gilead, I have come to the conclusion that the sepulchral theory is often quite untenable, though we cannot deny that such rude blocks were often piled up to form huge cists or chambers hidden beneath mounds, and intended to hold either the corpse or the ashes of the dead. Sepulchral chambers—dolmens, if you will—under mounds are widely found; but a trilithon on bare rock, not so covered, is clearly unfitted for a tomb, especially when it is not large enough to cover even the body of a child. Moreover, the stone table is sometimes supported by flat stones on the rock; and observers who have found bones under dolmens have not always proved that they are original interments. Nothing is more indestructible than an earthen mound, and in many cases in Moab it was certain that no mound had ever covered the stones. There was nothing but hard rock to be found, and no cairn had ever existed to fulfil the purpose of a mound.
Again, I say, we must turn to local superstitions in order fully to understand the use of trilithons and dolmens. Wild as are the legends, they preserve what was once the religion of the dolmen-building tribes. In the Talmud we find mention of such a monument as connected with idolatrous worship in the second century A.D., the trilithon being in this case placed in front of a menhir.[49] In 1872 I found such a monument on Gilboa, and another example has since been found in Bashan, while a similar combination is also known in one instance in Sweden. At the temple of Demeter in Arcadia, Pausanias mentions a trilithon called the Petroma, by which the Greeks swore, and under which they kept a certain sacred book, which was yearly read by a priest. At Larnaca, in Cyprus, a dolmen is said to exist in a chapel, and in Spain one is found in the crypt of a Church of St. Miguel in the Asturias, and another in a hermitage.[50] The modern Arabs beyond Jordan use miniature dolmens, generally on the west side of the circles round the graves of their chiefs, as little tables on which to place offerings to the spirits of the dead.
Dolmens are also connected with the old ceremony of “passing through,” which is observed in India as well as in our own islands. St. Willibald, in the eighth century, speaks of Christians squeezing between two pillars in the church on Olivet; and as late as 1881 the Moslems in Jerusalem squeezed between two pillars in the Aksa Mosque. Near Madras, the Hindus used to crawl through the hole in a sacred rock. In Ripon Cathedral, “threading the needle” was a similar rite. Children were also passed through ash and oak trees, and through hoops, or dragged through holes in the ground and under door-sills. At Craig Mady, in Stirlingshire, the newly wedded used to crawl through a dolmen.[51] In the Jordan Valley, near the Jabbok, and again in Bashan, dolmens exist having a hole in the end-stone, and many are surrounded by a circle of stones in both districts, as also were some Celtic dolmens. On the dolmens in Ireland, called “beds of Diarmed and Grain,” youths and girls used to deposit gifts of corn and of flowers. The Cyprus girls, according to Cesnola, in like manner visit the menhirs pierced with holes, and place in them offerings of jewellery, lighting candles before them,—which illustrates a previous remark as to these holes in the stones. There is a curious monument in the Jordan Valley, with a stone hollowed into a sort of arch a yard in diameter, through which it would be easy to crawl. From such notes it is clear that dolmens are intimately connected with ancient superstitious practices. The crawling through was always believed either to cure sickness or to ensure good fortune, and the dolmen has often been used as an altar.
After making measured drawings of about a hundred and fifty dolmens in Moab, I was able to obtain some general results. In some cases the top stone is raised only a foot from the ground, and in others the trilithon is so small that it would not serve as anything but a table or seat. Some examples on the hillsides consisted of a table stone resting on the rock at one end, and on a single side stone at the other. In others the table was supported by horizontal stones. In most cases it was slightly tilted, and in very few were the stones even roughly hewn in shape. Not only could we never find any trace of sepulture, or of a grave beneath, but often the size precluded the idea that the dolmen could have been either a hut or a tomb. In other cases a sort of box was formed which could have held a body, but it was not covered by any mound. The general purpose seemed clearly to be the production of a flat table-like surface.
It may, however, appear strange that if these dolmens occur in such numbers at one site, they should be regarded as altars;[52] but we must not forget the story of Balaam and Balak. Visiting in succession three mountain-tops, whence the enchanter was bid to curse Israel, he addresses Balak in each case in the words, “Build me here seven altars.” And on each of these mountains we found groups of dolmen still standing.
A curious circumstance in connection with dolmens is that they usually occur near springs and streams. The groups in Moab were all so placed, just as Kit’s Cotty-house stands near the Medway, or Stonehenge above the Avon, or like the dolmen near a sacred spring in Finisterre. Menhirs also, as we have seen, are similarly connected with water and with rain.
There is, perhaps, a simple reason for this circumstance. Stonehenge was near a British village, and the rude tribes which built the dolmens no doubt, like all early migrants, settled round the natural waters of the country. But it is also not impossible that water was required in connection with rites at the dolmen altars.
Another very interesting observation was the occurrence of cup-hollows—artificial pittings, in some cases connected by well-marked artificial ducts or channels—in the table stones of the dolmens. These cup-hollows were, in some cases, quite as well formed as any that I have seen in England. I found one very unmistakable example on the Holy Rock on Mount Gerizim, where, it is said, by the Samaritans, to mark the site of the laver in the court of the Tabernacle.
I am not aware that any accepted theory has been formed about these hollows;[53] but they are often found on high tops and on or near dolmens. We must not forget that wild tribes of Asia and of Europe have always attached great virtue to the healing power of dew, especially the dews of spring-time. Perhaps dew may have been collected in these hollows and used for superstitious rites.
Two other classes of rude stone structures in Moab have still to be mentioned. The first of these is the class of great circles with walls made by heaps of stones piled up like cairns. These I have never found elsewhere, though they recall the earthen mounds which form circles in England, sometimes surrounding menhirs or dolmens, and sometimes I believe used as meeting-places or courts of justice. A splendid specimen occurs on a spur at Hadânieh above a great spring on the slopes near Mount Nebo. Inside this circle, as a precaution against thieves, I set up my whole camp and stabled my horses. Hadânieh means “sepulture,” and a small circle outside the great structure here surrounds the grave of an Arab chief. The great circle is 250 feet across, the walls are thirty to forty feet thick and some five feet high, and a smaller wall inside divides the area unequally. There is an enormous cairn on the hill above about three-quarters of a mile away on the east.
Another circle of equal size was found by Lieutenant Mantell on the south slope of Mount Nebo, and east of ’Ammân two more about sixty feet in diameter. Yet another occurs at Kom Yajuz, measuring 200 feet across, and we visited two others of nearly the same size. To one of these the name El Mahder applies, which is radically the same word as Hazor, “the enclosure.” There is nothing to show the age or object of these works, which must have entailed considerable labour, as they are so much larger than the circles of stones which the Arabs now build up round the graves of their chiefs.
The last class of monuments consists of great disc stones, which resemble mill-stones, but are much too large to be used for such a purpose. One of these, in the Jordan Valley, lies flat, like a mighty cheese, by a thorn tree, and measures eleven feet across. It is called “the dish of Abu Zeid,” an Arab legendary hero, who is said to have heaped it with rice and with a whole camel as a feast to his allies. It weighs probably some twenty tons. Another example stands on end in a ruined village, and is 9½ feet in diameter. A third, on a prominent hill, surrounded by dolmens, also stands up like a wheel, and is six feet across, without any hole in the centre.
The origin of these monuments is also very uncertain, but we must not forget that one of the towns of Moab mentioned on the Moabite Stone and in the Bible was called Beth Diblathaim, which means “the house of the two discs” (or “cakes”). Mill-stones are common enough in Syrian ruins, as are the pillars of olive-presses, but no explorer who is familiar with these is likely to confound them with the great menhirs and disc stones which have been here described.
Such were the monuments which we discovered and described east of Jordan, and I have only to add a few words on the important questions of their age and distribution.
As regards age, these monuments—dolmens and menhirs—were erected apparently by a people who had little mechanical power. Very rarely are the stones shaped, however roughly, and the dolmens are hardly ever on hill-tops, but on slopes where they might be easily formed by dragging the stones down-hill, and sliding the cap-stones on to their supports. Probably the people that erected them was unable to sculpture or to write. In other countries such monuments are of high antiquity, and there is no reason why they should not be very ancient in Syria.
As regards distribution, these monuments are absent in Judea and Samaria. There is one example on Gilboa, and five or six in Upper Galilee, one of which is called “the stone of blood.” I have seen near Jeba, north of Jerusalem, what might be a fallen dolmen, and have found what might be cup-hollows, but more probably these were mortars scooped in the rock in which gleanings of the fields were crushed. East of Jordan there are such hollows, used for making gunpowder, not connected with dolmens. The surveyors, who found so many dolmens in Moab, found none at all south of Galilee. In Moab, Gilead, and Bashan they are more numerous than anywhere else in Western Asia, as at present known.
In a previous chapter I have noticed that pottery statuettes, found in abundance in Phœnicia, are almost unknown in Palestine proper, and have suggested the reason. The same reason holds good, perhaps, as regards the rude stone monuments. They may very probably have once existed, and may have been purposely destroyed. Israel was commanded to “smash” the menhirs of the Canaanites, to “upset” their altars, and to destroy their images. These commands Josiah, the zealous king of Judah, is recorded to have carried into practice. May not this, I would ask, be the true reason for their disappearance? The Greeks and the Romans would not have so acted, and dolmens still stand close to the Roman city of ’Ammân. The Arabs, who left them east of Jordan, and who regard them as “ghouls’ houses,” would not have destroyed them west of the river. Josiah and Hezekiah did not penetrate beyond Jordan. At Dan many of these monuments seem to have been purposely overthrown. It seems to me therefore probable that the absence of such monuments, like the absence of sculptures and of pottery images, is best explained by supposing their destruction in the time of the reforming kings of Judah. It seems to me also that the existing monuments, though not impossibly erected by Nabatheans or other pagan Arabs, are very probably the surviving work of Canaanite tribes, as are very certainly the hieroglyphic inscriptions of Northern Syria. The age so claimed for these remains is not equal to that of some of the monuments of Egypt and of Chaldea, which represent a more advanced civilisation, and the presence of dolmens on the slopes of Nebo cannot but recall the altars which Balak, king of Moab, is said to have erected on that mountain.[54]
The ruins of the cities of Heshbon and Medeba are those of Roman towns with later Byzantine additions. At Medeba there was a fine church, of which only foundations remain. Here the Jesuit Fathers claimed to have discovered four ancient Nabathean inscriptions, which I afterwards copied in Jerusalem; but I regret to say that learned opinion regards these as forgeries. Such texts should be found in Moab, and Sir Charles Warren obtained a copy of one said to exist farther south. At present, however, the Moabite Stone is the only important inscription from this region. It was found accidentally by a missionary, just as the Siloam text was discovered by a Jewish boy. Even of this monument the genuineness has been questioned by a learned writer, but his reasons seem to be insufficient. He says that the letters are much sharper than the water-worn surface of the stone, and hence argues that they were carved by the forger on an old cippus. My experience in respect to a very large number of ancient texts which I have copied is that the letters are generally better preserved than the surface. They get filled with mud, and are thus guarded against the weather, which wears the surface in which they are cut.
![]()
VIEW OF DEAD SEA FROM MOUNT NEBO.
There is one famous spot in Moab which requires special notice, namely, Mount Nebo, whence Moses is recorded to have gazed on the Promised Land. The celebrated “Pisgah view” has often been described, but some writers seem to have given accounts not based on notes taken on the spot. The value of all geographical descriptions depends on their being written with the scene before the eyes of the writer, for memory plays strange tricks, and in the present case accuracy is of the greatest importance. I not only made detailed notes sitting on the ruined cairn on Nebo, but I also drew an outline of the panorama which is preserved in my note-book. The most important fact is that the Mediterranean Sea is not in sight; and as the heights of Nebo and of the chief tops of the western watershed are now certainly known within four or five feet, it is possible to say with certainty that the Great Sea is invisible from Nebo, because it is hidden throughout by the western watershed of Judea and Samaria.[55] We had the advantage of being familiar with every hill-top in sight, and, moreover, saw the view in clear weather.
Mount Nebo is a site fixed beyond dispute. It retains the name Neba, which applies to the highest knoll on a long spur running out west from the plateau between Heshbon and Medeba. As already noted, there are traces of a ring of dolmens round the knoll, and it is curious that none of these particular examples are mentioned in any previous account of the site, as far as I can find. Lower down on the ridge is the ruin Siaghah, preserving the name Seath, which stands instead of Nebo in the Targum of Onkelos. To the north are the “Springs of Moses,” of which we have perhaps an early account in the sixth century. Antoninus the pilgrim says that certain hot springs called “Baths of Moses,” where lepers were cleansed, existed east of Jordan.[56] The plateau close to the Nebo knoll is called “Field of Zophim” in the Bible, and the name, I think, still survives close by in the Tal’at es Sufa, or “Ascent of Zoph,” on the north side of the spur. The view from the knoll or from the ruin of Siaghah is much the same. It cannot compare with the panorama from Hermon, and there are indeed several places east of Jordan which command a finer view; but Nebo is the nearest mountain to Shittim in the Jordan Valley, from which an extensive view is visible.
On the east the eye is met at a distance of only two miles by the edge of the Moab plateau, which shelves away eastward; and on the south a long ridge closes the scene at a distance of about five miles. On the north-east the hillocks on which Heshbon and Elealah were built stand above the plateau, and Jebel Osh’a in Gilead appears behind, shutting out the Sea of Galilee and Hermon. It is on the west that the scene is most extensive, including all the Judean watershed, all Samaria and Lower Galilee, to Tabor and Belvoir. Carmel is hidden behind Jebel Hazkin, which is close to the Jordan Valley, and 700 feet higher than Carmel.
On the south-west is Yukin, the city of the Kenites, perched high above the Jeshimon or desert of Judah, and in front of the great precipices of that desert lies the Dead Sea, of which the northern half only is seen. Herodium, Bethlehem, and Jerusalem are all in sight, and beneath are the traditional tomb of Moses—in the desert of Judah—the precipice of Quarantania, and below this the dark groves round ancient Jericho.
North of Jerusalem is seen Nebi Samwil with the mosque over the Crusading tomb of Samuel, and Baal Hazor with its oak clump, and Gerizim with Ebal to the right, and the deep cleft of the Vale of Shechem between them. Under these is the white cone of the Sartaba towering over the Jordan Valley, and at our feet the thorn groves of the plain of Shittim east of the river. To the north-west appear Hazkin and Tabor, as already noticed; and the chain of Gilboa with the dim outline of Galilean hills marks the farthest extent of the view. Seen in autumn, the whole was singularly bare and colourless, for the green hues of spring were absent, and the dusty valley of Jordan, with the white marl banks near the river, contrasted with the black snake-like jungles marking the course of the stream and of the various tributaries, such as the waters of Nimrim.
The view thus described appears to be in accordance with the Old Testament account (Deut. xxxiv. 1-3), and the eastern geography of the Pentateuch is as easy generally to trace on the ground as is the topography of the Book of Joshua west of the river. Naphtali, Gilead, Ephraim and Manasseh, Judah, and the Negeb, or “dry land” south of Hebron, are all in sight, with the plains of Jericho “unto Zoar.” The only difficulty lies in the mention of Dan and of the western sea, which are not in sight from this ridge.
The south limit of the Adwân country and of the Survey was formed by the magnificent gorge now called Zerka Main, the Callirrhoe of Josephus, where are the hot baths in which the miserable Herod was bathed during his last sickness. This valley seems to be noticed in the Pentateuch under the name Nahaliel, “Valley of God,” as one of the camping-places of Israel. The top of the cliffs is here 2500 feet above the Dead Sea, and the hot springs in the valley are 1600 feet above the same level. The cliffs, 900 feet high, are precipitous for the most part, but a winding descent leads down on the north. The scenery is magnificent. A black basalt bastion and brown limestone walls of rock face northwards, and on the north side are precipices of yellow, red, pink, and purple sandstone, with gleaming chalk above and the rich green of palm groves beneath. The hot streams flowing from the northern slopes are crusted along their course with yellow and orange sulphur deposits, and the hottest spring—about 140° Fahr.—has formed a breccia terrace near the remains of the Roman baths, a hundred feet above the bed of the torrent, which flows with cold water from springs higher up the valley. The Arabs still bathe, or rather steam themselves, sitting over this spring, to cure rheumatism, from which they often suffer. They have a legend of a demon slave of Solomon who found the spring, and Dr. Tristram mentions sacrifices at the spot, which—though I did not see any such performed—would be in accordance with Arab custom in other places in the deserts.
We found a great contrast between the Arabs and the Fellahin in the matter of folk-lore. The Fellah legends are, as a rule, of very little interest, and most of those which we collected are to be found in the Korân. But all the desert Arabs with whom I am acquainted are only in name Mohammedan, and are, strictly speaking, pagans; and they are very fond of legendary tales, so that we collected more of these in two months east of Jordan than we got in four years west of the river. I have devoted a chapter in a previous work to the legends which we collected in the Adwân country, including the story of Aly and the wishing well of Minyeh, which sprang up under his spear; of Aly and the city of Antar; of Aly and the City of Brass. The romantic tale of Zeid and Ghareisah, an Arab Romeo and Juliet, is connected with a rude inscription in Wâdy Jideid. The story of the “Dish of Abu Zeid” has already been mentioned; and at the ruin of Tyrus, farther north, we have the legend of the prince, his daughter, and the black slave. At a place near El Marighât called Hana wa Bana is localised an Arab version of Æsop’s fable of the man with an old and a young wife. This proverbial story is, however, known all over Syria. Then again in the Jordan Valley are shown the pits of the hero Zîr, legends concerning whom are known to the Maronites, but taken from printed story-books, which, I believe, come from Egypt. I would here only note that within a comparatively small district we collected from the Arabs no less than eight folk-lore tales in a few weeks, only one of which was previously known, and that one gathered from the Abu Nuseir Arabs at Jericho. The Arabs showed no reserve in relating these stories as soon as they saw that we also enjoyed them; and none of them, as far as I know, belong to the printed tales of Egyptian collections, except that of Zîr and Hakmun. This wealth of folk-tales contrasts with the barrenness of Fellah imagination; and though it is of course possible that something of interest may be extracted from the Fellahin, they cannot be said to be remarkable for their love of legendary tales. The Kalmuk Tartars, even, are far more imaginative and poetic in their folk-lore than are the peasants west of Jordan, and the Arabs, who produced so many poets, even earlier than Muhammad, are intellectually a finer race than the Fellahin.
As above observed, the Arabs of the desert are practically pagans. They do not pray as Moslems should do, and they are as much addicted to the worship of the dead as the Fellahin. The graves of famous chiefs and of dervishes, or reputed Welys, are visited by the Arabs, who there offer small objects, such as pieces of blue pottery, old coins, berries, and pebbles, placed on the little dolmen table on the west side of the surrounding circle. The wives cut off their hair, and the plaited pig-tails are hung on a string on the husband’s tomb. An Arab passing by a graveyard often kisses the tombstones. This seems to constitute their chief religious observance. They, however, celebrate the yearly feast while the Moslem pilgrims are at Mecca, slaying camels and eating the flesh; but this feast was an Arab festival long before Islam, and, as far as my experience goes, the true Arabs are ignorant of the Korân, and have no fanatical feeling. I have never actually seen them worshipping the sun or the moon, but they face the sunrise while visiting the tombs, and their frequent legends of Aly agree with the fact that down to the present century they belonged to the great faction of the Yemeni, as opposed to the Keis faction, to which the greater part of the villagers west of Jordan belonged. These factions represent the survival of a political feud as old as the seventh century A.D. between the adherents of Aly, including most of the Yemen Arabs, and the followers of the Damascus Khalifs. The Arabs east of Jordan are thus connected with Persia rather than with Palestine, and it was from Persia that all the most imaginative elements in the religion of Islam came first. Persian Muhammadism is the creed of Islam as influenced by the older creed of the Zoroastrians. Syrian Muhammadism is the creed of Islam as influenced by association with Christianity and Judaism.
The tribes among which we lived were very rich in camels. The droves were really countless, and were herded like cattle, and neither saddled nor fitted with halters. They were kept for milk and for breeding, not for transport, and the camel so seen east of Jordan was a different beast to his hard-worked brother in the villages. Property in this case depended on branding, and the brands were the tribe-marks of the owner’s tribe. I had thus an opportunity of studying at leisure the question of tribe-marks, concerning which most extraordinary theories have been broached, one writer regarding them as planetary signs, and another as rough sketches of totems. Of that which (by an unlucky misnomer) is called Totemism, I have never been able to find any traces in Syria, though I have studied it among the Bechuanas of South Africa. The simple fact as regards Arab tribe-marks is, that they are letters of the old Arab alphabets of the Nejed and of Yemen. This I have been able clearly to show in the case of every tribe-mark which we collected among the Arabs.
In closing this chapter, I ought to record the services of our ally, Sheikh Goblan en Nimr. His early adventures are well known, and he was one of the most remarkable men whom I met in Syria. He belonged to the junior branch, but to the elder generation, of the Adwân tribe, which is divided under two ruling families. Aly Diab, the ruling chief of the elder branch, is a friend of the Turks, but Goblan was a sturdy and independent leader of the free or anti-Turkish party. So strong were his feelings on this subject, that he could hardly hear the name of Turk with any patience. This strong feeling made him perhaps the most popular personage beyond Jordan, and wherever we went the tribesmen received him with marks of reverence and affection. He had earned the reputation of being greedy and grasping, and I have no doubt he regarded every stranger as fair prey, from whom the uttermost farthing was to be exacted. But in spite of this greed for money, which all Arabs alike show in dealing with travellers, Goblan was not a miser. The gold I gave him was scattered with royal munificence, and was gone as soon as he got it. There was very much in his character which was admirable, and yet more that was romantic. He was a man of honour, who having once sealed a treaty, stuck to his word, and smoothed our path when many even of his own sons and nephews were afraid to come near us. There is no doubt that if, instead of science, our object had been intrigue, we might without difficulty have raised a revolt in Moab, which Goblan would have headed with great satisfaction. At one time I think he suspected us of some such project, and was rather disappointed that we should submit to Turkish authority.
In his youth Goblan received a serious sword-cut in the face from an angry relative. The details of the story I have not heard, but it is well known how ashamed he was of this wound, which he always hid with his Kufeyeh shawl. He had also been guilty of murder, having run through with his lance the owner of a fine grey mare in the desert. He was, I believe, unaware that the man he slew was one of the Beni Sakhr chiefs, but the consequence was a blood feud which threatened his life for many years. Thus on the south and east he was in peril from the neighbouring tribesmen, while on the north the Turks lay in wait.
Some years before our visit to the country, a governor of the Belka summoned the Adwân chiefs to Nâblus, promising to make them Government officials with salaries, recognised as his lieutenants in their own country. Goblan counselled them not to go, and not to be tempted by such promises. They went and Goblan stayed behind. Those who went were cast into prison and fined, and Diab, the eldest, was so roughly handled that his leg was broken. He came to see me as a lame old man, who had abdicated in favour of his son, having lost all the reputation to which Goblan, by his superior judgment of the case, attained. A Russian Grand Duke at Jericho gave Goblan, rather later, a valuable ring, which this same governor at Nâblus found means to make him give up. These were the personal reasons for Goblan’s hate of the Turks, and it was on such grounds that he was able and willing to help us in our exploration of the forbidden ground. These lines can now be freely penned, for poor Goblan is no more. His wild life—an untaught savage life, not without its elements of greatness, of pathos, and of romance—has closed at a ripe old age in a peaceful death. Neither by Turkish jailor nor by Arab lance was his life ended; he died among his own people in the desert home of his race.
The peculiar position of the man led me into more than one adventure. Some of our trigonometrical stations were on the border of the Beni Sakhr country, which I had promised not to enter without their escort. The Beni Sakhr chiefs and Goblan had met in my tents, but there he was safe as my guest. Had we been caught, however, in their land, by a relation of the murdered man already mentioned, Goblan would have been slain, and I should have been placed in the dilemma of either leaving him to his fate, or else myself becoming a blood enemy to an Arab tribe. On such occasions, while we took angles on a high hill, Goblan sat with his eyes fixed on the distant camp of his foes, scanning the plateau, so that he should not be taken unawares. On another occasion, riding somewhat in advance of my party, I suddenly saw bearing down upon me a group of horsemen with long spears. We met and saluted, and the first question was, “Where is Goblan?” I never made out to what tribe these cavaliers belonged, but Goblan had vanished as though swallowed by the earth, and not till we were far away from this spot, near his own camp, did he reappear.
Another day he and I went out alone to survey the borderland between the two tribes. At one place, as I was taking angles, he came and pointed to distant figures. “All horsemen,” he said; “make haste and finish your work.” I noted my angles as fast as I could, when he again touched me. “They are only camels,” he said; “you can go on as long as you like.” However, as I got on my horse, he again pointed to the plain, where we saw three horsemen about a mile away. There were no friendly camps near, and so I gained experience of how an Arab acts in such a case. We rode away quietly on the side of the hill, where we could not be seen, but were able from time to time to look over the crest at the advancing figures. Finally, we came to a sort of dell by a ruin, with banks all round, and here we lay comfortably lurking, and saw the group following the road to my camp. When they had gone some way, Goblan boldly emerged, and we rode parallel with them in the open. The reason was soon apparent. Though quite near, they were separated from us by one of those great rents in the plateau which form narrow gorges many hundred feet deep. Coming to the brink, he called across and they answered, but could not reach us without riding round many miles; and besides this, we were now close to a camp of Goblan’s people. “It is well we did not stay,” said Goblan to me; “they are Satâm and his brothers.” These were the Beni Sakhr chiefs who had been to my camp, and who sought his life. Like David calling across the valley to Saul, Goblan stood thus within hearing of his helpless foes, and quietly greeted them. Such is the etiquette of Arab life. The blow may be struck when the time comes, but to revile one another would be discourteous between foes.
Another incident showed me Arab life in a more pleasing colour. We had ridden through Jordan, and were resting on the bank, when a poor Arab with his wife on a donkey came down to the river. Addressing Goblan in that simple way in which the meanest Arab addresses the greatest chief, he said, “Goblan! take my wife over the river.” The old chief at once complied, and ordered his son to take the woman on his horse behind him. Rather sulkily his handsome son obeyed, and went back through the river to the western bank. These men were the true sons of that great Arab who, having conquered all Syria, rode into Jerusalem on his camel in the simple garb of the desert.
The kindly greetings which Goblan bestowed on the men he met, on the women and children at the springs, and on the poorest of his fellows, showed perhaps that he had learned the secret of governing others, and his strength lay in the simplicity and steadfast constancy of his actions. They had but one opinion in Moab, that Goblan alone represented the freedom of earlier days.
Tall, gaunt, with a dusky colour, one eye red and sightless, one cheek furrowed with the sword, with a thick, straight, obstinate nose, and a few silver locks, usually hidden, the old chief was yet at times, when no one mentioned the Turks and the Beni Sakhr, of cheerful mien. He is one of the few Orientals I ever met with a sense of humour, and often laughed most heartily. He could neither write nor read, and he never smoked tobacco.
Peace be to his ashes; and I hope the monument which covers them is at least equal to that which is erected in Goblan’s own country to his great rival, Fendi el Faiz, who died on his way to the Beni Sakhr country.
NORTH of Heshbon the country rises slightly, and we enter the region surrounding the large ruined city of ’Ammân—the Rabbath Ammon of the Bible and the Roman Philadelphia. This was the most important ruin surveyed in Palestine, as regards its antiquarian interest, and the best specimen of a Roman town that I visited, except the still more wonderful ruins of Gerasa, which yield only to Baalbek and Palmyra among Syrian capitals of the second century of our era.
On the slopes below the plateau in this region is the still more interesting ruin of Tyrus, the only dated Jewish building of early age that we possess. Although it had often been visited, we were able to add some interesting architectural details, and to correct a false impression about the great Jewish inscription of five letters here boldly carved on the rock.
Tyrus, now called ’Arâk el Emîr, is our one relic of the Jewish architecture of the days of Judas Maccabæus. The priest Hyrcanus, who fled from his brothers beyond Jordan, committed suicide at this place (where he had lived seven years) on hearing of the approach of Antiochus in 176 B.C. His life was one of adventure and of constant warfare against the Arab or Nabathean tribes of the region. He first made himself a stronghold consisting of numerous caves in two storeys, with an open rock terrace leading to the upper tier, where, among other chambers, he cut a great stable for his horses. We measured this stable, and found mangers for a hundred steeds. Near this fortress he built his great palace, which is now fallen in, except the east wall. The palace was surrounded by a broad moat, and water was brought by an aqueduct from the stream, which here breaks down rapidly towards the Jordan Valley through dense bushes of oleander, which have grown to the size of forest trees. The walls of the palace were of stones six to eight feet in height and fifteen to twenty feet long. Only three courses were required to reach up to the roof. The top course above a narrow frieze was adorned at each corner by rude sculptured figures of lions, which were carved in relief by sinking back part of the face of the stone after it was placed in position.
The details of some fragments of cornice are rude imitations of Greek classic style, but the extraordinary capitals of great pillars belonging to the interior are unlike any that I have elsewhere seen, and they most resemble Egyptian work. They seem not to have been noticed by De Vogüé, whose work I have generally found to be very detailed and faithful.
Whether this great palace was ever quite finished seems doubtful. A stone which must weigh about fifty tons lies half-way between the building and the quarry, as though left on the last day when the building was stopped. A deliberate destruction of the walls seems also certainly to have occurred.
Here, then, we have an ancient dated Jewish inscription, belonging to an age singularly deficient in monumental remains, and to a time when the characters used in writing were slowly changing from the old Hebrew to the later square Hebrew letters. A photograph of these boldly-cut letters shows that some of the great authorities who have discussed it have unfortunately started with an incorrect copy. If we compare the letters with those of other alphabets, we find only one which properly accounts for these forms, namely, the alphabet of the Jewish coins which were struck in the same century in which Hyrcanus lived. The meaning of the text is still doubtful, but its date agrees with the comparison of the letters with those used west of Jordan in the same age.
In spite of the scantiness of our materials, the history of writing in Palestine is being gradually unfolded in a marvellous manner. When we look back on the old theories which made the square Hebrew of our own times an original alphabet, unchanged since the time of Moses, and on the equally crude criticism which denied that writing was practised before about 500 B.C., we become aware of the rapid advance of knowledge. First came the Phœnician inscriptions, for a few of which great antiquity is claimed, though the majority belong to Greek or Persian times. Then the Moabite Stone was found, and the inhabitants of Eastern Palestine were proved to have been acquainted with monumental writing in the ninth century B.C. Then came the Siloam inscription, giving almost an equal antiquity for the alphabet of Jerusalem. To these are added several inscriptions of the second or first century B.C., and quite a number which belong to the earliest Christian age. In this series of alphabets we trace the same steady and gradual change which has differentiated all known alphabets in the world. It would be impossible now to mistake, within fairly narrow limits, the date of such a text as that at Tyrus; and the same reasoning assures us of the age of the important and ancient inscriptions above noticed.
Equally valuable is the light thrown on history by the remains of the Tyrus palace. It belongs to the period just before the revolt of Judas Maccabæus against the Greeks. We see how strongly the builders were influenced by Greek art, while the sculptures of animals show that they were not limited by the commands of the Law which forbade such representations of living things. It is also interesting to notice that the stones in the wall, which are much larger than those in the Jerusalem Temple, are surrounded by a draft like that employed by Herod the Great. This drafting was a Greek method of finishing the stone. It occurs in the walls of the Acropolis at Athens, and it was used in the second century A.D. by the Roman builders of Gerasa and Baalbek, the stones in this latter case having in a few instances Greek letters for mason’s marks. There is, I believe, absolutely no foundation for the idea that the early Phœnicians used such a finish to their stones. Drafted stones are, it is true, used in Phœnicia, but the oldest occur on structures of Greek character, and the latest in the Crusading walls of Tyre.
It was the spread of this Greek influence in Palestine which led to the revolt of the zealous and orthodox followers of Judas Maccabæus. The monuments have begun to show us how strong and widely spread was this influence. On the borders of the Egyptian delta Greek cities begin to be known, through the admirable work of Mr. Petrie and others, which give us remains of Greek or semi-Greek art of a time earlier than that of which we speak. Of course the account of Naucratis in Herodotus; the story of the flight of the Jewish high priest Onias to Egypt, and of his opposition temple; and the account of the translation of the law into Greek at Alexandria in the third century B.C., were all well known, as are the chapters in the Book of Maccabees which describe the spread of Greek manners in Jerusalem; but the discovery of existing monuments brings this all more vividly before us; for we rightly attach a far higher value to such contemporary evidence than we do to the modern understanding of ancient literary works, especially when criticism deserts its proper sphere, and begins to invent and to dogmatise.
We know then already, from the monuments, that before the days of the revolt under Judas all the Levantine coast was permeated by Greek influence. Greek coins passed everywhere; Greek pottery is found along the coast; Greek architecture penetrated even into the wilds of Gilead beyond Jordan. The Greek kings of Antioch are said to have left no architectural remains, yet even as far away as southern Arabia the Greek influence extended, and down to the days of Herod the Great it remained one of the great civilising agents in the Levant.
At ’Ammân we find remains of later civilisation—of the great age of the Antonines, when all Syria remained for a time peaceful and prosperous; and in this town also exists one of the most remarkable architectural relics of the Sassanian period in Syria. The oldest remains at ’Ammân are the dolmens, of which, with other rude stone monuments, there are some twenty in all. Next to these come the old rock-cut tombs, which, from comparison with others, I should suppose to be of the early Hebrew period. The Roman remains are the most important, including two theatres, baths, a street of columns, and remains of what was once a very great temple on the highest part of the acropolis of the city. To this age also belong the magnificent private tombs surrounding the city—towers of well-cut masonry filled inside with well-arranged sarcophagi.
No inscriptions were found on these tombs, though inscriptions occur in ’Ammân. From the Greek texts which Sir C. Fellows collected in Lycia we know that these monuments belonged to rich families in Roman times, and that even then the Greek language predominated over Latin in Syria and in Asia Minor. Greek texts of this age also occur at Gerasa and elsewhere side by side with Latin inscriptions. The tomb-towers were under the protection of the Government of the country, and an illicit burial in any of the sarcophagi carved to await the death of the next member of the family, was punished, not only by the curse announced against such violation of a sepulchre, but also by a very substantial fine levied by the state. The tomb-towers round ’Ammân show us, therefore, that several noble families must have lived in the town.
The walls of the citadel may be of earlier date, perhaps of Greek origin; for, according to Polybius, Antiochus the Great here besieged Ptolemy Philopater’s forces in 218 B.C. The garrison held out until a prisoner discovered a secret communication with a water supply outside the walls. I was not aware of this statement in Polybius when we were at ’Ammân, but it explains a discovery which we then made, and I think there can be little doubt that we found both this water supply and also the secret passage. There is a great cavern in the hill on the north of the citadel, evidently once used as a reservoir for water, the stream which supplied the lower town being at some distance from the Acropolis. In the side of this cavern, high up near the entrance, I found a very narrow passage running away in the direction of the citadel walls. I pursued it as far as possible, but it is choked at the end before emerging above-ground. This cave probably contained the water supply on which the Egyptian Greek forces depended in their struggle against the Syrian Greek forces of Antiochus.
To a later period belongs what I have called a Sassanian or early Arab building. It is well known that Dr. Tristram discovered near the Haj Road, east of Heshbon, the remains of a very fine building, which Mr. Fergusson called the Palace of Chosroes. Whether it was really built during the short period of Persian rule in Palestine preceding the triumph of Islam, will probably not be settled until we have copies of the inscriptions which remain at this palace. I regret that the sudden stoppage of the Survey and the unfriendliness of the Beni Sakhr Arabs made it impossible for me to obtain such copies. It is, however, beyond dispute that the art of the Mashita palace is of Persian origin, or influenced by Persia, and it is perhaps not Moslem work; for whereas in the Dome of the Rock at Jerusalem the representation of animal life is absent from the mosaics, the stone carvings of Mashita give us many such forms in their elaborate arabesques.
At ’Ammân there is one building, and remains exist of another, which appear very clearly to belong to about the same age with the Mashita palace. The complete building is singularly perfect, though its decorations are unfinished. How it ever came to be described as a Byzantine church it is hard to understand, seeing how well known are the features of Byzantine churches in Palestine. Moreover, there is a ruined cathedral with two chapels at ’Ammân itself which are of the Byzantine age.
The building in the citadel is entirely different to any church. It is a square structure, with a central court and four deep alcoves under arched roofs, one on each side of the court. This arrangement is exactly that of some ruined buildings of the Sassanian age in Persia. The form of the arches, the adornment of the walls with arcades in low relief, and other features, are, equally with the plan, common to the ’Ammân buildings and to those of the Sassanians in Persia.
This building may, however, have been erected by Persian architects for one of the early Moslem Khalifs of Damascus. No birds, beasts, or other living things occur in the rich details of its stone tracery, which I carefully copied and measured, and of which Lieutenant Mantell took photographs. The building is of high importance for a period of art in the East concerning which very little as yet is known.
It may be noticed in passing that the walls of this kiosque at ’Ammân are in a style which throws some light on the history of the Dome of the Rock at Jerusalem. That building is pronounced by architectural authority to be the work of the Khalif Abd el Melek, just as the Arab chroniclers, nearly contemporary with its building, also tell us, and in accordance with the existing inscriptions; but, as I pointed out in 1878, there are reasons for thinking that the octagonal outer wall was built only in the ninth century A.D. The details of that wall are very like those of the ’Ammân building, and this comparison will, no doubt, some day prove instructive, especially if we can ascertain the age of the great Mashita palace in Moab.
There is a very old mosque at ’Ammân, with round arches and a short minaret. Unfortunately it is without inscription (save for a later scrawl over the door), and whether it is older than the kiosque may be doubtful, but it shows us that the Moslems built in this town at a very early date. From El Mukaddasy we have a Moslem account of the place as old as the tenth century A.D. He speaks of this very mosque as being near the market-place, and he calls the citadel “Goliah’s Castle,” and apparently alludes to the kiosque as a mosque over the tomb of Uriah. Thus the buildings we are discussing clearly existed in 985 A.D. The town appears to have been then prosperous; living was cheap and fruit plentiful; grain and honey are mentioned by the Moslem geographer, where now the only cultivation is that of a few wretched gardens tilled by Circassian exiles living in the theatre.
The Survey was extended only a few miles north of ’Ammân; the region as far as Gerasa I saw in 1882, when accompanying their Royal Highnesses Princes Albert Victor and George of Wales beyond Jordan. The region is extremely picturesque, including the wooded hills of Gilead, the bare heights of ’Ajlûn, and the uplands round Gerasa. It is remarkable that this great city beside its mountain stream seems to have been deserted earlier than ’Ammân, although the country near it now contains villages with a settled population, whereas south of Es Salt there are now no villages beyond Jordan, and the Circassians at ’Ammân are almost the only inhabitants who do not live in tents. To the antiquary this has been an advantage, since Gerasa remains a purely Roman ruin, only equalled by Palmyra. The area within the city walls at Palmyra (500 acres) was indeed greater than that included within the walls of Jerash (170 acres), but in some respects the architectural remains at the latter date are even of greater importance.
Some very interesting Greek inscriptions once belonging to the early church in Gerasa have been copied by De Vogüé, by Rev. R. B. Girdlestone, by Sir Charles Warren, and by myself. They appear to have gradually fallen into decay, so that my own copy is somewhat less complete than those of the text as it existed twenty years before. The longest of these texts is a poem in hexameter, consisting of thirteen lines, of which the eleventh is taken from Homer,[57] and the whole is a Homeric imitation.
The longest inscription that I copied is not written in regular lines, but runs on, the new line of hexameter being in one case divided from the preceding by a well-shaped Greek cross. The forms of the letters, which I very carefully preserved, are those used in Greek Byzantine inscriptions. This text consisted of six lines of poetry, and is written by a certain wrestler, Theodorus, whose soul is in the broad heaven and his body in the earth. The longer text belonged to the church door, and mentions the cross. It may be translated as follows, being one of the most curious of the early Christian inscriptions in Syria:—
The reference is clearly to the establishment of the Christian ritual, and to the abolition of sacrifices in the Pagan temple.
These inscriptions show us that Gerasa was still inhabited in early Byzantine times, and the church stands just south of the great heathen temple. My visit to Jerash only lasted a day, and it was thus not possible to explore the site very completely, but we found nine inscriptions in all, one of which seems to be new, though unfortunately only a fragment.
On the stylobate of the southern temple is a very boldly carved name, perhaps that of Pertinax, which would give a date towards the end of the second century.[58]
The city stood on the sides of an open mountain-valley, and through the midst flowed a stream, which, running south, breaks in a cascade just by the southern wall. The course is fringed with oleanders, but the hill slopes are bare and stony, though covered, when visited, with corn. The whole course of the city walls is traceable, the masonry lying in heaps, having probably been thrown down by the early Arab invaders from the south. Five gates are distinguishable at the ends of the streets, which were regularly laid out at right angles. The main street ran parallel to the stream on the west, and was flanked throughout, for a length of 700 yards, by columns supporting epistylia. On the south this colonnade ends in a peribolus, which has been supposed to be the forum, just in front of the southern temple. Fifty-eight pillars remain in a single oval 300 feet long, all having Roman Ionic capitals, but not all of equal height.
We approached the city from the south, where, nearly a quarter of a mile from the gate, the road is spanned by a Roman arch of triumph, supposed to be not earlier than the time of Trajan. The ground on the side is strewn in places with violated sarcophagi. On the left of the arch is the great Naumachia basin, surrounded by seats for the spectators, and filled by channels from the brook. On entering the town, a temple is found immediately to the left, and behind this is a theatre with twenty-eight tiers of seats, and capable of holding five thousand persons.
The street of columns from the oval forum consisted of pillars, generally about fifteen feet high and five yards apart. It is divided into three sections by tetrapylons where cross streets intersect. Towards the centre of the street the Corinthian order was found, with Ionic capitals in the northern and southern parts. Near the middle was a basilica to the right, where, no doubt, judgments were pronounced, and on the left a propyleum, behind which flights of steps appear to have led up to the great temple, which stood high on the hillside, having pillars thirty-eight feet high and six feet in diameter. North of this temple was another theatre, with sixteen tiers of seats—not an odeum, like the preceding, which had a stage, but probably intended only for gladiatorial shows. So also at ’Ammân an odeum with stage, quite as complete as that of the southern theatre of Gerasa, stands close to the larger semicircle, before which is the open area with its vomitoria.
To the right of the street of columns, opposite the northern theatre, and close to the stream, are well-preserved remains of the great baths of Gerasa. In the extreme north-east part of the city, not far from a spring is a third temple, well preserved, and by the spring itself there seems to have been a nymphæum with three altars. Ruins farther south, east of the brook, are thought to represent a market-place and its stables. There are two ancient bridges over the stream, one close to the central basilica, and just outside the south-east gate are the ruins of another church or chapel. It was interesting to note how the paving of the bridge was laid diagonally (as in the opus reticulatum), and ruts seemingly cut through it to guide the wheels of carts or of chariots. By the basilica also are remains of four porphyry columns, and since no such stone is found anywhere nearer than Egypt or Sinai, we see here, as at ’Ammân also and at Tyre, that great labour and expense were devoted to the adornment of the town. I also observed some double columns like those of the Galilean synagogues of the same age, or like the huge granite double monolith at Tyre, probably once belonging to the temple of Melcarth.
The most remarkable fact concerning Gerasa is the absence of historical notices of the city. It already existed in 78 B.C., and is mentioned by Josephus and by Pliny. It was still a place of importance in the fourth century, and there are allusions to the name in early Arab works and in Crusading history. Stephen of Byzantium says that Ariston Rhetor came thence. Origen, Jerome, and Epiphanius knew the place, and there were bishops of the city present at some of the Councils; but beyond this we know nothing, save that which we gather from the inscriptions still existing. So numerous and so magnificent were the Roman cities of the second century of our era, that even the fine buildings of a town as large as ancient Tyre excite no particular notice. So imperfectly was it known, that the old Roman map of the fourth century, which makes the Hieromax flow into the Dead Sea direct, appears to put Gerasa opposite Jericho, and the Persian Gulf immediately east of the city. Yet when we visit the ruins, we find that granite pillars were brought from Egypt to adorn its basilica; that its busy population (said to include descendants of some of Alexander’s soldiers) had their baths, their theatres, their public memorials. An Æthlophoros, become Christian, dedicates a church with Homeric hexameter verses, and the names of Antoninus and perhaps of Pertinax are boldly sculptured on public buildings. Few ruined cities so well attest the far-reaching power of imperial Rome.
The Crusading King Baldwin II., in 1121 A.D., made a raid into this country, and overturned a Moslem fortress near Jerash. The Crusaders had other outposts at Tibneh, at Salt, and on the conical hill of Rubud; but the broad plains of the Hauran, which Baldwin III. endeavoured in vain to conquer, were never wrested from the Sultans of Damascus.
The road to Jordan from Gerasa passes along in sight of the distant castle of Rubud and by the ancient village of Reimun, a well-watered place with ancient tombs. Here, I believe, we should probably place the celebrated Ramoth Gilead, which has, for no reason at all, been identified with Es Salt, a town which takes its name from the old episcopal title Saltus Hieraticus, due to the woods on the hill slopes not far off. From Reimun the path winds down into the beautiful “Valley of the Roebuck” (Wâdy Hamûr), full of picturesque glades. The valley was green with young corn when I visited it, and the stream bordered with oleanders. On the hillsides a dense wood of oaks was topped by dark pines on the higher part of the ridge. Lentisk, arbutus, oleaster, formed its underwood, and here, as on Carmel, the blackbird’s song may be heard. The jay, cuckoo, hoopoe, and tomtit I also found in these woods, with the “murmuring of innumerable doves,” as in the Nazareth oaks.
Among the flowers which I saw in spring on the slopes of Gilead are many of our English species. Clover, ragged-robin, red and white cistus, clematis, crow’s-foot, purple lupins, squills, the pink phlox, the red or blue anemone, cyclamen, corn-flowers, pheasant’s eye, salvia, asphodel (both blue and yellow), vetches, wild mustard, marigold, borage, moon-daisies, cytizus, orchids, and the white broom, Star of Bethlehem, poppies, tulips, and buttercups, all grow in the grassy dells. Mock orange, hawthorn, honeysuckle, and antirrhinum, the arbutus and the lauristinus, are among its shrubs. Nowhere else in Palestine save in the Jordan Valley have I seen such fields of flowers; but the ravines and hill-slopes of the beautiful Sorrento scenery near Naples both in fauna and flora very nearly approach the natural history of Gilead.
These scenes were among the last through which it was my lot to pass in Syria. Hurrying back from Damascus to Jerusalem, I rejoined my companions, and we went down to Jaffa, where we took the northern steamer in order to escape Alexandria by a longer sea-route. Rumours had already reached us of the massacres in Egypt, and my reports concerning the unsettled state of the Levant I found to have been already confirmed by the telegrams which were arriving in England when we returned. The steamer was crowded with refugees, and it was not many weeks later that I again stood in the familiar streets of Alexandria, and saw the city of gutted houses, and the ruins which covered the great square with heaps of stone and of plaster. Thus our explorations may be said to have been continued to the last days of peace, before the Levant became the theatre of historic events.
There is only one district of Palestine which has not been described in this volume, namely, the great plains of the Hauran and the volcanic regions of the Lejah and Jaulan. Full as this region is of rude stone monuments, of Roman towns, of Nabathean and Arab texts scrawled on the rock, of Greek temples and Greek inscriptions, it is yet perhaps less unknown and less interesting than the wild deserts of Moab and of Judah, the oak woods of Gilead, the fastnesses of Hermon, the romantic mountains of Northern Syria, which have here been described. Still it remains a matter of regret to me that the work which was so systematically carried out in other parts of Palestine has not yet been extended over the whole of the Hauran plains.
Such, then, is the present condition of exploration east of Jordan. About a quarter of that region has been surveyed and mapped, and nearly the whole region has been visited by modern trained explorers. Much, however, still remains to be done in the future in this interesting country.
Reference has already been made in the introductory chapter to the map made in this region by Herr G. Schumacher, a younger member of the German colony of Haifa, which has been published by the Palestine Exploration Fund. This map extends eastward of the Sea of Galilee for about twenty miles, and reaches on the north to Banias, and on the south to the region near Abila of Decapolis. An account of the country has also been published from Herr Schumacher’s notes. The curious volcanic region of the Jaulan is included in this area, and the most interesting discoveries, already noted, were the sites of Susieh (or Hippos) and of Kokaba, one of the towns mentioned in connection with the ancient Ebionite sectarians of the second century, A.D.
The unfinished work by De Vogüé remains, however, perhaps the most important contribution to our knowledge of this region. He was the first scientific explorer who exploded the popular fallacy of the “giant cities of Bashan,” by proving that not only were the stone towns of the Hauran of very ordinary dimensions, but that the Greek inscriptions on their walls showed them to have been built by Christians of the third and later centuries, A.D. The oldest remains in Bashan are apparently the dolmen groups discovered by Herr Schumacher, which are of the same character with those described further south. In the early Christian period the Ebionites flourished in Bashan, where they converted the invading Arabs who advanced from the south; and it is even said that the Arab king, Amr, erected monasteries as early as 180 A.D. The Græco-Roman buildings found in the Hauran belong chiefly to this period when the Arab capital was at Bosrah.
The Hauran is a great plateau stretching east to the isolated Jebel Kuleib, which lies on the borders of the Syrian desert. This plateau presents the chief cornfield of Palestine, and the wheat is thence brought down for export to Acre. The population is in great measure Druze, mixed with Arab and Circassian elements. The water supply is chiefly from wells and cisterns, and for this reason Bashan has always presented great difficulties to military expeditions, and the Crusaders never effected its conquest.
The Greek texts, pagan and Christian, here collected by Waddington, De Vogüé, and others, are very numerous, but less interesting as a rule than are the early Arab inscriptions copied by the same explorers. The Nabathean or North Arab texts of the Hauran range from 200 B.C. to 200 A.D., and are of great epigraphic importance, showing a population of the same stock then also existing in Petra. Yet further east Mr. Cyril Graham discovered inscriptions and rude sketches executed by another Arab stock which advanced from Yemen about the same period. Some seven hundred of these South Arab texts are now known, and in 1877 their relation to the alphabet of South Arabia was demonstrated by Halévy. It was this rising tide of northward migration which a few centuries later broke down the Roman power in Syria at the famous battle of the Yermuk (south-east of the Sea of Galilee), when Islam triumphed over the degenerate Byzantines.
PALESTINE proper—from Dan to Beersheba—extends only over the southern half of the Syrian coast which runs northwards to the Bay of Alexandretta, distant 370 miles from Gaza. Yet there is no true geographical division which separates Palestine from Syria, and it is only because the Land of Israel attracts our interest chiefly, that the northern region of Lebanon and the Land of the Hittites is less generally visited. The scenery is perhaps finer than that of Palestine, the antiquities are more important, and the ancient history of the region is equally interesting, though mainly traced through the fragmentary notices of monumental records. Mention has already been made of the ride in Northern Syria which led to our discovery of Kadesh on Orontes, and which extended over half the length of the region. In the following year I twice followed the coast by sea to Alexandretta, but found no opportunity of visiting Antioch and Aleppo. The travels of Mr. Tyrwhitt Drake in this region are published in Captain Burton’s “Unexplored Syria,” and among other modern explorers De Vogüé and Rey have perhaps done most to recover all that is of greatest interest, while valuable discoveries have been made by members of the American Missionary Society. On the coast also the excavations of Renan at Byblos produced important Phœnician discoveries, and the magnificent collection of the late M. Peretié, which he kindly showed to me at Beirut, was mainly gathered in Northern Syria. It is probable, however, that much still awaits the explorer in this region, hidden in the great mounds of the Buka’a, and in the truly Oriental towns on both sides of the Lebanon.
Northern Syria is divided into two regions by the River Eleutherus, which rises in a hollow plain on the watershed—a saddle dividing the Lebanon on the south from the Anseiriyeh Mountains (the old Mons Bargylus), which runs northwards to the valley of Antioch. East of these chains is the plateau of the Buka’a, watered towards the south by the Litâni River, but for the greater part of its length on the north by the Orontes, which finally turns sharply to the west, entering the valley of Antioch, and falling into the Mediterranean at Seleucia, the old port of Antioch, south of the Bay of Alexandretta. Farther east, the Anti-Lebanon runs out to the great bastion of Hermon, dividing the plains of Damascus from the Buka’a; and on the north this chain sinks into isolated white peaks, where the Buka’a broadens out, east of Homs, into the desert of Palmyra.
The east and west slopes of the Lebanon present a considerable contrast, due in part to the geological formation, and in part to climatic causes. On the west, the deep gorges in the ruddy sandstone are fringed with umbrella pines and tangled copses, and the green of the vineyards extends high up the slopes towards the iron-grey limestone of the upper ridges. On the east, the barren limestone and the gleaming chalk below are only sparsely covered with stunted trees, though olive groves occur round the villages. This contrast is, however, not peculiar to the Lebanon—it is notable in all parts of Palestine. The western slopes of Gilead are clothed with oak woods, while the eastern slopes of the Palestine hills are barren deserts. The hills of Galilee, Samaria, and Judea west of the watershed are for the most part well covered with copses, and in the Anti-Lebanon also the same contrast is (though to a less degree) observable.
The reason of this contrast is very evident. The cool and humid western breezes blow from the Mediterranean, and all the vapour so carried inland is caught by the western slopes. Those which face the east are, on the other hand, exposed to the hot blast which blows from the Syrian deserts, while they are at the same time shut out from the sea-breeze. In the Anti-Lebanon the western slopes also are partly excluded from the same life-giving breeze by the superior height of the Lebanon range, while the more fertile sandstone is covered in the Anti-Lebanon by white chalk, grey limestone, and nummulitic beds, which, as a rule, have very little surface soil. The vine is, however, much grown on this range, and its broken ridges present a finer sky-line than is to be found, as a rule, in Lebanon itself. The broad valley which divides these ranges contains some of the best corn-land in Syria, and the Orontes is one of the brightest rivers that water this part of Asia.
The true source of the Orontes is found west of Baalbek, but the main supply of water is from the spring nearly thirty miles farther north, now called ’Ain el ’Asy. The river is here invisible from the plain, being hidden in a ravine some 300 feet deep. The pool, fringed with willows and full of cresses, is surrounded with tawny cliffs, and the full-grown river rushes rapidly northwards in a broad, shallow stream, breaking over a rocky bed between barren slopes dotted with wild olives. Above these slopes rises the grey and stony ridge of the Lebanon on the west, while the brown Buka’a stretches on the east. After about fifteen miles’ run the river emerges again on to the plain near Riblah, and flows by Kadesh to the long artificial lake of Homs, already noticed. Then breaking over the Roman dam in cascades, it again sinks into a trench in the plain, and flows by the gardens of Homs or Emesa, and so on to the hot and unhealthy gorge near Hamath, and to the marshy plain of El Omk, where it joins the Kara Su (“black water”), and suddenly bends to the west.
The limestone both on Lebanon and on Anti-Lebanon appears to be honeycombed with great subterranean caverns, in which underground rivers, fed by the snows of the higher ridges, flow towards the plains. The Abana, which rises in the plain of Zebdâny, west of the main ridge of the Anti-Lebanon, springs up in a blue pool of unknown depth, where the snow-cold water rises with great force and feeds a considerable stream, which, when increased by the rushing fountain at ’Ain Fiji (one of the most picturesque spots in the region), becomes the “River of Damascus,” which Naaman rightly preferred to the muddy waters of Jordan. At Beirut, also, the Dog River rises in magnificent stalagmitic caves in the bowels of the Lebanon, and farther north the old castle of Krak (already noticed) looks down on a narrow valley where is the monastery of St. George, near the cave in which rises the famous Sabbatic River, whose intermittent flow was reckoned among the wonders of Syria by the ancients. This river springs from a pool in the cave, and at intervals of between four and seven days a rumbling sound is heard in the mountains, and torrents of water flow forth from the cavern, pouring down the valley for several hours. In the Hermon region there is another similar phenomenon, which is, however, only to be seen in winter. The plain near the village of Kefr Kûk is said yearly to be turned into a lake by a torrent which rushes out of its cavern with a roaring noise like that of the Sabbatic River.
Josephus (VII. Wars, v. I) has given us a correct account of the rise of the Sabbatic River, which Titus visited on his return from the Jewish war, but Pliny has inverted the facts (H. N., xxxi. II), and supposes the river to observe the Sabbath, flowing all the week and resting on the seventh day. The Bordeaux pilgrim makes the same mistake. In the Middle Ages the legend of the River Sambation became famous among the Jews, who identified it with the Ganges, and held that the ten tribes existed beyond its banks, and there awaited the day when, on the appearance of the Messiah, its waters should be dried up. Thus the true origin of the story was forgotten, and the situation of the river, which, however, still preserves its ancient name in the modern Arabic title, Nahr es Sebta.
The western slopes of the Lebanon fall abruptly into the sea, and the flat ground at the foot of the mountains is at most a narrow strip, while the coast road often leads over the rugged stony limestone of the promontories. There is no real harbour along the shore at all comparable to that of Smyrna, but the Phœnicians made the most of outlying reefs and shallow bays to construct their little ports. The harbour of Tripoli is reckoned the best in Syria by the captains of coasting steamers. The Bay of St. George at Beirut is subject to storms, as is also the gulf at Alexandretta, where in winter the gusts from the mountains are often very dangerous. At Latakia there is only an open roadstead, and Gebal or Byblus, famous as its sailors were in early historic times, presents only a shelving beach.
The shore scenery is throughout of most picturesque character, not unlike some of the South Italian coast; and the steep slopes, pine-dotted and riven with great gorges, rise to snowy summits, often wrapped in cloud even in summer. Near Tripoli the shore plain widens, and the Eleutherus flows through an open sandy flat. This river, which formed the boundary of Jewish conquest in the Hasmonean age, has often been mistaken for the Sabbatic River. Its source is in a sort of crater west of the Lake of Homs, a picturesque basaltic hollow plain, marshy and dotted with oak trees. The black basalt extends westwards along the open valley, which leads down seaward, confining Lebanon on the north; and the pass, which has always been important in history, is commanded by the great castle of the Knights Hospitallers, already mentioned, and perhaps the best preserved of the Crusading strongholds.
Into the wilder mountains of the Anseiriyeh it was not my good fortune to be able to penetrate. The thick copses here cover remains of ancient cities, of which but little is known. On the north the vale of Antioch divides this ridge from the great spur of the Taurus, which rises over the gloomy Gulf of Alexandretta. The steep mountains here spring from the sea, and a narrow, pestilent, swampy shore lies at their feet, making this port at the “gates of Syria” the most notoriously unhealthy place in the Levant. Many suggestions for draining the swamp may be found in consular reports; but the difficulty is that its level is only a few feet above the sea, allowing no fall for any irrigatory channels. If ever the great railway which may connect the Mediterranean with the Persian Gulf is made, it is to be hoped that the port will be chosen at the old harbour of Seleucia, at the mouth of the Orontes, and not in the fever-stricken and mountain-locked bay of Issus, as the Alexandretta Gulf was called when Alexander won on its shores the great victory over the Persians which made him master of all Western Asia.
The climate of the Lebanon is superior to that of Palestine on account of the brisk mountain air, some 4000 feet above the highest points reached by even the Galilean mountains, while the snow-fed rivers and streams give an abundant water-supply throughout. The modern inhabitants are a hardy and ruddy-faced people, whose cheerful independence contrasts with the dull fatalism of the Southern peasants. Thus from the dawn of history there has been perhaps more energy, enterprise, and civilisation in Syria than in Palestine; and trade and art flourished in Phœnicia and among the Hittites, while in the south the wandering Shasu ranged over an unsettled land. In order to preserve some method in briefly describing the early civilisation of this country, it will be best to adopt an historic sequence, for the centres of power were constantly changing, and a geographical treatment of the subject is difficult.
The earliest known notice of Northern Syria is in the time of Thothmes III., about 1600 B.C. After the great battle of Megiddo, which laid Palestine at his feet, the hardy Nubian advanced northwards, even beyond Aleppo and across the Euphrates. At Karnak he has recorded the names of 218 towns in Syria and Aram which he claimed to have conquered; and from this list we know that even as early as the seventeenth century B.C. many famous cities of later times were already in existence, including Hamath, Aleppo, Calchis, Circesium, Nisibis, Aradus, Carchemish, Pethor, and Kadesh on the Orontes.
Even earlier, however, than this time it appears that the Hittites dwelt in Northern Syria, which is called also the “Land of the Hittites” in the Book of Joshua. Thothmes I. is believed to have reigned about 1700 B.C., and began his career by attacking the Hittites, who, however, at that early period, may have extended their rule farther south.
Seven years after the battle of Megiddo, Thothmes III. attacked Kadesh on Orontes, and cut down the trees near it. Twice again in later campaigns he stormed the town on his way to Mesopotamia, and carried off silver and precious stones as tribute; but on his death the Hittites recovered their independence, and about 1540 B.C. they became a formidable power. The recently discovered Tell el Amarna tablets show us that an early Babylonian conquest of Phœnicia dates from that period. The kings of Egypt and of Mesopotamia were then in alliance, and governors who used the cuneiform script appear even to have been posted at Tyre and at Sidon; but the Semitic invaders were jealous of the Hittite power, and Tunep (now Tennib) appears then, as well as later, to have been a Hittite city.
Two centuries passed, and Rameses II. found the Hittite power as formidable as ever. The great battle of this period was fought near Kadesh; and the celebrated battle picture at Abu Simbel gives us most lively portraits of these great Mongol warriors in their chariots, and of their walled and tower-crowned city, with its name written over it, and its bridges over the Orontes and the smaller western stream, which together surrounded the mound now known as Tell Nebi Mendeh. The Egyptian advance followed the coast-line north of Beirut, where Rameses left his bas-reliefs cut on the cliff by the Dog River, and the army reached a town called Shabatuna, which some scholars place near the Sabbatic River, in which case their road lay, no doubt, up the valley of the Eleutherus, already noticed as the highway from Tripoli to Homs. Kadesh, we learn, was on “the west bank of Hanruta” or Orontes; and the incautious advance of the Pharaoh very nearly led to his defeat and death. The city was, however, again taken, and the great alliance, which included auxiliary forces from Aradus, Cyprus, Carchemish, and even from Mæonia and Southern Asia Minor, was defeated. The Egyptian conqueror pursued his way far north and west, and left his cartouche on Mount Sipylus, where the old figure of the “Weeping Niobe” had already been carved.
In this same reign we have also an incidental notice of the same region in the celebrated “Travels of an Egyptian,” which were carried as far north as Kadesh. Speaking of the Lebanon, he says: “The sky is darkened by the cypresses, the oaks, and the cedars, which grow to heaven. There also are lions found, and wolves and hyenas, which the Shasu hunt.” Yet the spoils taken and tribute offered in Syria at that time abundantly witness the civilisation of the Hittites and of the Phœnicians, whose “holy city Gebal” is noticed in this early papyrus with Sidon, Sarepta, and Tyre.
Two centuries passed by, and, with the decreasing power of Egypt, the freedom and prosperity of the independent kingdoms of Israel and of the Hittites increased. Yet while Samuel was still a child we find Tiglath Pileser I. hunting in the Lebanon. The account recovered from a cuneiform tablet is of great interest, seeming to show that the Lebanon ridge was the division between the Semitic Phœnicians on the coast and the Mongolic Hittites along the Orontes. The broken obelisk in the British Museum records of Tiglath Pileser that “in ships of Arvad he rode, a porpoise in the great sea he slew, wild bulls (rimi) fierce and fine he slew at the city Araziki, which is opposite to the land of the Hittites at the foot of Lebanon.” Thus the wild bull, which is mentioned in the Bible, was still found in Syria as late as 1100 B.C.
The foundation of our knowledge of the Hittite hieroglyphic system of writing, which was probably in use as early as 2000 B.C., was laid by Burckhardt’s discovery of one of their monuments at Hamath. That great traveller and observer describes a stone, now in the Constantinople Museum, but then in a wall in the city of Hamath, as covered with hieroglyphics which differed from those of Egypt. Yet the discovery was without further result until the stone, with four others, was rediscovered by the American visitor Mr. J. A. Johnson in 1870. The further finds at Carchemish, and in Asia Minor, of similar monuments have shown that Northern Syria possessed a written character of its own, and that a language akin to the old speech of the Medes and Akkadians was spoken by the Hittite chieftains as well as by their relatives, the Lydians, Carians, and early Cappadocians.
As we advance to the eighth century B.C., we find the power of this Mongolic stock decreasing, while that of the Semitic race increases. Among the most interesting discoveries of this period is that of the general diffusion of the worship of Jehovah throughout all Syria and Assyria. As early as 822 B.C. the names of Assyrian officials are compounded with the divine name, and yet earlier, in 887, the name Abijah occurs in Assyria. In the time of Sargon, Yaubidi was king of Hamath, and the names of Joram, king of Edom, Zedekiah, king of Ascalon, Padiah, king of Ekron,[59] tell the same tale as does the name of Joel in a Phœnician text from Malta. The adoration of Jehovah was not peculiar to the Hebrews, nor does the Bible state it to have been. It was common, as early at least as the tenth century B.C., to all the Semitic peoples of Western Asia as far east as Nineveh; for, as Malachi wrote somewhat later, “From the rising of the sun to the going down of the same, My name is great among the Gentiles ... saith Jehovah Sabaoth” (Mal. i. 11).
In spite of such community of religion, the growth of Assyria brought troublous times on Northern Syria.[60] About 854 Assur Nazir Pal defeated the Hittites, and advanced as far as Tyre; but a great battle was fought on the Orontes, in which we find Ahab of Sirlai[61] leagued with the kings of Damascus, Arvad, and Ammon—a force in all of 85,000 men, and this league for a time stopped the Assyrian advance. In the same long reign, however, about 842 B.C., another battle was fought near Hermon, and Damascus was besieged and the Hauran overrun by Assyrian armies. From that time forward the road to Palestine began to be open. Tiglath Pileser II. advanced in 740 to Hamath, and six years later invaded the Land of Israel and marched to Ascalon and Gaza. In 720 Sargon takes Samaria and quells an outbreak in Hamath; and about this time the system of deportation, which was the ordinary Assyrian policy, led to the establishment of North Syrian, Chaldean, and Thamudite Arab colonies in Palestine, and to the captivity of the Ten Tribes. In 717 Carchemish fell to Sargon, and the power of the Hittites was finally overthrown, and six years later the Assyrians were at Ashdod in Philistia. Sennacherib followed in 701, and penetrated even to Petra in 688. Yet the internal troubles of the Assyrian Empire gave a brief respite after his death, when a new foe appeared in the northward march of the Arabs and Nabatheans, who raided through Eastern Palestine and the Hauran into Northern Syria in 650 B.C. With the fall of Assyria a period of peace followed, but a century later we find Nebuchadnezzar on his way to Jerusalem, following the defeated Egyptians from Carchemish.
Of this troublous history the rocks of Syria themselves give evidence. At the mouth of the Dog River, near Beirut, where Rameses II. had erected three bas-reliefs in honour of Ptah, Ra, and Ammon, Tiglath Pileser I.—the hunter already noticed who also conquered the Hittites—left his statue about 1100 B.C., and another Assyrian tablet on this spot is thought to be even older. Four more tablets were added later, between 885 and 681 B.C., by Assur Nazir Pal, by Shalmanezer III., by Sennacherib, and by Esarhaddon, showing that all these conquerors passed by Beirut. Near this group of tablets mutilated inscriptions of Nebuchadnezzar have also been found, and quite recently, in 1884, other inscriptions by Nebuchadnezzar have been recovered on the eastern slope of the Lebanon not far from Kadesh.
The Medes swept away the Babylonians, the Persians succeeded the Medes, and the Syrians continued to preserve their own civilisation, as witnessed by the art of Phœnicia, which throve especially in the Persian period. The battle of Issus raised a new power in Asia, and with the successors of Alexander a new capital arose in the valley of the Orontes at Antioch. It is remarkable, considering the power and wealth of these Greek monarchs, that they should have left us no monuments in Syria, as far as is at present known. Their coins are frequently found, and are often of great beauty, being among the earliest on which the head of a king appears portrayed from life. During this age, even as late as 307 B.C., the Greek kings of Cyprus were still using the peculiar script called the Cypriote syllabary, but no trace of its use has yet been discovered in Syria, where the simpler Phœnician alphabet reigned supreme, while on the Greek coins of the Seleucids the kindred Greek characters appear.
Nor are the troublous times of the great struggle which gave Syria to the Romans represented by monuments; but with the Antonines a great architectural period began, when Baalbek was built, as well as many great cities throughout Syria. It has often been supposed that the enormous stones which form part of the outer wall at Baalbek are remains of a Phœnician temple preceding the Roman fane, but the visitor can satisfy himself that these huge blocks—more than sixty feet in length, and unrivalled elsewhere in Syria—stand on Roman masonry; and we have nothing to lead us to suppose that the Phœnicians ever used such enormous masonry. The Baalbek Temple is indeed one of the most certainly-dated buildings in Syria, and the Latin inscription on the east wall, copied by Ward and Dawkins, but now almost illegible, gives the names of Antoninus Pius and Julia Domna, who appear to have founded the huge sanctuary in honour of the “great gods of Heliopolis.”
In the wild mountains of the Anseiriyeh other remains of the same period have been found. Though attributed by popular tradition to Solomon, these buildings, by the details of their architecture, and by the Roman eagle, whose winged form occurs here as well as at both Baalbek and at Rukhleh on Hermon, are to be ascribed to the Roman period, to which also we must refer the curious monument near the source of the Orontes called Kamu’at el Hirmil, on which, in bas-relief, is represented the chase of the stag, the boar, and the bear.
Homs, the ancient Emesa, was the birthplace of Julia Domna, the mother and bride of emperors. This city also had a famous fane—that of the Black Stone, which was transported to Rome. When El Mukaddasi in the tenth century visited the city, he found a remarkable statue still standing in the mosque—“the figure of a man in brass standing on a fish, and the same turns to the four winds.” It was regarded as a talisman against scorpions, and was apparently a kind of weathercock. It was perhaps to this statue that the Greek inscription which I copied in the same mosque originally belonged, the text, when translated, reading thus:—
El Mukaddasi says that this mosque was formerly a church, and its nave and aisles I found still clearly traceable in the later Moslem building.
The third century saw the rise and fall of Palmyra, the great Syrian trading city which formed the emporium of Northern Syria, connecting the coast towns with the Euphrates by a route across the desert from its oasis. As the bulwark of the Roman Empire against Persia, the Palmyrene colony was allowed privileges amounting almost to independence, and under Odenathus and his widow Zenobia it flourished until rebellion brought down on that famous queen the heavy Roman hand. Its celebrated buildings show how strong was the influence of Græco-Roman art on the Aramaic inhabitants; but its numerous inscriptions are for the most part in the native script—a late form of the old Phœnician alphabet—and its gods are the old Phœnician deities, though Christian heretics found shelter at Zenobia’s capital. Whether any remains of earlier ages are to be found in the desert city is still perhaps open to inquiry, since a very curious Aramean tablet was recovered from the vicinity by M. Peretié. The ruins as yet known are of Zenobia’s time, but tradition points to Palmyra as the Tadmor or Tamar in the wilderness founded by Solomon—Tamar, which is perhaps the better-authenticated reading, being the Hebrew name (“palm tree”) equivalent to the classic title Palmyra.
In the later days of Paganism Northern Syria was very famous for its temples—the shrine of Daphne, in its oleander thickets near Antioch; the yet more picturesque site at the source of the Adonis River, where stood, under a theatre of barren crags, high up on Lebanon, the shrine of the mourning Venus; and the curious temple of the Dea Syria at Heliopolis (the ancient Carchemish) on the Euphrates. Three statues existed at the latter shrine, one representing the mother goddess seated on the lion—whose image, standing on the same, has been found carved by the Hittites—the second the father god on a bull, and the third a deity of unknown name. Two lofty obelisks stood in the porch, and to their summits the priests went up, and remained for seven days in converse with the gods and never sleeping. It was perhaps the memory of this strange rite (not, however, peculiar to Syria, but known also in India) which led Simeon the Stylite to ascend his column four centuries later at a site not very far west of the old temple of the Dea Syria, for the ruins of the great monastery erected over the base of his pillar are still to be seen at Kal’at Sima’an, between Aleppo and Turmanin.
The temples of Daphne and Afka were famous for their licentious rites, the temple-women who served Aphrodite in Cyprus and in Babylon here remaining recognised until suppressed by Constantine. At Afka the statue of Venus was represented with its hands covered by its robes, and the lamentations which were part of the midsummer ritual were but the survival of the old Akkadian and Phœnician “mourning for Tammuz,” which was observed even in the Temple at Jerusalem. A star was believed to fall annually into the great pool or lake at the temple, where the sacred river, which falls in cascades in a deep and wooded gorge, to flow into the sea at Byblus, had its spring. The river itself was said to run red with the blood of Adonis in spring-time, and I have crossed it on Easter Day when it was turbid and ruddy with the rich red sandstone soil from Lebanon. It was at this season that the Phœnician women at Byblus used to set little papyrus cradles floating on its stream, holding an image of the infant sun-god.
The disciples of Simon Stylites were spread all over Syria, and even as late as the twelfth century they sat on solitary pillars. This may account for the single columns which are to be found standing alone in the plains of Syria in more than one case. West of Baalbek one of these pillars is to be seen, called “the pillar of the maidens,” and there is another not far from Acre. In the eleventh century the monastery already mentioned, called Kal’at Sim’an, still held no less than sixty Georgian monks, and Phocas mentions another of their establishments at St. Gerasimus, on the banks of Jordan, in the Jericho valley, where was “a hermit’s pillar.” At present the hermits are content to inhabit inaccessible caves on the Quarantania Mountain, where the pious go to fill the baskets which they lower down the cliff.
In Justinian’s time a perhaps more useful invention was brought to Syria by monks from China, who introduced the silkworm. The Roman silk was imported from the far East, but in the sixth century it began to be manufactured in Syria and in Cyprus, and continues to be made on the slopes of Lebanon, and even as far south as Tyre. The mulberry gardens round Beirut are cultivated to feed the worms. Under the Crusading rule the silks of Tripoli and Antioch were also famous. In the tenth century El Mukaddasi speaks of the silkworms of Ascalon as renowned.
Considering how eagerly the Christian pilgrims sought out every site of Bible interest, it is curious that the early notices of the cedars of Lebanon are so few. The destruction of the cedar forests, however, began early. Assyrian and Babylonian monarchs, not less than Solomon, appear to have sought out the Lebanon cedar-wood to adorn their palaces and temples. Justinian could hardly get cedar enough to roof the great Church of the Virgin which he built at Jerusalem, and in the Middle Ages the private houses of Sidon were ceiled with cedar. The trees usually visited at Ehden are not, however, the only survivors, for within the last fifty years at least other groves existed, and perhaps still exist, in the Northern Lebanon east of Tripoli. Seetzen, in 1805, found thousands of cedars at Etnub, and the less known forests have probably the better chance of surviving.
Northern Syria was overrun by the Moslems before Jerusalem fell. Abu Obeideh advanced from Damascus to Homs, Hamah, Latakia, Jibeil, Aleppo, and Tarsus, before the Byzantine army took the field; and though he was forced to beat a rapid retreat to the Yermuk, south-east of the Sea of Galilee, his great victory on that river confirmed his conquests. This Arab raid of the seventh century A.D. repeats in a curious manner the old incursion of the Arabs in the seventh century B.C., to which allusion has already been made. The Crusaders, in like manner, after the fall of Antioch, followed the same route which the various Assyrian conquerors had taken, and after passing Hamath and Homs, went down by the Eleutherus to Tripoli, and thence south along the sea-shore by the historic tablets of Rameses and Tiglath Pileser.
In the twelfth century Northern Syria was divided into two great fiefs—Beirut and Tripoli—belonging to the kingdom of Jerusalem, and embracing all the Lebanon; while the Anseiriyeh Mountains were part of the principality of Antioch. The Buka’a appears generally to have been under the rule of the Turkish Sultans of Aleppo and Damascus, and the border castles were on the eastern slopes of the Anseiriyeh chain. In this region, also, the famous Assassins established an independent colony, which was only subject to tribute in the times when Christian rule was strongest. The Normans were forced in this region to enter into treaty with the Saracen rulers, whose dread of the Tartars rendered them long indifferent to the cause of Islam.
Mention has already been made of the many mystic sects which dwelt in Palestine, and more especially in Northern Syria, in the Middle Ages. Even in the tenth century El Mukaddasi speaks of a considerable population of Shi’ah—or Persian Moslems—in Syria, whose descendants still survive as Metâwileh, Anseiriyeh, and Ismailiyeh, the latter representing the mediæval Assassins or “hemp-smokers.” This sect was founded in the eleventh century, but whether the curious Paradise story, according to which the young devotee was initiated for a few days into the joys of the Moslem Eden, has any foundation in fact may be doubted. It is, however, not doubtful that the influence of the Sheikh el Jebel, or “old man of the mountain,” over his disciples caused the murder of many well-known Crusaders and Norman princes, including Conrad of Montferrat and Raymond of Tripoli, as well as of an Egyptian Khalif and of several Turkoman and Arab princes. In 1174 the Assassins attempted the life of Saladin himself, and in 1172 of Prince Edward of England at Acre. Hence came the suppression of the order by Saladin, and by the Mongols in Persia, the original seat of the society. The Assassins owned ten castles, according to William of Tyre, extending their sway as far west as Tortosa.
There were two famous places of pilgrimage in North Syria in Crusading times. One of these was Tortosa, on the sea-coast, which the good Joynville visited, and where was one of the pictures of the Virgin painted by St. Luke. At that time it appears that the Mother of God was absent in Egypt helping St. Louis (who sadly needed help), a fact which the pious knight states to have been immediately reported to the Legate.
The other shrine was that of Notre Dame de la Roche at Sardenay—the present Jacobite convent of Saidnaiya (“Our Lady”), north of Damascus. This was venerated by Christians and Moslems alike. The Jacobites were friendly to the Normans, and were then more numerous than they now are. They preserved the old rite of circumcision, which they received from the early Ebionite Christians, who dwelt in the Hauran in the second century A.D. They preserved also the old Syriac language—almost the same spoken in Palestine in the time of Christ—and their old alphabet, a late form of the Palmyrene. In our own time the Maronite churches of Lebanon still contain curious pictures dating back to the Middle Ages, with Syriac inscriptions; but the Syriac language is said only to survive in three villages not far from Saidnaiya.
The miraculous image at this place had a long legendary history. It was said to be partly of wood, partly of flesh, and from its breasts distilled a sacred oil which was used to light the lamps in the church, and carried away to France, where it was treasured in many abbeys. In the present age the image is not shown to the faithful, as it is said that any who look upon it would be struck dead; but the saint is still believed to be able to grant offspring to her adorers, and it is reported that her chapel is filled with indecent pictures. She is, in short, a Lucina, who no doubt traces her descent from the old Ashtoreth of Syria, adored by Hittites and Phœnicians alike.
It might be thought that miraculous pictures and images had ceased to work wonders in the nineteenth century, but the Roman sect has no monopoly of such marvels, nor is human credulity limited to any period of time. Colonel Churchill, in 1853, was still able to report the existence of a miraculous sweating picture of St. George in the Maronite church at Heitât, producing a liquid eagerly purchased by Christians; and many a survival of early Paganism may yet be traced among the priest-ridden peasantry of the Lebanon.
The Normans held on to their North Syrian possessions almost to the end of the thirteenth century, and till the fall of Acre they still kept possession of the shore towns. The success of Saladin and Bibars seems to have led the Franks to look to a Tartar alliance as the best means of retaining their power. It was generally believed that the Tartars—to whom the Armenians were tributary—were Christians, and the legend of Prester John, the Christian king of Central Asia, was eagerly accepted. For this reason St. Louis sent Rubruquis even as far as Siberia offering his alliance, and the plan was still in favour apparently in 1282, when Sir Joseph de Cancy wrote his letter home to Edward I., for he says, in describing the battle between the Egyptians and the Tartars near Homs, that “the King of Cyprus not being yet come up, could not join the Tartars.” It appears that the Mongol princes, who were then following the steps of their Mongol predecessors, the Hittites, were willing, in a very politic manner, to nurse such illusions for their own purposes, and indeed the tolerance shown to Christians, Moslems, and Buddhists by Genghiz Khan and his descendants contrasted in a marked manner with the zeal of the Arab and Turkish Moslems.
There is no part of Syria where the past is more vividly recalled than in the little-visited regions of the Northern Lebanon. Standing on the ramparts of Kal’at el Hosn, where the great towers retain their battlements, and the great oak door still swings in the gateway, the traveller, as he looks down on the village which nestles at the foot of the fortress, climbing the steep sides of the hill, might almost expect to see the mailed knights ride forth, or the Turkoman princes advancing under their emblazoned banners[62] from the east. At Homs the picturesque bazaars are still girt by the black basalt walls with their round gate-towers, which no doubt existed when, in 1281, the power of the Mongols was broken in the plain before them, and which may have been built before Zenghi attacked the town in 1130, by Normans or by Turkoman princes. The influence of Europe had not visibly reached this city in 1881, when I explored its narrow lanes, and it stands amid its green gardens by the Orontes much as it was some seven centuries ago.
Yet, on the other hand, the Lebanon district presents us with the one bright spot in the Turkish Empire, the freest and best governed of the Sultan’s provinces. Under the guardianship of European states, with a Christian governor, a constitution, a taxation amounting to only a shilling a head, a smart mounted police, and a coach-road over the mountain, the Lebanon province has become prosperous and happy, filled with a cheerful population, and covered with vineyards and gardens, thus presenting a most remarkable contrast to the ill-ruled province of Tripoli on the north and the ruined regions of Palestine on the south.
I PROPOSE to conclude this volume by a slight sketch of the results which have been gathered by exploration in Palestine. In journals or memoirs the importance of these results is hardly to be appreciated in their scattered form, and I find that they have certainly not yet been grasped even by learned writers who have penned accounts of the country quite recently in England. These results are geological, geographical, physical, antiquarian, ethnical, and biblical, or, more widely speaking, historical, and under these six headings they may successively be considered.
Geological research was not one of our principal objects, but a knowledge of the geology of a country is indispensable, if the explorer would rightly estimate, not only its geographical character, but the possibilities of ancient cultivation and natural history. I was taught the elements of geology by more than one specialist well known by name in England, and though the studies of Lartet and others left no great discoveries to be made, I always felt the necessity of studying the structure and the mineralogy of every district which we visited.
The great geological problem of Palestine had long been solved when we entered the country. It was interesting to trace the smaller faults in the Jordan Valley, and to discover volcanic outbreaks on Carmel which were previously unknown; but the fact that the Dead Sea and the valley were formed by a mighty fault 200 miles long, leaving the sandstone of the lower beds bare on the east side, and producing violent dips in the limestone on the west, had already been explained. Professor Hull has since given scientific accounts of the formations south of the Dead Sea, but Canon Tristram described the sea-beaches in the valley in 1876, before I mentioned the existence of a very remarkable example north of Jericho.
What chiefly interests us from a general point of view is the relation which geology bears to the question of the ancient fertility of the country. Porous strata must have been porous in all historical periods, and impervious strata impervious. The last convulsions had long given place to the slow processes of denudation on the Palestine hills before man existed, and though the Jordan Valley was formed after the chalk age, the great lakes had dried up, leaving only the Sea of Galilee, Merom, and the Dead Sea in existence when history opened.
It seems clear, then, that the well-watered parts of Palestine now existing are those which were so when the Old Testament was penned; that where wells and cisterns are now used, they were then also in use; that what is now trackless and waterless desert was so in the time of David. The snow of Hermon is mentioned in the Bible as well as the saltness of the Bitter Sea. Palestine is still a land of corn, wine, and oil, as of yore, and sheep are still fed in the same pastoral regions, the same vineyards are still famous, the corn of its plains still yields an hundredfold. I am unable to see that in any respect, either in climate or in natural productions, can the land have changed, excepting always that a decrease in population has led to decreased cultivation, and that goats and peasants have often wrought havoc among the trees. Palestine can hardly have been more healthy in Bible times than it now is. Plagues, famines, fever, and leprosy are mentioned in the history of the Hebrews, and in the New Testament we find the poor stricken with eyesore, fever, and palsy quite as much as they now are. There are still “former and latter rains,” and the rose of Sharon has not withered: the purple iris is still royally robed: the imagery of the Song of Songs is still easy to apply. Except in the disappearance of the lion and the wild bull—which are also represented on Assyrian bas-reliefs, yet no longer found in Assyria—there is no change in the fauna: the deer, the antelope, the fox, the wolf, the hyena, and the jackal, the ostrich, and the crocodile still survive in the wilder parts of the land, with the great boars which delight in the marshes; the leopard lurks in the jungles and the coney in the rocks; the wild goat leaps on the precipices, and the wild ass in the distant eastern deserts is not unknown.
Considering how complete was the examination of the fauna by Canon Tristram, it was certainly an unexpected stroke of good fortune to discover an unknown quadruped in Palestine; but the bones of the Yahmur deer, which we sent home from Carmel, were pronounced to belong to the same species with the English roebuck; and we thus recover in existence one of the species mentioned in the Pentateuch, and which furnished venison to King Solomon’s table.
The seasons, not less than the fauna and flora of Palestine, are unchanged. Indeed, the names of the old Aramaic months, as now translated by aid of Assyrian, show us this uniformity, while the spoils taken by Thothmes III. (as already noted) carry back the agricultural prosperity of the country to a time earlier than the Exodus. The spring brings grass and flowers; the corn ripens even in April in the Jordan Valley, and in May on the hills; the olive harvest and the vintage follow in the early autumn, when the threshing-floors are full of grain, over which the old threshing-sledge of Hebrew times is still driven. With the first rains the ploughing begins, and with January comes the snow, with ice and hail. In one year, at Jerusalem, we had seven falls of snow. The top of Mount Salmon was white for days, recalling the words of the psalm; and the occasional occurrence of a sudden storm in harvest-time also agrees with a passage in the Books of Samuel. There is no exaggeration in the statement that Palestine is unchanged, and the best comment on the physical incidents mentioned in the Bible is found in the meteorological observations of Palestine explorers.
The geographical results of the Survey are, of course, among its most important scientific claims. The best previous maps depended on a few observations of latitude and longitude, and on the calculation of distances by time. Many of these distances were better known in the fourth century than they were in 1872; for the Romans placed milestones along their great routes, which will be found marked on the Survey maps; and these were known to Eusebius, to Jerome, and to other travellers, and are mentioned in the Onomasticon. On the maps sent out for my use I not only found many omissions, but large villages were placed on the wrong sides of valleys, and the courses of many important watercourses were wrongly laid down. The level of the Sea of Galilee was uncertain within three hundred feet, the fords of Jordan were unknown, and the affluents of Jordan had not been traced. The number of important ruins was, of course, large in districts hardly approached by former travellers, and even on the hills near the Sharon plain villagers told me that I was the first Frank they had ever seen, which was no doubt true, as they rarely travel more than ten miles from home.
Ancient geography has equally benefited by the work. The names of the old towns and villages mentioned in the Bible remain for the most part almost unchanged. I believe that I was able to add to future maps about 150 of these old sites west of the river and some thirty east of Jordan. Among these may be reckoned some places of great importance for the understanding of the Bible, such as Bethabara, Bezek, Debir, Etam, Gilgal, Jeshanah, Kadesh, Kirjath-jearim, Luz, Megiddo, Nephtoah, Rakkon, Sorek, the Valley of Zephathah, the important border-towns of Dabbasheth and Ataroth Adar, with Bamoth Baal, Peor, and Nehaliel, Minnith, Luhith, and other places beyond Jordan. These discoveries have already found their place on the Bible Society’s maps published in 1887; and by such recovery of ancient sites it became possible to lay down the boundaries of the tribes, and of the later divisions of Judea, Samaria, and Galilee, with an amount of certitude before unattainable. Very considerable changes have thus been made on the new Bible maps, which will be seen when they are compared with the old; and the acceptation of these results in standard works shows that the arguments by which they were enforced were clear enough to overcome the most conservative geographers. The fact that each name was carefully recorded in Arabic letters made it possible to compare with the Hebrew in a scientific and scholarly manner. The wild shots which have been made by those who compare the English of the Bible with the English of the Palestine maps might serve to discredit such comparisons; but when the Hebrew and the Arabic are shown to contain the same radicals, the same gutturals, and often the same meanings, we have a truly reliable comparison. The scholar knows that Hazor and Hadirah are the same words, and he at once sees the fallacy of comparing Jiphtah-el with Jefât. In the one case the words are identical in lettering and in meaning; in the other, the actual Arabic of Jiphthah-el is Fath Allah—a name which still survives in the Jordan Valley.
There are still points disputed in Palestine geography, which is for the most part due to the meagre information which we possess. Some of these questions of opinion may remain always unsettled, but we have now recovered more than three-quarters of the Bible names, and are thus able to say with confidence that the Bible topography is a genuine and actual topography, the work of Hebrews familiar with the country, and free from contradictions such as are presented, for instance, in the Book of Tobit by a writer ignorant of the places of which he speaks.
It is not only the Bible geography which has thus been explained. The topography of Josephus, of the Talmud, of the Byzantine pilgrim writers, of the Crusading chronicles, are equally illustrated by our maps. The Memoirs, which give a detailed account of every hill range, stream, spring, village, town, ruin, and large building in Palestine, also contain notes of every statement as to topography which I was able to gather from Jewish, Samaritan, Greek, Latin, and Norman French notices of Palestine. Not only Josephus and the Bible, but Pliny, Strabo, the Rabbinical writers, the Samaritan chroniclers, the Onomasticon, the early Christian pilgrims, the Crusading and Arab chronicles, have been put under contribution, and we can now prepare not only a map of Canaanite Syria as known to the Egyptians or one of the Twelve Tribes or of the Roman provinces, but a Byzantine map of fifth-century bishoprics, or a yet fuller map of the Crusading kingdom, with its Norman and Normanised Arab names, some of the former even of which are now preserved.
The Memoirs to which I refer fill three quarto volumes, full of plans and pictures, special surveys of important places, and detailed accounts. A volume on Jerusalem and another on special subjects are added, and the set includes, in other volumes, Dr. Hull’s geological account, Canon Tristram’s natural history, and Professor Palmer’s editing of the name lists. Yet another volume of natural history is promised from the observations of Mr. Chichester Hart, and the volume of my Moabite Survey has just appeared, making the ninth. It must not be forgotten that the Survey was no mere compass sketch. It is based on a triangulation with three carefully measured bases. All important mountain tops are laid down within a circle having a diameter of ten yards. All important heights are determined within five feet. The levels of the Sea of Galilee and of the Dead Sea are known within a few inches. The hill features are represented not by conventionalised lines, but by actual tracing of every spur and by actual survey of every top. Whatever disputes may arise as to the meaning of an Arabic or Hebrew word, or as to the identification of some obscure site, there can be no dispute as to the geographical position or the elevation of any spot shown on the Palestine Survey, for the principles of the work are the same on which our original Ordnance Survey in England was carried out; and although the appliances at our command would of course not allow of the same minute accuracy of instrumental measurement, still, on the scale of one inch to a mile such minutiæ are invisible to the eye.
I had occasion very often to test work done some time before by my surveyors: it always stood the test; and when we were informed from home that a “village had been left out,” I was not alarmed, for I had checked the map by the Turkish Government list of villages under taxation, and we found to our amusement, when the actual prismatic compass came into our hands, with which our critic took angles at the so-called village (which was a ruin actually shown on the map), that the instrument had no needle, which explained why no three angles of those given to us could be made to intersect in a single point. The survey of Jordan and the position of points east of Jordan were subjected to severe tests by an independent authority, with the result that our work was pronounced to be the only accurate representation of the ground. I always felt sure that my companions recognised their responsibility to the public, and that the work was done in earnest by men who took pride in its being good. Such criticisms were therefore welcome, as opportunities of demonstrating that, as far as in us lay, our work was thorough and conscientious. I have often been amused at the “mares’ nests” which have arisen from misunderstanding the accounts of other travellers, and then attempting to apply to the map. Those who quote these earlier maps must remember that we had them before us, and that if we omitted names thereon shown, we did so after due inquiry, either because they are wrong, or because they are at least doubtful.
Turning to antiquarian questions, some disappointment has been expressed that we found nothing very sensational, to compare with the Moabite Stone for instance, or with the cuneiform tablets. It is true that we did not bring home the ark, or the calves of Dan, or Ahab’s ivory house, or Joseph’s mummy, but I doubt if this detracts from the scientific value of our work. I was offered Samson’s coffin, and a contemporary account of the Crucifixion. I was often presented with ancient MSS. and early pottery, but no record will be found of these wonders in the work of the Survey. The dolmens of Moab, the true copy of the Siloam inscription, the shekels sent home by Mr. Drake, the plan of the Hebron Haram, are the most ancient antiquarian results we have been able to place before the public. We have not offered Shapira Pentateuchs, or seals of David in square Hebrew, but the drier records of decipherment and measurement.
As regards epigraphy, it is true that our Memoirs contain only one Hebrew text of great antiquity, with three Hebrew tomb-inscriptions; but these form a very substantial addition to previous materials. The number of Greek texts scattered over the whole country and previously uncopied is large, including the interesting text from the door of a ruined basilica, reading, “This is the gate of the Lord; the righteous shall enter in;” and, as mentioned previously, the twelfth-century frescoes in the Jordan Valley, which are reproduced in their colours, have since been completely destroyed.
Since the finding of the Moabite Stone no discovery has been as important as that of the Siloam inscription. The exact forms of the letters, and the question whether these forms were exactly repeated, were points of the greatest interest. The first copies were most misleading in these respects, and the difficulty of copying was very great; the earliest correct representation published in Europe was taken from our squeezes; and it may be compared with the cast which was made for us, and which is now in England. The text opened out a new chapter in the history of the alphabet, and gave the first monumental evidence of the civilisation of the Hebrews in the days of their kings.
As regards antiquarian questions which depend on accurate survey and levelling, the most important are those which concern Jerusalem. It is disappointing to find that the cogency of such evidence is not always understood, especially by scholars who have not travelled or studied survey. Quite recently allusion has been made by one writer to “imaginary contours” as the work of Palestine explorers; as though there existed some kind of contours which were not imaginary. I have never been in a country where actual contours could be found, but the accuracy of contours depends on the accuracy and number of the levelled points which they represent. For general purposes, sections of ground may be recommended as better understood by laymen. In the present instance, the accuracy of the levelling by which the lie of the rock in Jerusalem is determined is happily beyond dispute; and the observations of the rock surface exposed in tanks, wells, and excavations are fortunately most numerous in just the places where they are most wanted. From these results there is no escape for those who wish to found their theories on facts.
It is curious, however, to note that not even a scaled survey will appeal in all cases to the antiquary. Plans of Jerusalem have been put forward which reduce the size of the city to that of a gentleman’s garden—not exceeding five acres for the older town, and fifteen acres in all. This is gravely propounded in face of the surveys of Tyre, Cæsarea, and other cities, which, though placed on restricted sites, have an area of 100 to 200 acres each. Jerusalem, in Hebrew times, really occupied some 200 acres, with a population of more than 10,000 souls, even in Nehemiah’s time. A modern village of 500 souls in Palestine is larger than the “Pre-Exilic” Jerusalem of writers who put no scale to their plans. It is not, I fear, unnecessary to point out the importance of mastering the results of scientific survey, especially in the case of scholars who have not been in Palestine. No amount of literary ingenuity can destroy the actual results of measurement and excavation, and as these become more familiar the theories which ignore them must become obsolete.
After surveying and planning a very large number of ruins, it became possible to form some opinion as to comparative dates, and, from instances where history or inscriptions furnished a clue, to obtain starting-points of comparison in other cases. In this work I found most assistance from the writings of De Vogüé and Rey, and from Fergusson’s “Handbook of Architecture.” Many fallacies thus came to be exposed, and the discovery of pointed arches often transferred a building from the Phœnicians to the Crusaders. The number of really ancient remains naturally proved to be small, for we must remember that the antiquary in Palestine ends nearly where he begins in England. A Saxon church is a very great rarity at home. In Palestine, where we go back some three thousand years earlier, many important ruins are six or seven centuries older than our Saxon chapels (such as that of Bradford). In England we point with pride to Norman Winchester. In Palestine we regard the Crusading Cathedral of the Holy Sepulchre as quite modern. The Dome of the Rock was the model of our Temple chapels, and so old was it when the Temple Order was instituted, that it was confounded by the Knights with Herod’s Temple, still seven centuries older. Yet even Herod’s work does not content us in the East, where we look to find the walls built by Solomon. Some antiquaries have failed to remember the many great builders—Hadrian, Constantine, Justinian, the Khalifs, the Crusaders, the later Moslems—who followed Herod and Solomon. Palestine has an ancient history of eight centuries between the date of the Crucifixion and the time when England became a state. This is a truism, yet it is one which is not unfrequently forgotten.
Among the most important results was the classification of various kinds of rock-sepulchre in Palestine. To convince us that an ancient site has really been discovered, it is not enough to find a ruin with the required name. When neither inscription nor architecture gives a date, and when no measured distances along Roman roads point to the spot, we must often rely on the evidence of rock-cut tombs. It is not enough to find even these, unless they are really Hebrew tombs. It was our practice not only to record their existence, but to measure and describe them. They fall thus into categories—Hebrew, Greek, Roman, Early Christian, and Crusading—all rock-cut, but all presenting differences. Some were inscribed, and served to date the class to which they belonged. In some cases tombs of the earlier class had been enlarged later, the inner chambers presenting different arrangements to the outer or older. In some cases Jewish tombs were half destroyed by more recent excavators of caves, which were thus proved not to be as old as formerly thought. It was finally clear that tombs with kokim, that is, with tunnels in the walls of the chamber running in lengthways, so that the corpse was placed with its feet towards the chamber, were the oldest; and that this style of sepulture was Hebrew and preceded the Greek age. In Phœnicia similar tombs occur; but the tombs at the bottom of a deep shaft, as in Egypt, which occur at Tyre, are unknown in Palestine, where the entrance is in the face of a rock.
When kokim tombs occur at a ruined site, they may now be considered good evidence of the antiquity of the place. They are found at most of the sites which have been otherwise proved to be Hebrew towns, but their antiquity is demonstrated by independent means.
There are in Palestine eight great periods of building, beginning with the rude stone or pre-historic age, and including Hebrew, Greek, Roman, Byzantine, Arab, Crusading, and Saracenic.
The rude stone monuments have been already noticed, and are probably the earliest remains in the country. Hebrew remains are chiefly represented by rock-cut tombs, rock scarps, tunnels, and pools (as at Siloam), the great Tells or mounds beside springs and streams, and a very few inscriptions. The wall on Ophel, found by Sir C. Warren, is probably as old as Nehemiah, and in the extreme north we have Phœnician sculptures, tombs, and sarcophagi of equal antiquity. The Greek age presents several examples of native art under Greek influence, such as the palace of Hyrcanus, and some of the Jerusalem tombs. To the earliest Roman period belong the walls of the Jerusalem and Hebron harams, with the temple at Siah, the colonnade at Samaria, the earliest remains at Masada and Cæsarea. Advancing to the second century of our era, we find Syria to have been suddenly covered with Roman cities, Roman roads, Roman temples and inscriptions, funerary and official; and this period, to which the synagogues also belong, is one of the greatest building ages in Palestine. The Roman work gradually gives place to the Christian architecture of the Byzantines. Chrysostom’s description of Syrian civilisation fully agrees with the discovery of countless Greek chapels and churches of this age, with cities, castles, and other buildings. At Bethlehem we have one of the oldest churches in the world, the fourth-century pillars still standing in place. The church was five hundred years old when England became a kingdom.
The early Arabs have left us very few buildings beyond the Dome of the Rock at Jerusalem, the great Damascus mosque, and perhaps the buildings beyond Jordan mentioned in the fifth chapter. They employed Persian and Greek architects, and brought no original style of their own from the deserts of Arabia. The Crusaders, who followed, were great builders, civil and ecclesiastical; the country is full of their castles and of their churches. The Italian-Gothic style was slowly modified during the two centuries of Norman supremacy; the latest buildings being those along the western coast, which was latest held. The nearest approach to their architecture that I have seen is found in Palermo and in Messina; and it was to Norman success against Islam in Sicily that the establishment of the Latin kingdom in Syria was due. The Normans were succeeded by the Egyptians, to whom Syria owes many of its finest architectural monuments, dating from the fifteenth century. The Turks have added very little of any interest to the architectural remains of the country.
These various epochs and styles are distinguishable by the student who has studied dated monuments of each age. The forms of the arches, the dressing of the masonry, the mortar even and the plaster, tell their tale to the practised eye. Crusading work is distinguished by its mason’s marks, of which we made a large collection, and which are often the same used about the same time in England and in Scotland. They are neither marks of individuals, nor do they show the position intended for the stone, but clearly they were put only on the best finished stones, and often they are luck-marks, which, from a remote antiquity, have been widely used in Asia and in Europe. Neither the earlier Arabs nor the later Saracens seem to have used such marks, and they form the most distinctive peculiarity of Crusading work in the East.
Next in order we must consider one of the most interesting subjects studied by the explorers, namely, that of ethnology. Very little was really known as to the peculiarities of the natives of Syria. I find that it is still thought in England that they are Turks, though the number of Turks in the country south of Damascus might perhaps be counted only by tens. For six years I carefully studied every class of the population, and collected facts concerning race, religion, and language, which form the most important considerations in such study, and on which manners and customs must chiefly depend.
The population of Palestine, though very sparse, is also very mixed. In addition to the Moslem peasantry, who are mainly of an Aramaic stock, and the Arabs, who are more or less of pure southern extraction, we have to deal with native Greek Christians; with the Lebanon Maronites; with the Druzes, Metâwileh, Ismailiyeh, Anseiriyeh; with Greeks, Jews, Samaritans, and with yet later colonies of Germans; with Italian monks and French priests; with the annual hordes of pilgrims, Russian, Armenian, or Georgian, and the annual inroad of European tourists. Some European stocks, such as the Italian and German, have left their mark on the racial types of the country. We cannot study the question of ethnology practically on the assumption that the population is of pure stock, and represents without mixture that existing three thousand years ago. Not only has there been some admixture of late years, but there have been from the dawn of history various races in Syria. The Crusaders who married Maronite and Armenian wives originated the Poulains, who remained in the land. The soldiers of Rome or of Alexander, whose colonies were found even as far east as Gerasa, no doubt intermarried with natives; as the Palmyrene archer of York wedded a wife of the Catuvellauni. In the time of Christ Greek was spoken in Palestine, and the inhabitants of Decapolis were probably in many cases of Greek descent. The Arabs from the south were then pushing northwards to meet the descending Aramaic stream from Palmyra. When we go back to Nehemiah’s time, we find the Jews as strangers, surrounded by a peasantry of mixed race. Yet earlier, the Assyrians brought colonists from the east and planted them in Samaria. When we go back to the time of Rameses II., we already find, side by side with the Semitic inhabitants, a race which was akin to the Medes and other ancient Mongolic peoples of Western Asia. The “Canaanite was then in the land” when Abraham began his migrations from the north.
These two great stocks, Semitic and Turanian, have contended ever since in Syria, with varying fortunes; and from the third century B.C. downwards the Aryans also have been always present. We have seen already how far south the Turkoman hordes pushed in Palestine, still surviving in the plain of Sharon; and, as in all other countries, there are gypsies in Syria, representing another element of Aryan origin from India; while among the Druzes I believe a Persian stock is also present.
If, therefore, ethnology is to be studied in Palestine, it must be with these facts kept steadily before us. If peasants are to be asked to have their heads measured, we must know something of their genealogies also. If skulls are to be collected, we must find out what skulls they are. I have known the skulls of peasants recently murdered to be sent home as types of the ancient population of the country. I have read of blue eyes attributed to the Amorites, when probably a much more recent admixture of Aryan blood might account for this most abnormal occurrence.[63]
Even the studies of religion or of language present less difficulty than that of race. We are constantly reminded that race and language are not synonymous. It is no doubt true, since a conquered people often learns the language, and sometimes adopts the creed, of the conquerers. In Palestine, gypsies and Turkomans talk Arabic, for it is a necessity that the minority should speak the tongue of the majority; yet, as regards the more important stocks in Syria, there has been no great change. The peasantry speak almost as they spoke in Jerome’s days, almost as the Galileans spoke in the time of our Lord. The Arab tongue as spoken by the wild Bedu of Moab was admired for its classic expressions by my educated scribe, and was hardly understood by my Maronite servants. The speech of townsmen differs from that of the peasantry in its sounds as well as in its words, and the Lebanon muleteer’s jargon would certainly not be understood by an university professor of Arabic.
As regards the Moslem religion in Syria something has already been said. To study only one phase of Islam, as represented by educated Turks or Circassians in a city like Cairo, which has so long been open to European influence, will give only a partial and misleading picture of the creed, even when the good faith of such latitudinarians is undoubted. In Damascus, in Homs, in Hamah, in the remote villages, in the sanctuaries of Hebron and Jerusalem, another and a very different tone prevails. Let the student of Islam run the gauntlet of the fanatical guards of these sanctuaries, let him be stoned for a dog and denied a drink of water as a Kâfir, and then acknowledge that the stern prejudices of the Middle Ages are not extinct. Guarded by an English garrison, in a country where subservience to England is a necessity, how can he judge the real temper of Moslems? Rather should he reflect on the ruins of Alexandria, on the dervishes who surrounded Arabi at Tell-el-Kebir, on the curses which will meet him in Hebron or in Acre. It is not by their words, but by their actions that Orientals, like Westerns, must be judged; and it is not by the opinions of the most advanced and civilised that the strength of prejudice among the many is to be gauged.
The ethnological study to which I devoted most of my time was that of the Moslem peasantry and of the nomadic Arabs. “We recorded their customs, their beliefs, their superstitious practices. We described their dress and food, and studied the peculiarities of their dialect. We found among them good, bad, and indifferent, honest and upright men, and scoundrels or hypocrites. Some were intelligent and able, others were stupid. We cannot generalise concerning them, any more than we can generalise at home. The average standard is very low as regards morality, truth, and intellect. Education they have none, and their courage, though generally remarkable, is not always to be relied on. The Arab is superior in many respects to the Fellah, but he is quite as untruthful and as greedy.
The feeling that is left on the mind by constant and lengthy communion with such a peasantry is not easy to describe; they are “as sheep having no shepherd,” even as in the ancient days. What heart could fail to pity them in their weakness and ignorance, tortured by want, by debt, and by disease; cruelly ground down by robbers and taskmasters; torn from their homes to fight in Balkan snows, and left to find their way back without money or aid? I believe that in the minds of the present Sultan and of the present Khedive a real compassion for these poor creatures exists, though neither is able much to help them. The gratitude expressed for very little kindness, and the good feeling excited by common acts of justice among them, I shall not forget. There is but one state more miserable than that in which they usually live, and that is their condition in time of war. Whoever wins, whoever is covered with decorations, the poor at least are certain to suffer. I have seen them so suffer in Egypt in a campaign carried out by civilised and merciful Englishmen, but I have only heard from them what they underwent in the horrors of the great struggle with Russia in 1877. At Gibeon I found a young Sheikh who alone had made his way back out of all the conscripts taken from the village; and the peasantry in 1881 were forced to sell themselves and their families into practical slavery to foreign merchants, so ruined were they by the war. The horrible revenge that they took in a village, and on a European whom I well knew, cannot here be told. It is one of the many things beneath the surface which one learns by living long in a country, and which cannot be appreciated by the visitor of a season.
As regards race and language, enough has been said; and as regards religion, I have striven to show that the faith of mosques and Mollahs is hardly more in sympathy with peasant superstition than it is with the scepticism of Moslem philosophers. It was not, however, only with the peasantry that our work brought us in contact. I have conversed with men who traced their lineage from the companions of Omar, and with respectable merchants and learned doctors, as well as with Fellahin. The first step to a genuine understanding with such men is that there shall be no pretence on your part. The Oriental sees through such things more quickly than the European. He despises an affectation of consent on your part, and pays you in your own coin. Even as the home-made vest of an unhappy European disguised as a Syrian Christian was seen beneath his jubbeh, and as his blue eyes betrayed him while his speech did not, so the would-be Oriental Englishman deceives himself when he thinks he is gaining ground with Moslems. In his own colours he is accepted on his merits, and may claim such acquaintance as may exist between Moslem and Christian; but the Korân forbids the making of a Christian intimacy (v. 56). “Take not Jew or Christian,” says the Prophet, “for a friend.”
Few men could be more respected or more worthy of respect than the famous Abd-el-Kader, whose acquaintance I was honoured by making. Strict and stern as was his creed, countless Christians owed their lives to his influence in the massacres of 1860. With him I would contrast my so-called friend the Sheikh of the Jerusalem Haram. He belonged to the new school, which prophesies smooth things, and cries peace where there is no peace. A milder-mannered man I never met. He went out of his way to propose that he should start excavations for us near the mosque, and that he should let us see down into the Well of Souls. He never meant a word he said. I never believed him; and I knew his object was merely to get money on promises never to be fulfilled. Finding exactly where I wanted to excavate, he used to see no difficulty in the way. The next time I went to the Haram, a huge mound of earth had arisen before the walled-up archway which he promised to open. It was the stupidity of the Pasha, he explained (a Christian and an educated man), and he was still anxious to do something else. He could smatter a little English, and could ask for a copy of the Gospels. From such a man I could fancy the words to come easily that “Moslems and Christians were just the same;” but among all Muhammadans of Syria I despised no one else so heartily.
It is not the Moslem only who takes the measure of your foot in the East. I have heard the dragoman, who is so obsequious and respectful, describe the peculiarities of his convoy in their absence with considerable humour. There have been well-known prelates of Oriental Churches whose “printing-press funds” have not been visibly devoted to the benefit of their flocks. As long as the Turk is thought to be stupid and the Eastern believed to be eager for our teaching, he possesses the great advantage of being undervalued. The Turks have not allowed railways to be made, but they have adopted the electric telegraph; they have stopped explorations, but they are careful to collect antiquities having a saleable value. The Syrians have not adopted hard hats or French bonnets, but they buy lucifer-matches, and they use guns and gunpowder. They, like the Caffres, have keenly observed the manners of Europe, and have adopted only what seemed to them practical improvements. It is difficult to convey the results of experience in words. We go out to other countries supposing that we can carry all before us. We come home after a time to doubt whether in all respects our civilisation is superior to that of peoples who in Asia were the heirs of an ancient culture when we were painted with woad. If we are ignorant at first of the manners and beliefs of Eastern lands, the shock to our prejudices must be very great; but I cannot believe that long acquaintance with Moslem life can fail to dispel the charm of our first contact with the dignity and courtesy of the East.
There is another important question bound up with Palestine exploration on which a few words may be here permitted, namely, the relation which it bears to the study of the Bible. There is hardly a historic chapter which I was not able to read with the scene of the events recorded before my eyes; there is not a poetic line in the Old Testament which is not more vividly brought home by a memory of Eastern scenery and life. The conditions under which we study the Bible at home are most peculiar. We read it in translation, and in a country which has little or nothing in common with the home of Hebrew prophets or of Galilean disciples. We learn, as a rule, hardly a word of the original language, and while we never feel that Dante or Goethe are known to those who read translations and who have never been in Italy or in Germany, we regard the Bible as intelligible to every reader. Not that the translation is other than the most wonderful in existence—except Luther’s—and not that Englishmen were ignorant of the Holy Land in the days when it was first rendered from the original. Queen Elizabeth had her fleet on the Euphrates and her consuls in the Levant; Maundrell was chaplain at Aleppo in 1697, and addressed the record of his travels to the Bishop of Rochester. Not, again, that such familiar names as those of the roebuck and the fallow-deer are misnomers, or that “green pastures” are unknown in Palestine, but because the average reader who has not seen the East cannot but colour that which he reads with the colouring of familiar scenes.
It is not only the uncritical reader to whom this applies: the literary critic is no better off. I have studied much that has been written by Colenso, by Ewald, by Kuenen, and by Wellhausen; but there is perhaps only one critic of eminence to whom the East is familiar, and in whose eyes the antiquarian discoveries of explorers seem to have primary value, namely, Renan; and the tone of those authors who write without practical and long experience of the East at once betrays their deficiency. Their criticism smells of the lamp, not of the desert; and the arguments which seem so strong in their eyes have often little force in those of an Oriental traveller.
It has always been the fate of genius to be criticised by narrower minds. The Book of Job, for instance, is a work which cannot be truly appreciated anywhere but in the desert. It breathes the desert air, it tells of desert beasts and plants, of the pastoral patriarch with his flocks and herds, of the Chaldean raiders from the east, of the whirlwind, the frost, and the stars. Here you read of the broom still burned for charcoal—“sharp arrows of the mighty with coals of juniper.” In Job you hear the poet speak of the “eyelids of the dawn.” “The ghosts tremble beneath the waters, even the inhabitants thereof.” The stork and the ostrich, the wild ass and the ibex on the cliffs, are familiar to his memory. Of his critics he asks a question which may puzzle them yet: “Knowest thou the time when the wild goats of the rock bring forth? or canst thou mark when the hinds do calve? Canst thou number the months that they fulfil? or knowest thou the time when they bring forth?” Even after criticising the language and dividing out the “documents,” I fear it is to the Arab hunter that the most learned Hebraist in England must go for the answer.
The Song of Solomon is another Hebrew book which is equally full of Eastern colour. The vineyards of Lebanon, the secret places in the “stairs” of the rocks where the wild dove hides, the roes on the mountains, are among its images. Over the Moab plateau you may see the dawn stretching her wings as Joel beheld her, and from the mountains of Judah you may see her sinking in the “uttermost parts of the sea,” as the Psalmist describes. Surely in the days of a “modern theory of the Pentateuch,” it is not amiss that we should at times be reminded that the Hebrews knew better their own land, and even their own history, than strangers in a remote and very different clime, in the midst of a very different civilisation and theory of life, and at a time separated by some twenty-five centuries from that which is studied.
Every fact that is collected in the East serves better to explain the Bible and more and more to control critical views. Surely those who write of “peasant proprietors” in Solomon’s days cannot be aware that individual property in agricultural land has never been an Eastern tenure. As in India, in Russia, or among Bechuana tribes, so also in Palestine to the present day, the lands are held on “village tenure.” If Isaiah’s writings were ever circulated as “broad-sheets,” I would ask who read them in a country where only a few scribes here and there had acquired the great art of writing?
The tenth chapter of Genesis has been put on one side, as though unworthy of scientific notice, by those who have assumed that there was only one stock and only one language in Syria and Chaldea. Now that the monuments tell us of other races and other languages, its distinctions become valuable, and serve to guide scientific research; while the full elucidation of its geography has only been attained by the painful travels of explorers. In this way, also, we are now able to restore, bit by bit, the topography of Palestine as described in the Bible. It is found easy to recognise the most important towns, to trace the borders of the tribes, and to explain the scene of David’s wanderings or of Gideon’s pursuit. In the peasant’s mouth you may still hear the old language almost unchanged, with its terse idiom, its vigorous wording, and its naturally religious tone. It is not the language of the grammatical pedant that comes from his lips, but the mother-tongue of earlier days.
In all things founded on actual knowledge of the land, the labours of the explorers have added materially to the knowledge of the Bible. The seasons, the climate, the fauna and flora, the crops, the native customs and speech, the remains of Hebrew architecture, art, engineering, and monumental writing, have been described. Even as regards the question of transmission of ancient documents and the method of their preservation, some new hints have been collected.
It seems to me impossible for any one familiar with Oriental ideas to accept the ordinary theory of edited “documents,” which German scholarship has taken as its datum, since Astruc’s discovery of parallel passages in Genesis. Nor is it correct for critics to speak of the modern “theory of the Pentateuch.” There is more than one such theory, and their respective upholders are not in accord. If we take such a work as the Book of Kings, it seems to me that light is thrown on the method of its construction by the practice of the Samaritan high priests, who, as already explained, have continued their very sober chronicle from 1149 A.D. to 1859 A.D. by successive additions, and a knowledge of the documentary history of the Talmud or of the Zendavesta shows us that in Asia it is with the “commentator,” and not with the “editor,” that we have to deal—with sacred books preserved by loving care and reverence, not with a modern literature to be compared with our daily press.
I have been led to make these remarks, not through any want of respect for English scholarship and erudition, but because we are now entering on a new epoch of scientific study, and because the great importance of the change wrought by the increase of our actual knowledge is at times not recognised. We no longer depend on literature alone. We have actual monuments before our eyes. We have inscriptions, coins, seals, statues, chased metal-work, and pottery; we have collected measurements of tombs, walls, synagogues, and reliable photographs of every famous place. We have accounts of race, language, custom, and tradition, not hastily gathered, but the results of sifting and repeated inquiry. From such materials facts totally unexpected have been brought to light. Fifteen years ago no one knew that in Syria there was a system of hieroglyphics quite distinct from any other.[64] Forty years ago no scholar suspected the early civilisation of a forgotten Turanian race in Chaldea, whose language was recovered by the genius of Sir Henry Rawlinson. Now it is generally admitted by the few who have turned their attention to the matter that an old Mongolic people ruled over the Semitic dwellers in Palestine before the time of the Exodus. But this discovery has as yet found its way into no critical work on the Bible, save one hasty attempt to show that it contradicts Genesis. It is evident that in the future, when the subject is more fully understood, it must modify many conclusions previously supposed final. The Hebrew language itself was not perfectly understood until the knowledge of Assyrian had been sufficiently advanced to permit of comparison. Even now further steps are possible, and are being cautiously taken, by scholars familiar with the Akkadian, which show beyond dispute how words foreign to the Hebrew language, but proper to the Turanian speech of Western Asia, have found a place even in the earliest books of the Old Testament. This fact, only dimly suspected by Gesenius, has been brought to light entirely by monumental research.
Even in the nineteenth century, then, we are only beginning to understand the Bible from its historical and natural point of view. New maps, new dictionaries, new handbooks have already been found requisite to keep pace with the advance of knowledge due to exploration; and even these cannot pretend to be final or complete presentments of all that it is possible to know.
I may conclude, then, by a few words concerning the work which still remains to be done, which should be in two directions—excavation and the study of native life.
As regards excavation, there is very much to be done. At Cæsarea, at Herodium, at Jerusalem itself, at Samaria probably, at Gerasa, and Baalbek, there are secrets hidden still beneath the soil. The great Hittite Tells near Homs ought all to be examined by digging. The ruins of Carchemish have only been scratched over. Lebanon and Amanus are as yet but little known. New hieroglyphic texts may be expected from Northern Syria, and the Siloam inscription cannot be unique. Unfortunately the state of the East is very unfavourable to the antiquarian; but it must not be supposed that exploration is complete while fields as yet hardly worked exist all along the eastern shores of the Mediterranean.
As regards ethnological study, there is also much yet to be done. This can only properly be undertaken by residents. The observations of a stranger are not reliable. The inquirer must know the personal characters of those with whom he deals, and must be able to select those whose statements are worth recording. The peasantry especially should be studied, and their confidence will not be given to any save those with whom they are intimate.
The best ethnological information that I collected in Syria came from a respected German resident among the Samaritans, who was known to all the townsmen of Shechem as “the Father of Peace.” The object of those interested in such study should be to organise inquiries from sympathetic residents. The linguistic studies of Mr. C. Landberg at Sidon have been the most important of recent additions to our knowledge of the language, proverbs, and customs of the Syrian peasantry.[65]
A complete Fellah vocabulary should be collected in Syria. The vulgar pronunciation should be preserved, the vulgar idiom and grammatical blunders. A great many archaic words which are not in lexicons would thus be unearthed, just as we find valuable survivals in the dialects of our own provinces. To this vocabulary every legend, song, proverb, or mythical tale that can be gathered should be added, and every custom noted. The charms and amulets worn, the burial, birth, and marriage rites, the common oaths and salutations, the peasant ideas of etiquette and ceremony, every one of these has an unknown scientific value. Some attempt has already been made by the Palestine Exploration Fund to start such an inquiry; and until peace reigns and confidence is restored on the Sultan’s dominions, no more useful method of increasing our knowledge can be devised.
I will take leave, then, of my readers in the words of the old knight whose work in Palestine has not yet been proved to be other than an account of his own travels:—
“And forasmuch as it is long time past that there was no general passage or voyage over the sea, and many men desiring to hear speak of the Holy Land and have thereof great solace and comfort, ... I shall devise you some part of things that are there, when time shall be as it shall best come to my mind; ... for I have oftentimes passed and ridden the way with good company of many gentles. God be thanked!”
THE most celebrated of the controversies connected with Palestine refer to the site of the Temple of Herod and to that of the Holy Sepulchre. I have given an estimate of the results of exploration as affecting both subjects in various works, but since their publication other writers (not the majority) have in some cases reverted to the views which were held before exploration commenced, and which were deduced from literary researches.
The latest work on the subject (Professor Hayter Lewis’ “The Holy Places of Jerusalem,” Murray, 1888), very fully supports the views which I have advocated for the last ten years.
As regards these questions, it is clear that we are now in a position to study them from monumental evidence, which is safer and more convincing than any argument drawn from literary studies. The views now more generally adopted depend almost entirely on the consideration of such monumental evidence, and on study of the rock rather than on the vague and brief accounts of ancient writers.
As regards the Temple, the excavations have proved to us that a great building exists on the site having masonry of the same general character on its east, west, and south walls. The difference in finish of the ancient stones in some parts may most probably be supposed not to indicate any difference of date, but to be due to the work being in some places intended to be seen and in other cases hidden under earth. There is no evidence that any of this masonry is as old as Solomon. It resembles the work at Arak el Emir (second century B.C.), and the Greek style of the Acropolis (sixth century B.C.), and the Roman masonry of Baalbek (second century A.D.). The masons’ marks found by Sir C. Warren, and resembling Phœnician or Aramean letters, do not necessitate the idea that these stones are of Solomon’s age. The old alphabet was still but little changed in Herod’s days.
Various scholars have taken Josephus’ statement, that the Temple was a stadium square—a statement made, writing in Rome, by an author whose measurements are often self-contradictory[66]—and have thus sought to confine Herod’s Temple to an area 600 feet square in the south-west angle of the Haram. To this theory, which originated with the late Mr. Fergusson, several objections seem to me fatal.
(1.) Josephus, whom they quote, also says that the town-wall of Jerusalem on Ophel, south of the Temple, joined the eastern cloister of the Temple (Wars, V. iv. 2). This wall Sir Charles Warren discovered joining the east wall of the Haram. Thus, according to Josephus himself, the south-east angle of the present Haram was the south-east angle of Herod’s Temple.
(2.) No walls such as are required by these theorists are known inside the Haram, nor is there any break in the south wall at the point where they suppose the S.E. angle to have been.
(3.) There is also the statement by Josephus that the Temple was on the top of the hill, and I have shown by sections published in the Builder (January 25, 1879), that according to their theory foundations of between thirty and ninety feet are inevitably necessary to carry down to the known levels of the rock the heavy base of the great central fane. Writers who treat only of the plan without taking this practical builder’s objection into consideration may not admit the strength of this argument, but to those who have themselves built it should have force, and no ingenuity can escape from the necessity of such foundations. In the same paper I have shown that a plan, placing the Holy House on the present Sakhrah rock, necessitates only three or four feet of foundation in all parts of the Temple area. (See further Conder’s “Handbook to the Bible,” pp. 359-385, and “Tent Work in Palestine,” vol. i. chap, xii., for full details as to the levels).
(4.) The site of Antonia, as described by Josephus, most plainly agrees with the present rock at the north-west corner of the Haram. Such a site for Antonia cannot be reconciled with the theory confining the Temple to a small portion of the Haram.
(5.) These scholars also ignore the very important and detailed account in the Talmud, which cannot be reconciled with the small area in question. This account dates from only about half a century after the time of Josephus, a time when the ruins of the Temple might still be traceable and known to the author. The account gives us every measurement, enabling us to make a plan, and by aid of the number of steps stated—in agreement with Josephus—to calculate the levels of the various courts. My plan, based on these measurements, occurs in the books above quoted and in the Jerusalem volume of the “Memoirs of Western Palestine.” By this restoration we are able to account for the great passages north of the Dome of the Rock, and can identify the gates mentioned in the Talmud with existing gateways.
The theory in question seems to me, therefore, to strain the meaning of one particular statement and to ignore several others equally important by the same author. It declines to accept the outcome of exploration in the recovery of the Ophel wall; and it supposes walls and a rock scarp to exist where no traces are found of such walls and where such a scarp is impossible. It must, therefore, be regarded as the survival of earlier opinion, which will in time give place to the facts clearly indicated by excavation.
As regards the site of the Holy Sepulchre, Mr. Fergusson’s theory may be considered defunct. Professor Hayter Lewis has taken up the argument which I attempted in 1878, and has added further details of architectural criticism. He agrees with others in accepting the historic accounts contained in inscriptions and in Arab chronicles which attribute the Dome of the Rock to Abd el Melek, and he accepts my three propositions:—1st, That older material was re-used in the structure; 2nd, That the outer walls are attributable to the restoration of the building in the ninth century; 3rd, That the Dome of the Chain was the model of the Dome of the Rock. These three propositions were argued in 1878 (“Tent Work in Palestine”).
It is now generally agreed that Constantine’s basilica of the Holy Sepulchre stood on the present site of the church, and there are, of course, many who regard Constantine’s site as of necessity the true one, while other writers have adopted the theory to which I drew attention in 1878, placing Calvary at the present Jeremiah’s Grotto. The main argument against the traditional site is that it must have been within the “second wall,” which was then the outer wall on the north, whereas we learn from the Epistle that “Christ suffered without the gate” (Heb. xiii. 12). It is certain that the position is suspiciously central. Some have tried to draw the second wall so as to exclude the church. The recovery of the rock sections shows how impossible is the line they propose, which is drawn in a valley commanded from outside. The west end of the second wall was discovered in 1886 within a few feet of the point shown as probable on my plan of 1878, and I believe this discovery to be the death-blow to the claims of the traditional site.
Out of these 422 names of towns, valleys, mountains, streams, and springs in Palestine mentioned in the Old Testament, and now identified on the ground, those marked †, which amount to 144 in all, were discovered by the present author. The more important are described in the text, with the reasons for their identification.
The more important of these 47 sites are noticed in the text.
The Roman numerals refer to the Maps upon which the localities mentioned
will be found.
Latitudes and Longitudes are merely approximate.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, W, Y, Z
Abana, river (33° 32´ N. 36° 20´ E.), 78, 193. I.
Abarah, ford (32° 32´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 74. I.
Abd el Kader, 234.
Abila (Abilene) (32° 32´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 130, 187. I.
Abu Muin Nasir, 8.
Abu Zeid, dish of, 154.
Acre (32° 55´ N. 38° 5´ E.), 92. I.
Adonis, river (34° 5´ N. 35° 40´ E.), 205. V.
Adullam, cave of (31° 40´ N. 35° E.), 49. I.
Adwan Arabs (32° N. 35° 40´ E.), 161, 162, 165.
Afka (34° 8´ N. 35° 52´ E.), 206.
Agriculture in Palestine, 217.
Ahamant, Crus. castle, 107.
Ai (31° 5´ N. 35° 17´ E.)., I.
Aid el Mia (anc. Adullam) (31° 40´ N. 35° E.), 50. I.
Ain el Asy (Aasi) (34° 2´ N. 36° 5´ E.), 192. VII.
Ajlun (32´ 20 N. 35° 45´ E.), 179.
Aleppo (36° 10´ N. 37° 10´ E.), 13.
Alexandretta (36° 33´ N. 36° 10´ E.), 190, 195.
Alphabets, ancient, 173, 203.
Aly Agha, Emir, 104.
Amman. See Rabbath Ammon.
Anderson, Major, 19.
Anazeh Arabs (32° 30´ N. 36° 30´ E.), 141. VII.
Anseiriyeh, mounts of the (35° N. 36° 20´ E.), 191.
Anti-Lebanon, 192. I.
Antioch (36° 11´ N. 36° 10´ E.), 191, 203.
Antoninus Martyr, 5, 94.
Arabs, mode of life, 55;
legends, 162;
customs, 163;
religion, 164;
blood-feuds, 167.
Arculphus, bishop, 6.
Architecture, epochs of, 226.
Armageddon (Megiddo) (32° 28´ N. 35° 27´ E.), 85.
Armstrong, Mr. George, 29, 106.
Ascalon (31° 39´ N. 34° 33´ E.), 47, 48, 50, 51. I.
Ashdod (31° 45´ N. 34° 39´ E.), 50, 202. I.
Assassins, sect of the, 209.
Azotus, same as Ashdod.
Baalbek (34° N. 36° 10´ E.), 135, 192, 203. I.
Baal Hazor (31° 59´ N. 35° 16´ E.), 160. I.
Bamoth Baal (31° 43´ N. 35° 42´ E.), 156.
Banias (31° 15´ N. 35° 41´ E.), 13, 97, 107, 116, 127. I., VI.
Bar Simson, Rabbi, 10.
Bartlett, Mr., 16.
Bashan (32° 45´ N. 36° 15´ E.), 77, 131, 187. I., IV.
Beaufort. See Belfort.
Beauvoir (Belvoir) (32° 33´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 76, 108. VI.
Bedu, plural of bedawi = Arab (nomad).
Beersheba (31° 14´ N. 34° 47´ E.), 32, 36, 52, 53. I.
Beirut (33° 55´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 135, 195. I.
Belfort (Beaufort) (33° 20´ N. 35° 31´ E.), 107. VI.
Belka, El (31° 45´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 137. VII.
Belvoir (Beauvoir) (32° 35´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 107, 108. VI.
Beni Sakhr Arabs (31° 30´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 139. VII.
Benjamin, country of (31° 50´ N. 35° 15´ E.), 31. IV.
Benjamin of Tudela, 10, 33.
Bernard the Wise’s visit to Palestine, 7.
Beth Abarah (32° 32´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 74. I.
Beth Diblathaim (in Southern Moab), 154.
Bethel (31° 56´ N. 35° 14´ E.), 32. I.
Bethesda, pool of, east of Jerusalem, 25, 26.
Bethlehem (31° 41´ N. 35° 12´ E.), 42, 57. I.
Bethsaida (or Julias) (32° 55´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 100
Bethshean (32° 30´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 74. I.
Biblical critics, 237.
Birim, Kefr (33° 3´ N. 34° 56´ E.), 90.
Black, Serjeant, 31.
Blancheward (Blanchegarde) (31° 42´ N. 34° 50´ E.), 107. VI.
Bongars, 9.
Bordeaux pilgrim, 3.
Bosrah (32° 33´ N. 36° 27´ E.), 188. I.
Bozez, cliff of (31° 52´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 32.
Brocquière, Sir B. de la, 13.
Buckingham, 15.
Bukáa (El Bekaa) (33° 45´ N. 35° 50´ E.), 191. I.
Burckhardt, 15.
Buttauf, plain of (32° 50´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 96. I.
Byblos (34° 5´ N. 35° 40´ E.), 191, 195, 199.
Cæsarea (32° 30´ N. 34° 53´ E.), 70. I.
Callirhoe (31° 36´ N. 35° 40´ E.), 143, 161. I.
Calvary, its site, 30. I., inset.
Cana of Galilee (33° 45´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 74, 95. I.
Capernaum (32° 52´ N. 35° 32´ E.), 101. I.
Carchemish (36° 50´ N. 38° E.), 84, 135, 206.
Carmel, Mount (32° 45´ N. 35° E.), 35, 86, 87. I.
Cartulary of Holy Sep. Ch., 10.
Cedron, See Kedron.
Chaplin, Dr., 30.
Chastel Blanc, 107.
Château du Roi (32° 54´ N. 35° 10´ E.), 107.
Château neuf (33° 11´ N. 35° 32´ E.), 107. VI.
Château Pelerin (32° 42´ N. 34° 56´ E.), 108.
Château rouge, 108.
Cherith, brook of (31° 50´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 42. I.
Chorazin (32° 55´ N. 35° 34´ E.), 100. I.
Chosroes, palace of, at Mashita (31° 45´ N. 36° 5´ E.), 177. I.
Churchill, Colonel, 211.
Crocodile River (32° 33´ N. 34° 54´ E.), 70. I.
Cromlechs near Heshbon, 144.
Crusaders’ castles, 106.
Damascus (33° 32´ N. 36° 18´ E.), 131. I.
Dan (33° 15´ N. 35° 39´ E.), 128. I.
Daniel, Abbot, 9.
Darum (31° 23´ N. 34° 20´ E.), 47, 107. VI.
Dead Sea (31° 60´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 43. I.
Debir (31° 25´ N. 34° 58´ E.), 53. I.
Deer (“Yahmur”), 216.
Dervish orders, 125.
Dog River (Nahr el Kelb), (33° 58´ N. 35° 35´ E.), 193. I.
Dolmens, 128, 150.
Dothan (32° 24´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 54. I.
Drake, C. F. Tyrwhitt, 31, 32, 73, 81, 88.
Druzes, 116.
Ebal, mount (32° 15´ N. 35° 16´ E.), 63. I.
Ecdippa (33° 5´ N. 35° 6´ E.), 110. V.
Ekron (31° 51´ N. 34° 48´ E.), I.
Elah, valley of (31° 42´ N. 34° 55´ E.), 49. I.
Eleutheropolis (31° 37´ N. 34° 54´ E.), 50. V.
Eleutherus river (34° 38´ N. 35° 58´ E.), 71, 135, 191. V.
Elisha’s Fountain near Jericho (31° 52´ N. 35° 26´ E.), 42.
Elusa (31° 3´ N. 34° 40´ E.), 57. I.
Emesa or Hemesa, mod. Homs (34° 43´ N. 36° 40´ E.), 13, 135, 136, 204, 212. V.
Engedi (31° 28´ N. 35° 23´ E.), 38. I.
En Rogel (Virgin’s Fountain), (31° 46´ N. 35° 14´ E.), 26.
Ernuald, château (31° 22´ N. 35° 5´ E.), 107.
Ernoul, chronicle, 11.
Esdraelon or Jezreel, plain (32° 33´ N. 35° 19´ E.), 71, 86. I.
Eshtaol (31° 47´ N. 35° E.), 49.
Etam, rock (31° 44´ N. 35° 3´ E.), 49.
Esh el Ghurab, in Jordan valley, 73.
Ethnology of Palestine, 228.
Eusebius, Onomasticon, 3.
Fabri, Felix, 14.
Fellahin of Palestine, 61.
Fergusson, Mr., 177.
Fusail, Wady (Phasaelis), (32° 5´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 79.
Gadara (32° 41´ N. 35° 42´ E.), 77. I.
Galilee, Sea of (32° 50´ N. 35° 35´ E.), 98. I.
Gamala (32° 45´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 100.
Ganneau, Clermont, 49.
Gath (31° 42´ N. 34° 50´ E.), 50. I.
Gaza (31° 30´ N. 34° 27´ E.), 50, 51, 115. I.
Gebal or Byblos, 199.
Genesis, Book of, 239.
Geological notes, 77, 214.
Gerar (31° 24´ N. 34° 26´ E.), 52. I.
Gerasa (32° 17´ N. 35° 55´ E.), 179. I.
Gerizim, Mount (32° 12´ N. 35° 16´ E.), 63, 70, 173. I.
Gezer (31° 51´ N. 34° 55´ E.), 115.
Gibeon (31° 51´ N. 35° 11´ E.), 233. I.
Gibilin, castle (31° 37´ N. 34° 55´ E.), 107, 108.
Gilboa (32° 28´ N. 35° 25´ E.), 85. I.
Gilead (32° 15´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 171. IV.
Gilgal (51° 51´ N. 35° 29´ E.), 43. I.
Girdlestone, Rev. R. B., 180.
Goblan en Nimr, Sheikh, 138, 141, 165.
Golgotha. See Calvary.
Gordon, General, 30, 37.
Gotapata (32° 50´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 102. V.
Graham, Cyril, 188.
Greeks in Palestine, 8, 174.
Guthe, Dr., 27.
Hadanieh (31° 45´ N. 35° 45´ S.), 153.
Hamam, Wady (32° 50´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 99.
Hamath (35° 8´ N. 36° 42´ E.), 137, 200.
Hammath (32° 46´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 77, 100. I.
Hammon (33° 7´ N. 35° 10´ E.), 110.
Haris, Kefr (32° 7´ N. 35° 9´ E.), 70.
Hasbany, river, Upper Jordan (33° 20´ N. 35° 35´ E.), 116. I.
Hasbeya (33° 25´ N. 35° 40´ E.), 127. I.
Hatta (32° 7´ N. 34° 57´ E.), 51.
Hattin (32° 48´ N. 35° 25´ E.), 92, 96. VI.
Hauran (32° 45´ N. 35° 25´ E.), 188. I.
Hebron (31° 32´ N. 35° 6´ E.), 32, 41. I.
Heitat, 211.
Heliopolis. See Baalbek.
Hermon (33° 24´ N. 35° 47´ E.), 73, 116, 127, 129. I.
Heshbon (31° 48´ N. 35° 48´ E.), 141, 157.
Hezekiah’s “waterworks” at Jerusalem, 26, 28. I., inset.
Hieroglyphics, Hittite, 240.
Hieromax. See Jabbok.
Hippos, mod. Susieh (32° 43´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 20, 100, 187. I.
Hittites, 51, 54, 115, 135, 197, 198 (portraits), 241.
Hivites of Shechem, 54.
Homs, anc. Emesa (34° 43´ N. 36° 40´ E.), 13, 135, 136, 204, 212. VI.
Hospitallers, their castles, 108.
Huleh, lake (33° 4´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 107, 129. I.
Hull, Prof., 20, 215, 220.
Ibelin, castle (31° 52´ N. 34° 44´ E.), 107. VI.
Inscriptions, early, 173, 180, 186, 188, 199, 202.
See also Moabite stone, Siloam.
Irby and Mangles, 15.
Islam in Palestine, 122, 231.
Ismailiyeh, sect of the, 119.
Jabbok or Hieromax (32° N. 35° 32´ E.), 72. I.
Jacob’s ford (33° 1´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 107. VI.
Jacob’s Well (32° 13´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 63.
Jaffa (32° 3´ N. 34° 45´ E.), 22. I.
Jahalin Arabs (31° 10´ N. 35° 15´ E.), 38. VII.
Jamnia (31° 51´ N. 34° 44´ E.), 90, I.
Jaulan (32° 55´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 99, 186. I.
Jeba (31° 51´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 155.
Jenin (32° 28´ N. 35° 18´ E.), 15. I.
Jericho (31° 52´ N. 35° 27´ E.), 35, 42. I.
Jerusalem (31° 47´ N. 35° 14´ E.), 21;
Temple of Herod, 24, 246;
Antonia citadel, 25;
Holy Sepulchre, 243;
Bethesda, 25. I., inset.
Jeshanah (31° 58´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 88.
Jeshimon or desert of Judah (q.v.).
Jezreel or Esdraelon (32° 33´ N. 35° 19´ E.), 71, 74, 86, 88, 92. I.
Jideid, Wady (31° 45´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 142.
Job, Book of, 237.
Johnson, J. A., 200.
Joinville, 12.
Jordan (source, 33° 27´ N. 35° 42´ E.), 71, 116.
Jordan valley canal, 77.
Josephus, the historian, 2, 102, 193, 246.
Joshua’s tomb, (32° 7´ N. 35° 9´ E.), 70.
Judah, desert of, or Jeshimon (31° 30´ N. 35° 18´ E.), 35, 41, 160. I.
Judas Maccabæus, 46.
Julias. See Bethsaida.
Kadesh (34° 28´ N. 36° 30´ E.), 71, 135, 198. IV.
Kanah village (33° 12´ N. 35° 18´ E.), 110. I.
Kedron. See Kidron.
Kefr (Arabic) = village. See Kefr Haris, &c.
Kelt or Cherith, brook (31° 50´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 42, 45. I.
Kerak, anc. Tarichæa (32° 43´ N. 35° 34´ E.)., 99. V.
Kerak, anc. Kir Moab (31° 10´ N. 35° 45´ E.).[, 41. I.
Kheta. See Hittites.
Kidron, brook (31° 46´ N. 35° 14´ E.), 26. I., inset.
Kir Moab. See Kerak.
Kishon, river, (32° 49´ N. 35° 2´ E.), 92. I.
Kitchener, Lieut., 83, 105.
Kokaba (33° 26´ N. 36° 10´ E.), 20, 187. I.
Kom Yajuz (32° 2´ N. 35° 56´ E.), 154.
Krak des Chevaliers, mod. Kala’t el Hosn (34° 45´ N. 36° 17´ E.), 107, 108, 109, 193, 212. VI.
Kud, Kefr (32° 35´ N. 35° 10´ E.), 15.
Kuleib or Kleb, Jebel (32° 36´ N. 36° 37´ E.), 188. I.
Kurn Sartaba. See Sartaba.
Kusr Hajlah (31° 48´ N. 35° 28´ E.), 44.
Landberg, Mr. C., 243.
Languages of Palestine, 60.
Latakia (35° 30´ N. 35° 48´ E.)
Litani, river (33° 20´ N. 35° 15´ E.), 131, 191. I.
Lebanon, 131, 191. I.;
cedars of, 208.
Legends, Arab, 162.
Legio (32° 35´ N. 35° 10´ E.), 84. V.
Lejah (33° 5´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 186. I.
Lewis, Prof. Hayter, 245, 247.
Lynch, 16.
Magdala (32° 50´ N. 35° 31´ E.), 91, 100. I.
Maimonides, 96.
Majuma (31° 31´ N. 34° 25´ E.), 50. V.
Maleh, Wady (32° 22´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 76, 78.
Mandeville, Sir John, 13.
Mantell, Lieut., 27, 111, 135, 138, 154.
Mareighat, el (31° 39´ N. 35° 42´ E.), 147.
Margat, castle (35° 9´ N. 35° 58´ E.), 108.
Mar Marrina, near Tripolis, on coast, 45.
Maronites, 120.
Marsaba monastery (St. Saba), (31° 42´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 37. VI.
Masada (mod. Sebbeh), (31° 19´ N. 35° 22´ E.), (siege by the Romans), 39. I.
Mashita (palace of Chosroes), (31° 45´ N. 36° 5´ E.), 177. I.
Maundrell, 15.
Medeba (31° 42´ N. 35° 48´ E.), 157. I.
Megiddo (mod. Mujedda), (32° 28´ N. 35° 28´ E.), 83, 85. I.
Meirun (in Galilee), (33° N. 35° 27´ E.), 106.
Mejr ed Din, 14.
Merash (N. Syria), (37° 33´ N. 36° 53´ E.), 110.
Michmash (31° 53´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 32. I.
Mirabel, castle (32° 7´ N. 34° 55´ E.), 107. VI.
Moab (31° 20´ N. 35° 43´ E.), 134. I.
Moabite stone, 145, 157.
Modin (mod. Medyeh), (31° 56´ N. 34° 59´ E.), 47.
Mont Ferrand (34° 53´ N. 36° 25´ E.), 107.
Montfort (mod. el Kurein), (33° 3´ N. 35° 12´ E.), 107. VI.
Montreal (30° 27´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 107.
Moreh, plain of (E. of Shechem), 63.
Nablus (anc. Shechem), (32° 13´ N. 35° 15´ E.), 59. I.
Nain, view of (32° 38´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 93. I.
Naphtali, mts. of (33° N. 35° 30´ E.), 83. IV.
Nazareth (32° 42´ N. 35° 18´ E.), 94. I.
Nebi Dhahy (32° 37´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 86.
Nebi Samwil (31° 50´ N. 35° 10´ E.), 160. I.
Nebo, Mount (31° 46´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 154, 157. I.
Negeb, plain (31° N. 34° 45´ E.), 52. I.
Nehaliel (mod Zerka Main), (31° 36´ N. 35° 34´ E.), 161. I.
Neubauer, 100.
Nuseir Arabs (32° N. 35° 30´ E.), 42. VII.
Orontes, river (mouth 36° 3´ N. 36° E.), 191.
Ortelius, map of, 14.
Osha, Jebel (32° 5´ N. 35° 42´ E.), 160. I.
Palestine Exploration Fund, 19, 23.
Palmer, Prof., 220.
Palmyra (34° 40´ N. 38° 5´ E.), 205.
Paula’s Travels, 4.
Pelerin, Mont (near Tripolis), 107.
Pella (32° 29´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 76. I.
Peretié, M., 191.
Petra (30° 16´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 146.
Peutinger’s Table, 4.
Phasaelis (mod. Fusail), (32° 5´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 79. I.
Philadelphia (mod. Amman), 171. I.
Philistia (31° 30´ N. 34° 30´ E.), 35, 36, 50. IV.
Phœnicia, 109.
Phœnician Antiquities, 118.
Phocas, John, 9.
Pisgah (31° 46´ N. 35° 43´ E.), 154. I.
Poloner, John, 14.
Porter, 16.
“Poulains,” 229.
Procopius (in Palestine), 5.
Ptolemy’s map of Palestine, 2.
Quarantania (31° 52´ N. 35° 22´ E.),
160. VII.
Rabbath Ammon (mod. Amman), (31° 57´ N. 35° 56´ E.), 143, 154, 171, 175. I.
Rakkath (32° 47´ N. 35° 32´ E.), 100.
Ramadan, fast, 56.
Ramoth Gilead (32° 16´ N. 35° 50´ E.), 185. I.
Rawlinson, Sir Henry, 241.
Raymond of Tripolis, 97.
Rehoboth (30° 59´ N. 34° 34´ E.), 52. I.
Reimun (32° 16´ N. 35° 50´ E.), 185. I.
Rénan, M., 110, 191.
Renaud of Chatillon, 98.
Rey, M. E., 107, 109.
Richard Lion-heart, 11, 47.
Robinson, Dr. (portrait), 16, 27, 30, 95, 101.
Rubud (32° 22´ N. 35° 38´ E.), 185. VI.
Russian monastery at Kusr Hajleh (31° 48´ N. 35° 28´ E.), 44.
Sabbatic river (34° 40´ N. 36° 20´ E.), 192, 193.
Sæwulf’s pilgrimage, 9.
Safed (32° 58´ N. 35° 30´ E.), 77, 92, 104. I.
St. John of Chozeboth (31° 50´ N. 35° 32´ E.), 45. V.
Salt, es (32° 2´ N. 35° 44´ E.), 185. I.
Samaria (32° 17´ N. 35° 11´ E.), 59, 67. I.
Samaritans, sect of, 64.
Sambation. See Sabbatic.
Samson’s exploits, 49.
Sannin, Jebel (33° 58´ N. 35° 50´ E.), 132. I.
Sanuto, Marino, 12.
Saone (castle in N. Syria), 107.
Sartaba, Kurn (or Surtubeh), (32° 7´ N. 35° 26´ E.), 43, 68, 69. I.
Sardenay (33° 42´ N. 36° 20´ E.), 210. VI.
Saron. See Sharon.
Saulcy, M. de, 16.
Sayce, Professor, 27.
Schick, Konrad, 20.
Schumacher, G., 20, 100, 187.
Seetzen, 15.
Seffurieh (32° 45´ N. 35° 16´ E.), 92. I.
Seleucia (36° 9´ N. 35° 57´ E.), 191, 196.
Sepphoris (mod. Seffurieh), 92, 97. V.
Sepulchres and tombs, 176, 225.
Shabatuna, Hittite city near Sabbatic river, 198.
Sharon, plain of (32° 30´ N. 34° 55´ E.), 35, 48, 70. I.
Shechem (mod. Nablus), (32° 13´ N. 35° 15´ E.), 31, 59, 63, 64. I.
Shems-ed-din el Mukkadasi, 7.
Shephelah (31° 40´ N. 34° 55´ E.), 35, 36, 46. I.
Shittim, plain of (31° 50´ N. 35° 35´ E.), 141. I.
Shunem (32° 36´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 93. I.
Sidon (33° 34´ N. 35° 22´ E.), 113. I.
Siloam (31° 46´ N. 35° 14´ E.), pool, 27;
inscription, 26, 28. I., inset.
Simon the Stylite, 207.
Sinnabris (32° 44´ N. 35° 33´ E.), 100. V.
Sipylus, Mount, North of Homs, 198.
Solomon, Song of, 238.
Sorek, Valley of (31° 56´ N. 34° 42´ E.), 49. I.
Stewart, Capt., 31.
Stone monuments, 106, 128, 143, 150, 175;
comp. Dolmen, Cromlech.
Survey work, 59, 80.
Susieh. See Hippos.
Sychar (mod. Askar), 32° 13´ N. 35° 17´ E.), 63. I.
Taamireh tribe (31° 35´ N. 35° 15´ E.), 38. VII.
Taanach (32° 31´ N. 35° 13´ E.), 84. IV.
Tabor, Mount (32° 41´ N. 35° 23´ E.), 85, 86, 87.
Tadmor (Palmyra), (34° 40´ N. 38° 5´ E.), 205.
Taphilah (Tophel), (30° 50´ N. 35° 37´ E.), 107. I.
Taricheœ, mod. Kerak (32° 43´ N. 35° 34´ E.), 100. V.
Taiyibeh (31° 57´ N. 35° 18´ E.).
Templars, Knight, 97;
their castles, 107.
Theodorus on Palestine, 5.
Thomson, 16.
Tiberias or Rakkath (32° 47´ N. 35° 32´ E.), 90, 97, 100. I.
Tibneh (32° 30´ N. 35° 45´ E.), 185. I.
Töbler, 15.
Tombs, ancient, 176, 225.
Toron, now Tibnin (33° 10´ N. 35° 20´ E.), 106. VI.
Tortosa (34° 54´ N. 35° 53´ E.), 210;
castle 108.
Tripoli (34° 27´ N. 35° 40´ E.), 194. V., VI., VII.
Tristram, Dr., 162, 177, 216, 220.
Tunep, mod. Tennib, 197.
Turkomans in Palestine, 71, 136.
Tyre (33° 16´ N. 35° 12´ E.), 111. I.
Tyrus, mod. Arak el Emir (31° 52´ N. 35° 43´ E.), 171. V.
Umm el Amed (33° 8´ N. 35° 9´ E.), 110.
Umm ez Zeinat (32° 39´ N. 35° 4´ E.), 89.
Velde, Van de, 16.
Vinsauf, Geoffrey de, 11, 47.
Vogüé, M. de, 9, 16 172, 180, 187, 190.
Volcanic action, 77.
Volcanic outbreaks on Carmel, 215.
Waddington, 17.
Warren, Sir C., 18, 23, 24, 27, 138, 180.
William of Tyre, 8.
Willibald, St., 6.
Wilson, Sir C. W., 17, 23, 27, 33, 72, 100, 102.
Yermuk, river (32° 38´ N. 35° 34´ E.), 189. I.
Yukin of the Kenites (31° 30´ N. 35° 9´ E.), 160.
Zerka Main (anc. Callirhoe), 160.
Zophim, field of (31° 45´ N. 35° 46´ E.), 159.
Zoreah, Zareah or Zorah (31° 47´ N. 34° 59´ E.), 49.
[1] The latitudes and longitudes given by Ptolemy (see Reland’s Palestina Illustrata, p. 456-466) are not reliable. Those nearest the coast are the most correct; those farther east are very wild. The little sketch given above sufficiently illustrates this.
[2] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. V., translated by Aubrey Stewart, M.A., annotated by Sir C. W. Wilson.
[3] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. II., translated by Aubrey Stewart, M.A., 1887.
[4] See the Latin edition of Töbler. These are not yet published in English translation.
[5] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. III., annotated by Professor Hayter Lewis.
[6] Ibid., No. I., translated by Aubrey Stewart, M.A., annotated by Sir C. W. Wilson.
[7] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. X., translated and annotated by Rev. J. R. Macpherson, B.D.
[8] See Early Travels in Palestine, Bohn’s Series.
[9] See Early Travels in Palestine, Bohn’s Series.
[10] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. IV., “El Mukaddasi,” translated by Mr. Guy Le Strange, 1886; No. IX., “Nâsir i Khusrau,” by the same translator, 1888.
[11] These works, with Jaques de Vitray (1220 A.D.) and Marino Sanuto (1321 A.D.), I studied in the great collection of Latin Chronicles, also containing William of Tyre, by Bongars, called Gesta Dei per Francos, Hanover, 1611.
[12] See Early Travels in Palestine, Bohn’s Series.
[13] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. VI., annotated by Sir C. W. Wilson.
[14] Fetellus in Latin is given by De Vogüé, Églises de la Terre Sainte, p. 410. This account was republished by Leo Allatius, under the name of Eugesippus, in the thirteenth century. He dates it 1040, but the true date appears to be 1151-57 A.D.
[15] See the Latin version, Töbler’s edition. Neither are yet published in English.
[16] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. XI., translated by Aubrey Stewart, M.A. This, like Fetellus, was recovered in MS. by Leo Allatius.
[17] Cartulaire de l’Église du S.S. de Jerusalem, E. de Rosière, Paris, 1849.
[18] See E. Rey’s Colonies Franques de Syrie, Paris, 1883. The work, however, remains to be further perfected by aid of the Survey map. I find some 700 places mentioned in all in Western Palestine.
[19] Early Travels in Palestine, Bohn’s Series.
[20] E. Carmoly, Itinéraires de La Terre Sainte, Paris, 1847.
[21] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. VIII., translated from the old French (edition of Société de l’Orient Latin), by Major Conder, and annotated by him with map of Jerusalem in 1187 A.D.
[22] See Chronicles of the Crusades, Bohn’s Series, for both these works. Other accounts of the thirteenth century, which, however, are less valuable, are those by Willibrand of Oldenburgh, Tetmar, Epiphanius of Hagiopolis, and Brocardus.
[23] Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society, No. VII.
[24] For these two, see Early Travels in Palestine, Bonn’s Series.
[25] See the Latin text, Tobler’s edition.
[26] The best and most recent translations are by Mr. Guy Le Strange.
[27] Early Travels in Palestine, Bonn’s Series.
[28] Memoirs of the Survey of Western Palestine, Jerusalem volume. Tent Work in Palestine, vol. i. chaps. xi., xii. See also Conder’s Handbook to the Bible, Part II. chaps. vii., viii. Palestine Pilgrims’ Text Society’s publications; and Picturesque Palestine (edited by Sir C. W. Wilson.)
[29] For those who are unfamiliar with the methods of professional surveyors, it is perhaps well here to state distinctly that the professional opinion as to the level of the rock throughout the city and the Temple area does not depend on “imaginary contours,” but on a large number of observations of level. The rock base of the mountains is fixed in seventy-five places throughout the Temple area, and in more than 120 other places in the city by excavations, where it is not seen on the surface. In some of the most important parts long sections were visible in the great reservoirs recently excavated. On the little Ophel spur alone fifty such measurements were taken by Sir Charles Warren, besides the 200 above mentioned. There is thus no doubt in the mind of any one who knows these facts as to the position of the hills and depth and width of the ancient valleys; and the imaginary gully which some theorists have drawn on their maps to suit the requirements of their version of Josephus’ account has decidedly no existence.
The south-east corner of the Temple was the most important to fix, in view of conflicting theories. It was at this corner that the Ophel wall joined the “eastern cloister of the Temple” (Josephus, V. Wars, iv. 2). Sir Charles Warren found this wall joining the east wall of the Haram at the present south-east angle of the Haram, and thus appears to have set the question at rest, if Josephus’ account is to be received. This question is fully treated in Conder’s Handbook to the Bible, pp. 366-368, third edition.
[30] The Jewish tradition was first published in “Tent Work in Palestine” in 1878. The account of this question, given by Mr. L. Oliphant in “Haifa,” is abstracted from my later paper in the Jerusalem volume of the Survey Memoirs, published in 1881, and again in 1883, where I have given the Talmudic passages in full. Many other writers have also copied my account since.
[31] See Early Travels in Palestine, Bohn’s Series, p. 86.
[32] See the full account in the Memoirs of the Survey, vol. iii.
[33] Something of the kind, but better drawn, exists on the walls of the Lady Chapel at Winchester, the work, I believe, of Flemish artists of the fifteenth century, representing the miracles of the Virgin. Those at Mar Marrina are probably not later than the thirteenth century.
[34] Judas Maccabæus. Marcus Ward, 1879.
[35] This is usually written Nablous, but the accent is on the first syllable.
[36] I have published a paper on this subject in the Palestine Exploration Fund Quarterly Statement for July 1889.
[37] See Memoirs of Palestine Survey, Vol. Special Papers. This chronicle was edited and published by Dr. Neubauer in 1869. The Samaritan Book of Joshua was published by Juynboll in 1848.
[38] The following are the Kings said in the Book of Kings to have been buried at Samaria:—Omri, Ahab, Ahaziah (probably), Jehu, Jehoahaz, Joash, Jeroboam II., Menahem (probably).
[39] Conder’s Handbook to the Bible (3rd edit.), p. 310.
[40] The fallacy of this scheme I pointed out in a well known magazine in 1883. My arguments are also reproduced by Mr. L. Oliphant in “Haifa.”
[41] The details of this discovery are recorded in the “Memoirs of the Survey,” vol. ii. pp. 90-99.
[42] The question is worked out in detail in the Survey Memoirs. See my note, vol. i. p. 367, and cf. p. 392. The Crusaders called Kefr Kenna the Casale Robert, from its owner.
[43] Sinnabris I recovered, in 1872, from a list of ruins kindly prepared by a resident. It was afterwards fixed by the surveyors. The identity of Hippos and Susieh was suggested by Dr. Neubauer in 1868, and the site has been recently discovered by Herr Schumacher.
[44] The Druzes took from the older Ismailiyeh sect the words Natek and Asas, which are not Semitic words. They represent the two powers in Nature. The first might be connected with the Mongol word Natagai for the chief deity, and the latter with the word Asa for “god” in the same language.
[45] The immorality of the Palestine peasantry, though hidden by their decent manners, is, I have been assured by respectable residents, very great. Their vengeance on women who have gone astray is often very savage. I have visited a cavern in the Judean hills with a deep pit in it, down which such unfortunate women used to be thrown, and I believe there is another in the Lebanon.
[46] This theory I put forward in 1883. The late Dr. Birch held the same view. Dr. Isaac Taylor in 1887 published his belief that the Hittites were Mongolians. Mr. G. Bertin, the Akkadian scholar, favours the same conclusion. At the British Association, 1888, Professor Sayce admitted that the general opinion favoured this view.
[47] See “Heth and Moab,” chaps, vii., viii.
[48] An antiquary familiar with Indian and British stone monuments, writing from Edinburgh, tells me that “cups and smoothed sloping hollows are common enough in Keltic standing-stones. The best I have seen,” he adds, “are the two on the menhirs east and west of the Frodart parish church, Strathpeffer. I think they were swearing-holes, in which the vower placed his fingers, for they are worn as smooth as glass.”
[49] See a detailed note, Pal. Expl. Quarterly Statement, January 1885.
[50] This curious connection between churches and rude stone monuments, also remarked in Britain and in France, is no doubt explained by Pope Gregory’s letter (Greg. Pap. Epist., xi. 71), advising the early missionaries not to suppress the rites and sanctuaries of the Saxons, but to reconsecrate them to Christian use.
[51] The practice has also been noted at Kerlescant in Brittany, at Rollrich, and at Ardmore. There is a similar rite in China of “passing the door” to cure sickness. In Cornwall, the Men-an-tol, or “holed-stone,” near Morvah, is a stone ring two feet in diameter, flanked by two menhirs in a line which passes through the hole.—Dymond, Journal, Brit. Arch. Assoc, June 30, 1877.
[52] The following are the principal groups which I drew and measured:—
| El Maslubiyeh, south of Nebo | 150 | examples. |
| El Mareighat, farther south | 150 | ” |
| El Kurmiyeh, west of Heshbon | 50 | ” |
| Tell Mataba’ and neighbourhood | 300 | ” |
| Ammân, in Mount Gilead | 20 | ” |
In some cases rows of these monuments exist almost touching each other on the hillsides.
[53] The Rev. E. B. Savage, writing to me from the Isle of Man, says, “These cup-hollows are used to the present day in remote parts of Norway for making offerings to the spirits of the departed, such as lard, honey, butter, &c.”
[54] One of these places visited by Balaam was called Bamoth Baal, and appears to be a hill now covered with dolmens. The word Bamah (plural Bamoth) is rendered “high place,” and is sometimes connected with sepulture (Ezek. xliii. 7; Isaiah liii. 9). Gesenius compares the Greek Bōmos, a sepulchral mound or an altar. On the Moabite Stone the word occurs as meaning the stone itself. It seems probable, therefore, that the Bamoth were rude stone monuments.
[55] The height of Mount Nebo is 2643.8 feet above the Mediterranean. The western watershed is from 3000 to 2500 feet above the same level.
[56] Sir C. Wilson, however, places these in the Jordan Valley.
[57] Palestine Exploration Fund Quarterly Statement, September 1870, October 1882, April 1883. I find that my copy supplies a few words not in the earlier copies, and is deficient in some letters previously visible.
[58] The letters are Greek capitals, written on the stylobate of the southern temple. Pertinax was a Piedmontese. He was prefect of a cohort in Syria during the Parthian war, when he may very well have visited Gerasa. He was afterwards consular legate of Syria, and Emperor from 1st January to 29th March 193 A.D.
[59] See Schrader, Cuneiform Inscriptions and Old Testament, pp. 25 and 50. Pinches’ Proc. Bib. Arch. Soc, November 1885.
[60] See George Smith’s Account. Quarterly Statement Pal. Expl. Fund, October 1872.
[61] The confusion of chronology, due to the hasty identification of this prince with Ahab of Israel, has led scholars of late to replace Sirlai in the Lebanon.
[62] The Turkic princes used armorial bearings before they came into use in Europe.
[63] Native Syrians state that the Metâwileh (who are of Persian origin) are usually blue-eyed. They inhabit Upper Galilee and the hills east of Sidon.
[64] The so-called “Hittite” system. The monuments in this character as yet found in situ occur in Armenia, Asia Minor, and Northern Syria. The most southerly sculpture of the kind yet known was discovered in a mound near Damascus excavated by Sir C. W. Wilson. The earliest found examples were five stones at Hamath, one of which Buckhardt saw. Other examples were discovered at Aleppo, and by George Smith at Carchemish. The system as at present known includes about 130 signs, some fifty of which are very frequently repeated. There is no doubt that these read (like the early Akkadian texts) in lines with syllables arranged in columns. Some of the emblems resemble those found in the earliest examples of other Asiatic systems (Egyptian, Akkadian, and Old Chinese), and by analogy it is probable that each emblem represents a word—noun, verb, or other grammatical form. My reasons for supposing the language to be a Turkic or Mongolic dialect are simple. 1st, The names of Hittites and Hittite cities known to us appear to be in such a dialect; 2nd, the short bilingual agrees with this view; and 3rd, the commonest signs (of which we know the sound through later hieratic forms) can be shown to represent common Mongolic words, such as pronouns and case-endings, &c. Many other suggestions have been made for comparing with Hebrew, Georgian, Armenian, and Egyptian, but in no case has it been shown that these languages supply a key to the sounds or to the bilingual. Take, for instance, the Hittite royal title Tarku. It exists only in the Turanian languages—Turkic Tarkan, Mongol Dargo, Cossack Turughna, Etruscan Tarchu and Tarquin, all meaning “a chief.” The number of words which I have so compared now amounts to a hundred in all, and I believe it places the character of the language on a sound and scientific basis.—See Journal Anthropological Institute, August 1889.
[65] Proverbes et Dictons du Peuple Arabe, vol. i. Saida. Carlo Landberg. Leyden, 1883.
[66] As an example of the inexactitude of Josephus’ measurements, I may instance the length which he gives for the Samaria colonnade (Ant., XV. viii. 5). He gives 20 furlongs or 12,000 feet, the real length being 5500 feet. Again, he says that the harbour at Cæsarea equalled the Piræus (Ant., XV. ix. 6). The Piræus was twenty times as large as the Cæsarea harbour. He makes the third wall of Jerusalem 8000 yards long, yet he gives the total circuit of the city as 6600 yards long in the same account (Wars, V. iv. 3). He places Gabaoth Saule four miles from Jerusalem in one passage (Wars, V. ii. 1), and nearly double that distance in another (Wars, II. xix. 1), the real distance being 5½ miles. It has long been known that the chronological calculations of Josephus do not agree together, either through his own inaccuracy or through the corruptions of copyists (see the foundation of the Temple in the eighteenth year of Herod, Ant., XV. xi. 1; or in the fifteenth, Wars, I. xxi. 1), and the comparisons which Josephus gives between Jewish and Greek weights in eight different passages do not agree in any one instance. The historian wrote in Rome in 75 and 93 A.D. Such is the accuracy of the author whom a critic like Dr. Robertson Smith is disposed to quote against the results of actual measurements of walls and rock, which are exact within the decimal of a foot. The general statements of Josephus are very valuable, but his measurements are quite unreliable.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Palestine, by Claude Reignier Conder
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK PALESTINE ***
***** This file should be named 43588-h.htm or 43588-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/3/5/8/43588/
Produced by Heiko Evermann, Chuck and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This book was
created from images of public domain material made available
by the University of Toronto Libraries
(http://link.library.utoronto.ca/booksonline/).)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
[email protected]. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
[email protected]
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.