
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Historic Highways of America (Vol. 12), by
Archer Butler Hulbert
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
Title: Historic Highways of America (Vol. 12)
Pioneer Roads and Experiences of Travelers (Volume II)
Author: Archer Butler Hulbert
Release Date: October 11, 2012 [EBook #41030]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK HISTORIC HIGHWAYS OF AMERICA, VOL 12 ***
Produced by Greg Bergquist and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)
Transcriber’s Note: Obvious errors in spelling and punctuation have been corrected. Footnotes have been moved to the end of the text body. Also images have been moved from the middle of a paragraph to the closest paragraph break, causing missing page numbers for those image pages and blank pages in this ebook.

THE ARTHUR H. CLARK COMPANY
CLEVELAND, OHIO
1904
COPYRIGHT, 1904
BY
The Arthur H. Clark Company
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
| PAGE | ||
| Preface | 9 | |
| I. | The Old Northwestern Turnpike | 13 |
| II. | A Journey in Northern Virginia | 43 |
| III. | A Pilgrim on Braddock’s Road | 64 |
| IV. | The Genesee Road | 95 |
| V. | A Traveler on the Genesee Road | 117 |
| VI. | The Catskill Turnpike | 143 |
| VII. | With Dickens Along Pioneer Roads | 164 |
| I. | Part of a “Map of the Route between Albany and Oswego” (drawn about 1756; from original in British Museum) | 97 |
| II. | Part of a “Map of the Grand Pass from New York to Montreal ... by Thomas Pownall” (drawn about 1756; from original in the British Museum) | 113 |
| III. | Western New York in 1809 | 123 |
This volume is devoted to two great lines of pioneer movement, one through northern Virginia and the other through central New York. In the former case the Old Northwestern Turnpike is the key to the situation, and in the latter the famous Genesee Road, running westward from Utica, was of momentous importance.
A chapter is given to the Northwestern Turnpike, showing the movement which demanded a highway, and the legislative history which created it. Then follow two chapters of travelers’ experiences in the region covered. One of these is given to the Journal of Thomas Wallcutt (1790) through northern Virginia and central Pennsylvania. Another chapter presents no less vivid descriptions from quite unknown travelers on the Virginian roads.
The Genesee Road is presented in chap[Pg 10]ter four as a legislative creation; the whole history of this famous avenue would be practically a history of central New York. To give the more vivid impression of personal experience a chapter is devoted to a portion of Thomas Bigelow’s Tour to Niagara Falls 1805 over the Genesee Road in its earliest years, when the beautiful cities which now lie like a string of precious gems across this route were just springing into existence. For a chapter on the important “Catskill Turnpike,” which gives much information of road-building in central New York, we are indebted to Francis Whiting Halsey’s The Old New York Frontier.
The final chapter of the volume includes a number of selections from the spicy, brilliant descriptions of pioneer traveling in America which Dickens left in his American Notes, and a few pages describing an early journey on Indian trails in Missouri from Charles Augustus Murray’s Travels in North America.
A. B. H.
Marietta, Ohio, January 26, 1904.
We have treated of three historic highways in this series of monographs which found a way through the Appalachian uplift into the Mississippi Basin—Braddock’s, Forbes’s, and Boone’s roads and their successors. There were other means of access into that region. One, of which particular mention is to be made in this volume, dodged the mountains and ran around to the lakes by way of the Mohawk River and the Genesee country. Various minor routes passed westward from the heads of the Susquehanna—one of them becoming famous as a railway route, but none becoming celebrated as roadways. From central and southern Virginia, routes, likewise to be followed by trunk railway lines, led onward toward the Mississippi Basin, but none, save only Boone’s track, became of prime importance.[Pg 14]
But while scanning carefully this mountain barrier, which for so long a period held back civilization on the Atlantic seaboard, there is found another route that was historic and deserves mention as influencing the westward movement of America. It was that roadway so well known three-fourths of a century ago as the Old Northwestern Turnpike, leading from Winchester, Virginia, to the Ohio River at Parkersburg, Virginia, now West Virginia, at the mouth of the Little Kanawha.
The earliest history of this route is of far more interest than importance, for the subject takes us back once more to Washington’s early exploits and we feel again the fever of his wide dreams of internal communications which should make the Virginia waterways the inlet and outlet of all the trade of the rising West. It has been elsewhere outlined how the Cumberland Road was the actual resultant of Washington’s hopes and plans. But it is in place in a sketch of the Old Northwestern Turnpike to state that Washington’s actual plan of making the Potomac River all that the[Pg 15] Erie Canal and the Cumberland Road became was never even faintly realized. His great object was attained—but not by means of his partisan plans.
It is very difficult to catch the exact old-time spirit of rivalry which existed among the American colonies and which always meant jealousy and sometimes bloodshed. In the fight between Virginia officers in Forbes’s army in 1758 over the building of a new road through Pennsylvania to Fort Duquesne, instead of following Braddock’s old road, is an historic example of this intense rivalry. A noted example, more easily explained, was the conflict and perennial quarrel between the Connecticut and Pennsylvania pioneers within the western extremity of the former colony’s technical boundaries. That Washington was a Virginian is made very plain in a thousand instances in his life; and many times it is emphasized in such a way as must seem odd to all modern Americans. At a stroke of a pen he shows himself to be the broadest of Americans in his classic Letter to Benjamin Harrison, 1784; in the next sentence he is urging Virginia to look[Pg 16] well to her laurels lest New York, through the Hudson and Mohawk, and Pennsylvania, through the Susquehanna and Juniata, do what Virginia ought to do through her Potomac.
The powerful appeal made in this letter was the result of a journey of Washington’s in the West which has not received all the attention from historians it perhaps deserves. This was a tour made in 1784 in the tangled mountainous region between the heads of the branches of the Potomac and those of the Monongahela.[1] Starting on his journey September 1, Washington intended visiting his western lands and returning home by way of the Great Kanawha and New Rivers, in order to view the connection which could be made there between the James and Great Kanawha Valleys. Indian hostilities, however, made it unwise for him to proceed even to the Great Kanawha, and the month was spent in northwestern Virginia.
On the second, Washington reached Leesburg, and on the third, Berkeley; here, at his brother’s (Colonel Charles[Pg 17] Washington’s) he met a number of persons including General Morgan. “... one object of my journey being,” his Journal reads, “to obtain information of the nearest and best communication between the Eastern & Western Waters; & to facilitate as much as in me lay the Inland Navigation of the Potomack; I conversed a good deal with Genl. Morgan on this subject, who said, a plan was in contemplation to extend a Road from Winchester to the Western Waters, to avoid if possible an interference with any other State.” It is to be observed that this was a polite way of saying that the road in contemplation must be wholly in Virginia, which was the only state to be “interfered” with or be benefited. “But I could not discover,” Washington adds, “that Either himself, or others, were able to point it out with precision. He [Morgan] seemed to have no doubt but that the Counties of Frederk., Berkeley & Hampshire would contribute freely towards the extension of the Navigation of Potomack; as well as towards opening a Road from East to West.”
It should be observed that the only route[Pg 18] across the mountains from northwestern Virginia to the Ohio River was Braddock’s Road; for this road Washington was a champion in 1758, as against the central route Forbes built straight west from Bedford to Fort Duquesne.[2] Then, however, Braddock’s Road, and even Fort Duquesne, was supposed to lie in Virginia. But when the Pennsylvania boundaries were fully outlined it was found that Braddock’s Road lay in Pennsylvania. Washington now was seeking a new route to the West which would lie wholly in Virginia. The problem, historically, presents several interesting points which cannot be expanded here. Suffice it to say that Washington was the valiant champion of Braddock’s Road until he found it lay wholly in Maryland and Pennsylvania.
Gaining no satisfaction from his friends at Berkeley, Washington pushed on to one Captain Stroad’s, out fourteen odd miles on the road to Bath. “I held much conversation with him,” the traveler records of his visit at Stroad’s, “the result ... was,—that there are two Glades which go[Pg 19] under the denomination of the Great glades—one, on the Waters of Yohiogany, the other on those of Cheat River; & distinguished by the name of the Sandy Creek Glades.—that the Road to the first goes by the head of Patterson’s Creek[3]—that from the accts. he has had of it, it is rough; the distance he knows not.—that there is a way to the Sandy Creek Glades from the great crossing of Yohiogany (or Braddocks Road) [Smithfield, Pennsylvania] & a very good one; ...” At the town of Bath Washington met one Colonel Bruce who had traversed the country between the North Branch (as that tributary of the Potomac was widely known) and the Monongahela. “From Colo. Bruce ... I was informed that he had travelled from the North Branch of Potomack to the Waters of Yaughiogany, and Monongahela—that the Potomk. where it may be made Navigable—for instance where McCulloughs path crosses it, 40[Pg 20] Miles above the old fort [Cumberland], is but about 6 Miles to a pretty large branch of the Yohiogany ...—that the Waters of Sandy Creek which is a branch of cheat River, which is a branch of Monongahela, interlocks with these; and the Country between, flat—that he thinks (in order to evd. [evade] passing through the State of Pennsylvania) this would be an eligible Road using the ten Miles Ck. with a portage to the Navigable Waters of the little Kanhawa; ...”
This was the basis of Washington’s plan of internal communication from Potomac; he now pressed forward to find if it were possible to connect the Youghiogheny and North Branch of the Potomac, the Youghiogheny and Monongahela, and the Monongahela and Little Kanawha. Of course the plan was impossible, but the patient man floundered on through the foothills and mountains over what was approximately the course mentioned, the “McCullough’s Path” and Sandy Creek route from the Potomac to the Monongahela. In his explorations he found and traversed one of the earliest routes westward through this[Pg 21] broken country immediately south of the well known resorts, Oakland and Deer Park, on the Baltimore and Ohio Railway. This was the “McCullough’s” Path already mentioned. Having ascended the Monongahela River from near Brownsville, Pennsylvania, Washington, on September 24, arrived at a surveyor’s office (the home of one Pierpoint) eight miles southward along the dividing ridge between the Monongahela and Cheat Rivers.[4] On the twenty-fifth—after a meeting with various inhabitants of the vicinity—he went plunging eastward toward the North Branch of the Potomac “along the New Road [which intersected Braddock’s Road east of Winding Ridge] to Sandy Creek; & thence by McCullochs path to Logstons [on the North Branch of the Potomac] and accordingly set of [off] before Sunrise. Within 3 Miles I came to the river Cheat abt. 7 Miles from its Mouth—.... The Road from Morgan Town or Monongahela Ct. House, is said to be good to this ferry [Ice’s]—distance [Pg 22]abt. 6 Miles[5] ... from the ferry the Laurel Hill[6] is assended ... along the top of it the Road continues.... After crossing this hill the road is very good to the ford of Sandy Creek at one James Spurgeons,[7] ... abt. 15 Miles from Ice’s ferry. At the crossing of this Creek McCullocks path, which owes its origen to Buffaloes, being no other than their tracks from one lick to another & consequently crooked & not well chosen, strikes off from the New Road.... From Spurgeon’s to one Lemons, which is a little to the right of McCullochs path, is reckoned 9 Miles, and the way not bad; but from Lemons to the entrance of the Yohiogany glades[8] which is estimated 9 Miles more thro’ a deep rich Soil ... and what is called the briery Mountain.[9] ... At the entrance of[Pg 23] the above glades I lodged this night, with no other shelter or cover than my cloak. & was unlucky enough to have a heavy shower of Rain.... 26th.... passing along a small path ... loaded with Water ... we had an uncomfortable travel to one Charles friends[10] about 10 Miles.... A Mile before I came to Friends, I crossed the great Branch of Yohiogany.... Friend ... is a great Hunter.... From Friends I passed by a spring (distant 3 Miles) called Archy’s from a Man of that name—crossed[Pg 24] the backbone[11] & descended into Ryans glade.[12]—Thence by Thos. Logston’s ... to the foot of the backbone, about 5 Miles ... across the Ridge to Ryans glade one mile and half ...—to Joseph Logstons 1½ Miles ...—to the No. Branch at McCullochs path 2 Miles[13]—infamous road—and to Thos. Logstons 4 more.... 27th. I left Mr. Logston’s ...—at ten Miles I had ... gained the summit of the Alligany Mountain[14] and began to desend it where it is very steep and bad to the Waters of Pattersons Creek ... along the heads of these [tributaries], & crossing the Main [Patterson’s] Creek [Pg 25]& Mountain bearing the same name[15] (on the top of which at one Snails I dined) I came to Colo. Abrahm. Hites at Fort pleasant on the South Branch[16] about 35 Miles from Logstons a little before the Suns setting. My intention, when I set out from Logstons, was to take the Road to Rumney [Romney] by one Parkers but learning from my guide (Joseph Logston) when I came to the parting paths at the foot of the Alligany[17] (abt. 12 Miles) that it was very little further to go by Fort pleasant, I resolved to take that Rout ... to get information....”
This extract from Washington’s journal gives us the most complete information obtainable of a region of country concern[Pg 26]ing which it is difficult to secure even present-day information. The drift of the pioneer tide had been on north and south lines here; the first-comers into these mountains wandered up the Monongahela and Youghiogheny Rivers and their tributaries. Even as early as the Old French War a few bold companies of men had sifted into the dark valleys of the Cheat and Youghiogheny.[18] That it was a difficult country to reach is proved by the fact that certain early adventurers in this region were deserters from Fort Pitt. They were safe here! A similar movement up the two branches of the Potomac had created a number of settlements there—far up where the waters ran clear and swift amid the mountain fogs. But there had been less communication on east and west lines. It is easy to assume that McCulloch’s path was the most important route across the ragged ridges, from one glade and valley[Pg 27] to another. It is entirely probable that the New Road, to which Washington refers, was built for some distance on the buffalo trace which (though the earlier route) branched from the New Road. An old path ran eastward from Dunkard’s Bottom of which Washington says: “... being ... discouraged ... from attempting to return [to the Potomac] by the way of Dunkars Bottom, as the path it is said is very blind & exceedingly grown up with briers, I resolved to try the other Rout, along the New Road ...” as quoted on page 21. The growth of such towns as Cumberland and Morgantown had made a demand for more northerly routes. The whole road-building idea in these parts in the last quarter of the eighteenth century was to connect the towns that were then springing into existence, especially Morgantown and Clarksburg with Cumberland. Washington’s dream of a connected waterway was, of course, hopelessly chimerical, and after him no one pushed the subject of a highway of any kind between the East and the West through Virginia. Washington’s own[Pg 28] plans materialized in the Potomac Navigation Company, and his highway, that should be a strong link in the chain of Federal Union between the improved Potomac and the Ohio, became the Cumberland Road; and it ran just where he did not care to see it—through Maryland and Pennsylvania. Yet it accomplished his first high purpose of welding the Union together, and was a fruit of that patriotic letter to Governor Harrison written a few days after Washington pushed his way through the wet paths of the Cheat and Youghiogheny Valleys in 1784.
These first routes across the mountains south of the Cumberland Road—in Virginia—were, as noted, largely those of wild beasts. “It has been observed before,” wrote Washington in recapitulation, “to what fortuitous circumstances the paths of this Country owe their being, & how much the ways may be better chosen by a proper investigation of it; ...” In many instances the new roads built hereabouts in later days were shorter than the earlier courses; however it remains true here, as elsewhere, that the strategic geog[Pg 29]raphical positions were found by the buffalo and Indian, and white men have followed them there unwaveringly with turnpike and railway.
When Washington crossed the North Branch of the Potomac on the 26th of October, 1784 at “McCullochs crossing,” he was on the track of what should be, a generation later, the Virginian highway across the Appalachian system into the Ohio Basin. Oddly enough Virginia had done everything, it may truthfully be said, toward building Braddock’s Road to the Ohio in 1755, and, in 1758, had done as much as any colony toward building Forbes’s Road. All told, Virginia had accomplished more in the way of road-building into the old Central West by 1760 than all other colonies put together. Yet, as it turned out, not one inch of either of these great thoroughfares lay in Virginia territory when independence was secured and the individual states began their struggle for existence in those “critical” after-hours. These buffalo paths through her western mountains were her only routes; they coursed through what was largely an[Pg 30] uninhabited region, and which remains such today. Yet it was inevitable that a way should be hewn here through Virginia to the Ohio; the call from the West, the hosts of pioneers, the need of a state way of communication, all these and more, made it sure that a Virginia Turnpike should cross the mountains.
Before that day arrived the Cumberland Road was proposed, built, and completed, not only to the Ohio River, but almost to the western boundary of the state of Ohio; its famous successor of another generation, the Baltimore and Ohio Railway, was undertaken in 1825. These movements stirred northern Virginians to action and on the twenty-seventh of February, 1827, the General Assembly passed an act “to incorporate the North-western Road Company.”
Sections 1, 3, 4, and 5 of this Act are as follows:
“1. Be it enacted by the General Assembly of Virginia, That books shall be opened at the town of Winchester, in Frederick county, under the direction of Josiah Lockhart, William Wood, George S. Lane, Abraham Miller, and Charles Brent, or any[Pg 31] two of them; at Romney, in Hampshire county, under the direction of William Naylor, William Donaldson, John M’Dowell, Robert Sherrard, and Thomas Slane, or any two of them; at Moorfield, in Hardy county, under the direction of Isaac Van Meter, Daniel M’Neil, Benjamin Fawcett, Samuel M’Machen, and John G. Harness, or any two of them; at Beverly, in Randolph county, under the direction of Eli Butcher, Squire Bosworth, Jonas Crane, Andrew Crawford, and William Cooper, or any two of them; at Kingwood, in Preston county, under the direction of William Sigler, William Johnson, William Price, Charles Byrne, and Thomas Brown, or any two of them; at Pruntytown, in Harrison county, under the direction of Abraham Smith, Frederick Burdett, Thomas Gethrop, Cornelius Reynolds, and Stephen Neill, or any two of them; at Clarksburg, in Harrison county, under the direction of John L. Sehon, John Sommerville, John Webster, Jacob Stealy, and Phineas Chapin, or any two of them; and at Parkersburg, in Wood county, under the direction of Jonas Beason, Joseph Tomlinson, Tillinghast Cook, James[Pg 32] H. Neal, and Abraham Samuels, or any two of them, for purpose of receiving subscriptions to a capital stock of seventy-five thousand dollars, in shares of twenty dollars, to be appropriated to the making of a road from Winchester to some proper place on the Ohio river, between the mouths of Muskingum, and Little Kanawha rivers, according to the provisions of this act....
“3. The proceedings of the first general meeting of the stockholders, shall be preserved with subsequent proceedings of the company, all of which shall be entered of record in well bound books to be kept for that purpose: And from and after the first appointment of directors, the said responsible subscribers, their heirs and assigns, shall be, and they are hereby declared to be, a body politic and corporate, by the name of ‘The North western Road Company;’...
“4. It shall be the duty of the Principal Engineer of the State, as soon as existing engagements will permit, to prescribe such plans or schemes for making the whole road, or the several parts or sections[Pg 33] thereof, as he shall think best calculated to further its most proper and speedy completion, and to locate and graduate the same, or part or parts thereof, from time to time, make estimates of the probable cost of making each five miles, (or any shorter sections,) so located and graduated, and to make report thereof to the Board of Public Works at such time or times as shall be convenient.
“5. The said president and directors shall, from time to time, make all contracts necessary for the completion of the said road, and shall require from subscribers equal advances and payments on their shares, and they shall have power to compel payments by the sale of delinquent shares, in such a manner as shall be prescribed by their by-laws, and transfer the same to purchasers: Provided, That if any subscriber shall at any time be a contractor for making any part of the said road, or in any other manner become a creditor of the company, he shall be entitled to a proper set-off in the payment of his stock, or any requisition made thereon....”[19][Pg 34]
A mistake which doomed these plans to failure was in arbitrarily outlining a road by way of the important towns without due consideration of the nature of the country between them. The mountains were not to be thus mocked; even the buffalo had not found an east and west path here easily. As noted, the towns where subscriptions were opened were Winchester, Romney, Moorefield, Beverly, Kingwood, Pruntytown, Clarksburg, and Parkersburg. When the engineers got through Hampshire County by way of Mill Creek Gap in Mill Creek Mountain and on into Preston County, insurmountable obstacles were encountered and it was reported that the road would never reach Kingwood. From that moment the North-western Road Company stock began to languish; only the intervention of the state saved the enterprise. However, in 1831, a new and very remarkable act was passed by the Virginia Assembly organizing a road company that stands unique in a road-building age. This was “An act to provide for the construction of a turnpike road from Winchester to some point on the Ohio river.” The governor[Pg 35] was made president of the company and he with the treasurer, attorney-general, and second auditor constituted the board of directors. The 1st, 2d, and 4th sections of this interesting law are as follows:
“1. Be it enacted by the general assembly, That the governor, treasurer, attorney general, and second auditor of the commonwealth for the time being, and their successors, are hereby constituted a body politic and corporate, under the denomination of ‘The President and Directors of the North-Western Turnpike Road,’ with power to sue and be sued, plead and be impleaded, and to hold lands and tenements, goods and chattels, and the same to sell, dispose of, or improve, in trust for the commonwealth, for the purposes hereinafter mentioned. And three of the said commissioners shall constitute a board for the transaction of such business as is hereby entrusted to them; of which board, when present, the governor shall be president: And they shall have power to appoint a clerk from without their own body, and make such distribution of their duties among themselves respectively, and such[Pg 36] rules and regulations ... as to them may seem necessary....
“2. Be it further enacted, That the said president and directors of the North-Western turnpike road be, and they are hereby empowered as soon as may be necessary for the purposes herein declared, to borrow on the credit of the state, a sum or sums of money not exceeding one hundred and twenty-five thousand dollars, and at a rate of interest not exceeding six per centum per annum....
“4. Be it further enacted, That the said president and directors, out of the money hereby authorized to be borrowed, shall cause to be constructed a road from the town of Winchester, in the county of Frederick, to some point on the Ohio river, to be selected by the principal engineer. And for the purpose aforesaid, the principal engineer, as soon as may be after the passage of this act, shall proceed to lay out and locate the said road from the points above designated. He shall graduate the said road in such manner that the acclivity or declivity thereof shall in no case exceed five degrees. The width of the said road[Pg 37] may be varied, so that it shall not exceed eighteen feet, nor be less than twelve feet. Through level ground it shall be raised in the middle one-twenty-fourth part of its breadth, but in passing along declivities it may be flat. Bridges, side ditches, gutters, and an artificial bed of stone or gravel, shall be dispensed with, except in such instances as the said principal engineer may deem them necessary....”[20]
Other sections stipulated that the state had the right to survey any and all routes the engineers desired to examine, and that persons suffering by loss of land or otherwise could, if proper application was made within one year, secure justice in the superior or county courts; that the company appoint a superintendent who should have in charge the letting of contracts after such were approved by the company; that, as each stretch of twenty miles was completed, toll gates could be erected thereon, where usual tolls could be collected by the company’s agents, the total sum collected to be paid into the state treasury; that the[Pg 38] company had the right to erect bridges, or in case a ferry was in operation, to make the ferryman keep his banks and boats in good condition; that the company make annual reports to the State Board of Public Works; and that the road be forever a public highway.
The roadway was now soon built. Not dependent upon the stock that might be taken in the larger towns, the road made peace with the mountains and was built through the southern part of Preston County in 1832, leaving Kingwood some miles to the north. Evansville was located in 1833, and owes its rise to the great road. The route of the road is through Hampshire, Mineral, Grant, Garrett, Preston, Taylor, Harrison, Doddridge, Ritchie, and Wood Counties, all West Virginia save Garrett which is in Maryland. Important as the route became to the rough, beautiful country which it crossed, it never became of national importance. Being started so late in the century, the Baltimore and Ohio Railway, which was completed to Cumberland in 1845, stopped in large part the busy scenes of the Old Northwestern Turnpike.[Pg 39]
Yet to the historic inquirer the old turnpike, so long forgotten by the outside world, lies where it was built; and can fairly be said to be a monument of the last of those stirring days when Virginia planned to hold the West in fee. Hundreds of residents along this road recall the old days with intense delight. True, the vast amount of money spent on the Cumberland Road was not spent on its less renowned rival to the south, but the Cumberland Road was given over to the states through which it ran; and, in many instances, was so neglected that it was as poor a road as some of its less pretentious rivals. A great deal of business of a national character was done on the Northwestern Turnpike. Parkersburg became one of the important entrepôts in the Ohio Valley; as early as 1796, we shall soon see, a pioneer traversing the country through which the Northwestern Turnpike’s predecessor coursed, speaks of an awakening in the Monongahela Valley that cannot be considered less than marvelous. Taking it through the years, few roads have remained of such constant benefit to the[Pg 40] territory into which they ran, and today you will be told that no railway has benefited that mountainous district so much as this great thoroughfare.
But in a larger sense than any merely local one, Virginia counted on the Northwestern Turnpike to bind the state and connect its eastern metropolis with the great Ohio Valley. Virginia had given up, on demand, her great county of Kentucky when the wisdom of that movement was plain; at the call of the Nation, she had surrendered the title her soldiers had given her to Illinois and the beautifully fertile Scioto Valley in Ohio. But after these great cessions she did not lose the rich Monongahela country. It had been explored by her adventurers, settled by her pioneers—and Virginia held dear to her heart her possessions along the upper Ohio. In the days when the Northwestern Turnpike was created by legislative act, canals were not an assured success, and railways were only being dreamed of. And the promoters of canals and railways were considered insane when they hinted that the mountains could be conquered by[Pg 41] these means of transportation. With all the vast need for improvements, the genius of mankind had never created anything better than the road and the cart; what hope was there that now suddenly America should surprise the world by overthrowing the axioms of the centuries past?
And so, in the correct historical analysis, the Northwestern Turnpike must be considered Virginia’s attempt to compete successfully with Maryland, Pennsylvania, and New York, in securing for herself a commanding portion of the trade of the West. In all the legislative history of the origin of the Northwestern Turnpike, it is continually clear that its origin was of more than local character. It was actually the last roadway built from the seaboard to the West in the hope of securing commercial superiority; and its decline and decay marks the end of pioneer road-building across the first great American “divide.” In a moment the completion of the Erie Canal assured the nation that freight could be transported for long distances at one-tenth the cost that had prevailed on the old land highways. Soon after, the com[Pg 42]pletion of the Pennsylvania Canal proved that the canal could successfully mount great heights—and Virginia forgot her roads in her interest in canals.
Thomas Wallcutt of Massachusetts served through the Revolutionary War as hospital steward and received in payment therefor one share in the Ohio Company.[21] He went out to Marietta in 1790, and returned eastward by the half-known Virginia route. His Journal[22] forms an interesting chapter of travel on American pioneer roads:
“Monday, 8 March, 1790.[23] Pleasant, clear, cold, and high winds. We were up before sunrise, and got some hot breakfast, coffee and toast; and Captain Prince, Mr. Moody, Mr. Skinner, Captain Mills and[Pg 44] brother, Mr. Bent, &c., accompanied us over the river[24] to Sargent’s or Williams’s, and took leave of us about nine o’clock, and we proceeded on our journey. We had gone but a little way when we found the path[25] so blind that we could not proceed with certainty, and I was obliged to go back and get a young man to come and show us the way. When we had got back to our companions again, they had found the road, and we walked twenty miles this day. Weather raw, chilly, and a little snow. The country after about five or six miles from the Ohio is very broken and uneven, with high and sharp hills.
“Tuesday, 9 March, 1790. The weather for the most part of the day pleasant, but cold winds, northerly. The country very rough, the hills high and sharp.[26] One third of the road must go over and on the ridges, and another third through the val[Pg 45]leys. We walked this day about twenty-three or twenty-four miles, and slept near the forty-fourth or forty-fifth mile tree.
“Wednesday, 10 March, 1790. Weather raw and moist. To-day we crossed several of the large creeks and waters that fall into the Ohio. This occasioned a loss of much time, waiting for the horse to come over for each one, which he did as regularly as a man would. The country much the same, but rather better to-day, except that a great deal of the road runs along through the streams, and down the streams such a length with the many bridges that will be wanted, that it will be a vast expense, besides the risk and damage of being carried away every year by the floods. We had so much trouble in crossing these streams that at last we forded on foot. One of the largest in particular, after we had rode it several times, we waded it four or five times almost knee-deep, and after that a number of times on logs, or otherwise, without going in water. Two of the streams, I doubt not, we crossed as often as twenty times each. We walked this day about fifteen miles.[Pg 46]
“Thursday, 11 March, 1790. With much fatigue and pain in my left leg, we walked about fifteen miles to-day. They all walked better than I, and had got to Carpenter’s and had done their dinner about two o’clock when I arrived. They appear to be good farmers and good livers, have a good house, and seem very clever people. Mr. C. is gone down the country. They have been a frontier here for fifteen years, and have several times been obliged to move away. I got a dish of coffee and meat for dinner, and paid ninepence each, for the doctor and me. We set off, and crossed the west branch of the Monongahela over to Clarksburgh. The doctor paid his own ferriage. We went to Major Robinson’s, and had tea and meat, &c., for supper. I paid ninepence each, for the doctor and me. Weather dull and unpleasant, as yesterday.
“Friday, 12 March, 1790. Weather good and pleasant to-day. We set off before sunrise and got a little out of our road into the Morgantown road, but soon got right again. We breakfasted at Webb’s mill, a good house and clever folks. Had coffee, meat, &c.; paid sixpence each, for me and[Pg 47] the doctor. Lodged at Wickware’s, who says he is a Yankee, but is a very disagreeable man for any country, rough and ugly, and he is very dear. I paid one shilling apiece for the doctor’s and my supper, upon some tea made of mountain birch, perhaps black birch, stewed pumpkin, and sodden meat. Appetite supplies all deficiencies.
“Saturday, 13 March, 1790. Beautiful weather all day. Set off not so early this morning as yesterday. The doctor paid his ferriage himself. Mr. Moore, a traveller toward his home in Dunker’s Bottom, Fayette County, Pennsylvania, [?] set out with us. He seems a very mild, good-natured, obliging old gentleman, and lent me his horse to ride about two miles, while he drove his pair of steers on foot. The doctor and I being both excessively fatigued, he with a pain in his knee, and mine in my left leg, but shifting about, were unable to keep up with our company, and fell much behind them. Met Mr. Carpenter on his return home. He appears to be a very clever man. When we had come to Field’s, I found Mr. Dodge had left his horse for us to ride, and to help us along, which we[Pg 48] could not have done without. We got a dish of tea without milk, some dried smoked meat and hominy for dinner; and from about three o’clock to nine at night, got to Ramsay’s. Seven miles of our way were through a new blazed path where they propose to cut a new road. We got out of this in good season, at sundown or before dark, into the wagon road, and forded Cheat River on our horses. Tea, meat, &c., for supper. Old Simpson and Horton, a constable, had a terrible scuffle here this evening.
“Lord’s Day, 14 March, 1790. Mr. Dodge is hurrying to go away again. I tell him I must rest to-day. I have not written anything worth mention in my journal since I set out, until to-day, and so must do it from memory. I want to shave a beard seven days old, and change a shirt about a fortnight dirty; and my fatigue makes rest absolutely necessary. So take my rest this day, whether he has a mind to go or stay with us. Eat very hearty of hominy or boiled corn with milk for breakfast, and boiled smoked beef and pork for dinner, with turnips. After dinner shaved[Pg 49] and shirted me, which took till near night, it being a dark house, without a bit of window, as indeed there is scarce a house on this road that has any.
“Monday, 15 March, 1790. Waited and got some tea for breakfast, before we set out. Settled with Ramsay, and paid him 9d. per meal, for five meals, and half-pint whiskey 6d. The whole came to eight shillings. Weather very pleasant most of the day. We walked to Brien’s about half-past six o’clock, which they call twenty-four miles. We eat a little fried salt pork and bit of venison at Friends’,[27] and then crossed the great Youghiogeny. About two miles further on, we crossed the little ditto at Boyles’s.... We walked about or near an hour after dark, and were very agreeably surprised to find ourselves at Brien’s instead of Stackpole’s, which is four miles further than we expected. Eat a bit of Indian bread, and the woman gave us each about half a pint of milk to drink, which was all our supper.[Pg 50]
“Tuesday, 16 March, 1790. We were up this morning, and away about or before sunrise, and ascended the backbone of the Alleghany, and got breakfast at Williams’s. I cannot keep up with my company. It took me till dark to get to Davis’s. Messers. Dodge and Proctor had gone on before us about three miles to Dawson’s. We got some bread and butter and milk for supper, and drank a quart of cider. Mr. Davis was originally from Ashford, county of Windham, Connecticut; has been many years settled in this country; has married twice, and got many children. His cider in a brown mug seemed more like home than any thing I have met with.
“Wednesday, 17 March. We were up this morning before day, and were set off before it was cleverly light. Got to Dawson’s, three miles, where Messers. D. & P. lodged, and got some tea for breakfast, and set off in good season, the doctor and I falling behind. As it is very miry, fatiguing walking, and rainy, which makes extremely painful walking in the clay and mud, we could not keep up with D. We stopped about a mile and a half from the Methodist[Pg 51] meeting near the cross roads at Cressops, and four from Cumberland, and got some fried meat and eggs, milk, butter, &c., for dinner, which was a half pistareen each. After dinner the doctor and I walked into Cumberland village about three o’clock, and put up at Herman Stitcher’s or Stidger’s. We called for two mugs of cider, and got tea, bread and butter, and a boiled leg of fresh young pork for supper. The upper part of the county of Washington has lately been made a separate county, and called Alleghany, as it extends over part of that mountain, and reaches to the extreme boundary of Maryland. The courts, it is expected, will be fixed and held at this place, Cumberland, which will probably increase its growth, as it thrives pretty fast already. We supped and breakfasted here; paid 2s. for each, the doctor and me. Pleasant fine weather this day. My feet exceedingly sore, aching, throbbing, and beating. I cannot walk up with my company.
“Thursday, 18 March. Paid Mr. Dodge 6s. advance. A very fine day. We stayed and got breakfast at Stitcher’s, and walked[Pg 52] from about eight o’clock to twelve, to Old Town, and dined at Jacob’s, and then walked to Dakins’s to lodge, where we got a dish of Indian or some other home coffee, with a fry of chicken and other meat for supper. This is the first meal I have paid a shilling L. M. for. The country very much broken and hilly, sharp high ridges, and a great deal of pine. About ... miles from Old Town, the north and south branches of the Potomac join. We walked twenty-five miles to-day.
“Friday, 19 March, 1790. Very fine weather again to-day. We walked twenty-four miles to McFarren’s in Hancock, and arrived there, sun about half an hour high. McFarren says this town has been settled about ten or twelve years, and is called for the man who laid it out or owned it, and not after Governor Hancock. It is a small but growing place of about twenty or thirty houses, near the bank of the Potomac, thirty-five miles below Old Town, and five below Fort Cumberland; twenty-four above Williamsport, and ninety-five above Georgetown. We slept at McFarren’s, a so-so house. He insisted on our sleeping in[Pg 53] beds, and would not permit sleeping on the floors. We all put our feet in soak in warm water this evening. It was recommended to us by somebody on the road, and I think they feel the better for it.
“Saturday, 20 March. A very fine day again. We have had remarkably fine weather on this journey hitherto. But two days we had any rain, and then but little. We stayed and got breakfast at McFarren’s, and set out about eight o’clock, and walked about twenty-one miles this day to Thompson’s, about half a mile from Buchanan’s in the Cove Gap in the North Mountain. My feet do not feel quite so bad this day, as they have some days. I expect they are growing stronger and fitter for walking every day, though it has cost me a great deal of pain, throbbing, beating, and aching to bring them to it. It seems the warm water last night did me some good.
“Lord’s Day, 21 March, 1790. Up and away before sunrise, and walked to breakfast to McCracken’s. He has been an officer in the continental army. I find it will not do for me to try any longer to keep[Pg 54] up with my company, and as they propose going through Reading, and we through Philadelphia, we must part to-night or to-morrow. I conclude to try another seven miles, and if I cannot keep up, we part at Semple’s, the next stage. They got to Semple’s before me, and waited for me. I conclude to stay and dine here, and part with Messrs. Proctor and Dodge. I am so dirty; my beard the ninth day old, and my shirt the time worn, that I cannot with any decency or comfort put off the cleaning any longer. I again overhauled the letters, as I had for security and care taken all into my saddle-bags. I sorted them and gave Mr. Dodge his, with what lay more direct in his way to deliver, and took some from him for Boston and my route.
“I paid Mr. Dodge three shillings more in addition to six shillings I had paid him before at the Widow Carrel’s, according to our agreement at twelve shillings to Philadelphia; and as we had gone together and he had carried our packs three hundred miles (wanting two), it was near the matter. He supposed I should do right to give him a shilling more. I told him as I had[Pg 55] agreed with him at the rate of fifty pounds, when they did not weigh above thirty-five, and at the rate of going up to Pitt instead of returning, which is but half price, I thought it was a generous price, and paid him accordingly as by agreement. We wished each other a good journey, and Mr. Proctor, the doctor, and I drank a cup of cider together. When we had got cleaned, a wagoner came along very luckily, and dined with us, and going our way, we put our packs in his wagon, and rode some to help. We gave him a quarter of a dollar for this half day and tomorrow. We got to Carlisle in the evening and put up with Adam at Lutz’s.
“This Carlisle is said to be extremely bad in wet weather. It probably is nearly & quite as bad as Pittsburg, Marietta, Albany. I went to Lutz’s because Adam puts up there, he being of his nation, but it is a miserable house, and Adam says he is sorry he carried us there. The victuals are good, but they are dirty, rough, impolite. We supped on bread and milk, and Lutz would insist on our sleeping in a bed and not on the floor; so we did so.[Pg 56]
“Tuesday, 23 March, 1790. A pleasant day and the roads very much dried, so that the travelling is now comfortable. We dined at Callender’s in more fashion than since I left home. Adam stopped at Simpson’s so long that it was dark when we got over the river to Chambers’s, where we stopped another half hour. Set off about seven o’clock, and got to Foot’s about eleven. All abed, but Adam got us a bit of bread and butter, and made us a fire in the stove, and we lay on the floor.
“Wednesday, 24 March, 1790. Old Foot is a crabbed.... He has been scolding and swearing at Adam all this morning about something that I cannot understand. It has rained last night, and the roads are again intolerable. Adam says he cannot go again until his father says the word, and that may not be this two or three days. But we cannot go and carry our packs on our backs now, the roads are so bad, and we should gain nothing to walk, but spend our strength to little or no purpose. We must wait for a wagon to go along our way, and join it, or wait for the roads to grow better.[Pg 57]
“Carried our dirty things to wash; two shirts, two pairs stockings, and one handkerchief for me; two shirts, two pair stockings, and one pair trowsers for the doctor. Went to several places to look for shoes for the doctor. He could not fit himself at the shoemakers, and bought a pair in a store for 8s. 4d. Pennsylvania, or 6s. 8d. our currency. He went to Henry Moore’s, the sign of the two Highlanders. I drank a quart of beer and dined. Old Foot is a supervisor, and is gone to Harrisburg to-day, to settle some of his business.
“Thursday, 25 March, 1790. The sun rises and shines out so bright to-day that I am in hopes the roads will be better, at least, when we go. Old Foot could not finish his business yesterday, and is gone again to-day. He is uncertain when he shall send Adam forward to Philadelphia, perhaps not until Monday. It will not do for us to stay, if we can somehow get along sooner. Time hangs heavy on our hands, but we do what we can to kill it. The doctor and I went down to Moore’s and dined together, which was a shilling L. M. apiece. We then came back to Foot’s and[Pg 58] drank a pint of cider-royal together. The house is for the most part of the day filled with Germans, who talk much, but we cannot understand them. We have coffee and toast, or meat for breakfast, and mush and milk for supper. Our time is spent in the most irksome manner possible; eating and drinking, and sleeping and yawning, and attending to the conversation of these Dutch. In the evening the house is crowded with the neighbors, &c., and for the ... Old Foot says, and Adam too, that he will not go till Monday. This is very discouraging.
“Friday, 26 March, 1790. A very dull prospect to-day. It rained very hard in the night, and continues to rain this morning. No wagons are passing, and none coming that we can hear of. We have no prospect now but to stay and go with Adam on Monday. We stay at home to-day and murder our time. We read McFingal, or Ballads, or whatever we can pick up. We had coffee and toast and fresh fried veal for breakfast, and ate heartily, and so we eat no dinner. The doctor goes out and buys us 8d. worth of cakes,[Pg 59] and we get a half-pint of whiskey, which makes us a little less sad. In comes a man to inquire news, &c., of two men from Muskingum. He had heard Thompson’s report, which had made so much noise and disquiet all through the country. He had three Harrisburg papers with him, which give us a little relief in our dull and unwelcome situation. At dark there come in two men with a wagon and want lodging, &c. They stay this night, and with them we find an opportunity of going forward as far as Lancaster, which we are determined to embrace.
“Saturday, 27 March, 1790. We stay and get a good breakfast before we set out, and agree to give Mr. Bailey 2s. L. M. for carrying our baggage. This is higher than anything it has cost us on the road in proportion, but we cannot help it. It is better than to waste so much time in a tavern. It rains steadily, and the road is all mush and water. Before I get on a hundred rods I am half-leg deep in mire. Set off about eight o’clock, and overtook the wagon about two miles ahead. However, it clears off before night, and the sun shines warm,[Pg 60] and the roads mend fast. We made a stay in Elizabethtown about two hours to feed and rest. The doctor and I had two quarts of beer and some gingerbread and buckwheat cakes for dinner. We got to Colonel Pedens to lodge, which is eighteen miles through an intolerable bad road, to-day. (Elizabethtown, about fifty houses; Middletown, about an hundred houses.) We paid our landlady this evening, as we are to start so early in the morning it would not do to wait till the usual time of getting up to pay then, and we have got nine miles to go to reach Lancaster.
“Lord’s Day, 28 March, 1790. We started this morning at day dawn, and got to —— at the Black Horse, four and a half miles to breakfast. The wagon went by us, and fed at Shoop’s. I left the doctor with them and to take care of the things, and walked into the town before them. Stopped at Gross’s, the Spread Eagle, and left word for the doctor, which they never told him. I heard the bell ring for church just as I got here, which made me go into town after waiting some time for them. Took leave of Mr. Bailey, &c. I went to[Pg 61] the English Episcopal Church, and then went back to look for the doctor, and he looking for me; we were some time in chase, and missed each other. Found we could not get served at the Angel, so took our baggage and walked down to Doersh’s, who keeps the stage. Got dinner here. Shaved, shirted, put on my boots, and went out into town. Stopped at the court-house and heard a Methodist. Walked further about; stopped and looked into the Catholic chapel, and talked with the priest. Looked into the churches, such as I could, and returned to tea at sundown. Spent the remainder of the time till bed reading newspapers. Washed my feet and went to bed just before ten.
“Monday, 29 March, 1790. After breakfast the doctor and I took a ramble about the town, to look at it and to inquire if we could find any wagon going to Philadelphia, that we can get our baggage carried. The most likely place we can hear of is to go to the Creek, about a mile from town. Immediately after our walk we settled and paid, and set out at just eleven o’clock. Paid toll over Conestoga bridge, and[Pg 62] stopped at Locher’s, at the Indian King, two miles from Lancaster, and drank a quart of beer. It was not good. Dined at Blesser’s, on a cold meal, which was 8d. L. M. apiece. Got to Hamilton’s at Salsbury, a very good house; nineteen miles. This is more than I expected when I set out at eleven o’clock. A very good supper; rye mush and milk, cold corn beef, and apple pie on the table. But 8d. L. M. for supper and lodging apiece. We have had very good weather for travelling, and the roads are drying fast. In hopes that we shall find some wagon going on the Philadelphia road, that we may get our packs carried part of the way.
“Tuesday, 30 March, 1790. We walked twenty-four miles this day, that is, from Hamilton’s to Fahnstock’s. Very pleasant weather, suitable for travelling; not too warm nor too cold. My feet very tender and sore, but we keep along steady. Got to Fahnstock’s, Admiral Warren, about eight o’clock. Got some bread and milk for supper. The doctor had nothing but a pint of cider for his supper. We slept[Pg 63] well, considering my being excessively fatigued. The post overtook us.
“Wednesday, 31 March. Stayed to breakfast this morning, which was very good, but I do not like the practice, at least I do not seem to need eating meat with breakfast every morning. I sometimes eat it two or three times a day because it is set before me, and it is the fashion to have meat always on the table. We dined about seven miles from Philadelphia; crossed the Schuylkill about sunset, and walked into town about dark. Crossed the Schuylkill over the floating bridge, and paid our toll, 1d. Pennsylvania each.”
A yellow letter, almost in tatters, lies before me written by one Samuel Allen to his father, Mr. Jason Allen of Montville, New London County, Connecticut, from Bellville, Virginia,[28] November 15, 1796. Bellville is in Wood County, West Virginia, eighteen miles by the Ohio River from Parkersburg.
This letter, describing a journey from Alexandria and Cumberland to the Ohio by way of “broadaggs [Braddock’s] old road,” gives a picture of certain of the more pathetic phases of the typical emigrant’s experience unequaled by any account we have met in print. Incidentally, there is included a mention of the condition of the road and, what is of more interest,[Pg 65] a clear glimpse into the Ohio Valley when the great rush of pioneers had begun after the signing of the Treaty of Greenville, the year before, which ended the Indian War.
“Bellville W. Va November the 15th 1796.
“Honoured Parents
Six months is allmost gone since I left N. London [New London, Connecticut] & not a word have I heard from you or any of the family I have not heard wheather you are dead or alive, sick or well. When I heard that Mr. Backus had got home I was in hopes of recieving a letter by him. but his brother was here the other day and sayes that he left his trunk and left the letters that he had in the trunk, so I am still in hopes of having one yet. There is an opertunity of sending letters once every week only lodge a letter in the post-offis in N. London & in a short time it will be at Belleville. The people that came with me has most all had letters from their friends in New England Mr Avory has had two or three letters from his Brother one in fiften dayes after date all of whitch came by the waye of the male.[Pg 66]
“General Putnam of Muskingdom [Marietta on the Muskingum] takes the New London papers constantly every week
“When we arrived to Allexandria [Alexandria, Virginia] Mr Avory found that taking land cariag from there to the Monongehaly would be less expence then it would be to go any farther up the Potomac & less danger so he hired wagoners to carry the goods across the mountains to Morgantown on the Monongahaly about one hundred miles above Pittsburg Mr Avorys expence in comeing was from N London to Allexndria six dollars each for the passengers and two shillings & six pence for each hundred weight. from Allexandria to Morgantown was thirty two shillings and six pence for each hundred weight of women & goods the men all walked the hole of the way. I walked the hole distance it being allmost three hundred miles and we found the rode to be pritty good untill we came to the Mountaing. crossing the blue Mountain the Monongehaly & the Lorral Mountains we found the roads to be verry bad.
“You doubtless remember I rote in my[Pg 67] last letter that Prentice was taken ill a day or two before he continued verry much so untill the 10th of July when he began to gro wors the waggoner was hired by the hundred weight & could not stop unless I paid him for the time that he stoped & for the Keeping of the horses that I could not affoard to do So we were obliged to keep on We were now on the Allegany Mountain & a most horrid rode the waggon golted so that I dare not let him ride So I took him in my arms and carried him all the while except once in a while Mr Davis would take him in his armes & carry him a spell to rest me. a young man that Mr Avory hired at Allexandria a joiner whose kindness I shall not forgit he kep all the while with us & spared no panes to assist us in anything & often he would offer himself. our child at this time was verry sick & no medecal assistance could be had on this mountain on the morning of the 13th as we was at breackfast at the house of one Mr Tumblestone [Tomlinson?] the child was taken in a fit our company had gone to the next house to take breakfast which was one mile on our way we were alone[Pg 68] in the room & went & asked Mrs Tumblestone to come into the room she said she did not love to see a person in a fitt but she came into the room Polly ask her if she new what was good for a child in a fitt she said no & immediately left the room & shut the door after her & came no more into the room when that fitt left him there came on another no person in the room but Mr Tumblestone who took but little notis of the child tho it was in great distress Polly said she was afraid the child would die in one of them fitts Mr Tumblestone spoke in a verry lite manner and sayes with a smile it will save you the trouble of carrying it any farther if it does die We then bundled up the child and walked to the next house ware we come up with our company I had just seated myself down when the child was taken in a fitt again when that had left it it was immediately taken in another & as that went off we saw another coming on the Man of the house gave it some drops that stoped the fitt he handed me a vial of the dropps—gave directions how to use them the child had no more fitts but seemed to be stuped all[Pg 69] day he cried none at all but he kept a whining & scouling all the while with his eyes stared wide open his face and his eyes appeared not to come in shape as before When we took dinner it was six mile to the next house the waggoners said they could not git through thro that night we did not love to stay out for fear our child would die in the woods so we set off & left the waggons I took the child in my arms and we traveled on Mr Davis set off with us & carried the child above half of the time here we traveled up & down the most tedious hills as I ever saw & by nine oclock in the evening we came to the house the child continued stayed all the night the next morning at break of day I heard it make a strange noise I percieved it grew worse I got up and called up the women [who] ware with us the woman of the house got up & in two hours the child dyed Polly was obliged to go rite off as soon as his eyes was closed for the waggoners would not stop I stayed to see the child burried I then went on two of the men that was with me were joiners & had their tools with them they stayed with[Pg 70] me & made the coffin Mr Simkins [Simpkins] the man of the house sent his Negroes out & dug the grave whare he had burried several strangers that dyed a crossing the mountain his family all followed the corps to the grave black & white & appeared much affected.
“When we returned to the house I asked Mr Simkins to give me his name & the name of the place he asked me the name of the child I told him he took his pen & ink & rote the following lines Alligany County Marriland July the 14th 1796 died John P Allen at the house of John Simkins at atherwayes bear camplain broadaggs old road half way between fort Cumberland & Uniontown.[29] I thanked him for the kindness I had received from him[Pg 71] he said I was verry welcome & he was verry sorry for my loss
“We then proceeded on our journey & we soon overtook the waggons & that nite we got to the foot of the mountain We came to this mountain on the 11th of the month and got over it the 19th at night We left the city of Allexandria on the Potomac the 30th day of June & arrived at Morgantown on the Monongahely the 18th day of July
“Thus my dear pearents you see we are deprived of the child we brought with us & we no not whather the one we left is dead or alive. I beg you to rite & let me no Polly cant bear her name mentioned without shedding tears if she is alive I hope you will spare no panes to give her learning.
“When we arrived at Morgantown the river was so lo that boats could not go down but it began to rain the same day that I got ther I was about one mile from there when it began to rain & from the 22d at night to the 23d in the morning it raised 16 feet the logs came down the river so that it was dangerous for boats to[Pg 72] go & on Sunday the 22d in the evening the boats set off three waggons had not arrived but the river was loreing so fast that we dare not wate the goods was left with a Merchant in that town to be sent when the river rises they have not come on yet one of my barrels & the brass Cittle is yet behind
“Mr Avory said while he was at Morgantown that Cattle were verry high down the river & them that wanted to by he thought had better by then he purchased some & I bought two cows and three calvs for myself & three cows for Mrs Hemsted & calves & a yoke of three year old stears. The next morning after the Boats sailed I set off by land with the cattle & horses with John Turner & Jonathan Prentice & arrived at Bellvill the 9th of August & found it to be a verry rich & pleasant country We came to the Ohio at Wheeling crick one hundred miles belo Pittsburg & about the same from Morgantown We found the country settled the hole of the way from Morgantown to Wheeling & a verry pleasant road we saw some verry large & beautiful plantations[Pg 73] here I saw richer land than I ever saw before large fields of corn & grane of a stout groath From Wheeling to Bellville it is a wilderness for the most of the way except the banks of the river this side —— which is one hundred miles we found it verry difficult to get victules to eat. I drove fifty miles with one meal of victules through the wilderness & only a foot path & that was so blind that we was pestered to keep it we could drive but a little wayes in a day whenever night overtook us we would take our blankets & wrap around us & ly down on the ground We found some inhabitance along the river but they came on last spring & had no provisions only what they brought with them
“The country is as good as it was represented to be & is seteling verry fast families are continually moveing from other parts into this beautiful country if you would give me all your intrest to go back there to live again it would be no temtation if you should sell your intrest there & lay your money out here in a short time I think you would be worth three or four times[Pg 74] so much as you now are. it is incredible to tell the number of boats that goes down this river with familys a man that lives at Redstone Old fort on the Monongehaly says that he saw last spring seventy Boats go past in one day with familys moveing down the Ohio. There is now at this place a number of familys that came since we did from Sesquehanah There is now at this place eighty inhabitance. Corn is going at 2.s pr bushel by the quantity 2.s 6.d by the single bushel. There has been between two & three thousand bushels raised in Bellville this season & all the settlements along the river as raised corn in proportion but the vast number of people that are moveing into this country & depending upon bying makes it scerce & much higher than it would be
“There is three double the people that passes by here then there is by your house there is Packets that passes from Pittsburg to Kentucky one from Pittsburg to Wheeling 90 miles one from that to Muskingdom 90 miles One from that to Gallipolees 90 miles the french settlement opisite the big Canawa [Kanawha] & from that there is[Pg 75] another to Kentucky —— of which goes & returns every week & —— loaded with passengers & they carry the male Mammy offered me some cloath for a Jacket & if you would send it by Mr Woodward it would be very exceptible for cloaths is verry high here Common flanel is 6s per yard & tow cloth is 3s 9d the woolves are so thick that sheep cannot be kept without a shephard they often catch our calvs they have got one of mine & one of Mrs Hemstid the latter they caught in the field near the houses I have often ben awoak out of my sleep by the howling of the wolves.
“This is a fine place for Eunice they ask 1s per yard for weaving tow cloth give my respects to Betsey & Eunice & tell them that I hope one of them will come with Mr Woodward when he comes on Horses are very high in this country & if you have not sold mine I should be [glad] if you would try to send him on by Mr. Woodward. I dont think Mr Avory will be there this year or two & anything you would wish to send you nead not be affraid to trust to Mr. Woodwards hands for he is[Pg 76] a verry careful & a verry honest man & what he says you may depend upon.
“Land is rising verry fast Mr Avory is selling his lots at 36 dollars apeace he has sold three since we came here at that price we was so long a comeing & provisions so verry high that I had not any money left when I got here except what I paid for the cattle I bought I have worked for Mr Avory since I came here to the amount of sixteen dollars I paid him 80 dollars before we left N London I am not in debt to him at preasent or any one else I have sot me up a small house and have lived in it upwards of a fortnight we can sell all our milk and butter milk at 2d per quart Mr Avory will give me three shillings per day for work all winter & find [furnish] me with victules or 4s & find myself I need not want for business I think I am worth more then I was when I came We have ben in verry good health ever since we left home.
“General St Clair who is now govener of the western teritoryes & General Wilkinson with their Adicongs [Aid-de-camps] attended by a band of soldiers in uniform lodged at Bellvill a few nights ago on their[Pg 77] way from headquarters to Philadelphia with Amaracan coulours a flying
“Please to give my respects to George & James & tell them that if they want an interest this is the country for them to go to make it Please to except of my kind love to yourselves & respects to all friends who may enquire do give my love to Mr Rogers & family & all my brothers and sisters & our only child Lydia Polly sends her love to you & all her old friends & neighbors
Your affectionate son
Samuel Allen”
The following is a translation of a letter written twelve years after Washington’s journey of 1784, by Eric Bollman, a traveler through Dunkard’s Bottom, to his brother Lewis Bollman, father of H. L. Bollman of Pittsburg:
“From Cumberland we have journeyed over the Alleghany Mountains in company with General Irwin, of Baltimore, who owns some 50,000 acres in this vicinity. The mountains are not so high and not so unproductive as I had imagined them to[Pg 78] be. Several points are rocky and barren, such as the Laurel Ridge, but even this with proper attention and ... European cultivation could be made productive. There are proportionately few such ranges as this, and for the greater part, the mountains are covered with fine timber.
“We spent the first night at West Port. Up to this point, at the proper seasons, the Potomac is navigable and could be made so quite a distance further. But even in the present state the land journey to the Monongahela, which is navigable and flows into the Ohio, is but a distance of 60 miles....
“The road is not in a bad condition and could be made most excellent. This will, without doubt, be accomplished just as soon as the country is sufficiently inhabited, since there is no nearer way to reach the Western waters.
“The next day we dined with Mr. M. McCartin, still higher up in the mountains. There are many settlements in this vicinity. We were entertained in a beautiful, cool, roomy house, surrounded by oat fields and rich meadows, where the sound of the bells[Pg 79] told that cattle were pasturing near by. We dined from delicate china, had good knives, good forks, spoons, and other utensils. Our hostess, a bright, handsome, healthy woman, waited upon us. After dinner, a charming feminine guest arrived on horseback; a young girl from the neighboring farm, of perhaps 15 years of age, with such bashful eyes and such rosy cheeks, so lovely and attractive in manner that even Coopley, our good mathematician, could not restrain his admiration.
“This is the ‘backwoods’ of America, which the Philadelphian is pleased to describe as a rough wilderness—while in many parts of Europe, in Westphalia, in the whole of Hungary and Poland, nowhere, is there a cottage to be found, which, taking all things together in consideration of the inhabitant, can be compared with the one of which I have just written.
“Four miles from this we reached the Glades, one of the most remarkable features of these mountains and this land. These are broad stretches of land of many thousand acres, covered with dense forests;[Pg 80] beyond this there is not a tree to be found, but the ground is covered knee-deep with grass and herbs, where both the botanist and the cattle find delicious food. Many hundred head of cattle are driven yearly, from the South Branch and other surrounding places, and entrusted to the care of the people who live here. What can be the cause of this strange phenomenon! One can only suppose that at one time these glades were covered with timber, which, overthrown by a mighty hurricane, gradually dried and fell into decay. But it would take too long to give the many reasons and arguments both for and against this supposition.
“Only lately have the Indians ceased roving in this vicinity; which has done much to delay its cultivation, but now it is being cleared quite rapidly, and in a short time will, without doubt, become a fine place for pasturage. We spent the second night with one named Boyle, an old Hollander. Early the next morning we could hear the howling of a wolf in the forest.
“We breakfasted with Tim Friend, a hunter, who lived six miles further on.[Pg 81] If ever Adam existed he must have looked as this Tim Friend. I never saw such an illustration of perfect manhood. Large, strong and brawny; every limb in magnificent proportion, energy in every movement and strength in every muscle, his appearance was the expression of manly independence, contentment and intelligence. His conversation satisfied the expectations which it awakened. With gray head, 60 years old, 40 of which he had lived in the mountains, and of an observing mind, he could not find it difficult to agreeably entertain people who wished for information. He is a hunter by profession. We had choice venison for breakfast, and there were around the house and near by a great number of deers, bears, panthers, etc. I cannot abstain from believing that the manly effort which must be put forth in the hunt, the boldness which it requires, the keen observation which it encourages, the dexterity and activity which are necessary to its success, act together more forcibly for the development of the physical and mental strength than any other occupation.[Pg 82]
“Agriculture and cattle-raising, in their beginning produce careless customs and indolence; the mental faculties remain weak, the ideas limited, and the imagination, without counterpoise, extravagant. Therefore we admire the wisdom and penetration of the North American Indian, his sublime eloquence and heroic spirit in contrast to the Asiatic shepherd, from whom we receive only simple Arabic fables. The man, of whatever color he may be, is always that which the irresistible influence of his surroundings has formed him. We left our noble hunter and his large, attractive family unwillingly and followed a roadway to Duncard’s Bottom, on Cheat river.
“We had ridden along uneventfully for about two hours. I was in advance, when Joseph, who rode behind me, cried: ‘Take care, sir. Take care. There is a rattlesnake.’ It lay upon the road and my horse had almost stepped upon it, which would have proved a disastrous thing. Joseph, a good active fellow, sprang instantly from his horse in order to kill it. The snake disappeared in the bushes and rattled. It[Pg 83] sounded so exactly like the noise of a grasshopper that I did not think it could be anything else. Joseph armed himself with a stout stick and heavy stone, followed the snake, found it, and killed it, but then jumped quickly back, for he saw close by another rattlesnake, which had coiled itself and was ready to spring at him. He hurried back again and killed the second. They were 3½ feet long and nine inches in circumference, in the thickest part of the body; one had nine rattles and the other five. We examined the poisonous fangs, took the rattles with us and hung the bodies on a tree. I had thought until now that the principle of life was as stubborn in a snake as in an eel, but found to my astonishment that a slight blow was sufficient to destroy it in this dangerous specimen. Other observations touching upon natural history I must keep for future discussion.
“We dined at Duncard’s Bottom, crossed the Cheat river in the afternoon, reached the Monongahela Valley, spent the night in a very comfortable blockhouse with Mr. Zinn, and arrived the next day at Morgan[Pg 84]town, on the Monongahela. We spent a day and a half here and were pleasantly entertained by Mr. Reeder and William M. Clary, and received much information, especially concerning sugar, maple trees and sugar making. From Morgantown we went to the mouth of George creek, Fayette county, Pennsylvania. As it was afternoon when we reached here we were overtaken by night and compelled to spend the night in a small blockhouse with Mr. McFarlain. We found Mr. McFarlain a respectable, intelligent farmer, surrounded as usual, by a large and happy family.
“Directly after our arrival the table was set, around which the entire family assembled. This appears to be the usual custom in the United States with all people who are in some measure in good circumstances. One of the women, usually the prettiest, has the honor of presiding at table. There were good table appointments, fine china, and the simple feast was served with the same ceremony as in the most fashionable society of Philadelphia. Never, I believe, was there in any place more equality than in this. Strangers who come at this time[Pg 85] of day at once enter the family circle. This was the case with us. Mr. McFarlain told us much about his farm and the misfortunes with which he struggled when he first cultivated the place upon which he now lives. He has lived here 30 years, a circumstance which is here very unusual, because the adventure loving nature, together with the wish to better their condition and the opportunity, has led many people to wander from place to place.
“‘But,’ said Mr. McFarlain, when we made this observation, ‘I have always believed there was truth in the saying, “A rolling stone gathers no moss.” With labor and industry I have at last succeeded, and can still work as well as my sons.’
“‘Oh,’ said his wife, a jolly woman, ‘he does not do much. The most he does is to go around and look at the work.’
“‘Let him, let him,’ interrupted the daughter, an energetic, pretty girl of perhaps 17 years, who was serving the coffee. ‘He worked hard when he was young.’ And no girl of finer education could have said it with more charming naivete or with the appearance of more unaffected love.[Pg 86]
“After the evening meal the eldest son showed us to our bed-room. ‘Shall I close the window?’ said he. ‘I usually sleep here and always leave it open; it does not harm me, and Dr. Franklin advises it.’
“The next morning when we came down we found the old farmer sitting on the porch reading a paper. Upon the table lay ‘Morse’s Geography,’ ‘The Beauty of the Stars,’ ‘The Vicar of Wakefield,’ and other good books. I have entered into particulars in my description of this family, because we were then only five miles from the home of Gallatin, where the people are too often represented as rough, uncultured, good-for-nothings. It is not necessary to mention that all families here are not as this, yet it is something to find a family such as this, living on this side of the mountains, 300 miles from the sea coast. We called upon Mr. Gallatin, but did not find him at home. Geneva is a little place, but lately settled, at the junction of George creek and the Monongahela.
“From here we went to Uniontown, the capital of Fayette county, where we saw excellent land and Redstone creek.[Pg 87] We dined the following day in Redstone or Brownsville; journeyed to Washington, the capital of the county of the same name, and arrived the following day in Pittsburg.
“Of this city and its magnificent situation between two mighty rivers, the Monongahela and the Allegheny, I shall write you another time. From the window where I now sit, I have a view of the first named river, a half mile long. It is as broad as the Thames in London. The bank on this side is high, but horizontal and level, covered with short grass, such as the sheep love, which reminds me of the rock at Brighthelmstein. It is bordered with a row of locust trees. The bank on the other side is a chain of hills, thickly shaded with oak and walnut trees. The river flows quietly and evenly. Boats are going back and forth; even now one is coming, laden with hides from Illinois. The people on board are wearing clothes made of woolen bed blankets. They are laughing and singing after the manner of the French, yet as red as Indians, and almost the antipodes of their fatherland.
“From here to the mouth of the Ohio it[Pg 88] is 1,200 miles and 3,000 to the mouth of the Mississippi. How enormous! How beautiful it is to see the dominion of freedom and common sense established. To see in these grand surroundings the development of good principle and the struggle toward a more perfect life; to admire the spirit of enterprise as it works toward a great plan, which seems to be in relation to the great plan which nature itself has followed, and at last to anticipate by a secret feeling, the future greatness and prosperity which lies before this growing country.”
Two years later Felix Renick passed this way and includes in his account a vivid picture of the earliest sort of taverns in the West:
“Some of our neighbors who had served in Dunmore’s campaign in 1774, gave accounts of the great beauty and fertility of the western country, and particularly the Scioto valley, which inspired me with a desire to explore it as early as I could make it convenient. I accordingly set out from the south branch of Potomac for that[Pg 89] purpose, I think about the first of October, 1798, in company with two friends, Joseph Harness and Leonard Stump, both of whom have long since gone hence. We took with us what provisions we could conveniently carry, and a good rifle to procure more when necessary, and further prepared ourselves to camp wherever night overtook us. Having a long journey before us, we traveled slow, and reached Clarksburgh the third night, which was then near the verge of the western settlements in Virginia, except along the Ohio river. Among our first inquiries of our apparently good, honest, illiterate landlord, was whether he could tell us how far it was to Marietta [Ohio], and what kind of trace we should have? His reply was, ‘O yes, I can do that very thing exactly, as I have been recently appointed one of the viewers to lay out and mark a road from here to Marietta, and have just returned from the performance of that duty. The distance on a straight line which we first run was seventy-five miles, but on our return we found and marked another line that was much nearer.’ This theory to Mr. Harness[Pg 90] and myself, each of us having spent several years in the study and practice of surveying, was entirely new: we however let it pass without comment, and our old host, to his great delight, entertained us till late in the evening, with a detailed account of the fine sport he and his associates had in their bear chases, deer chases, &c., while locating the road. We pursued our journey next morning, taking what our host called the nearest, and which he also said was much the best route. The marks on both routes being fresh and plain, the crooked and nearest route, as our host called it, frequently crossing the other, we took particular notice of the ground the straight line had to pass over, and after getting through we were disposed to believe that our worthy host was not so far wrong as might be supposed. The straight line crossing such high peaks of mountains, some of which were so much in the sugar-loaf form, that it would be quite as near to go round as over them.
“The first night after leaving the settlement at Clarksburgh, we camped in the woods; the next morning while our horses[Pg 91] were grazing, we drew on our wallets and saddlebags for a snack, that we intended should pass for our breakfast, and set out. We had not traveled far before we unexpectedly came to a new improvement. A man had gone there in the spring, cleared a small field and raised a patch of corn, &c., staying in a camp through the summer to watch it to prevent its being destroyed by the wild animals. He had, a few days before we came along, called on some of his near neighbors on the Ohio, not much more perhaps than thirty miles off, who had kindly came forth and assisted him in putting up a cabin of pretty ample size, into which he had moved bag and baggage. He had also fixed up a rock and trough, and exposed a clapboard to view, with some black marks on it made with a coal, indicating that he was ready and willing to accommodate those who pleased to favor him with a call. Seeing these things, and although we did not in reality need any thing in his way, Mr. Harness insisted on our giving him a call, observing that any man that would settle down in such a wilderness to accommodate travelers ought to[Pg 92] be encouraged. We accordingly rode up and called for breakfast, horse feed, &c. Then let me say that as our host had just ‘put the ball in motion,’ was destitute of any helpmate whatever, (except a dog or two,) he had of course to officiate in all the various departments appertaining to a hotel, from the landlord down to the shoe-black on the one side, and from the landlady down to the dishwash on the other. The first department in which he had to officiate was that of the hostler, next that of the bar keeper, as it was then customary, whether called for or not, to set out a half pint of something to drink. The next, which he fell at with much alacrity, was that of the cook, by commencing with rolled up sleeves and unwashed hands and arms, that looked about as black and dirty as the bears’ paws which lay at the cabin door, part of whose flesh was the most considerable item in our breakfast fare. The first operation was the mixing up some pounded corn meal dough in a little black dirty trough, to which the cleaner, and perhaps as he appeared to think him, the better half of himself, his dog, had free access[Pg 93] before he was fairly done with it, and that I presume was the only kind of cleaning it ever got. While the dodgers were baking, the bear meat was frying, and what he called coffee was also making, which was composed of an article that grew some hundred or one thousand miles north of where the coffee tree ever did grow. You now have the bill of fare that we sat down to, and the manner in which it was prepared; but you must guess how much of it we ate, and how long we were at it. As soon as we were done we called for our bill, and here follows the items: breakfast fifty cents each, horses twenty-five each, half pint of whisky fifty cents. Mr. Harness, who had prevailed on us to stop, often heard of the wilderness hotel, and whenever mentioned, he always had some term of reproach ready to apply to the host and the dirty breakfast, though we often afterwards met with fare somewhat similar in all respects.
“We camped two nights in the woods, and next day got to Marietta where the land office was then kept by general Putnam, and from his office we obtained maps[Pg 94] of the different sections of country we wished to explore.”[30]
The military importance of the Mohawk Valley and strategic portage at Rome, New York, was emphasized in our study of Portage Paths.[31] Throughout the French and Indian War and the Revolutionary struggle the water route to the Hudson from Lake Ontario, by way of the Onondaga, Lake Oneida, Wood Creek, and the Mohawk, was of great moment. But only because it was a route—a thoroughfare; not because the territory through which it coursed was largely occupied or of tremendous value. The French held the lakes and the English were constantly striving for foothold there. When Fort Oswego was built on the present site of Oswego, the first step by the English was taken; the route had been the river route with a portage at Fort Wil[Pg 96]liams (Rome). When Fort Niagara was captured in 1759 by Sir William Johnson, the French were driven from the Lakes; Johnson’s route to Niagara was by Lake Ontario from Oswego. It has been suggested that a volume of this series of monographs should be given to the campaigns of the English against Fort Niagara. These campaigns were made largely on waterways; they left no roads which became of any real importance in our national development. Certain campaigns of the Old French War left highways which have become of utmost significance; only of these routes and their story should this series be expected to treat. Despite the two wars which had created busy scenes in the Mohawk Valley, no landward route connected it with Niagara River and Lake Erie except the Iroquois Trail.[32] No military road was built through the “Long House of the Iroquois.” To gain the key of the western situation—Niagara—the common route was to Oswego. There were local roads along the lake shore, and these were used [Pg 99] more or less by the troops. In the Revolution no American general could get beyond Fort Stanwix by land. Leger himself came up the Oswego River to join Burgoyne.
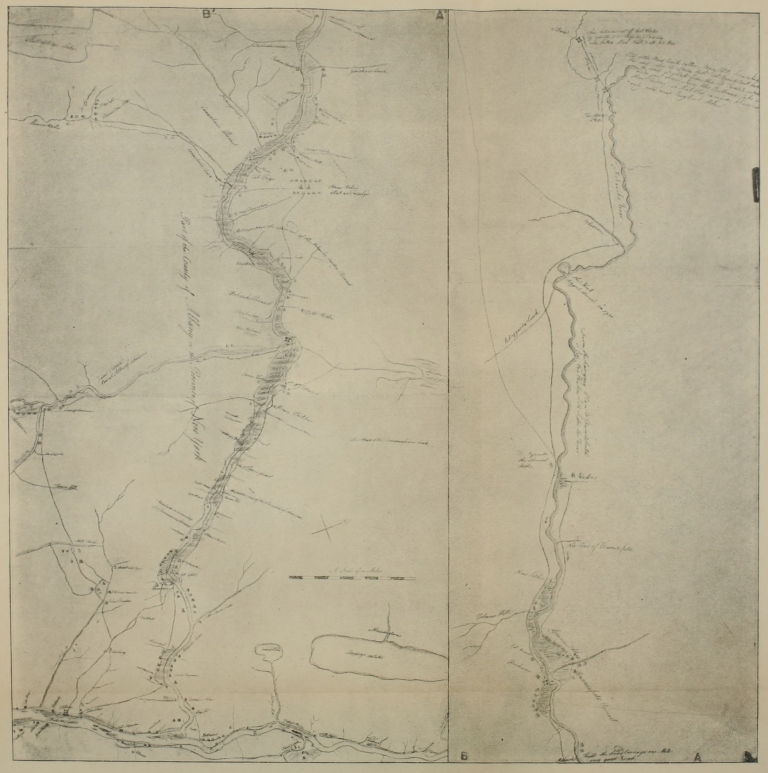
Click here for larger image size
Part of a “Map of the Route between Albany and Oswego”(Parts AA´ and BB´ belong opposite)
[Drawn about 1756; from original in British Museum]
As a consequence, the interior of New York was an almost unexplored wilderness at the end of the Revolution in 1783. With the opening of the Genesee country by the various companies which operated there, a tide of immigration began to surge westward from the upper Mohawk along the general alignment of the old-time Iroquois Trail. Utica sprang up on the site of old Fort Schuyler, and marked the point of divergence of the new land route of civilization from the water route.[33] This was about 1786. In 1789 Asa Danworth erected his salt works at Bogardus Corners, now the city of Syracuse. Geneva, Batavia, and Buffalo mark the general line of the great overland route from Utica and Syracuse across New York. It followed very closely the forty-third meridian, dropping somewhat to reach Buffalo.
The Great Genesee Road, as it was early[Pg 100] known, began at old Fort Schuyler, as a western extremity of the Mohawk Valley road and later turnpike, and was built to the Genesee River by a law passed March 22, 1794. In 1798 a law was passed extending it to the western boundary of the state. It was legally known as the Great Genesee Road and the Main Genesee Road until 1800. In that year the road passed into the hands of a turnpike company the legal name of which was “The President and Directors of the Seneca Road Company.” The old name clung to the road however, and on the map here reproduced we find it called the “Ontario and Genesee Turnpike Road.” It forms the main street of both the large cities through which it passes, Syracuse and Utica, and in both it is called “Genesee Street.”
The first act of legislation which created a Genesee Road from an Indian trail read as follows:
“Be it enacted by the People of the State of New York, represented in Senate and Assembly That Israel Chapin, Michael Myer, and Othniel Taylor shall be and hereby are appointed commissioners for the purpose[Pg 101] of laying out and improving a public road or highway to begin at Old Fort Schuyler on the Mohawk river and to run from thence in a line as nearly straight as the situation of the country will admit to the Cayuga Ferry in the county of Onondaga or to the outlet of the Cayuga lake at the discretion of the said commissioners and from the said outlet of the Cayuga lake or from the said Cayuga Ferry as the same may be determined on by the said commissioners in a line as nearly straight as the situation of the country will admit to the town of Canadaquai and from thence in a line as nearly straight as possible to the settlement of Canawagas on the Genesee river.
“And be it further enacted That the said road shall be laid out six rods wide, but it shall not be necessary for the said commissioners to open and improve the same above four rods wide in any place thereof. And the whole of the said road when laid out, shall be considered as a public highway and shall not be altered by the commissioners of any town or country [county?] through which the same shall run.[Pg 102]
“And be it further enacted That the treasurer of this State shall pay to the said commissioners or any two of them a sum or sums of money not exceeding in the whole the sum of six hundred pounds out of the monies in the treasury which have arisen or may arise from the sale of military lotts to be laid out and expended towards the opening and improving that part of the said road passing through the military lands.
“And be it further enacted That for the purpose of laying out opening and improving the remainder of the said road, the said treasurer shall pay unto the said commissioners or any two of them out of any monies in the treasury not otherwise appropriated at the end of the present session of the legislature a sum not exceeding fifteen hundred pounds which said sum shall be by them laid out and expended in making or improving the remainder of the said road as aforesaid. Provided that no larger proportion of the said sum of fifteen hundred pounds shall be appropriated towards the opening and improving of the said road in the county of Ontario then in the county of Herkemer.[Pg 103]
“And be it further enacted That it shall and may be lawful to and for the said commissioners or any two of them to improve the said road by contract or otherwise as to them may appear the most proper.
“And be it further enacted That where any part of the said road shall be laid out through any inclosed or improved lands the owner or owners thereof shall be paid the value of the said lands so laid out into an highway with such damages as he, she or they may sustain by reason thereof which value and damages shall be settled and agreed upon by the said commissioners or any two of them and the parties interested therein, and if they cannot agree, then the value of the lands and damages shall be appraised by two justices of the peace, on the oaths of twelve freeholders not interested in paying or receiving any part of such appraisement, otherwise than in paying their proportion of the taxes for the contingent charges of the county which freeholders shall be summoned by any constable not otherwise interested than as aforesaid, by virtue of a warrant to be issued by the said two justices of the peace[Pg 104] for that purpose, and the whole value of the said lands so laid out into an highway, and damages together with the costs of ascertaining the value of the said damages of the county in which the said lands shall be situated are levied collected and paid.
“And be it further enacted That each of the said commissioners shall be entitled to receive for their services the sum of sixteen shillings for every day they shall be respectively employed in the said business to be paid by the respective counties in which they shall so be employed which sums shall be raised levied and paid together with and in the same manner as the necessary and contingent charges of such county are raised levied and paid and that the said commissioners shall account with the auditor of this State for the monies they shall respectively receive from the treasurer of this State by virtue of this act on or before the first day of January one thousand seven hundred and ninety six.”[34]
A law entitled “An act appropriating monies for roads in the county of Onondaga[Pg 105] and for other purposes therein mentioned,” passed April 11, 1796, contained the following concerning the Genesee Road:
“And be it further enacted That the said commissioners shall and they are hereby strictly enjoined to expend two thousand dollars of the said monies in repairing the highway and bridges thereon heretofore directed to be laid out by law and now commonly called the Great Genesee road from the eastern to the western bounds of the said county of Onondaga and the residue of the money aforesaid to expend in the repair of such highways and the bridges thereon in the said county as will tend most extensively to benefit and accommodate the inhabitants thereof.
“And be it further enacted That it shall be the duty of the said commissioners and they are hereby strictly enjoined to cause all and every bridge which shall be constructed under their direction over any stream to be raised at least three feet above the water at its usual greatest height in the wettest season of the year and to construct every such bridge of the most durable and largest timber which can be[Pg 106] obtained in its vicinity, and that wherever it can conveniently be done the road shall be raised in the middle so as to enable the water falling thereon freely to discharge therefrom and shall pursue every other measure which in their opinion will best benefit the public in the expenditure of the money committed to them.”[35]
In an act, passed April 1, 1796, supplementary to an “Act for the better support of Oneida, Onondaga and Cuyuga Indians ...”, it was ordered that from the proceeds of all sales of lands bought of the Indians the surveyor-general should pay £500 to the treasurer of Herkimer County and a like amount to the treasurer of Onondaga County; this money was ordered to be applied to “mending the highway commonly called the Great Genesee Road and the bridges thereon.”[36]
A law of the year following, 1797, affords one of the interesting uses of the lottery in the development of American highways. It reads:
“Whereas it is highly necessary, that[Pg 107] direct communications be opened and improved between the western, northern and southern parts of this State. Therefore
“Be it enacted by the People of the State of New York, represented in Senate and Assembly, That for the purpose of opening and improving the said communications, the managers herein after named shall cause to be raised by three successive lotteries of equal value, the sum of forty-five thousand dollars. That out of the neat [net?] proceeds of the first lottery the sum of eleven thousand seven hundred dollars, and out of the neat proceeds of the third lottery, the further sum of two thousand two hundred dollars shall be and hereby is appropriated for opening and improving the road commonly called the Great Genesee road, in all its extent from Old Fort Schuyler in the county of Herkimer to Geneva in the county of Ontario....”[37]
The western movement to Lake Erie became pronounced at this time; the founders of Connecticut’s Western Reserve under General Moses Cleaveland emigrated in 1796. The promoters of the Genesee[Pg 108] country were advertising their holdings widely. The general feeling that there was a further West which was fertile, if not better than even the Mohawk and Hudson Valleys, is suggested in a law passed March 2, 1798, which contained a clause concerning the extension of the Genesee Road:
“And be it further enacted That the commissioner appointed in pursuance of the act aforesaid, to open and improve the main Genessee road, shall and he is hereby authorized and empowered to lay out and continue the main Genessee road, from the Genessee river westward to the extremity of the State. Provided nevertheless, that none of the monies appropriated by the said act shall be laid out on the part of the road so to be continued; and provided also that the said road shall be made at the expense of those who may make donations therefor.”[38]
The mania which swept over the United States between 1790 and 1840 of investing money in turnpike and canal companies was felt early in New York. The success of the[Pg 109] Lancaster Turnpike in Pennsylvania was the means of foisting hundreds of turnpike-road companies on public attention and private pocket-books. By 1811, New York State had at least one hundred and thirty-seven chartered roads, with a total mileage of four thousand five hundred miles, and capitalized at seven and a half millions.
It is nothing less than remarkable that this thoroughfare from the Mohawk to Lake Erie should have been incorporated as a turnpike earlier in point of time than any of the routes leading to it (by way either of the Mohawk Valley or Cherry Valley) from Albany and the East. The Seneca Road Company was incorporated April 1, 1800. The Mohawk Turnpike and Bridge Company was incorporated three days later. The Cherry Valley routes came in much later.
The Genesee Road was incorporated by the following act, April 1, 1800:
“An act to establish a turnpike road company for improving the State road from the house of John House in the village of Utica, in the county of Oneida, to the village of Cayuga in the county of Cayuga,[Pg 110] and from thence to Canadarque in the county of Ontario.
“Be it enacted by the People of the State of New York represented in Senate and Assembly That Benjamin Walker, Charles Williamson, Jedediah Sanger and Israel Chapin and all such persons as shall associate for the purpose of making a good and sufficient road in the form and manner herein after described from the house of John House ... observing as nearly the line of the present State [Genesee] road as the nature of the ground will allow, shall be and are hereby made a corporation and body politic in fact and in name, by the name of ‘The President and Directors of the Seneca Road Company’....”[39]
The road was to be under the management of nine directors and the capital stock was to be two thousand two hundred shares worth fifty dollars each. The directors were empowered to enter upon any lands necessary in building the road, specifications being made for appraisal of damages. The road was to “be six rods in width ... cleared of all timber except[Pg 111]ing trees of ornament, and to be improved in the manner following, to wit, in the middle of the said road there shall be formed a space not less than twenty four feet in breadth, the center of which shall be raised fifteen inches above the sides, rising towards the middle by gradual arch, twenty feet of which shall be covered with gravel or broken stone fifteen inches deep in the center and nine inches deep on the sides so as to form a firm and even surface.”
Tollgates were to be established when the road was in proper condition every ten miles; the rates of toll designated in this law will be of interest for comparative purposes:
Tolls in 1800 on Seneca Turnpike, New York
| Wagon, and two horses | .12½ |
| Each horse additional | .03 |
| Cart, one horse | .06 |
| Coach, or four wheeled carriage, two horses | .25 |
| Each horse additional | .03 |
| Carriage, one horse | .12½ |
| Each horse additional | .06 |
| Cart, two oxen | .08 |
| Each yoke additional | .03 |
| Saddle or led horse | .04 |
| Sled, between December 15 and March 15 | .12½ |
| Score of cattle | .06 |
| Score of sheep or hogs | .03 |
The old Genesee Road passed through as romantic and beautiful a land as heart could wish to see or know; but the road itself was a creation of comparatively modern days, in which Seneca and Mohawk were eliminated factors in the problem. Here, near this road, a great experiment was made a few years after its building, when a canal was proposed and dug, amid fears and doubts on the part of many, from Albany to Buffalo. One of the first persons to advocate a water highway which would eclipse the land route, sent a number of articles on the subject to a local paper, whose editor was compelled to refuse to print more of them, because of the ridicule to which they exposed the paper! Poor as the old road was in bad weather, people could not conceive of any better substitute.
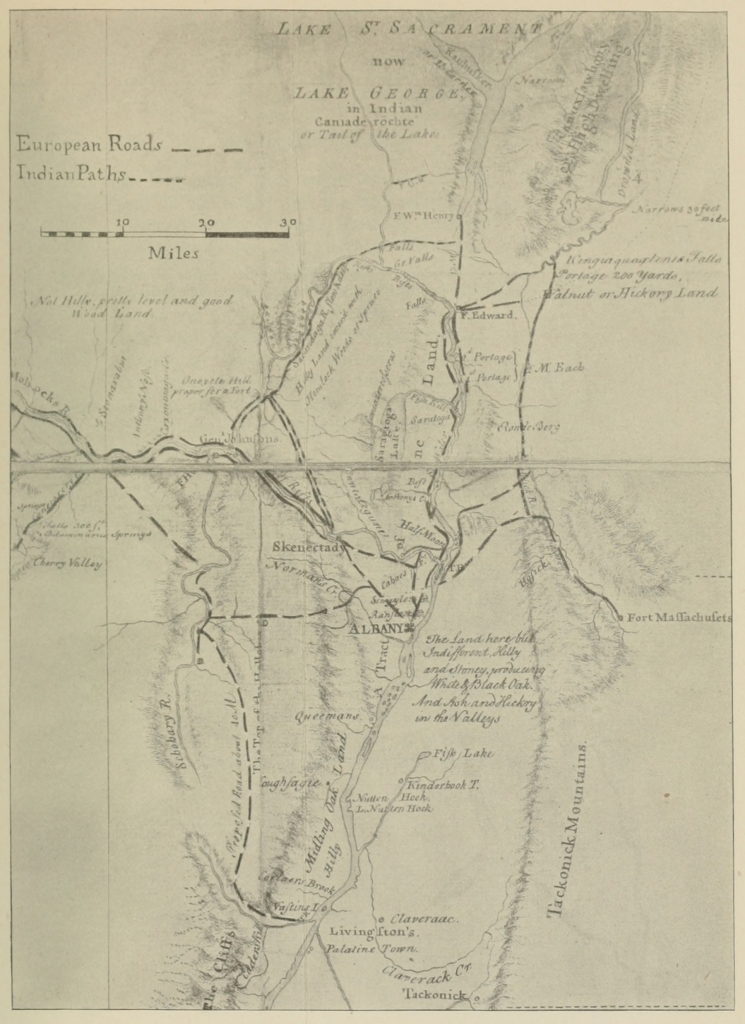
Click here for larger image size
Part of a “Map of the Grand Pass from New York to Montreal ... by Thos. Pownall”[Drawn about 1756; from original in British Museum]
When the Erie Canal was being built, so poor were the roads leading into the region traversed by the canal, that contractors were compelled to do most of their hauling in winter, when the ground was frozen and sleds could be used on the snow. Among the reasons given—as we shall see in a later monograph of this series—for delays [Pg 115] in completing portions of the canal, was that of bad roads and the impossibility of sending heavy freight into the interior except in winter; and a lack of snow, during at least one winter, seriously handicapped the contractors. But when the Erie Canal was built, the prophecies of its advocates were fulfilled, as the rate per hundred-weight by canal was only one-tenth the rate charged by teamsters on the Genesee Road. The old “waggoners” who, for a generation, had successfully competed with the Inland Lock Navigation Company, could not compete with the Erie Canal, and it was indeed very significant that, when Governor Clinton and party made that first triumphal journey by canal-boat from Buffalo to Albany and New York—carrying a keg of Lake Erie water to be emptied into the Atlantic Ocean—they were not joyously received at certain points, such as Schenectady, where the old methods of transportation were the principal means of livelihood for a large body of citizens. How delighted were the old tavern-keepers in central New York with the opening of the Erie Canal, on whose boats immigrants[Pg 116] ate and slept? About as happy, we may say, as were the canal operators when a railway was built, hurrying travelers on at such a rapid pace that their destinations could be reached, in many cases, between meals!
Yet until the railway came, the fast mail-stages rolled along over the Genesee Road, keeping alive the old traditions and the old breed of horses. Local business was vastly increased by the dawning of the new era; society adapted itself to new and altered conditions, and the old days when the Genesee Road was a highway of national import became the heritage of those who could look backward and take hope for the future, because they recognized better the advances that each new year had made.
Among the many records of travelers on the famous Genesee Road, that of Timothy Bigelow, as given in his Journal of a Tour to Niagara Falls in the Year 1805,[40] approaches perhaps most nearly to the character of a description of the old highway which should be presented here:
“July 14th. We proceeded [from Albany] to Schenectady to breakfast, fifteen miles, Beale’s tavern; a good house. A new turnpike is making from Albany to this place; it is constructed in a very durable manner, with a pavement covered with hard gravel. That part which is completed is now an excellent road; the remainder will soon be equally good. It was not disagreeable to us to be informed that this road, and indeed all the other turnpikes, and most other recent works which we met[Pg 118] with, which required uncommon ingenuity or labor, were constructed by Yankees.
“Schenectady seems not to be a word fitted to common organs of speech. We heard it pronounced Snacketady, Snackedy, Ksnackidy, Ksnactady, Snackendy, and Snackady, which last is much the most common. To Ballston, Bromeling’s, sixteen miles; a most excellent house. We found here about forty guests, but understood there were upwards of two hundred at Aldrich’s, McMasters’s, and the other boarding-houses near. Bromeling himself has accommodations in the first style for one hundred and thirty persons.
“We met with but few people here from Massachusetts. Mr. Henry Higginson and his wife, Mr. Bingham, the bookseller, and his family, were all we knew. The mineral water was not agreeable to us all upon the first experiment; but with others, and myself in particular, it was otherwise. It is remarkably clear and transparent; the fixed air, which is continually escaping from it, gives it a sparkling appearance, and a lively and full taste, not unlike to that of brisk porter or champagne wine,[Pg 119] while one is actually drinking.... We slept at Beals’s. July 17th, we took the western stage in company with a Mr. Row, a gentleman from Virginia, who was about to engage in trade at Geneva, on the Seneca Lake. We crossed over to the north side of the Mohawk soon after setting out, to Schwartz’s (still in Schenectady), a poor house, seven miles; thence to Pride’s in Amsterdam, nine miles. Pride’s is a handsome limestone house, built about fifty years since, as we were informed, by Sir William Johnson, for his son-in-law, Guy Johnson.... To Abel’s in Amsterdam, situated on Trapp’s Hill, opposite to the mouth of Schoharie River and the old Fort Hunter, to dine. The prospect to the south-west is extensive and romantic, exhibits an agreeable mixture of hills and plains, diversified with extensive forests almost in a state of nature, and cultivated fields scarce less extensive, now covered with a rich harvest of ripening wheat. The prospect was the principal thing which we found in this place to recommend it. The tavern is a poor one, and our dinner of course was[Pg 120] miserable. Four miles to Shepard’s, in Canajoharie, to sleep.... The Mohawk in many places was shoal, and interrupted with so many islands and sand-banks that we were often at a loss to conceive how loaded boats could pass, and yet we saw several going up-stream with heavy loads.... July 18th. To Carr’s at Little Falls, to breakfast, twenty miles; a very good house. In this stage, we passed the East Canada Creek. Observed for the very first time the cypress-tree. The gloomy, melancholy air of this tree, and the deep shade which it casts, resulting from the downward direction of its branches, as well as the form and color of its leaves, have very properly marked it out as emblematical of mourning.
“On approaching the Little Falls, we observed undoubted marks of the operation of the water on rocks, now far out of their reach, particularly the round holes worn out [by] pebbles kept in a rotatory motion by the current, so common at all falls. It is certain that heretofore the falls must have been some ways further down stream, and have been much greater than they[Pg 121] now are, and that the German flats, and other low grounds near the river above, must have been the bed of a lake. The falls occupy about half a mile. In some spots, the river is so crowded between rocks, that one might almost pass across it; in most places, however, it is broken into a number of streams by irregular masses of limestone rock. There is here a commodious canal for the passage of boats cut round these falls. The whole fall is fifty-four feet; and there are five locks, in each of which the fall is ten feet, besides the guard-lock, where it is four. The locks are constructed of hewn stone, and are of excellent workmanship; they are almost exactly upon the construction of those at the head of Middlesex canal. Most of the buildings in the neighborhood, as well as two beautiful bridges over the canal here, are also of limestone. Carr and his wife are from Albany, and are agreeable and genteel people.
“To Trowbridge’s Hotel, in Utica, to dine. The house is of brick, large, commodious, and well attended. We found good fare here; in particular, excellent[Pg 122] wine. From Little Falls to this is twenty-two miles. In this stage, we passed the German flats, an extensive and well-cultivated tract of internal land on both sides the Mohawk. The town of German Flats is on the south of the town of Herkimer, opposite thereto, on the north side of the river. Notwithstanding the celebrity of this spot for the excellence of its soil, we thought it not equal to that on Connecticut River. Having passed the West Canada Creek, the hills on both sides the river seem to subside, and open to the view an extensive and almost unbounded tract of level and fertile country, though of a much newer aspect than any we had seen before.
“At Utica, we passed over to the southern side of the Mohawk. The river here is about the size of the Nashua, and from this place bends off to the north-west. We happened to pass the bridge as a batteau was coming up to a store at the end of it, to discharge its cargo. The water was so shoal that the batteau grounded before it could be brought to its proper place. A pair of horses were attached to its bows, and it was not without the assistance of [Pg 125] several men, added to the strength of the horses, that it was got up to the landing-place at last.
“Morality and religion do not seem to have much hold of the minds of people in this region. Instances of rudeness and profanity are to be met with in almost every place, but the people engaged in unloading the batteau were much more extravagantly and unnecessarily profane than is common. Several persons also, whom I saw at Little Falls this morning, told me that they knew full well that Adam could not have been the first man, or that he must have lived much longer ago than the Scriptures declare, because they said it must be more than five thousand years for the Mohawk to have broken through the rocks, as it has done at those falls.
“Utica was begun to be settled sixteen years ago, and is now a little city, and contains several elegant dwelling-houses, some of which are of brick, and a few of stone, together with a great number of stores and manufactories of different kinds. The Lombardy poplar-tree is cultivated here in[Pg 126] great abundance. The facility of transportation by means of the Mohawk and Hudson Rivers on one side, and Wood Creek, Oneida, and Ontario Lakes on the other, together with the extraordinary fertility of the adjacent country, must at no great distance of time make Utica a place of great business and resort, and of course its population must rapidly increase. Moses Johnson, a broken trader, late of Keene, now of Manlius, a little above this place, whom we saw at Trowbridge’s, spoke of this country as not favorable for traders, and that a very few stores of goods would overstock the market. It is natural, however, for people in his situation to ascribe their misfortunes to anything rather than their own imprudence or misconduct, which others would probably consider as the true cause of them. Mr. Charles Taylor and his father, whom we had overtaken at Shepard’s, we left at Utica.
“July 19th. To Laird’s in Westmoreland, to breakfast, eleven miles; a very good house. Our breakfast here was garnished with a dish of excellent honey.[Pg 127] Every thing in and about the house was neat, and we were particularly struck with the genteel and comely appearance of two young ladies, daughters of our landlord, one of whom, we were told, had attended a ball in the neighborhood, I think at Paris, the evening before. This stage was over a tract of very fertile country, nearly level, but a little ascending; the growth was mostly of rock-maple and lime-tree. We passed a creek in New Hartford, called Sawguet, or Sogwet, or Sacada [Sauquoit], and another in a corner of Paris called Kerry, or Riscana, say Oriskany. The whole country from Utica to this place is thickly settled. The houses are mostly well built, and many of them handsome; very few log houses to be seen. Young orchards are numerous and thrifty, and Lombardy poplars line the road a great part of the way; and yet we saw not a single field which had not the stumps of the original forest trees yet remaining in it. Honey is sent from hence to Lake Ontario, in barrels.
“To Shethar’s in Sullivan, eighteen miles, to dine; a good tavern. The face[Pg 128] of the country is not so level here as about Utica, though it cannot be called hilly, even here. In addition to the forest trees which we had before seen, we here found the shag-bark nut tree in abundance. In this stage, we passed through the Oneida Indian village.... In this stage, we also passed the Skanandoa Creek, the first water we met with which discharges itself into the ocean by the St. Lawrence, as the Oriskany was the last which pays tribute to the Hudson.
“We next passed the Oneida Creek, which unites with the Skanandoa. The earth in some places here is of the same color with that on Connecticut River, where the red freestone is found. In the Oneida village, the fields are free from stumps, the first to be met that are so from Utica to this place.... To Tyler’s in Onondaga Hollow, to sleep, twenty-one miles. The last sixteen miles are over a very hilly country; the Canaseraga Mountain, in particular, is four or five miles over, and very steep....
“The country, as we approached Onondaga Hollow, we found had been longer[Pg 129] settled than nearer the Oneida village, because the last cession of the Oneidas on the west, and immediately contiguous to their present reservation, was made but six or eight years ago, whereas the country to the westward of that had begun to be settled some time before. The town of Manlius, in particular, has the appearance of a flourishing settlement. This town is the first in the Military Tract, which is the lands given by the State of New York as a gratuity to the officers and soldiers of their line in the Revolutionary Army. As we were descending into the Onondaga Hollow, we saw to the north-westward the Salina or Onondaga Lake....
“The Onondaga Creek, which is of a convenient size for a mill-stream, runs along the Hollow from south to north, as do all the other streams in this country. This creek passes near the celebrated Onondaga salt springs, which are situated about five or six miles northward from Tyler’s.... July 20th. Rose at half past two o’clock, and proceeded to Andrew’s, at Skaneateles, to breakfast, sixteen miles; a good tavern. The country[Pg 130] is still hilly, but very fertile. The soil is deep,—a mixture of loam and clay. The roads here must be very bad in wet weather. It rained last night for the first time since we commenced our journey; and the horses’ feet, in consequence thereof, slipped as if they were travelling on snow or ice.
“Rising out of Onondaga Hollow is a long and very steep hill. The road is constructed on the southern side of a precipice, in such a manner that, as you approach the top of the hill, you have a tremendous gulf on your left hand, at the bottom of which you hear the murmur of a brook fretting among the rocks, as it is passing on toward the Onondaga Creek, which it joins in the Hollow. There is a kind of railing or fence, composed of logs secured with stakes or trees, which is all that prevents the passenger, and even the road itself, from falling to the bottom of the gulf. On the hill we found the embryo of a village. A court-house is already built, and the frame of a hotel is raised. The hotel, we were told, is to be kept by one Brunson. It is an[Pg 131] accommodation much needed by travellers on this road.
“To Harris’s in Cayuga, fifteen miles, to dine. We here had an excellent dinner of beefsteaks. Mr. Harris told us that they could keep beef fresh four or five days, in hot weather, by hanging it upon the trees—wrapping it in flannel—as high as was convenient. Flannel is better to wrap it in than linen.
“The village of Cayuga is small, but pleasant and lively. It is in the township of Marcellus, on the eastern bank of the Cayuga Lake, within one or two miles of its northern extremity. This lake is about two miles wide in general, and almost forty miles long. Nearly north and south from the village, there are about fifteen miles of the lake in sight. The shores are mostly of hard land, except at the northern extremity, where there is a great deal of marsh, which is an unfavorable circumstance for the village, as it is not only disagreeable to the sight, but, I think, also to the smell. There is a wooden bridge across the lake, leading from Cayuga village towards Geneva, one mile long, wanting three[Pg 132] roods. It suffered so much by shocks of the ice last winter, that in some places it is hardly safe to pass it. This forenoon we had passed the outlet of the Owasco Lake, but did not see the lake itself, which we were told was about a mile south of the road. The country hitherto is somewhat uneven, though by no means so much so as near the Onondaga Hollow. The soil, however, is excellent in many places, and is of a reddish color.
“To Powell’s Hotel in Geneva, to sleep, sixteen miles; excellent accommodations. At Harris’s we had met with a Mr. Rees, a gentleman in trade at Geneva, who took passage in the stage with us for that place. From this gentleman, whom we found very intelligent and communicative, we learned many particulars concerning the salt springs, discovered about five years since upon the Cayuga outlet. These springs are about twelve miles below the Cayuga bridge, and are on both sides the outlet: that on the western side is in the township of Galen, and belongs to Mr. Rees and his partner in trade. These springs had long been known to the[Pg 133] Indians, but they had always been reserved in communicating their knowledge of the state of the country to the white settlers. It was not till most or all of those who lived near this outlet had died or moved away, except one, that he mentioned the existence of these springs; and for a reward he conducted some persons to the place where they are situated. The persons to whom he communicated this information endeavored to purchase the favored spot before the owner should be apprised of its inestimable value; but he accidentally obtained a knowledge of his good fortune, and of course refused to sell....
The road from Cayuga to Geneva is for a few miles along the southern or south-eastern side, and the rest along the northern or north-eastern side of the Seneca outlet. The face of the country near the road is more level; but the soil is more sandy and uninviting than we had lately seen, till we approached near to Geneva. The land there is excellent, as we were told it was, through all the tract which extends between the Cayuga and Seneca Lakes. This tract rises in a kind of regu[Pg 134]lar glacis from each lake, so that from the middle of it one can see both. It wants nothing but inhabitants and cultivation to make it an elysium. The Seneca outlet flows into the lower end of the Cayuga Lake. Towards its mouth there is a considerable fall, or rather rapid, which it is contemplated to lock, whereby a water communication will be opened between the two lakes. The stream is about half the size of the Winnipiseogee, and has a bluish-white appearance.
“We were within half a mile of Geneva before we came in sight of the Seneca Lake. This charming sheet of water extends southerly from this place to Catharine Town, forty miles, being from two to four miles wide. There is not a foot of swamp or marsh on its borders, from one extremity to the other; but it is everywhere lined by a clear, gravelly beach, and the land rises from it with a very gentle and graceful ascent in every direction....
“Not far from Geneva are some of the Indian orchards, which were cut down by General Sullivan in his famous expedition, scarce less barbarous than those of the[Pg 135] savages themselves. The trees now growing in these orchards sprouted from the roots of those which were cut down, and therefore grow in clusters, six or seven rising from one root. We saw Indian fields here free from stumps, the only ones which are to the westward of Utica, except those belonging to the Oneidas. We were told that, at this season of the year, the wind at Geneva blows constantly from the south in the forenoon, and from the north in the afternoon. We here quitted the stage, which runs no further than Canandaigua, and hired an open Dutch wagon and driver, and a single horse, to carry us to Niagara.... The turnpike road ends at this place [Canandaigua]. The whole length from Albany is two hundred and six or seven miles: it may properly be called two turnpikes, which join each other at Utica. A project is on foot for still extending the turnpike even to Niagara, a direct course to which would not probably exceed one hundred miles.
“Mr. Rees told us yesterday that he was engaged to proceed to-morrow with certain commissioners to mark out the[Pg 136] course of the road, and that the proprietors will begin to work upon it next year. The road may not be very good property at first, but will probably soon become so, judging from the astonishing rapidity with which this country is settled. It is ascertained that one thousand families migrated hither during the last year, two thirds of whom were from New England.
“To Hall’s in Bloomfield, to sleep, twelve miles; very good house. We had an excellent supper and clean beds. The town of Bloomfield has been settled about fifteen years, and is now in a flourishing state. Here is a handsome new meeting-house with a tasty steeple. The vane on the steeple is rather whimsical. It is a flying angel, blowing a trumpet against the wind.... To Hosmer’s in Hartford, to breakfast, twelve and a half miles. Between Bloomfield and this, we passed through Charleston, which has but recently been reclaimed from the wilderness. It is perfectly flat, the soil is pretty good, though better, and more settled at some distance from the road than near it. The reason of cutting the road where it goes was be[Pg 137]cause the country in that direction was open, when it was first explored, between this place and Lake Ontario, which is but twenty-eight miles distant, or to Gerundegut [now Toronto] Bay, but twenty-two miles....
“Hitherto we have found better roads since we left the turnpike than before, except that the bridges and causeways are mostly constructed with poles. Hosmer, our landlord, is an intelligent man and keeps a good tavern. We had for breakfast good coffee, excellent tea, loaf sugar, mutton chop, waffles, berry pie, preserved berries, excellent bread, butter, and a salad of young onions. I mention the particulars, because some of the articles, or such a collection, were hardly to be expected in such a depth of wilderness.
“To Gansen’s in Southampton, twelve and a half miles, to dine. Within about a mile of Hosmer’s, we passed the Genesee River. The outlet of the Conesus Lake joins this river about a mile above, or to the south. Where we crossed, there is a new bridge, apparently strong and well built; and yet the water last spring under[Pg 138]mined one end of it, so that it has sunk considerably....
“Gansen’s is a miserable log house. We made out to obtain an ordinary dinner. Our landlord was drunk, the house was crowded with a dozen workmen, reeking with rain and sweat, and we were, withal, constantly annoyed with the plaintive and frightful cries and screams of a crazy woman, in the next room. We hastened our departure, therefore, even before the rain had ceased.
“To Russell’s in Batavia, twelve miles, to sleep. One mile from Gansen’s, we crossed Allen’s Creek, at Buttermilk Falls, where there are mills, and five miles further the Chookawoonga Creek, near the eastern transit line of the Holland purchase. This line extends from the bounds of Pennsylvania to Lake Ontario, a distance of near ninety-four miles. So far, the road was the worst of any we had seen; and none can be much worse and be passable for wheels. Within six miles of Batavia, the road is much better, and the land of a good quality, heavily timbered all the way, but especially near the settlement. It[Pg 139] is but three years since this spot was first cleared, and it is now a considerable village. Here is a large building, nearly finished, intended for a court-house, jail, and hotel, under the same roof. The street is perfectly level, and is already a good and smooth road. Here is also an excellent mill, on a large and commodious scale, situated on the Tonawanda Creek, which is the first water we saw which passes over Niagara Falls. Russell’s is a poor tavern. We were told that our sheets were clean, for they had been slept in but a few times since they were washed.
“July 23d. To Luke’s in Batavia, to breakfast, five miles. We intended to have stopped at McCracken’s, one mile short of this, but we were told that we could not be accommodated. The exterior appearance of both houses was very much alike; they are log huts, about twelve feet square. Luke’s consisted of a single room, with a small lean-to behind, which served for a kitchen. It contained scarce any furniture, not even utensils enough to serve us comfortably for breakfast....
“It was but eighteen months since Luke[Pg 140] began a settlement here, and he was the first who made the attempt between Batavia and Vandevener’s, a distance of eighteen miles, though in that distance now there are several huts. Taverns like Luke’s are not uncommon in this vicinity; almost every hut we saw had a sign hung out on a pole or stump, announcing that it was an inn. Perhaps such complete poverty did not exist in them all as we found at Luke’s, yet, judging from external appearances, the difference could not be great.
“We passed the Tonawanda near Batavia court-house, and then kept along its southern bank to this place. The woods are full of new settlers. Axes were resounding, and the trees literally falling about us as we passed. In one instance, we were obliged to pass in a field through the smoke and flame of the trees which had lately been felled and were just fired.
“To Vandevener’s in Willink, thirteen miles. We had intended only to dine here; but by reason of a thunder shower, and the temptation of comfortable accommodations, we concluded not to proceed till next day. Our last stage was through the[Pg 141] Batavia woods, famed for their horrors, which were not abated by our having been informed at Russell’s, that not far from here a white man had lately been killed by the Indians. We found the road much better than we had anticipated; the last four miles were the worst. A little labor would make the road all very good, at least in dry weather. There is another way to come from Batavia here; but it is six miles further, and probably little or no better than this.
“It was but three years since Vandevener began here. He at first built a log house, but he has now a two-story framed house, adjoining that. His whole territory is five hundred acres, one hundred of which he has already got under improvement....
“July 23d. To Ransom’s in Erie, to breakfast, fourteen miles. Ransom came from Great Barrington in Massachusetts, and settled here last September.... The last three miles from Ellicott’s Creek to Ransom’s is a new road cut through a thick wood, and is as bad as any part of the road through the Batavia woods.
“To Crow’s at Buffalo Creek, eight[Pg 142] miles. In this stage, we passed the Four Mile Creek. Half the distance from Ransom’s was over open country, ... in which many young chestnut-trees are just sprouting from the ground. The rest of our way was through a thick wood, where the growth is the same kind as in the interior of Massachusetts....
“From Buffalo we passed along the beach of Lake Erie, to the ferry across its outlet on the Niagara River, at Black Rock, so called, three miles....”
So few writers have paid any attention to the influence of roads in the development of our country that it is a great pleasure to find in Francis Whiting Halsey’s The Old New York Frontier,[41] a chapter on the old Catskill Turnpike; through the kindness of the author it is possible to present here this story of that strategic highway of old New York:
“Before the Revolutionary War something of a road had been cut through the woods from Otsego Lake southward along the Susquehanna, and other primitive roads led to and from the lake; but these highways had almost disappeared during the later years of the war, when Nature had done her effective work of reclamation. The one leading from the lake southward was improved in 1786 as far as Hartwick, and others were speedily taken in hand.[Pg 144] Further down the river efforts were made to establish convenient communication with the Hudson, and out of this grew a road which eventually became the great highway for a large territory. It was called the Catskill Turnpike, and had its terminus on the Susquehanna at Wattles’s Ferry.[41]
“This road, as a turnpike, properly dates from 1802, but the road itself is much older. Its eastern end had been opened long before the Revolution with a terminus in the Charlotte Valley. It seems then to have been hardly more than a narrow clearing through the forest, what farmers call a ‘wood road,’ or frontiersman a ‘tote road.’ It served as a convenient route to the Susquehanna, because much shorter than the older route by the Mohawk Valley. Over this road on horseback in 1769, came Colonel Staats Long Morris and his wife, the Duchess of Gordon.
“After the war demands rose for a better road, and one was soon undertaken[Pg 145] with its terminus at Wattles’s Ferry. This terminus appears to have been chosen because the river here was deep enough to permit the use of ‘battoes’ during the low water that prevailed in summer. By the summer of 1788 the road was in passable condition. Alexander Harper and Edward Paine in February, 1789, declared that they had been to ‘a very great expense in opening the roads from Catskill and the Hudson to the Susquehanna River.’ In the same year a petition was filed for a road ‘from the Ouleout to Kyuga Lake.’ The road to Cayuga Lake (Ithaca) made slow progress, and in 1791 General Jacob Morris addressed to Governor Clinton a letter which shows that it was then still to be undertaken. Early in 1790 the State had taken the road to Catskill in charge. In August, G. Gelston made up from surveys a map from Catskill ‘running westerly to the junction of the Ouleout Creek with the Susquehanna River.’ The country had been previously explored for the purpose by James Barker and David Laurence.[42][Pg 146]
“In 1791 Sluman Wattles charged his cousin, Nathaniel Wattles, £4, 6s. for ‘carting three barrells from your house to Catskill,’ £1 for ‘five days work on the road,’ and 15 shillings for ‘inspecting road.’ Besides Nathaniel Wattles, Menad Hunt was interested in the work, and in 1792 the two men appealed to the state to be reimbursed for money paid out above the contract price.[43] During this year the father of the late Dr. Samuel H. Case, of Oneonta, emigrated to the upper Ouleout from Colchester, Conn., with his seven brothers. They drove cattle and sheep ahead of them, and consumed eight days in making the journey from the Hudson River. Solomon Martin went over the road in the same year, using Sluman Wattles’s oxen, for which he was charged £1, 17s. He went to Catskill, and was gone fifteen days. This road was only twenty-five feet wide. In 1792 a regular weekly mail-route was established over it.
“These are among the many roads which were opened in the neighborhood before the century closed—before the Catskill[Pg 147] Turnpike, as a turnpike, came into existence. Nearly every part of the town of Unadilla, then embracing one-third of Otsego County, had been made accessible before the year 1800. The pioneers had taken up lands all through the hill country. But the needs of the settlers had not been fully met. All over the State prevailed similar conditions. The demands that poured in upon State and town authorities for road improvements became far in excess of what could be satisfied. Everywhere fertile lands had been cleared and sown to grain, but the crops were so enormous that they could neither be consumed at home nor transported to market elsewhere. Professor McMaster says that ‘the heaviest taxes that could have been laid would not have sufficed to cut out half the roads or build half the bridges that commerce required.
“Out of this condition grew the policy of granting charters to turnpike companies, formed by well-to-do land-owners, who undertook to build roads and maintain them in proper condition for the privilege of imposing tolls. Men owning land and[Pg 148] possessed of ready money, were everywhere eager to invest in these enterprises. They not only saw the promise of dividends, but ready sales for their lands. At one time an amount of capital almost equal to the domestic debt of the nation when the Revolution closed was thus employed throughout the country. By the year 1811, no fewer than 137 roads had been chartered in New York State alone, with a total length of 4,500 miles and a total capital of $7,500,000. About one-third of this mileage was eventually completed.
“Eight turnpikes went out from Albany, and five others joined Catskill, Kingston, and Newburg with the Susquehanna and Delaware rivers. The earliest of these five, and one of the earliest in the State, was the Catskill and Susquehanna turnpike, that supplanted the primitive State road to Wattles’s Ferry. The old course was changed in several localities, the charter permitting the stockholders to choose their route. Among the names in the charter were John Livingston, Caleb Benton (a brother of Stephen Benton), John Kortright, Sluman Wattles, and Solomon[Pg 149] Martin. The stock was limited to $12,000 in shares of $20 each.
“The road ran through lands owned by the stockholders. Little regard was had for grades, as travellers well know. The main purpose was to make the land accessible and marketable. The road was completed in 1802, and soon became a famous highway to Central New York, and the navigable Susquehanna, and so remained for more than a quarter of a century. It was in operation four years earlier than the Great Western Turnpike, connecting Albany with Buffalo and running through Cherry Valley. Spafford in 1813 described it as ‘the Appian Way turnpike,’ in which it seems the pride felt in it, likened as it thus was to one of the best roads ever built by man—that Roman highway which still does service after the lapse of more than 2,000 years. In one sense this turnpike was like a Roman road: it followed straight lines from point to point regardless of hills, obstacles being squarely faced and defied by these modern men as by the old Romans.
“Ten toll-gates were set up along the[Pg 150] line, with the rates as follows: for twenty sheep and hogs, eight cents; for twenty horses and cattle, twenty cents; for a horse and rider, five cents; for a horse and chaise, twelve and one-half cents; for a coach or chariot, twenty-five cents; for a stage or wagon, twelve and one-half cents. In 1804, Caleb Benton, who lived in Catskill, was president of the corporation, and in 1805 the stage business of the road was granted as a monopoly to David Bostwick, Stephen Benton, Lemuel Hotchkiss, and Terence Donnelly. Two stages were to be kept regularly on the road, the fare to be five cents per mile. A stage that left Catskill Wednesday morning reached Unadilla Friday night, and one that left Unadilla Sunday reached Catskill Tuesday. The most prosperous period for the road was the ten years from 1820 to 1830.
“Two years after the road was built, Dr. Timothy Dwight, President of Yale College, during one of his regular vacation journeys, passed over it and stopped at Unadilla. He has left a full record of the journey. Dr. Dwight, accustomed long to the comforts of life in New England, had[Pg 151] no sooner crossed the State line from Massachusetts to New York than he observed a change. The houses became ordinary and ill repaired, and very many of them were taverns of wretched appearance.
“For sixteen or eighteen miles, he saw neither church nor school-house. Catskill contained about 100 houses, and much of the business was done by barter. The turnpike to the Susquehanna he described as a ‘branch of the Greenwood turnpike from Hartford to Albany, commencing from Canaan in Connecticut and passing to Wattles’s Ferry on the Susquehanna. Thence it is proposed to extend it to the county of Trumbull on the southern shore of Lake Erie.’ The road he thought ‘well made.’
“Connecticut families were found settled along the line. Now he came upon ‘a few lonely plantations recently begun upon the road,’ and then ‘occasionally passed a cottage, and heard the distant sound of an axe and of a human voice. All else was grandeur, gloom and solitude.’ At last after many miles of riding he reached a[Pg 152] settlement ‘for some miles a thinly built village, composed of neat, tidy houses,’ in which everything ‘indicated prosperity.’ This was Franklin. Coming down the Ouleout, the country, he said, ‘wore a forbidding aspect, the houses being thinly scattered and many of them denoted great poverty.’
“When Dr. Dwight reached Wattles’s Ferry, the more serious trials of his journey began. All the privations of life in a new country which he had met on the road from Catskill at last had overtaxed his patience, and he poured forth his perturbed spirit upon this infant settlement. When he made a second visit a few years later he liked the place much better. His first impressions are chronicled at some length. He says:
“‘When we arrived at the Susquehanna we found the only inn-keeper, at the eastern side of the river, unable to furnish us a dinner. To obtain this indispensable article we were obliged therefore to cross the river. The ferry-boat was gone. The inhabitants had been some time employed in building a bridge, but it was un[Pg 153]finished and impassable. There was nothing left us, therefore, but to cross a deep and rapid ford. Happily the bottom was free from rocks and stones.’
“Dr. Dwight appears to have found no satisfactory stopping-place in Unadilla, and proceeds to say:
“‘About four miles from the ferry we came to an inn kept by a Scotchman named Hanna. Within this distance we called at several others, none of which could furnish us a dinner. I call them inns because this name is given them by the laws of the State, and because each of them hangs out a sign challenging this title. But the law has nicknamed them, and the signs are liars.
“‘It is said, and I suppose truly, that in this State any man who will pay for an inn-keeper’s license obtains one of course. In consequence of this practice the number of houses which bear the appellation is enormous. Too many of them are mere dramshops of no other use than to deceive, disappoint and vex travellers and to spread little circles of drunkenness throughout the State. A traveller after passing from[Pg 154] inn to inn in a tedious succession finds that he can get nothing for his horse and nothing for himself.’
“The remedy he prescribed for this was to license ‘only one inn where there are five or six.’ The evil was general. In 1810 the people of Meredith made a formal and vigorous protest against the growth of intemperance and crime as caused by public houses. There were ten hotels in that town alone, besides a number of distilleries. Many citizens banded themselves in behalf of order and decency, and their protest abounded in an energy of language that would have delighted the soul of Dr. Dwight. Of his further experience at Mr. Hanna’s hotel, he says:
“‘We at length procured a dinner and finding no house at a proper distance where we could be lodged concluded to stay where we were. Our fare was indeed bad enough, but we were sheltered from the weather. Our inn-keeper besides furnishing us with such other accommodations as his home afforded, added to it the pleasures of his company and plainly considered himself as doing us no small favor.[Pg 155] In that peculiar situation in which the tongue vibrates with its utmost ease and celerity, he repeated to us a series of anecdotes dull and vulgar in the extreme. Yet they all contained a seasoning which was exquisite, for himself was in every case the hero of the tale. To add to our amusement, he called for the poems of Allan Ramsay and read several of them to us in what he declared to be the true Scottish pronunciation, laughing incessantly and with great self-complacency as he proceeded.’
“Dr. Dwight remarks that ‘a new turnpike road is begun from the ferry and intended to join the Great Western road either at Cayuga bridge or Canandaigua. This route will furnish a nearer journey to Niagara than that which is used at present.’ We see from this what were the plans of that day, as to the future central highway of New York State. Of Unadilla Dr. Dwight says:
“‘That township in which we now were is named Unadilla and lies in the county of Otsego. It is composed of rough hills and valleys with a handsome collection of inter[Pg 156]vales along the Susquehanna. On a remarkably ragged eminence immediately north-west of the river, we saw the first oaks and chestnuts after leaving the neighborhood of Catskill. The intervening forests were beach, maple, etc. The houses in Unadilla were scattered along the road which runs parallel with the river. The settlement is new and appears like most others of a similar date. Rafts containing each from twenty to twenty-five thousand feet of boards are from this township floated down the Susquehanna to Baltimore. Unadilla contained in 1800 eight hundred and twenty-three inhabitants.’[44]
“On September 27, 1804, Dr. Dwight left Mr. Hanna’s inn and rode through to Oxford. The first two miles of the way along the Susquehanna were ‘tolerably good and with a little labor capable of being excellent.’ He continues:
“‘We then crossed the Unadilla, a river somewhat smaller but considerable longer[Pg 157] (sic) than the Susquehanna proper, quite as deep and as difficult to be forded. Our course to the river was south-west. We then turned directly north along the banks of the Unadilla, and travelling over a rugged hill, passed through a noble cluster of white pines, some of which though not more than three feet in diameter, were, as I judged, not less than 200 feet in height. No object in the vegetable world can be compared with this.’
“Eleven years later, Dr. Dwight again passed over the turnpike on his way to Utica. ‘The road from Catskill to Oxford,’ he said, ‘I find generally bad, as having been long neglected. The first twenty miles were tolerable, the last twenty absolutely intolerable.’ After noting that in Franklin ‘religion had extensively prevailed,’ he wrote:
“‘Unadilla is becoming a very pretty village. It is built on a delightful ground along the Susquehanna and the number of houses, particularly of good ones, has much increased. A part of the country between this and Oxford is cultivated; a considerable part of it is still a wilderness. The[Pg 158] country is rough and of a high elevation.’
“In some reminiscences[45] which my father wrote in 1890, he described the scenes along this road that were familiar to him in boyhood at Kortright—1825 to 1835. The road was then in its most prosperous period. It was not uncommon for one of the hotels, which marked every few miles of the route, to entertain thirty or forty guests at a time. The freight wagons were huge in size, drawn by six and eight horses, and had wheels with wide tires. Stages drawn by four and six horses were continually in use. Not infrequently came families bound for Ohio, where they expected to settle—some of these Connecticut people, who helped to plant the Western Reserve settlements. This vast traffic brought easy prosperity to the people along the turnpike and built up towns and villages. My father records the success of the Rev. Mr. McAuley’s church at Kortright—a place that has now retrograded so that it is only a small hamlet, just capa[Pg 159]ble of retaining a post office. But Mr. McAuley’s church at one time, more than sixty years ago, had five hundred members, and was said to be the largest church society west of the Hudson valley.
“A change occurred with the digging of the Erie Canal and the building of the Erie Railway. Morever, in 1834 was built a turnpike from North Kortright through the Charlotte Valley to Oneonta. The white man having tried a route of his own over the hills, reverted to the route which the red man had marked out for him ages before. Much easier was the grade by this river road, and this fact exercised a marked influence on the fortunes of the settlements along the olden line. Freight wagons were drawn off and sent by the easier way. Stages followed the new turnpike and the country between Wattles’s Ferry and Kortright retrograded as rapidly as it had formerly improved.[46]
“The building of the Catskill Turnpike really led to the founding of Unadilla vil[Pg 160]lage on its present site. It had confined to this point a growth which otherwise would probably have been distributed among other points along the valley. Here was a stopping-place, with a river to be crossed, horses to be changed, and new stages taken, and here had been established the important market for country produce of Noble & Hayes. Unadilla became what might be called a small but thriving inland river port. Here lumber was sawed and here it came from mills elsewhere for shipment along with farm products to Baltimore. Here grain was ground, and here were three prosperous distilleries.
“The building of the turnpike along the Charlotte was not the only blow that came to the western portion of the Catskill Road. Another and permanent one came to the whole length of the turnpike when the Erie[Pg 161] Canal was built, followed later by the Erie Railroad. Otsego County, in 1832, had reached a population of 52,370, but with the Erie Canal in operation it ceased to grow. At the present time the showing is considerably less than it was in 1832, and yet several villages have made large increases, the increase in Oneonta being probably tenfold.
“Contemporary with the Erie Canal was an attempt to provide the Susquehanna with a canal. It became a subject of vast local interest from Cooperstown to the interior of Pennsylvania. The scheme included a railway, or some other method of reaching the Erie Canal from the head of Otsego Lake. Colonel De Witt Clinton, Jr., son of the governor, made a survey as far as Milford, and found that in nine miles there was a fall of thirty feet, and that at Unadilla the fall from the lake was 150 feet, while in 110 miles from the lake it was 350 feet. In 1830 a new survey showed that 144 miles out of 153 were already navigable, the remaining distance requiring a canal. Some seventy locks would be needed and sixty-five dams.[Pg 162] Judge Page, while a member of Congress, introduced a bill to aid slack-water navigation from Cooperstown to tide-water. It was his opinion that the failure of the bill was due to the spread of railroads.
“With the ushering in of the great railroad era, the Susquehanna Valley saw started as early as 1830 many railroad projects which could save it from threatened danger. Their aim was to connect the upper Susquehanna with the Hudson at Catskill, and the Mohawk at Canajoharie. None ever got beyond the charter stage. Strenuous efforts were afterward made to bring the Erie from the ancient Cookoze (Deposit) to the Susquehanna at a point above Oghwaga, but this also failed.
“Indeed it was not until after the Civil War that any railroad reached the headwaters of the Susquehanna; but it was an agreeable sign of the enterprise which attended the men of 1830 and following years that at the period when the earliest railroad in this State, and one of the earliest on this continent, had just been built from Albany to Schenectady, serious projects existed for[Pg 163] opening this valley to the outer world. Even the great Erie project languished long in consequence of business depression. It was not until 1845 that it was completed as far as Middletown, and not until 1851 that it reached Dunkirk.
“Not even to the Erie was final supremacy on this frontier assured, but the upper Susquehanna lands, more than those through which the Erie ran, were doomed to a condition of isolation. Nature itself had decreed that the great route of transportation in New York State was to run where the great trail of the Iroquois for centuries had run—through the Mohawk Valley. Along that central trail from Albany, ‘the Eastern Door,’ to Buffalo, ‘the Western door of the Long House,’ the course of empire westward was to take its way.”
Some of the most interesting descriptions of pioneer traveling are from the racy pages of Charles Dickens’s American Notes, a volume well known to every reader. No description of early traveling in America would be complete, however, without including a number of these extremely witty, and, in some instances, extremely pathetic descriptions of conditions that obtained in Virginia and Ohio in Dickens’s day. The following description of a negro driver’s manipulation of reins, horses, and passengers may be slightly exaggerated, but undoubtedly presents a typical picture of southern stage driving:
“Soon after nine o’clock we come to Potomac Creek, where we are to land; and then comes the oddest part of the journey. Seven stage-coaches are preparing[Pg 165] to carry us on. Some of them are ready, some of them are not ready. Some of the drivers are blacks, some whites. There are four horses to each coach, and all the horses, harnessed or unharnessed, are there. The passengers are getting out of the steamboat, and into the coaches, the luggage is being transferred in noisy wheel-barrows; the horses are frightened, and impatient to start; the black drivers are chattering to them like so many monkeys; and the white ones whooping like so many drovers: for the main thing to be done in all kinds of hostlering here, is to make as much noise as possible. The coaches are something like the French coaches, but not nearly so good. In lieu of springs, they are hung on bands of the strongest leather. There is very little choice or difference between them; and they may be likened to the car portion of the swings at an English fair, roofed, put upon axle-trees and wheels, and curtained with painted canvas. They are covered with mud from the roof to the wheel-tire, and have never been cleaned since they were first built.
“The tickets we have received on board[Pg 166] the steamboat are marked No. 1, so we belong to coach No. 1. I throw my coat on the box, and hoist my wife and her maid into the inside. It has only one step, and that being about a yard from the ground, is usually approached by a chair: when there is no chair, ladies trust in Providence. The coach holds nine inside, having a seat across from door to door, where we in England put our legs: so that there is only one feat more difficult in the performance than getting in, and that is getting out again. There is only one outside passenger, and he sits upon the box. As I am that one, I climb up; and while they are strapping the luggage on the roof, and heaping it into a kind of tray behind, have a good opportunity of looking at the driver.
“He is a negro—very black indeed. He is dressed in a coarse pepper-and-salt suit excessively patched and darned (particularly at the knees), grey stockings, enormous unblacked high-low shoes, and very short trousers. He has two odd gloves: one of parti-coloured worsted, and one of leather. He has a very short whip, broken in the middle and bandaged up with[Pg 167] string. And yet he wears a low-crowned, broad-brimmed, block hat: faintly shadowing forth a kind of insane imitation of an English coachman! But somebody in authority cries ‘Go ahead!’ as I am making these observations. The mail takes the lead in a four-horse wagon, and all the coaches follow in procession: headed by No. 1.
“By the way, whenever an Englishman would cry ‘All right!’ an American cries ‘Go ahead!’ which is somewhat expressive of the national character of the two countries.
“The first half mile of the road is over bridges made of loose planks laid across two parallel poles, which tilt up as the wheels roll over them: and in the river. The river has a clayey bottom and is full of holes, so that half a horse is constantly disappearing unexpectedly, and can’t be found again for some time.
“But we get past even this, and come to the road itself, which is a series of alternate swamps and gravel-pits. A tremendous place is close before us, the black driver rolls his eyes, screws his mouth up very[Pg 168] round, and looks straight between the two leaders, as if he were saying to himself, ‘We have done this often before, but now I think we shall have a crash.’ He takes a rein in each hand; jerks and pulls at both; and dances on the splashing board with both feet (keeping his seat, of course) like the late lamented Ducrow on two of his fiery coursers. We come to the spot, sink down in the mire nearly to the coach windows, tilt on one side at an angle of forty-five degrees, and stick there. The insides scream dismally; the coach stops; the horses flounder; all the other six coaches stop; and their four-and-twenty horses flounder likewise: but merely for company, and in sympathy with ours. Then the following circumstances occur.
“Black Driver (to the horses). ‘Hi!’
Nothing happens. Insides scream again.
Black Driver (to the horses). ‘Ho!’
Horses plunge, and splash the black driver.
Gentleman inside (looking out). ‘Why, what on airth—’
Gentleman receives a variety of splashes and draws his head in again, without finish[Pg 169]ing his question or waiting for an answer.
Black Driver (still to the horses). ‘Jiddy! Jiddy!’
Horses pull violently, drag the coach out of the hole, and draw it up a bank; so steep, that the black driver’s legs fly up into the air, and he goes back among the luggage on the roof. But he immediately recovers himself, and cries (still to the horses),
‘Pill!’
No effect. On the contrary, the coach begins to roll back upon No. 2, which rolls back upon No. 3, which rolls back upon No. 4, and so on, until No. 7 is heard to curse and swear, nearly a quarter of a mile behind.
Black Driver (louder than before). ‘Pill!’
Horses make another struggle to get up the bank, and again the coach rolls backward.
Black Driver (louder than before). ‘Pe-e-e-ill!’
Horses make a desperate struggle.
Black Driver (recovering spirits). ‘Hi! Jiddy, Jiddy, Pill!’
Horses make another effort.[Pg 170]
Black Driver (with great vigour). ‘Ally Loo! Hi. Jiddy, Jiddy. Pill. Ally Loo!’
Horses almost do it.
Black Driver (with his eyes starting out of his head). ‘Lee, dere. Lee, dere. Hi. Jiddy, Jiddy. Pill. Ally Loo. Lee-e-e-e-e!’
“They run up the bank, and go down again on the other side at a fearful pace. It is impossible to stop them, and at the bottom there is a deep hollow, full of water. The coach rolls frightfully. The insides scream. The mud and water fly about us. The black driver dances like a madman. Suddenly we are all right by some extraordinary means, and stop to breathe.
“A black friend of the black driver is sitting on a fence. The black driver recognizes him by twirling his head round and round like a harlequin, rolling his eyes, shrugging his shoulders, and grinning from ear to ear. He stops short, turns to me, and says:
“‘We shall get you through sa, like a fiddle, and hope a please you when we get you through sa. Old ’ooman at home sir:[Pg 171]’ chuckling very much. ‘Outside gentleman sa, he often remember old ’ooman at home sa,’ grinning again.
“‘Aye aye, we’ll take care of the old woman. Don’t be afraid.’
“The black driver grins again, but there is another hole, and beyond that, another bank, close before us. So he stops short: cries (to the horses again) ‘Easy. Easy den. Ease. Steady. Hi. Jiddy. Pill. Ally. Loo!’ but never ‘Lee!’ until we are reduced to the very last extremity, and are in the midst of difficulties, extrication from which appears to be all but impossible.
“And so we do the ten miles or thereabouts in two hours and a half; breaking no bones though bruising a great many; and in short getting through the distance, ‘like a fiddle.’
“This singular kind of coaching terminates at Fredericksburgh, whence there is a railway to Richmond....”
Dickens, the student of human nature, surely found vast material for inspection and observation in our American coaches. The drivers particularly attracted his attention as we have seen; their philosophical[Pg 172] indifference to those under their charge as well as their anxieties on certain occasions caused him to marvel. The stage-drivers of Dickens’s day were marvels and offer character studies as unique as they were interesting. For the general air of conscienceless indifference on the part of drivers, and exasperated verbosity of passengers, perhaps no sketch of Dickens is more to the point than the following which describes, with lasting flavor, a ride from York, Pennsylvania, to Harrisburg:
“We left Baltimore by another railway at half-past eight in the morning, and reached the town of York, some sixty miles off, by the early dinner-time of the Hotel which was the starting-place of the four-horse coach, wherein we were to proceed to Harrisburg.
“This conveyance, the box of which I was fortunate enough to secure, had come down to meet us at the railroad station, and was as muddy and cumbersome as usual. As more passengers were waiting for us at the inn-door, the coachman observed under his breath, in the usual self-communicative voice, looking the while at his mouldy[Pg 173] harness, as if it were to that he was addressing himself:
“‘I expect we shall want the big coach.’
“I could not help wondering within myself what the size of this big coach might be, and how many persons it might be designed to hold; for the vehicle which was too small for our purpose was something larger than two English heavy night coaches, and might have been the twin-brother of a French diligence. My speculations were speedily set at rest, however, for as soon as we had dined, there came rumbling up the street, shaking its sides like a corpulent giant, a kind of barge on wheels. After much blundering and backing, it stopped at the door: rolling heavily from side to side when its other motion had ceased, as if it had taken cold in its damp stable, and between that, and the having been required in its dropsical old age to move at any faster pace than a walk, were distressed by shortness of wind.
“‘If here ain’t the Harrisburg mail at last, and dreadful bright and smart to look at too,’ cried an elderly gentleman in some excitement, ‘darn my mother![Pg 174]’
“I don’t know what the sensation of being darned may be, or whether a man’s mother has a keener relish or disrelish of the process than anybody else; but if the endurance of this mysterious ceremony by the old lady in question had depended on the accuracy of her son’s vision in respect to the abstract brightness and smartness of the Harrisburg mail, she would certainly have undergone its infliction. However, they booked twelve people inside; and the luggage (including such trifles as a large rocking-chair, and a good-sized dining-table), being at length made fast upon the roof, we started off in great state.
“At the door of another hotel, there was another passenger to be taken up.
“‘Any room, sir?‘ cries the new passenger to the coachman.
“‘Well there’s room enough,’ replies the coachman, without getting down, or even looking at him.
“‘There an’t no room at all, sir,’ bawls a gentleman inside. Which another gentleman (also inside) confirms, by predicting that the attempt to introduce any more passengers ‘won’t fit nohow.[Pg 175]’
“The new passenger, without any expression of anxiety, looks into the coach, and then looks up at the coachman: ‘Now, how do you mean to fix it?’ says he, after a pause: ‘for I must go.’
“The coachman employs himself in twisting the lash of his whip into a knot, and takes no more notice of the question: clearly signifying that it is anybody’s business but his, and that the passengers would do well to fix it, among themselves. In this state of things, matters seem to be approximating to a fix of another kind, when another inside passenger in a corner, who is nearly suffocated, cries faintly,
“‘I’ll get out.’
“This is no matter of relief or self-congratulation to the driver, for his immoveable philosophy is perfectly undisturbed by anything that happens in the coach. Of all things in the world, the coach would seem to be the very last upon his mind. The exchange is made, however, and then the passenger who has given up his seat makes a third upon the box, seating himself in what he calls the middle: that is,[Pg 176] with half his person on my legs, and the other half on the driver’s.
“‘Go a-head cap’en,’ cries the colonel, who directs.
“‘Go-lang!’ cries the cap’en to his company, the horses, and away we go.
“We took up at a rural bar-room, after we had gone a few miles, an intoxicated gentleman who climbed upon the roof among the luggage, and subsequently slipping off without hurting himself, was seen in the distant perspective reeling back to the grog-shop where we had found him. We also parted with more of our freight at different times, so that when we came to change horses, I was again alone outside.
“The coachmen always change with the horses, and are usually as dirty as the coach. The first was dressed like a very shabby English baker; the second like a Russian peasant; for he wore a loose purple camlet robe with a fur collar, tied round his waist with a parti-coloured worsted sash; grey trousers; light blue gloves; and a cap of bearskin. It had by this time come on to rain very heavily, and[Pg 177] there was a cold damp mist besides, which penetrated to the skin. I was very glad to take advantage of a stoppage and get down to stretch my legs, shake the water off my great-coat, and swallow the usual anti-temperance recipe for keeping out the cold....
“We crossed this river [Susquehanna] by a wooden bridge, roofed and covered in on all sides, and nearly a mile in length. It was profoundly dark; perplexed, with great beams, crossing and recrossing it at every possible angle; and through the broad chinks and crevices in the floor, the rapid river gleamed, far down below, like a legion of eyes. We had no lamps; and as the horses stumbled and floundered through this place, towards the distant speck of dying light, it seemed interminable. I really could not at first persuade myself as we rumbled heavily on, filling the bridge with hollow noises, and I held down my head to save it from the rafters above, but that I was in a painful dream; for I have often dreamed of toiling through such places, and as often argued, even at the time, ‘this cannot be reality.[Pg 178]’
“At length, however, we emerged upon the streets of Harrisburg....”
Coachmen are further described by Dickens during his stagecoach trip from Cincinnati to Columbus in Ohio:
“We often stop to water at a roadside inn, which is always dull and silent. The coachman dismounts and fills his bucket, and holds it to the horses’ heads. There is scarcely any one to help him; there are seldom any loungers standing round; and never any stable-company with jokes to crack. Sometimes, when we have changed our team, there is a difficulty in starting again, arising out of the prevalent mode of breaking a young horse; which is to catch him, harness him against his will, and put him in a stage-coach without further notice: but we get on somehow or other, after a great many kicks and a violent struggle; and jog on as before again.
“Occasionally, when we stop to change, some two or three half-drunken loafers will come loitering out with their hands in their pockets, or will be seen kicking their heels in rocking-chairs, or lounging on the window sill, or sitting on a rail within the[Pg 179] colonnade: they have not often anything to say though, either to us or to each other, but sit there idly staring at the coach and horses. The landlord of the inn is usually among them, and seems, of all the party, to be the least connected with the business of the house. Indeed he is with reference to the tavern, what the driver is in relation to the coach and passengers: whatever happens in his sphere of action, he is quite indifferent, and perfectly easy in his mind.
“The frequent change of coachmen works no change or variety in the coachman’s character. He is always dirty, sullen, and taciturn. If he be capable of smartness of any kind, moral or physical, he has a faculty of concealing it which is truly marvellous. He never speaks to you as you sit beside him on the box, and if you speak to him, he answers (if at all) in monosyllables. He points out nothing on the road, and seldom looks at anything: being, to all appearance, thoroughly weary of it, and of existence generally. As to doing the honours of his coach, his business, as I have said, is with the horses. The coach follows because it is attached to[Pg 180] them and goes on wheels: not because you are in it. Sometimes, towards the end of a long stage, he suddenly breaks out into a discordant fragment of an election song, but his face never sings along with him: it is only his voice, and not often that.
“He always chews and always spits, and never encumbers himself with a pocket-handkerchief. The consequences to the box passenger, especially when the wind blows toward him, are not agreeable.”
Hiring a special express coach at Columbus, Dickens and his party went on to Sandusky on Lake Erie alone. His description of the rough, narrow corduroy road is unequaled and no one but Dickens could have penned such a thrilling picture of the half-conquered woodland and its spectral inhabitants:
“There being no stage-coach next day, upon the road we wished to take, I hired ‘an extra,’ at a reasonable charge, to carry us to Tiffin, a small town from whence there is a railroad to Sandusky. This extra was an ordinary four-horse stage-coach, such as I have described, changing horses and drivers, as the stage-coach would, but[Pg 181] was exclusively our own for the journey. To ensure our having horses at the proper stations, and being incommoded by no strangers, the proprietors sent an agent on the box, who was to accompany us all the way through; and thus attended, and bearing with us, besides, a hamper full of savoury cold meats, and fruit, and wine; we started off again, in high spirits, at half-past six o’clock next morning, very much delighted to be by ourselves, and disposed to enjoy even the roughest journey.
“It was well for us, that we were in this humour, for the road we went over that day, was certainly enough to have shaken tempers that were not resolutely at Set Fair, down to some inches below Stormy. At one time we were all flung together in a heap at the bottom of the coach, and at another we were crushing our heads against the roof. Now, one side was down deep in the mire, and we were holding on to the other. Now, the coach was lying on the tails of the two wheelers; and now it was rearing up in the air, in a frantic state, with all four horses standing on the top of[Pg 182] an insurmountable eminence, looking coolly back at it, as though they would say ‘Unharness us. It can’t be done.’ The drivers on these roads, who certainly get over the ground in a manner which is quite miraculous, so twist and turn the team about in forcing a passage, corkscrew fashion, through the bogs and swamps, that it was quite a common circumstance on looking out of the window, to see the coachman with the ends of a pair of reins in his hands, apparently driving nothing, or playing at horses, and the leaders staring at one unexpectedly from the back of the coach, as if they had some idea of getting up behind. A great portion of the way was over what is called a corduroy road, which is made by throwing trunks of trees into a marsh, and leaving them to settle there. The very slightest of the jolts with which the ponderous carriage fell from log to log, was enough, it seemed, to have dislocated all the bones in the human body. It would be impossible to experience a similar set of sensations, in any other circumstances, unless perhaps in attempting to go up to the top of St. Paul’s in an[Pg 183] omnibus. Never, never once, that day, was the coach in any position, attitude, or kind of motion to which we are accustomed in coaches. Never did it make the smallest approach to one’s experience of the proceedings of any sort of vehicle that goes on wheels.
“Still, it was a fine day, and the temperature was delicious, and though we had left Summer behind us in the west, and were fast leaving Spring, we were moving towards Niagara and home. We alighted in a pleasant wood towards the middle of the day, dined on a fallen tree, and leaving our best fragments with a cottager, and our worst with the pigs (who swarm in this part of the country like grains of sand on the sea-shore, to the great comfort of our commissariat in Canada), we went forward again, gaily.
“As night came on, the track grew narrower and narrower, until at last it so lost itself among the trees, that the driver seemed to find his way by instinct. We had the comfort of knowing, at least, that there was no danger of his falling asleep, for every now and then a wheel would[Pg 184] strike against an unseen stump with such a jerk, that he was fain to hold on pretty tight and pretty quick to keep himself upon the box. Nor was there any reason to dread the least danger from furious driving, inasmuch as over that broken ground the horses had enough to do to walk; as to shying, there was no room for that; and a herd of wild elephants could not have run away in such a wood, with such a coach at their heels. So we stumbled along, quite satisfied.
“These stumps of trees are a curious feature in American travelling. The varying illusions they present to the unaccustomed eye as it grows dark, are quite astonishing in their number and reality. Now, there is a Grecian urn erected in the centre of a lonely field; now there is a woman weeping at a tomb; now a very comonplace old gentleman in a white waist-coat, with a thumb thrust into each arm-hole of his coat; now a student poring on a book; now a crouching negro; now, a horse, a dog, a cannon, an armed man; a hunch-back throwing off his cloak and stepping forth into the light. They were often as entertaining to me as so many glasses in[Pg 185] a magic lantern, and never took their shapes at my bidding, but seemed to force themselves upon me, whether I would or no; and strange to say, I sometimes recognized in them counterparts of figures once familiar to me in pictures attached to childish books, forgotten long ago.
“It soon became too dark, however, even for this amusement, and the trees were so close together that their dry branches rattled against the coach on either side, and obliged us all to keep our heads within. It lightened too, for three whole hours; each flash being very bright, and blue, and long; and as the vivid streaks came darting in among the crowded branches, and the thunder rolled gloomily above the tree tops, one could scarcely help thinking that there were better neighbourhoods at such a time than thick woods afforded.
“At length, between ten and eleven o’clock at night, a few feeble lights appeared in the distance, and Upper Sandusky, an Indian village, where we were to stay till morning, lay before us.”
Dickens’s description of his visit to “Looking-Glass Prairie” from St. Louis is[Pg 186] full of amusement, and contains many vivid pictures of pioneer roads and taverns in the Mississippi Valley:
“As I had a great desire to see a Prairie before turning back from the furthest point of my wanderings; and as some gentlemen of the town had, in their hospitable consideration, an equal desire to gratify me; a day was fixed, before my departure, for an expedition to the Looking-Glass Prairie, which is within thirty miles of the town. Deeming it possible that my readers may not object to know what kind of thing such a gipsy party may be at that distance from home, and among what sort of objects it moves, I will describe the jaunt....
“I may premise that the word Prairie is variously pronounced paraaer, parearer, and paroarer. The latter mode of pronunciation is perhaps the most in favour. We were fourteen in all, and all young men: indeed it is a singular though very natural feature in the society of these distant settlements, that it is mainly composed of adventurous persons in the prime of life, and has very few grey heads among it. There were no ladies: the trip being a fatiguing[Pg 187] one: and we were to start at five o’clock in the morning punctually....
“At seven o’clock ... the party had assembled, and were gathered round one light carriage, with a very stout axletree; one something on wheels like an amateur carrier’s cart; one double phaeton of great antiquity and unearthly construction; one gig with a great hole in its back and a broken head; and one rider on horseback who was to go on before. I got into the first coach with three companions; the rest bestowed themselves in the other vehicles; two large baskets were made fast to the lightest; two large stone jars in wicker cases, technically known as demi-johns, were consigned to the ‘least rowdy’ of the party for safe keeping; and the procession moved off to the ferry-boat, in which it was to cross the river bodily, men, horses, carriages, and all as the manner in these parts is.
“We got over the river in due course, and mustered again before a little wooden box on wheels, hove down all aslant in a morass, with ‘merchant tailor’ painted in very large letters over the door. Hav[Pg 188]ing settled the order of proceeding, and the road to be taken, we started off once more and began to make our way through an ill-favoured Black Hollow, called, less expressively, the American Bottom....
“We had a pair of very strong horses, but travelled at the rate of little more than a couple of miles an hour, through one unbroken slough of black mud and water. It had no variety but in depth. Now it was only half over the wheels, now it hid the axletree, and now the coach sank down in it almost to the windows. The air resounded in all directions with the loud chirping of the frogs, who, with the pigs (a coarse, ugly breed, as unwholesome-looking as though they were the spontaneous growth of the country), had the whole scene to themselves. Here and there we passed a log hut; but the wretched cabins were wide apart and thinly scattered, for though the soil is very rich in this place, few people can exist in such a deadly atmosphere. On either side of the track, if it deserve the name, was the thick ‘bush;’ and everywhere was stagnant, slimy, rotten, filthy water.[Pg 189]
“As it is the custom in these parts to give a horse a gallon or so of cold water whenever he is in a foam with heat, we halted for that purpose, at a log inn in the wood, far removed from any other residence. It consisted of one room, bare-roofed and bare-walled of course, with a loft above. The ministering priest was a swarthy young savage, in a shirt of cotton print like bed-furniture, and a pair of ragged trousers. There were a couple of young boys, too, nearly naked, lying idly by the well; and they, and he, and the traveller at the inn, turned out to look at us....
“When the horses were swollen out to about twice their natural dimensions (there seems to be an idea here, that this kind of inflation improves their going), we went forward again, through mud and mire, and damp, and festering heat, and brake and bush, attended always by the music of the frogs and pigs, until nearly noon, when we halted at a place called Belleville.
“Belleville was a small collection of wooden houses, huddled together in the very heart of the bush and swamp....[Pg 190] The criminal court was sitting, and was at that moment trying some criminals for horse-stealing; with whom it would most likely go hard: for live stock of all kinds being necessarily very much exposed in the woods, is held by the community in rather higher value than human life; and for this reason, juries generally make a point of finding all men indicted for cattle-stealing, guilty, whether or no. The horses belonging to the bar, the judge, and witnesses, were tied to temporary racks set up roughly in the road; by which is to be understood, a forest path, nearly knee-deep in mud and slime.
“There was an hotel in this place which, like all hotels in America, had its large dining-room for the public table. It was an odd, shambling, low-roofed out-house, half cowshed and half kitchen, with a coarse brown canvas table-cloth, and tin sconces stuck against the walls, to hold candles at supper-time. The horseman had gone forward to have coffee and some eatables prepared, and they were by this time nearly ready. He had ordered ‘wheat-bread and chicken fixings,’ in preference to[Pg 191] ‘corn-bread and common doings.’[47] The latter kind of refection includes only pork and bacon. The former comprehends broiled ham, sausages, veal cutlets, steaks, and such other viands of that nature as may be supposed, by a tolerably wide poetical construction, ‘to fix’ a chicken comfortably in the digestive organs of any lady or gentleman....
“From Belleville, we went on, through the same desolate kind of waste, and constantly attended, without the interval of a moment, by the same music; until, at three o’clock in the afternoon, we halted once more at a village called Lebanon to inflate the horses again, and give them some corn besides: of which they stood much in need. Pending this ceremony, I walked into the village, where I met a full sized dwelling-house coming down-hill at a round trot, drawn by a score or more of oxen. The public-house was so very clean and good a one, that the managers of the jaunt resolved to return to it and put up there for the night, if possible. This[Pg 192] course decided on, and the horses being well refreshed, we again pushed forward, and came upon the Prairie at sunset.
“It would be difficult to say why, or how—though it was possibly from having heard and read so much about it—but the effect on me was disappointment. Looking towards the setting sun, there lay, stretched out before my view, a vast expanse of level ground; unbroken, save by one thin line of trees, which scarcely amounted to a scratch upon the great blank; until it met the glowing sky, wherein it seemed to dip: mingling with its rich colours, and mellowing in its distant blue. There it lay, a tranquil sea or lake without water, if such a simile be admissible, with the day going down upon it; a few birds wheeling here and there; and solitude and silence reigning paramount around. But the grass was not yet high; there were bare black patches on the ground; and the few wild flowers that the eye could see, were poor and scanty. Great as the picture was, its very flatness and extent, which left nothing to the imagination, tamed it down and cramped[Pg 193] its interest. I felt little of that sense of freedom and exhilaration which a Scottish heath inspires, or even our English downs awaken. It was lonely and wild, but oppressive in its barren monotony. I felt that in traversing the Prairies, I could never abandon myself to the scene, forgetful of all else; as I should do instinctively, were the heather underneath my feet, or an iron-bound coast beyond; but should often glance towards the distant and frequently-receding line of the horizon, and wish it gained and passed. It is not a scene to be forgotten, but it is scarcely one, I think (at all events, as I saw it), to remember with much pleasure, or to covet the looking-on again, in after life.
“We encamped near a solitary log-house, for the sake of its water, and dined upon the plain. The baskets contained roast fowls, buffalo’s tongue (an exquisite dainty, by the way), ham, bread, cheese, and butter; biscuits, champagne, sherry; lemons and sugar for punch; and abundance of rough ice. The meal was delicious, and the entertainers were the soul of kindness and good humour. I have often recalled[Pg 194] that cheerful party to my pleasant recollection since, and shall not easily forget, in junketings nearer home with friends of older date, my boon companions on the Prairie. Returning to Lebanon that night, we lay at the little inn at which we had halted in the afternoon. In point of cleanliness and comfort it would have suffered by no comparison with any village ale-house, of a homely kind, in England....
“After breakfast, we started to return by a different way from that which we had taken yesterday, and coming up at ten o’clock with an encampment of German emigrants carrying their goods in carts, who had made a rousing fire which they were just quitting, we stopped there to refresh. And very pleasant the fire was; for, hot though it had been yesterday, it was quite cold to-day, and the wind blew keenly. Looming in the distance, as we rode along, was another of the ancient Indian burial-places, called The Monks’ Mound; in memory of a body of fanatics of the order of La Trappe, who founded a desolate convent there, many years ago, when there were no settlers within a thou[Pg 195]sand miles, and were all swept off by the pernicious climate: in which lamentable fatality, few rational people will suppose, perhaps, that society experienced any very severe deprivation.
“The track of to-day had the same features as the track of yesterday. There was the swamp, the bush, the perpetual chorus of frogs, the rank unseemly growth, the unwholesome steaming earth. Here and there, and frequently too, we encountered a solitary broken-down waggon, full of some new settler’s goods. It was a pitiful sight to see one of these vehicles deep in the mire; the axletree broken; the wheel lying idly by its side; the man gone miles away, to look for assistance; the woman seated among their wandering household gods with a baby at her breast, a picture of forlorn, dejected patience; the team of oxen crouching down mournfully in the mud, and breathing forth such clouds of vapour from their mouths and nostrils, that all the damp mist and fog around seemed to have come direct from them.
“In due time we mustered once again before the merchant tailor’s, and having[Pg 196] done so, crossed over to the city in the ferry-boat: passing, on the way, a spot called Bloody Island, the duelling-ground of St. Louis, and so designated in honour of the last fatal combat fought there, which was with pistols, breast to breast. Both combatants fell dead upon the ground; and possibly some rational people may think of them, as of the gloomy madmen on the Monks’ Mound, that they were no great loss to the community.”
For purposes of comparison, the following description of experiences in later times with Indian trails of the West will be of interest. Much that has been deduced from a study of our pioneer history and embodied in the preceding pages finds strong confirmation here; in earlier days, with forests covering the country, the trails were more like roads than in the open prairies of the West; but, as will be seen, many laws governed the earlier and the later Indian thoroughfares, alike. I quote from the Hon. Charles Augustus Murray’s memoirs, written three-quarters of a century ago, of a tour in Missouri:[Pg 197]
“On the 18th we pursued our course, north by east: this was not exactly the direction in which I wished to travel, but two considerations induced me to adopt it at this part of the journey. In the first place, it enabled me to keep along the dividing ridge; an advantage so great, and so well understood by all prairie travellers, that it is worth making a circuit of several miles a day to keep it; and the Indian trails which we have crossed since our residence in the wilderness, convince me that the savages pay the greatest attention to this matter. In a wide extent of country composed of a succession of hills and ridges, it is evident there must be a great number of steep banks, which offer to an inexperienced traveller numerous obstacles, rendering his own progress most toilsome, and that of loaded packhorses almost impossible. If these ridges all ran in parallel lines, and were regular in their formation, nothing would be more simple than to get upon the summit of one, and keep it for the whole day’s journey: but such is not the case; they constantly meet other ridges running in a transverse direc[Pg 198]tion; and, of course, large dips and ravines are consequent upon that meeting. The ‘dividing ridge’ of a district is that which, while it is, as it were, the back-bone of the range of which it forms a part, heads at the same time all the transverse ravines, whether on the right or on the left hand, and thereby spares to the traveller an infinity of toilsome ascent and descent.
“I have sometimes observed that an Indian trail wound through a country in a course perfectly serpentine, and appeared to me to travel three miles when only one was necessary. It was not till my own practical experience had made me attend more closely to this matter, that I learnt to appreciate its importance. I think that the first quality in a guide through an unknown range of rolling prairie, is having a good and a quick eye for hitting off the ‘dividing ridge;’ the second, perhaps, in a western wilderness, is a ready and almost intuitive perception (so often found in an Indian) of the general character of a country, so as to be able to bring his party to water when it is very scarce....
A few miles farther we crossed an old[Pg 199] Indian trail I think it was of a Pawnee party, for it bore north by west ... it had not been a war-party, as was evident from the character of the trail. A war-party leaves only the trail of the horses, or, of course, if it be a foot party, the still slighter tracks of their own feet; but when they are on their summer hunt, or migrating from one region to another, they take their squaws and children with them, and this trail can always be distinguished from the former, by two parallel tracks about three and a half feet apart, not unlike those of a light pair of wheels: these are made by the points of the long curved poles on which their lodges are stretched, the thickest or butt ends of which are fastened to each side of the pack-saddle, while the points trail behind the horse; in crossing rough or boggy places, this is often found the most inconvenient part of an Indian camp equipage.... I was fortunate enough to find an Indian trail bearing north by east, which was as near to our destined course as these odious creeks would permit us to go. We struck into it, and it brought us safely, though[Pg 200] not without difficulty, through the tangled and muddy bottom in which we had been involved: sometimes a horse floundered, and more than once a pack came off; but upon the whole we had great reason to congratulate ourselves upon having found this trail, by which we escaped in two hours from a place which would, without its assistance, probably have detained us two days. I was by no means anxious to part with so good a friend, and proceeded some miles upon this same trail; it was very old and indistinct, especially in the high and dry parts of the prairie. I left my horse with the rest of the party and went on foot, in order that I might more easily follow the trail, which became almost imperceptible as we reached an elevated district of table-land, which had been burned so close that I very often lost the track altogether for fifty yards. If a fire takes place on a prairie where there is already a distinct trail, it is as easy to follow it, if not more so than before; because the short and beaten grass offering no food to the fire, partly escapes its fury, and remains a green line upon a sea of black;[Pg 201] but if the party making the trail pass over a prairie which is already burnt, in the succeeding season when the new grass has grown, it can scarcely be traced by any eye but that of an Indian.... After we had travelled five hours ... I found that the trail which we had been following, merged in another and a larger one, which appeared to run a point to the west of north. This was so far out of our course that I hesitated whether I should not leave it altogether; but, upon reflection, I determined not to do so ... if I attempted to cross the country farther to the eastward, without any trail, I should meet with serious difficulties and delays.... I therefore struck into it, and ere long the result justified my conjecture; for we came to a wooded bottom or valley, which was such a complete jungle, and so extensive, that I am sure, if we had not been guided by the trail, we could not have made our way through it in a week. As it was, the task was no easy one; for the trail, though originally large, was not very fresh, and the weeds and branches had in many places so overgrown[Pg 202] it, that I was obliged to dismount and trace it out on foot. It wound about with a hundred serpentine evolutions to avoid the heavy swamps and marshes around us; and I repeatedly thought that, if we lost it, we never should extricate our baggage: even with its assistance, we were obliged frequently to halt and replace the packs, which were violently forced off by the branches with which they constantly came in contact ... ‘where on earth is he taking us now?—why we are going back in the same direction as we came!’ I turned round and asked the speaker (a comrade) ... to point with his finger to the quarter which he would make for if he were guiding the party to Fort Leavenworth. He did so; and I took out my compass and showed him that he was pointing south-west, i.e. to Santa Fé and the Gulf of California: so completely had the poor fellow’s head become puzzled by the winding circuit we had made in the swamp.”[48]
[1] Washington’s Journal Sept. 2nd to Oct. 4th, 1784.
[2] Historic Highways of America, vol. v, ch. 3.
[3] This creek rises in Hardy County, Virginia, and flows northeastward through Hampshire County, entering the North Branch of the Potomac River about eight miles southeast of Cumberland, Maryland.
[4] Union Township, Monongalia County, West Virginia.
[5] Oliphant’s Iron Furnace, Union Township?
[6] The mountainous boundary line between Monongalia and Preston Counties.
[7] Bruceton’s Mills, Grant Township, Preston County, West Virginia?
[8] Southwestern corner of Maryland, some twenty miles north of Oakland.
[9] Briery Mountain runs northeast through the eastern edge of Preston County, bounding Dunkard Bottom on the east as Cheat River bounds it on the west.
[10] The Friends were the earliest pioneers of Garrett County, John Friend coming in 1760 bringing six sons among whom was this Charles. The sons scattered about through the valley of the Youghiogheny, Charles settling near the mouth of Sang Run, which cuts through Winding Ridge Mountain and joins the Youghiogheny about fifteen miles due north from Oakland. Washington, moving eastward on McCulloch’s Path probably passed through this gap in Winding Ridge. A present-day road runs parallel with Winding Ridge from Friendsville (named from this pioneer family) southward to near Altamont, which route seems to have been that pursued by McCulloch’s Path. See Scharf’s History of Western Maryland, vol. ii, p. 1518; Atlas of Maryland (Baltimore, 1873), pp. 47-48; War Atlas 1861-65, House Miscellaneous Documents, vol. iv, part 2, No. 261, 52d Cong. 1st Sess. 1891-92, Plate cxxxvi.
[11] Great Back Bone Mountain, Garrett County, Maryland, on which, at Altamont, the Baltimore and Ohio Railway reaches its highest altitude. It was about here that Washington now crossed it, probably on the watershed between Youghiogheny and Potomac waters west of Altamont.
[12] Ryan’s Glade No. 10, Garrett County.
[13] This point is pretty definitely determined in the Journal. We are told that the mouth of Stony River (now Stony Creek) was four miles below McCulloch’s crossing. This would locate the latter near the present site of Fort Pendleton, Garrett County, Maryland, the point where the old Northwestern Turnpike crossed the North Branch.
[14] Greeland Gap, Grant County, West Virginia.
[15] Knobby Mountain.
[16] Near Moorefield, Hardy County, West Virginia.
[17] Mt. Storm, Grant County. The Old Northwestern Turnpike bears northeast from here to Claysville, Burlington and Romney. Washington’s route was southwest along the line of the present road to Moorefield. Evidently the buffalo trace bore southwest on the watershed between Stony River and Abraham’s Creek—White’s West Virginia Atlas (1873), p. 26. Bradley’s Map of United States (1804) shows a road from Morgantown to Romney; also a “Western Fort” at the crossing-place of the Youghiogheny.
[18] Dunkard’s Bottom, in Portland Township, Preston County, West Virginia, was settled about 1755 by Dr. Thomas Eckarly and brothers who traversed the old path to Fort Pleasant on South Branch.—Thwaites’s edition of Withers’s Chronicles of Border Warfare (1895), pp. 75-76.
[19] Laws of Virginia (1826-1827), pp. 85-87.
[20] Laws of Virginia (1831), pp. 153-158; Journal of the Senate ... of Virginia (1830-31), p. 165.
[21] See Historic Highways of America, vol. ix, pp. 60-64.
[22] Journal of Thomas Wallcutt in 1790, edited by George Dexter (Proceedings of the Massachusetts Historical Society, October, 1879).
[23] The Journal begins at the Ohio Company’s settlement at Marietta, Ohio.
[24] They crossed the Ohio River to the present site of Williamstown, West Virginia, named from the brave and good pioneer Isaac Williams.
[25] The Monongahela Trail; see Historic Highways of America, vol. ii, pp. 122-124.
[26] For an early (1826) map of this region that is reasonably correct, see Herman Böye’s Map of Virginia in Massachusetts Historical Society Library.
[27] Near Friendsville, Maryland—named in honor of the old pioneer family; see note 10, ante; cf. Corey’s map of Virginia in his American Atlas (1805), 3d edition; also Samuel Lewis’s Map of Virginia (1794).
[28] Bellville was the earlier Flinn’s Station, Virginia.—S. P. Hildreth’s Pioneer History, p. 148.
[29] The author has, for several years, been looking for an explanation of this interesting obituary; “broadaggs” is, clearly, a corruption of “Braddock’s.” Of “atherwayes” no information is at hand; it was probably the name of a woodsman who settled here—for “bear camplain” undoubtedly means a “bare campagne,” or clearing. The word campagne was a common one among American pioneers. Cf. Harris’s Tour, p. 60. A spot halfway between Cumberland and Uniontown would be very near the point where the road crossed the Pennsylvania state-line.
[30] A reminiscent letter written in 1842 for the American Pioneer (vol. i, pp. 73-75).
[31] Historic Highways of America, vol. vii, pp. 139-148.
[32] Historic Highways of America, vol. ii, pp. 76-85.
[33] The Iroquois Trail likewise left the river valley at this spot.
[34] Laws of New York, 1794, ch. XXIX.
[35] Laws of New York, 1796, ch. XXVI.
[36] Id., ch. XXXIX.
[37] Laws of New York, 1797, ch. LX.
[38] Laws of New York, 1798, ch. XXVI.
[39] Laws of New York, 1797-1800, ch. LXXVIII.
[40] Boston, 1876, pp. 11-53.
[41] Published by Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1901.
[41] This name long since was abandoned. On the opposite side of the river, however, a new settlement grew up under the name of Unadilla, the beginnings of which date about 1790. See the same author’s “The Pioneers of Unadilla Village” (Unadilla, 1902).—Halsey.
[42] State Land Papers.—Halsey.
[43] Sluman Wattles’s Account Book.—Halsey.
[44] Dr. Dwight’s figures are for the township, not for the village, which was then a mere frontier hamlet, of perhaps one hundred souls.—Halsey.
[45] “Reminiscences of Village Life and of Panama and California from 1840 to 1850,” by Gains Leonard Halsey, M. D. Published at Unadilla.—Halsey.
[46] A stage line, however, for long years afterward supplied these settlements with a means of communication with Unadilla, and it is within the memory of many persons still calling themselves young that for a considerable series of years, trips twice a week were regularly made by Henry S. Woodruff. After Mr. Woodruff’s death a large and interesting collection of coaches, sleighs, and other stage relics remained upon his premises—the last survival of coaching times on the Catskill Turnpike, embracing a period of three-quarters of a century.—Halsey.
[47] See Historic Highways of America, vol. xi, p. 199, note.
[48] Travels in North America (London, 1839), vol. ii, pp. 29-48.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Historic Highways of America (Vol. 12), by
Archer Butler Hulbert
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK HISTORIC HIGHWAYS OF AMERICA, VOL 12 ***
***** This file should be named 41030-h.htm or 41030-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/1/0/3/41030/
Produced by Greg Bergquist and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
[email protected]. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
[email protected]
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.