The Project Gutenberg EBook of Noteworthy Mammals from Sinaloa, Mexico, by
J. Knox Jones, Jr. and Ticul Alvarez and M. Raymond Lee
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: Noteworthy Mammals from Sinaloa, Mexico
Author: J. Knox Jones, Jr.
Ticul Alvarez
M. Raymond Lee
Release Date: March 18, 2010 [EBook #31683]
Language: English
Character set encoding: UTF-8
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK MAMMALS ***
Produced by Chris Curnow, Simon Gardner and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net
University of Kansas Publications Museum of Natural History
Volume 14, No. 12, pp. 145-159, 1 fig. in text
May 18, 1962
Noteworthy Mammals from Sinaloa, Mexico
J. KNOX JONES, JR., TICUL ALVAREZ, AND M. RAYMOND LEE
University of Kansas
Lawrence
1962
University of Kansas Publications, Museum of Natural History
Editors: E. Raymond Hall, Chairman, Henry S. Fitch,
Theodore H. Eaton, Jr.
Volume 14, No. 12, pp. 145-159, 1 fig. in text
Published May 18, 1962
University of Kansas
Lawrence, Kansas
PRINTED BY
JEAN M. NEIBARGER, STATE PRINTER
TOPEKA, KANSAS
1962
29-3000
Noteworthy Mammals from Sinaloa, Mexico
BY
J. KNOX JONES, JR., TICUL ALVAREZ, and M. RAYMOND LEE
In several of the past twelve years field parties from the Museum
of Natural History have collected mammals in the Mexican state of
Sinaloa. Most of the collections contained only a modest number
of specimens because they were made by groups that stopped for
short periods on their way to or from other areas, but several collections
are extensive. Field work by representatives of this institution
now is underway in Sinaloa with the aim of acquiring materials
suitable for treating the entire mammalian fauna of that state.
Among the mammals thus far obtained are specimens of twenty
species that represent significant extensions of known range, are of
especial taxonomic or zoogeographic interest, or that complement
published information, and it is these records that are reported
herein.
The following persons obtained specimens mentioned beyond:
J. R. Alcorn (1950); J. R. and A. A. Alcorn (1954 and 1955); R. H.
Baker and a party of students (1955); W. L. Cutter (1957); S. Anderson
and a party of students (1959); M. R. Lee (1960 and 1961);
and J. K. Jones, Jr., accompanied by R. R. Patterson and R. G.
Webb (1961). The Kansas University Endowment Association and
the American Heart Association provided funds that helped to defray
the cost of field operations.
In the accounts that follow, all measurements are in millimeters
and all catalogue numbers refer to the mammal collection of the
Museum of Natural History, The University of Kansas. Placenames
associated with specimens examined are indicated on the
accompanying map (Fig. 1).
Notiosorex crawfordi (Coues).—A non-pregnant female (75184)
was obtained on November 29, 1957, at El Fuerte by W. L.
Cutter. Comparison of this specimen with topotypes of N. evotis
(see below) and with undoubted examples of N. crawfordi proves
our specimen to be referable to the latter. We presume that the
shrew reported as evotis on geographic grounds from El Carrizo
by Hooper (1961:120) also is referable to crawfordi. External
measurements of our female are: total length, 77; length of tail, 20
(tip missing); length of hind foot, 11; length of ear from notch, 8;
weight in grams, 4. Cranial measurements of this individual are
given in Table 1.
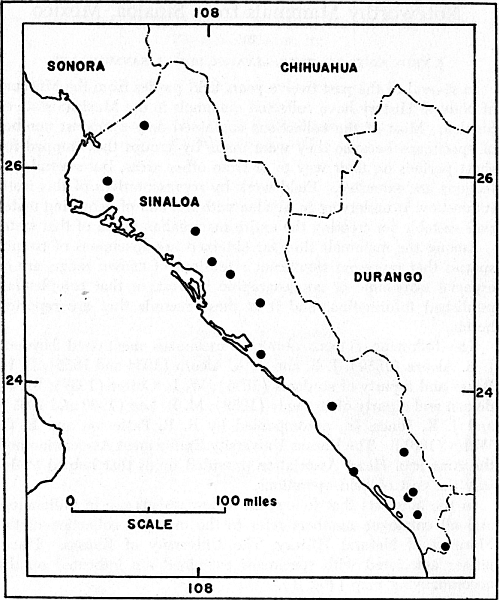 Fig. 1. Map of Sinaloa on which are plotted symbols representing placenames
mentioned in text. From north to south, these are: El Fuerte; San
Miguel; Los Mochis; Guamúchil; Terrero; Pericos; Culiacán; El Dorado;
Piaxtla and Camino Reál (one symbol); Pánuco; Mazatlán; Matatán; Rosario;
Escuinapa; Concepción.
Fig. 1. Map of Sinaloa on which are plotted symbols representing placenames
mentioned in text. From north to south, these are: El Fuerte; San
Miguel; Los Mochis; Guamúchil; Terrero; Pericos; Culiacán; El Dorado;
Piaxtla and Camino Reál (one symbol); Pánuco; Mazatlán; Matatán; Rosario;
Escuinapa; Concepción.
Notiosorex evotis (Coues).—Four topotypes (85533-36), all
males, were collected by Lee at Mazatlán. One was caught on December
17, 1960, in a museum special trap set "in low weeds near
thorn bush" in a sandy field at the north edge of Mazatlán, less than
a mile from the ocean. A few trees and some grasses grew in this
area; Mus musculus and Perognathus pernix were taken in the same
line of traps. Additional trapping at this locality failed to produce
more shrews. The other three specimens were captured alive on
February 1 (one) and February 2 (two), 1961, in the wake of a
bulldozer that was clearing land adjacent to the place where the
first specimen was trapped. The ground cover being cleared away
consisted mostly of dry, dense weeds and short, thorny scrub; the
latter was sparse in some places and formed dense thickets in others.
One individual that was kept alive for a short time in a can ate
crickets and roaches readily and ate one spider, but refused isopods.
On one occasion it ate six crickets in about three hours. Wet oatmeal
and oatmeal mixed with peanut butter both were refused.
Table 1. Cranial Measurements of Two Species of Notiosorex.
| Catalogue number, or number of specimens averaged, and sex |
Condylobasal length |
Interorbital constriction |
Maxillary breadth |
Cranial breadth |
Palatal length |
Length of maxillary tooth-row |
|---|
| Notiosorex crawfordi, Huachuca Mts., Arizona[A] |
| Average 6 (2♂, 4♀) | 16.01 | 3.72 | 5.08 | 8.32 | 6.59 | 5.93 |
| Minimum | 15.7 | 3.6 | 4.9 | 7.8 | 6.3 | 5.8 |
| Maximum | 16.5 | 3.85 | 5.2 | 8.8 | 7.15 | 6.2 |
| El Fuerte, Sinaloa |
| 75184 KU, ♀ | 16.5 | 3.7 | 5.0 | 8.4 | 6.9 | 6.1 |
| SW Guadalajara, Jalisco |
| 33318 KU, ♂ | .. | 3.6 | 4.9 | .. | 7.1 | 5.7 |
| 42583 KU, ? | 15.0+ | 3.5 | 4.6 | .. | 6.6 | 5.4± |
| 42584 KU, ? | .. | 3.6 | 4.9 | .. | 7.1± | 6.1± |
| 2 mi. E La Palma, Michoacán |
| 42586 KU, ? | .. | 3.8 | 4.9 | .. | 6.9 | .. |
| 42587 KU, ? | .. | 3.8 | 4.8 | .. | 6.9 | 6.0 |
| 42588 KU, ? | .. | .. | 4.9 | .. | 6.9 | 6.2 |
| Notiosorex evotis, Mazatlán, Sinaloa |
| Average 4 (♂) | 17.68 | 4.05 | 5.37 | 8.68 | 7.60 | 6.58 |
| Minimum | 17.4 | 4.0 | 5.3 | 8.5 | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| Maximum | 17.9 | 4.1 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 7.7 | 6.7 |
Average and extreme external measurements of the four males are as follows:
total length, 93.2 (90-98); length of tail, 25.5 (23-27); length of hind
foot, 11.9 (11-13); length of ear from notch, 7.7 (7-8); weight in grams, 5.4
(4.4-6.3). Cranial measurements are given in Table 1.
Notiosorex evotis was described by Coues (1877:652) on the basis
of a single specimen, obtained at Mazatlán by Ferdinand Bischoff
in 1868, that originally had at least the partial skull inside. Subsequently
the skull was removed and evidently lost (Poole and
Schantz, 1942:181). Coues named evotis as a species distinct from
crawfordi (described by him in the same paper) on the basis of
larger size, shorter tail, and alleged slight differences in color. He
did not describe the skull, but did note that the dentition was "substantially
the same as that of N. crawfordi." Evidently, the only
other correctly identified specimen of evotis on record is an individual
from Mazatlán in the British Museum, the skull of which
was figured by Dobson (1890:pl. 23, fig. 20).
Merriam (1895:34) characterized evotis, known to him by only
the holotype, as: "Similar to N. crawfordi, but slightly larger and
darker." He did not examine the skull, which by that time had
been "lost or mislaid." Merriam reduced evotis to subspecific status
under crawfordi with the following remarks: "In the absence of
sufficient material of N. evotis, it is impossible to determine its exact
relations to crawfordi. Dobson did not recognize it as distinct, but
figured its teeth under the name crawfordi [loc. cit., possibly a
lapsus]. For the present it seems best to retain it as a subspecies."
Merriam's arrangement of evotis as a subspecies of crawfordi has
been followed by subsequent workers, mostly, we suppose, because
additional material of undoubted evotis has not until now been
available. Comparisons of our four specimens with specimens
(from Jalisco, Sinaloa and Tamaulipas) and published descriptions
and measurements (see especially Hoffmeister and Goodpaster,
1954:46-47, 51) of crawfordi reveal that evotis has a longer body
and hind foot than crawfordi but a relatively (sometimes actually)
shorter tail and ear, and a distinctly larger, heavier skull (see Table
1). The upper parts of our specimens average pale brownish
gray and are paler, not darker, than the upper parts of crawfordi.
But, all of the latter were obtained in the warm months of the year
except one November-taken individual from El Fuerte, Sinaloa, the
dorsal pelage of which approaches in color that of the darkest of
the evotis. The pelage of both kinds probably is paler in winter
than in summer and may be indistinguishable in the same season.
Ventrally, all four evotis are grayish white, faintly to moderately
tinged with brownish buff.
Notiosorex evotis differs cranially from Notiosorex crawfordi as
follows: larger (see measurements); mesopterygoid fossa squared
rather than broadly U-shaped anteriorly; rounded process on maxillary
at posterior border of infraorbital canal well developed (faint
or lacking in crawfordi); occipital condyles smaller and, in lateral
view, elevated above basal plane of skull; upper molars slightly
more crowded in occlusal view. These differences, although admittedly
slight, appear to be constant in the specimens we have
seen, but ought to be used cautiously owing to the small samples
studied.
Shrews of the genus Notiosorex have been reported twice previously
from localities in west-central México, other than from Mazatlán,
as follows: 21 mi. SW Guadalajara (remains from owl pellets)
and 13 mi. S, 15 mi. W Guadalajara, Jalisco, by Twente and
Baker (1951:120-121); and Cerrito Loco, 2 mi. E La Palma, Michoacán
(remains from owl pellets), by Baker and Alcorn (1953:116).
The remains were referred to evotis on geographic grounds in one
instance and were so referred inferentially in the other. Examination
of the specimens upon which these reports were based reveals
that all are crawfordi on the basis of characters previously cited. As
a result, N. evotis is known only from the type locality at Mazatlán,
whereas N. crawfordi is widely distributed on the Mexican Plateau
as far south as Jalisco and northern Michoacán, and occurs on the
west side of the Sierra Occidental as far south as northern Sinaloa.
The two kinds obviously are closely related and intergradation
eventually may be demonstrated between them. But, for the present,
we adopt a conservative course and treat evotis as a full species
owing to its distinctive features, restricted geographic distribution,
and the lack of evidence of intergradation between it and crawfordi.
Balantiopteryx plicata pallida Burt.—Thirty-five specimens from
two adjacent localities along the Río del Fuerte in northern Sinaloa,
3 mi. NE San Miguel, 300 ft. (84944-48) and 10 mi. NNE Los Mochis
(60572-75, 60667-78, 60681-94), provide the first records of the
subspecies from the state. Individuals from both localities were
shot at dusk as they foraged among trees in the valley of the river.
Fifteen of 18 females from 10 mi. NNE Los Mochis, collected on
June 5, 6 and 7, 1955, were pregnant; each contained a single embryo,
the embryos ranging from 7 to 15 mm. in crown-rump length.
B. p. pallida previously has been reported from the southern parts
of Baja California and Sonora.
Balantiopteryx plicata plicata Peters.—Specimens in the Museum
of Natural History from the following localities, several of which
are marginal, document better than previously has been done the
distribution of this subspecies in Sinaloa: 32 mi. SSE Culiacán
(60699); 10 mi. SE Escuinapa (68629); 17 mi. SSE Guamúchil
(60576); 5 mi. NW Mazatlán (85537-61, 85901-04); 1 mi. SE Mazatlán,
10 ft. (39461-76); 1 mi. S Pericos (60697-98, 60700); ½ mi. E
Piaxtla (60701); ½ mi. W Rosario, 100 ft. (39477-79); 5 mi. SSE
Rosario (60702-03); 4 mi. N Terrero (60695-96).
Pregnant females, each with a single embryo, were recorded in
1954 from 4 mi. N Terrero, 2 (June 9), 1 mi. S Pericos, 2 (June 13),
and 5 mi. SSE Rosario, 2 (June 20). None of 16 December-taken
females from 5 mi. NW Mazatlán was pregnant.
The specimen from 17 mi. SSE Guamúchil, preserved in alcohol,
is provisionally referred to B. p. plicata on geographic grounds inasmuch
as specimens from the nearby localities of 1 mi. S Pericos
and 4 mi. N Terrero, although more grayish on the average than
specimens from southern Sinaloa, are somewhat darker and distinctly
larger than specimens of B. p. pallida from along the Río del
Fuerte in northern Sinaloa. Specimens from southern Sinaloa
average only slightly paler than typical plicata examined from
southern México and Nicaragua.
Pteronotus psilotis (Dobson).—A total of six specimens from two
localities in southern Sinaloa provide the first records from the state
and are the northernmost records in western México. The two localities
are: ½ mi. S Concepción, 250 ft. (84987-90); 1 mi. W Matatán
(84985-86). The two individuals from the last-mentioned place
extend the known range of the species approximately 275 miles
north-northwest from a locality 7 mi. W, ½ mi. S Santiago, Colima
(Anderson, 1956:349), and place the limit of the known distribution
of P. psilotis farther to the north in western México than in the eastern
part of the country. We follow Burt and Stirton (1961:24-25)
in use of the generic name Pteronotus for this species.
The two specimens from 1 mi. W Matatán were shot at late dusk
as they foraged with other bats, presumably of the same species, low
over water at the place where the Río San Antonio joins the larger
Río Baluarte. The four individuals from ½ mi. S Concepción were
captured in mist nets stretched across the Río de las Cañas at the
Sinaloa-Nayarit border, and were taken shortly after dark at heights
of three feet or less above the water. Our six specimens all are
males. Five are in the reddish color phase and one is in the brownish
phase.
Average and extreme measurements of the six males, which average slightly
smaller than specimens examined from Colima and Guerrero, are as follows:
total length, 66.8 (65-69); length of tail, 16.3 (15-18); length of hind foot,
11.8 (11-12); length of ear from notch, 16.9 (16.5-17.0); length of forearm
(dry), 41.5 (40.6-42.4); weight in grams, 8.3 (6.9-9.8); greatest length of
skull, 15.4 (15.2-15.5); zygomatic breadth, 8.3 (8.2-8.4); interorbital constriction,
3.4 (3.3-3.6); mastoid breadth, 8.7 (8.6-8.8); length of maxillary tooth-row,
5.8 (5.8-5.9); breadth across M3, 5.4 (5.3-5.6).
Sturnira lilium parvidens Goldman.—The first specimens to be
reported from Sinaloa are as follows: 32 mi. SSE Culiacán (61087);
1 mi. S El Dorado (75207); Pánuco, 22 km. NE Concordia (85648-50).
The three bats from the last-mentioned locality were caught
after midnight in a mist net stretched across a road adjacent to a
nearly dry stream bed. The vegetation in the vicinity of the net
consisted mostly of dry weeds and grass along with some low shrubs,
but a tree-filled canyon was about one-fourth mile above the net.
We lack details about the capture of the other two bats.
S. l. parvidens has been reported only once from farther north in
western México than Sinaloa. Anderson (1960:7) recorded five
specimens from along the Río Septentrión, 1½ mi. SW Tocuina, Chihuahua.
Artibeus lituratus palmarum Allen and Chapman.—This species
has been reported once previously from Sinaloa (from 1 mi. S El
Dorado by Anderson, 1960:3). Six specimens (85668-72, 85674),
all males, collected on December 23 and 24, 1960, at Pánuco, 22 km.
NE Concordia, provide the second known occurrence in the state.
Artibeus toltecus (Saussure).—A male (85666) from Pánuco, 22
km. NE Concordia, provides the first record of this species from
Sinaloa and extends the known range northwestward approximately
182 miles from Ambas Aguas [= 6½ km. SW Amatlán de Jora],
Nayarit (Andersen, 1908:300). Our specimen was taken on December
22, 1960, in a mist net placed across a road in an area where
vegetation consisted mostly of weeds, grasses and shrubs. Two
Glossophaga soricina leachii and two Choeronycteris mexicana were
taken in the same net.
Davis' (1958:165-166) key is useful in separating the small Mexican
members of the genus Artibeus, but we have found some adults
of toltecus to be smaller than the key indicates. For example, in the
12 Mexican specimens (Oaxaca, 6, Tamaulipas, 3, Jalisco, 2, Sinaloa,
1) examined by us the total length of skull varies from 19.7 to
21.0 and the forearm from 36.3 to 42.6.
Dalquest (1953) and more recently Koopman (1961) regarded
A. toltecus and the larger A. aztecus, which occurs in the same areas
but at higher elevations than toltecus, as subspecies of the more
southerly A. cinereus. Davis (op. cit.), on the other hand, recognized
toltecus, aztecus, and cinereus as distinct species. More specimens
of small and medium-sized Artibeus are needed from México
before this baffling complex can be studied adequately, but on the
basis of specimens examined we are inclined to agree with Davis
as concerns the specific distinctness of toltecus and aztecus. In
Tamaulipas (the mammalian fauna of which is currently under
study by Alvarez) for example, toltecus is known from Rancho
Pano Ayuctle at an elevation of 300 feet in tropical deciduous forest,
whereas aztecus has been taken only four miles away at Rancho del
Cielo, but at an elevation of 3000 feet in cloud forest. The altitudinal
difference between ranges of the two kinds in Tamaulipas corresponds
to that found in Sinaloa (see Koopman, loc. cit.) and is
of approximately the same magnitude found by Davis at higher elevations
in Guerrero. This relationship suggests that the two kinds
are neither subspecies of a single species, nor individual variants
of a widespread, monotypic species, but probably are two different
species. We agree that one, most likely the smaller toltecus, may
eventually prove to be a northern subspecies of cinereus.
Myotis occultus Hollister.—A single specimen of this species
(67491) from 1 mi. N, ½ mi. E San Miguel provides the first certain
record from Sinaloa, and is indistinguishable from specimens from
Alamos, Sonora, that were referred to occultus by Hall and Dalquest
(1950:587). Miller and Allen (1928:100) identified a skin alone
from Escuinapa as occultus, but Hall and Dalquest (loc. cit.) later
assigned this specimen provisionally to M. fortidens on geographic
grounds and because it agreed in color with undoubted specimens
of the latter from Guerrero. Specimens from south of San Miguel
and north of the undoubted range of fortidens are needed in order
to ascertain whether the two kinds are distinct species or instead
only subspecies of a single species.
The Sinaloan bat was taken in a mist net stretched over a drainage
ditch adjacent to the Río del Fuerte on the night of June 19-20,
1955, by R. H. Baker. Several other kinds of bats were obtained
(shot or netted) at the same place, among which was one specimen
of Myotis velifer. The specimens studied of occultus from Sinaloa
and Sonora are clearly separable from specimens of velifer from the
same region (Sonora and northern Sinaloa) in having paler (more
reddish) pelage, shorter forearm, smaller skull, relatively broader
rostrum, and four fewer teeth.
Myotis velifer velifer (J. A. Allen).—Three specimens from the
following localities in northern Sinaloa provide the first records of
the species from the state: El Fuerte (75234); Río del Fuerte, 1
mi. N, ½ mi. E San Miguel (67490); Río del Fuerte, 10 mi. NNW
Los Mochis (61149). The subspecies M. v. velifer has been reported
previously from the adjacent states of Chihuahua, Durango,
and Sonora.
A female (61149) obtained on June 8, 1954, carried a single embryo
that measured 3 mm. in crown-rump length.
Lasiurus borealis teliotis (H. Allen).—A female from 10 mi.
NNW Los Mochis (61172), obtained on June 8, 1954, represents
the first record of the species from Sinaloa, and is tentatively referred
to this subspecies. It resembles cranially, but is paler than,
Californian specimens seen of teliotis.
Molossus ater nigricans Miller.—This large free-tailed bat previously
has been reported no farther north in western México than
the type locality, Acaponeta, Nayarit. Nineteen specimens from
four different localities in Sinaloa are as follows: 1 mi. SE Camino
Reál, 400 ft. (85093-99); 32 mi. SSE Culiacán (61279-87); 1 mi. S
Pericos (61277-78); ½ mi. E Piaxtla (61288). The specimens labeled
with reference to Camino Reál and Piaxtla were obtained
along the Río Piaxtla at approximately the same place. Those from
1 mi. S Pericos extend the known range of the species approximately
225 miles northwestward.
M. a. nigricans is characteristically an early flier. Along the Río
Piaxtla, 1 mi. SE Camino Reál, where bats probably found daytime
retreats in the rocky walls of the steep-sided valley of the river, individuals
first appeared early in the evening when the sun was still
on the western horizon, but were gone before other species of bats
were seen. A female from 32 mi. SSE Culiacán, taken on June 18,
1954, contained one embryo that was 18 mm. in crown-rump length.
Each of the color phases of the species, reddish (8) and black (11),
are represented among our specimens. We follow Goodwin (1960)
in the use of the specific name ater for this bat.
Dasypus novemcinctus mexicanus Peters.—Two armadillos
(85402-03) from the valley of the Río del Fuerte, 3 mi. NE San
Miguel, 300 ft., are the first of the species to be reported from
northern Sinaloa. They extend the known range northwestward in
the state approximately 285 miles from Escuinapa (Russell, 1953:25)
and signal the possible occurrence of D. n. mexicanus in southern
Sonora. Sign of the armadillo was abundant at the place where
our two specimens were collected. Because it was felt that the
species possibly had been introduced along the Río del Fuerte, a
number of local residents were questioned on the point, but all insisted
that armadillos were native to the area.
External measurements of 85402 (female) and 85403 (male) are, respectively,
as follows: total length, 725, 748; length of tail, 351, 357; length of
hind foot, 87, 89; length of ear from notch, 39, 39.
Sylvilagus audubonii goldmani (Nelson).—This cottontail has
been reported from Sinaloa only from Bacubirito, Culiacán (type
locality), and Sinaloa (Nelson, 1909:226). Additional records are:
12 mi. N Culiacán (67561-62); 6 mi. N El Dorado (75263); 6 mi. N,
1½ mi. E El Dorado (75264-66); 7 mi. NE El Fuerte (81076-77); and
1 mi. S Pericos (61292-93). Specimens from the vicinity of El Dorado
extend the known range some 30 miles southward from the
type locality. A female from 1 mi. S Pericos that was taken on
June 13, 1954, carried three embryos that measured 29 mm. in
crown-rump length.
Sciurus truei Nelson.—Three specimens (61300-02) of this species
collected by A. A. Alcorn on June 19, 1954, 32 mi. SSE Culiacán
extend the known range approximately 210 miles south-southeast
from Guirocoba, Sonora (Burt, 1938:38), and provide the first record
from Sinaloa. Two of the specimens are females and each was
pregnant, one with two embryos and the other with three.
Our specimens generally agree in color with S. truei, but are
larger than typical individuals and in this respect approach S. sinaloensis
of southern Sinaloa. Probably truei and sinaloensis both are
only subspecies of the more southerly S. colliaei. The three nominal
species currently constitute the S. colliaei group in which the presence
or absence of P3 seems to vary geographically. The tooth frequently
is absent in the northern truei and usually present (invariably
in the specimens we have examined) in colliaei. Only one of
our Sinaloan specimens is accompanied by a skull; in it P3 is present
on the right side and absent on the left.
External measurements of the male and two females are, respectively: total
length, 512, 508, 504; length of tail, 263, 263, 252; length of hind foot, 64, 63,
64; length of ear from notch, 28, 29, 28. Cranial measurements of 61300 (a
female) are: greatest length of skull, 56.2; zygomatic breadth, 32.6; interorbital
constriction, 17.9; postorbital constriction, 17.9; length of nasals, 17.3;
alveolar length of maxillary tooth-row (on side lacking P3), 10.9.
Thomomys umbrinus atrovarius J. A. Allen.—Two specimens
(85104-05) from the valley of the Río Piaxtla, 1 mi. SE Camino
Reál, 400 ft., resemble the description of atrovarius and agree in
size, color and most cranial details with a specimen (85744) from
5 mi. NW Mazatlán. The first-mentioned specimens extend the
known range of the subspecies some 50 miles northward from Mazatlán
(Bailey, 1915:96), and indicate the probable occurrence of
the species at lower elevations in other parts of central Sinaloa.
Peromyscus merriami goldmani Osgood.—This subspecies has
been reported previously only from the type locality, Alamos, Sonora.
Eight specimens were collected in Sinaloa by W. L. Cutter
in the autumn of 1957 as follows: 6 mi. N, 1½ mi. E El Dorado
(75368-72); 2½ mi. N El Fuerte (75365-66); El Fuerte (75367).
The first-mentional locality is approximately 200 miles south-south-east
of the type locality. All specimens collected by Cutter were
taken in lowland areas, supporting remarks by Commissaris (1960)
concerning habitat preferences of P. merriami as compared with
those of the closely related P. eremicus.
Two of three females from northeast of El Dorado were pregnant
on November 18 and 19; one carried four embryos (8 mm. in crown-rump
length) and the other three (11 mm.).
External and cranial measurements of P. m. goldmani previously were
known only for the holotype (Osgood, 1909:252, 267). Measurements of
five adults, a male (75370) and four females (75365, 75369, 75371-72) are,
respectively, as follows: total length, 204, 225, 215, 214, 210; length of tail,
105, 120, 110, 108, 109; length of hind foot, 21, 23, 23, 22, 22; length of ear
from notch, 21, 21, 21, 20, 21; weight in grams, 29, 19, 35 (pregnant), 33, 34
(pregnant); greatest length of skull, 26.6, 26.5, 26.9, 26.5,——; zygomatic
breadth, 13.8, 13.9, 14.1, 13.4,——; interorbital constriction, 3.9, 3.8, 4.0,
4.0,——; mastoid breadth, 11.8, 11.9, 11.8, 11.9, 11.5; length of nasals, 10.1,
9.4, 10.0, 10.0,——; length of maxillary tooth-row, 4.5, 4.3, 4.1, 4.1, 4.1.
Onychomys torridus yakiensis Merriam.—Only one specimen of
this grasshopper mouse has been reported previously from Sinaloa
(from the town of Sinaloa by Hollister, 1914:471). Thirteen specimens
in the Museum of Natural History better define the range of
the species in the state as follows: 12 mi. N Culiacán (67981-82); 6
mi. N, 1½ mi. E El Dorado (75374-80); 2½ mi. N El Fuerte (75373);
1 mi. S Pericos (62118-20). The individuals from northeast of El
Dorado extend the known range of the species some 115 miles south-southeast
from Sinaloa.
A female taken on November 17, 1957, from 6 mi. N, 1½ mi. E El
Dorado carried two embryos that measured 23 mm. in crown-rump
length. A female obtained on November 18 at the same place carried
four embryos that measured 10 mm.
Neotoma albigula melanura Merriam.—Four specimens from
northern Sinaloa, two (85379-80) from 3 mi. N, 1 mi. E San Miguel,
350 ft., and two (75386-87) from 2½ mi. N El Fuerte, provide the
first records of the species from the state. N. a. melanura has been
known previously from adjacent parts of Sonora and Chihuahua
(see Hall and Kelson, 1959:687-688). The specimens from northeast
of San Miguel were trapped in runways under cholla cactus,
in which nests also were found, on a slope above a rocky arroyo.
Spilogale pygmaea Thomas.—Two pygmy spotted skunks from
5 mi. NW Mazatlán (85898-99) are the fifth and sixth of the species
to be reported (see Van Gelder, 1959:381) and the second and third
taken in Sinaloa (the holotype of pygmaea was obtained at Rosario).
One of our specimens, an adult male, was shot on the night
of January 10, 1961, as it foraged near an old hollow tree in weedy-thorn
bush habitat adjacent to the Pacific Ocean. The hollow tree
contained the nest of a woodrat. The second, an adult female, was
trapped nearby in a commercial rat trap baited with peanut butter
and set near a burrow in a forested area having little undergrowth.
The two individuals here reported fit fairly well the description of color
pattern given for the species by Van Gelder (op. cit.: 379), but are larger
(considering sex), externally and cranially, than any of the four specimens reported
previously. Measurements of the male and female are, respectively:
total length, 291, 270; length of tail, 65, 58; length of hind foot, 38, 35; length
of ear from notch, 25, 23; weight in grams, 247.0, 190.5; condylobasal length,
46.0, 42.9; occipitonasal length, 45.0, 41.4; zygomatic breadth, 29.0, 27.3;
mastoid breadth, 23.9, 22.5; interorbital constriction, 14.3, 13.6; postorbital
constriction, 14.8, 14.1; palatilar length, 15.6, 14.6; postpalatal length, 23.2,
22.4; cranial depth, 16.6, 15.2; length of maxillary tooth-row, 14.2, 13.4.
Cranial measurements were taken in the manner described by Van Gelder
(op. cit.: 236-237).
LITERATURE CITED
Andersen, K.
1908. A monograph of the Chiropteran genera Uroderma, Enchistenes,
and Artibeus. Proc. Zool. Soc. London, pp. 204-319, illustrated,
September.
Anderson, S.
1956. Extension of known ranges of Mexican bats. Univ. Kansas Publ.,
Mus. Nat. Hist., 9:347-351, August 15.
1960. Neotropical bats from western México. Univ. Kansas Publ., Mus.
Nat. Hist., 14:1-8, October 24.
Bailey, V.
1915. Revision of the pocket gophers of the genus Thomomys. N. Amer.
Fauna, 39:1-126, 8 pls., 10 figs., November 15.
Baker, R. H., and A. A. Alcorn
1953. Shrews from Michoacán, México, found in barn owl pellets. Jour.
Mamm., 34:116, February 9.
Burt, W. H.
1938. Faunal relationships and geographic distribution of mammals in
Sonora, Mexico. Misc. Publ. Mus. Zool., Univ. Michigan, 39:1-77,
26 maps, February 15.
Burt, W. H., and R. A. Stirton
1961. The mammals of El Salvador. Misc. Publ. Mus. Zool., Univ. Michigan,
117:1-69, 1 fig., September 22.
Commissaris, L. R.
1960. Morphological and ecological differentiation of Peromyscus merriami
from southern Arizona. Journ. Mamm., 41:305-310, 2 figs.,
August 15.
Coues, E.
1877. Precursory notes on American insectivorous mammals, with descriptions
of new species. Bull. U. S. Geol. Surv. Territories, 3:631-653,
May 15.
Dalquest, W. W.
1953. Mexican bats of the genus Artibeus. Proc. Biol. Soc. Washington,
66:61-65, August 10.
Davis, W. B.
1958. Review of the Mexican bats of the Artibeus "cinereus" complex.
Proc. Biol. Soc. Washington, 71:163-166, 1 fig., December 31.
Dobson, G. E.
1890. A monograph of the Insectivora, systematic and anatomical. Part
III (includes only plates XXIII-XXVIII), Gurney and Jackson,
London, May.
Goodwin, G. G.
1960. The status of Vespertilio auripendulus Shaw, 1800, and Molossus
ater Geoffroy, 1805. Amer. Mus. Novit, 1994:1-6, 1 fig., March 8.
Hall, E. R., and W. W. Dalquest
1950. Pipistrellus cinnamomeus Miller 1902 referred to the genus Myotis.
Univ. Kansas Publ., Mus. Nat. Hist., 1:581-590, 5 figs., January 20.
Hall, E. R., and K. R. Kelson
1959. The mammals of North America. Ronald Press, New York, 2:viii+547-1083+79,
illustrated, March 31.
Hoffmeister, D. H., and W. W. Goodpaster
1954. The mammals of the Huachuca Mountains, southeastern Arizona.
Illinois Biol. Monog., 24:v+1-152, 27 figs., December 31.
Hollister, N.
1914. A systematic account of the grasshopper mice. Proc. U. S. Nat.
Mus., 47:427-489, pl. 15, 3 figs., October 29.
Hooper, E. T.
1961. Notes on mammals from western and southern Mexico. Jour.
Mamm., 42:120-122, February 20.
Koopman, K. F.
1961. A collection of bats from Sinaloa, with remarks on the limits of the
Neotropical Region in northwestern Mexico. Jour. Mamm., 42:536-538,
November 20.
Merriam, C. H.
1895. Revision of the shrews of the American genera Blarina and Notiosorex.
N. Amer. Fauna, 10:5-34, pls. 1-3, 2 figs., December 31.
Miller, G. S., Jr., and G. M. Allen
1928. The American bats of the genera Myotis and Pixonyx. Bull. U. S.
Nat. Mus., 144:viii+1-218, 1 pl., 1 fig., 13 maps, May 25.
Nelson E. W.
1909. The rabbits of North America. N. Amer. Fauna, 29:1-314, 13 pls.,
19 figs., August 31.
Osgood, W. H.
1909. Revision of the mice of the American genus Peromyscus. N. Amer.
Fauna, 28:1-285, 8 pls., 12 figs., April 17.
Poole, A. J., and V. S. Schantz
1942. Catalog of the type specimens of mammals in the United States
National Museum, including the Biological Surveys collection.
Bull. U. S. Nat. Mus., 178:xiii+1-705, April 9.
Russell, R. J.
1953. Description of a new armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) from
Mexico with remarks on geographic variation of the species. Proc.
Biol. Soc. Washington, 66:21-25, March 30.
Twente, J. W., and R. H. Baker
1951. New records of mammals from Jalisco, Mexico, from barn owl
pellets. Jour. Mamm., 32:120-121, February 15.
Van Gelder, R. G.
1959. A taxonomic revision of the spotted skunks (genus Spilogale).
Bull. Amer. Mus. Nat. Hist., 117:229-392, 47 figs., June 15.
Transmitted March 15, 1962.
29-3000
Transcriber's Notes
Corrected typo: semi-colon for comma in "postpalatal length, 23.2, 22.4;".
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Noteworthy Mammals from Sinaloa, Mexico, by
J. Knox Jones, Jr. and Ticul Alvarez and M. Raymond Lee
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK MAMMALS ***
***** This file should be named 31683-h.htm or 31683-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/3/1/6/8/31683/
Produced by Chris Curnow, Simon Gardner and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
[email protected]. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
[email protected]
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.
 Fig. 1. Map of Sinaloa on which are plotted symbols representing placenames
mentioned in text. From north to south, these are: El Fuerte; San
Miguel; Los Mochis; Guamúchil; Terrero; Pericos; Culiacán; El Dorado;
Piaxtla and Camino Reál (one symbol); Pánuco; Mazatlán; Matatán; Rosario;
Escuinapa; Concepción.
Fig. 1. Map of Sinaloa on which are plotted symbols representing placenames
mentioned in text. From north to south, these are: El Fuerte; San
Miguel; Los Mochis; Guamúchil; Terrero; Pericos; Culiacán; El Dorado;
Piaxtla and Camino Reál (one symbol); Pánuco; Mazatlán; Matatán; Rosario;
Escuinapa; Concepción.