
Sarah Bernhardt as Cleopatra.
Project Gutenberg's Great Men and Famous Women, Vol. 8 (of 8), by Various
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
Title: Great Men and Famous Women, Vol. 8 (of 8)
A series of pen and pencil sketches of the lives of more
than 200 of the most prominent personages in History
Author: Various
Editor: Charles F. Horne
Release Date: July 8, 2009 [EBook #29352]
Language: English
Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1
*** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK GREAT MEN AND FAMOUS WOMEN ***
Produced by Sigal Alon, Christine P. Travers and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)
Transcriber's note: Obvious printer's errors have been corrected, all other inconsistencies are as in the original. The author's spelling has been maintained.

Sarah Bernhardt as Cleopatra.
A Series of Pen and Pencil Sketches of
THE LIVES OF MORE THAN 200 OF THE MOST PROMINENT PERSONAGES IN HISTORY.
VOL. VIII.
Copyright, 1894, by SELMAR HESS
Edited By Charles F. Horne
New-York: Selmar Hess Publisher
Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.
VOLUME VIII.
PHOTOGRAVURES
| ILLUSTRATION | ARTIST | To face page |
| SARAH BERNHARDT AS CLEOPATRA, | Georges Clairin | Frontispiece |
| MICHAEL ANGELO AND VITTORIA COLONNA, | Hermann Schneider | 220 |
| ALBERT DÜRER VISITS HANS SACHS, | Richard Gross | 234 |
| MARIE DE MEDICI AT THE HOUSE OF RUBENS, | Florent Willems | 240 |
| CONNOISSEURS AT REMBRANDT'S STUDIO, | Adolphe-Alexandre Lesrel | 244 |
| MEISSONIER'S ATELIER, | Georges Bretegnier | 272 |
| MOZART SINGING HIS REQUIEM, | Thomas W. Shields | 314 |
| AN ANECDOTE ABOUT BEETHOVEN, | Paul Leyendecker | 322 |
| FRANZ LISZT, | Fortuné-Joseph-Seraphin Layraud | 334 |
| WAGNER AND HIS FRIENDS, | Wilhelm Beckmann | 340 |
| RACHEL AS THE MUSE OF GREEK TRAGEDY, | Jean Léon Gérôme | 368 |
| JOE JEFFERSON AS BOB ACRES, | From life | 376 |
WOOD-ENGRAVINGS AND TYPOGRAVURES
| RAPHAEL INTRODUCED TO DA VINCI, | Brune Pagès | 212 |
| LEO X. AT RAPHAEL'S BIER, | Pietro Michis | 224 |
| A FÊTE AT THE HOUSE OF TITIAN, | F. Kraus | 228 |
| ALBERT DÜRER'S WEDDING, | A. Bodenmüller | 232 |
| HOGARTH SKETCHING THE HIGHWAY OF QUEENBOROUGH, | 248 | |
| BENJAMIN WEST, PRESIDENT OF THE ROYAL ACADEMY, | Sir Thomas Lawrence | 258 |
| ROSA BONHEUR, | E. Dubufe | 278 |
| HANDEL'S RIVER-CONCERT FOR GEORGE I., | A. Hamman | 304 |
| HAYDN COMPOSING HIS "CREATION," | A. Hamman | 318 |
| PAGANINI IN PRISON, | Louis Boulanger | 326 |
| GARRICK AS RICHARD III., | William Hogarth | 346 |
| FORREST AS METAMORA, | From Photograph | 352 |
| CHARLOTTE CUSHMAN AS MRS. HALLER, | Watkins | 360 |
Phidias, one of the greatest sculptors the world has seen, and whose name has become, as it were, the synonym of his art, was born at Athens about 500 B.C. He belonged to a family of artists, none of whom indeed were distinguished in their profession, but their varied occupations furnished the atmosphere in which such a talent as that of Phidias could best be fostered and brought to maturity. His father was Charmides, who is believed to have been an artist, because the Greeks, in their inscriptions, did not associate the name of the father with that of the son unless both were of the same calling. A brother of Phidias, Panœnos, was a painter, and is mentioned among those artists, twenty or more in number, who in conjunction with Polygnotus, one of the chief painters of his day, were employed in the decoration of the Pœcile or Painted Portico, one of the many beautiful buildings erected by Cimon. The Pœcile was simply a long platform, with a roof supported by a row of columns on one side and by a wall on the other. It was called "the painted," because the wall at the back was covered with a series of large historical pictures containing many figures, and recording some of the chief events of the time, together with others relating to an earlier and more shadowy epoch. The subject of the painting, executed, at least in part, by the brother of Phidias, was the Battle of Marathon, in which great event it is thought he may himself have taken part.
The boyhood of Phidias fell in a time of national revival, when under the influence of an ennobling political excitement, all the arts were quickened to a fresh, original, and splendid growth. The contest between the Greeks and Persians, which had begun with the Ionian revolt, was in full activity at the time of his birth. He was ten years old when the battle of Marathon was fought, and when he was twenty, four of the most striking events in the history of Greece were crowded into a single year; the battle of Thermopylæ, the victory at Salamis, and the twin glories of Platæa and Mycale. His early youth, therefore, was nourished by the inspiring influences that come from the victorious struggle of a people to maintain their national life. He was by no means the only sculptor of his time whom fame remembers, but he alone, rejecting trivial themes, consecrated his talent to the nobler subjects of his country's religious (p. 204) life and the ideal conception of her protecting gods. No doubt, Phidias, like all who are born with the artistic temperament, would be interested from childhood in the progress of the splendid works with which Athens was enriching herself under the rule of Cimon. But his interest must have been greatly increased by the fact that his brother Panœnos was actively engaged in the decoration of one of those buildings. It would be natural that he should be often drawn to the place where his brother was at work, and that the sight of so many artists, most of them young men, filled with the generous ardor of youth, and inspired by the nature of their task, should have stirred in him an answering enthusiasm. It gives us a thrill of pleasure to read in the list of these youths the name of the great tragic poet, Euripides, who began life as a painter, and in whose plays we find more than one reference to the art. It cannot be thought unreasonable to suppose that two such intelligences as these must have had an attraction for one another, and that, as in the case of Dante and Giotto, the great poet and the great artist would be drawn together by a likeness in their taste and aims.
Phidias studied his art first at Athens, with a native sculptor, Hegias, of whom we know nothing except from books. Later, he went to Argos, and there put himself under the instruction of Ageladas, a worker chiefly in bronze, and very famous in his time, of whom, however, nothing remains but the memory of a few of his more notable works. For us, his own works forgotten, he remains in honor as the teacher of Myron, of Polycletus, and of Phidias, the three chief sculptors of the next generation to his own. On leaving the workshop of Ageladas, Phidias executed several statues that brought him prominently before the public. For Delphi, he made a group of thirteen figures in bronze, to celebrate the battle of Marathon and apotheosize the heroes of Attica. In this group, Miltiades was placed in the centre, between Athena, the tutelary goddess of Athens, and Apollo, the guardian of Delphi; while on each side were five Athenian heroes, Theseus and Codrus with others, arranged in a semicircle. This important work was paid for by Athens out of her share in the spoils of Marathon. Another important commission executed by Phidias was a statue of Athena made for her temple at Platæa, and paid for with the eighty talents raised by the contributions of the other Grecian states as a reward for the splendid services of the Platæans at Marathon, where they played somewhat the same part as the Prussians at the battle of Waterloo. The head, hands, and feet of this statue were of marble, but the drapery was of gold; so arranged, probably, as in the case of the great statue of Athena designed later by Phidias for the Parthenon, as to be removable from the marble core at pleasure. Phidias made so many statues of the virgin goddess Athena, that his name became associated with hers, as at a later day that of Raphael was with the Virgin Mary. In the first period of his artistic career, moved perhaps by his patriotic gratitude for her intervention in behalf of his native state, he had represented the goddess as a warlike divinity, as here at Platæa; but in his later conceptions, as in a statue made for the Athenians of Lemnos, Athena appeared invested with milder attributes, and with a graceful and winning type of beauty.
(p. 205) In their invasion of Attica the Persians had destroyed the city of Athens, and the people, who had fled to all quarters of the peninsula to seek refuge from the enemy, returned after the victory at Salamis and the flight of the Persians, to find their homes a heap of ruins. The dwelling-houses of the Greeks were everywhere, even in their largest cities, built of mean materials: walls of stubble overlaid with stucco and gayly painted. It was not long, therefore, before Athens resumed something of her old appearance, with such improvements as always follow the rebuilding of a city. The most important change effected was that brought about in the character of the great plateau, the fortified rock of the Acropolis. Here, as in many Greek cities, the temples of the gods had been erected, and about them, as about the cathedrals of the Middle Ages, there had grown up a swarm of houses and other buildings built by generations of people who sought there at once the protection of the stockade which enclosed the almost inaccessible site, and the still further safeguard of the presence of the divinities in their temples. The destructive hand of the Persian invaders had swept this platform clear of all these multiplied incumbrances, and in the rebuilding of the city it was determined to reserve the Acropolis for military and religious uses alone.
The work of improvement was begun by Cimon, who, however, confined his attention chiefly to the lower city that clustered about the base of the Acropolis. Here, among other structures, he built the temple of Theseus and the Painted Portico, and he also erected, near the summit of the Acropolis, on the western side, the little gem-like temple of the Wingless Victory, Nike Apteros, in commemoration of the success of the Athenian arms at the battle of the Eurymedon. It was from Cimon that Phidias received his first commission for work upon the Acropolis, where later he was to build such a lasting monument to his own fame and to the fame of his native land. The commission given him by Cimon was to erect a bronze statue of Athena which was to stand on the citadel, at once a symbol of the power of Athens and a tribute to the protecting goddess of the city. The work upon the statue was probably begun under Cimon, but according to Ottfried Müller it was not completed at the death of Phidias. It stood in the open air, and nearly opposite the Colonnade at the entrance of the great flight of marble steps that led from the plain to the summit of the Acropolis, and was the first object to meet the eye on passing through the gateway. It represented the goddess, armed, and in a warlike attitude, from which it derived its name, Athena Promachos: Athena, the leader of the battle. With its pedestal it stood about seventy feet high, towering above the roof of the Parthenon, the gilded point of the brazen spear held by the goddess flashing back the sun to the ships as in approaching Athens they rounded the promontory of Sunium. We read that the statue was still standing so late as 395 A.D., and it is said that its towering height and threatening aspect caused a panic terror in Alaric and his horde of barbarians when they climbed the Acropolis to plunder its temple of its treasure.
But it was under the rule of Pericles that Phidias was to find at Athens his richest employment. Pericles had determined, probably by the advice of Phidias, (p. 206) to make the Acropolis the seat and centre of the new and splendid city that was to arise under his administration. The first great undertaking was the building of a temple to Athena Parthenos, Athena the Virgin, a design believed to have been suggested to Pericles by Phidias. The plans were intrusted to Ictinus, an Athenian, one of the best architects of the day; but the general control and superintendence of the work were given to Phidias. As the building rose to completion, workmen in all branches of the arts flocked to Athens from every part of Greece and were given full employment by Phidias in the decoration and furnishing of the temple.
The taste of Phidias controlled the whole scheme of decoration applied to the building, into which color entered, no doubt, to a much greater extent than was formerly believed. Even after time and the destructive hand of man have done their worst, there still remain sufficient traces of color to prove that the sculpture, and the whole upper part of the temple, were painted in bright but harmonious colors, and that metal ornaments and accessories accented the whole scheme with glittering points of light reflected from their shining surfaces.
The sculptures with which the Parthenon was adorned by Phidias, and which were executed under his immediate superintendence, consisted of two great groups that filled the eastern and western pediments; of groups of two figures each in the ninety-two metopes or panels above the outer row of columns; and, finally, the famous frieze that ran completely round the temple itself, just below the ceiling of the colonnade, and at a height of about thirty-nine feet from the floor.
The subject of the group that filled the eastern pediment, the one above the entrance door of the temple, was the birth of Athena. Just how the event was represented we do not know because quite half the group, including the principal figures, disappeared very early in our era, and no description of them remains in any ancient or modern writer. The group in the western pediment represented the contest between Athena and Poseidon for the dominion over Attica. According to the legend, the strife between the two divinities took place in an assembly of the gods on the Acropolis, who were to determine which of the two contestants should be the protector of the city. To prove his power, Poseidon struck the rock with his trident, and a salt spring leaped forth, as if the sea itself had obeyed the call of its lord. Athena struck the ground, and an olive-tree sprang up, the emblem of peace and of the victories of commerce, and the assembly awarded the prize to her. The goddess having thus received the sovereignty of Athens, it was but natural that a day should be set apart for her special honor, and a festival instituted to commemorate the great event. This was the greater Panathenaia, or All Athenians Day, which was celebrated every fourth year in honor of the goddess, and which, as its name implies, was taken part in by all the people of the city. It occurred in the early summer and lasted five days. On the fifth day, it closed with a procession which went through all the chief streets of the city and wound its way up the Great Stairway to the Acropolis, bearing the peplos or embroidered robe woven by young virgin ladies of Athens, chosen from the highest families, and known for their skill in this (p. 207) kind of work. After the peplos had been consecrated in the temple it was placed with due solemnities upon the ancient and venerable figure of the goddess, made of olive-wood, and said to have descended from heaven. From its subject, which thus celebrates the Panathenaic procession, the frieze is often called the Panathenaic frieze.
It is carved from Pentelic marble, of which material the marble building is constructed. Its original length, running as it did around the entire building, was 522.80 feet, of which about 410 feet remain. Of this portion, 249 feet are in the British Museum in slabs and fragments; the remainder is chiefly in the Louvre, with scattered fragments in other places. As a connected subject this was the most extensive piece of sculpture ever made in Greece. From all that can be gathered from the study of the fragments that remain, the design of the frieze was of the utmost simplicity and characterized by the union of perfect taste and clear purpose that marks all the work of the great sculptor. The subject begins in the frieze at the western end of the temple, where we watch the assembling of the procession. It then proceeds along the northern and southern sides of the building, in what we are to suppose one continuous line, moving toward the east, since all the faces are turned that way; and at the eastern end, directly over the main entrance to the building, the two parts of the procession meet, in the presence of the magistrates and of the divinities who had places of worship in Athens.
Of the grace, the skill in arrangement, the variety of invention, the happy union of movement and repose shown in this work, not only artists—men best fitted to judge its merits from a technical point of view—but the cultivated portion of the public, and a large and ever-increasing circle of every-day people, have by common consent agreed in praise. By the multiplication of casts, to be found now in all our principal museums, we are enabled to study and to enjoy the long procession even better than it could have been enjoyed in its original place, where it must have been seen at a great disadvantage in spite of the skill shown by Phidias in adapting it to its site; for, as the frieze stood thirty-nine feet from the floor, and as the width of the portico between the wall and the columns was only nine feet, it was seen at a very sharp angle, and owing to the projection of the roof beyond the wall of the temple the frieze received only reflected light from the marble pavement below.
Apart from the marble sculptures on the exterior of the Parthenon, the two most famous works of Phidias were the statues of Athena, made for the interior of the Parthenon, and of Zeus for the temple of the god at Olympia in Elis. Both these statues were of the sort called Chryselephantine, from the Greek chrousous, golden, and elephantinos, of ivory; that is, they were constructed of plates of gold and ivory, laid upon a core of wood or stone. The style was not new, though its invention was at one time ascribed to Phidias. It came from the East, but it was now employed for the first time in Greece in a work of national importance.
In the Athena, the face, neck, arms, hands, and feet were made of ivory, and the (p. 208) drapery and ornaments, the helmet, the shield, and the sandals of gold, which as in the case of the statue made for Platæa, was removable at pleasure. The height of the statue, including the pedestal, was nearly forty feet. The goddess stood erect, clothed with a tunic reaching to the ankles, and showing her richly sandalled feet. She had the ægis on her breast, her head was covered with a helmet, and her shield, richly embossed with the Battle of the Amazons, rested on the ground at her side. In one hand she held a spear, and in the other, an image of Victory six feet high.
A still more splendid work, and one which raised the fame of Phidias to the highest point, was the statue of the Olympian Zeus, made for the Eleans. In this statue, Phidias essayed to embody the Homeric ideal of the supreme divinity of the people of Greece sitting on his throne as a monarch, and in an attitude of majestic repose. The throne, made of cedar-wood, was covered with plates of gold, and enriched with ivory, ebony, and precious stones. It rested on a platform twelve feet high, made of costly marble and carved with the images of the gods who formed the council of Zeus on Olympus. The feet of the god rested on a footstool supported by lions, and with the combat of Theseus and the Amazons in a bas-relief on the front and sides. In one hand Zeus held the sceptre, and in the other a winged Victory. His head was crowned with a laurel wreath; his mantle, falling from one shoulder, left his breast bare and covered the lower part of his person with its ample folds of pure gold enamelled with flowers. The whole height of the statue with the pedestal was about fifty feet; by its very disproportion to the size of the temple it was made to appear still larger than it really was. This statue was reckoned one of the wonders of the world. In it the Greeks seemed to behold Zeus face to face. To see it was a cure for all earthly woes, and to die without having seen it was reckoned a great calamity.
The downfall of Pericles, due to the jealousies of his rivals, carried with it the ruin of Phidias, his close friend, to whom he had entrusted such great undertakings. An indictment was brought against the sculptor, charging him with appropriating to himself a portion of the gold given him for the adornment of the statue of Athena; and according to some authorities Pericles himself was included in the charge. The gold had, however, been attached to the statue in such a manner that it could be taken off and weighed, and in the proof, the charge had to be abandoned. But Phidias did not escape so easily. He was accused of sacrilege in having introduced portraits of himself and Pericles on the shield of the goddess, where, says Plutarch, in the bas-relief of the Battle of the Amazons, he carved his own portrait as a bald old man lifting a stone with both hands, and also introduced an excellent likeness of Pericles fighting with an Amazon.
Phidias died in prison before the trial came off, and his name must be added to the long list of those whom an ungrateful world has rewarded for their services with ignominy and death.[Back to Contents]

Leonardo da Vinci seems to present in his own person a résumé of all the characteristics of the age in which he lived. He was the miracle of that age of miracles. Ardent and versatile as youth; patient and persevering as age; a most profound and original thinker; the greatest mathematician and most ingenious mechanic of his time; architect, chemist, engineer, musician, poet, painter—we are not only astounded by the variety of his natural gifts and acquired knowledge, but by the practical direction of his amazing powers. The extracts which have been published from MSS. now existing in his own handwriting show him to have anticipated by the force of his own intellect some of the greatest discoveries made since his time. "These fragments," says Mr. Hallam, "are, according to our common estimate of the age in which he lived, more like revelations of physical truths vouchsafed to a single mind than the superstructure of its reasoning upon any established basis. The discoveries which made Galileo, Kepler, Castelli, and other names illustrious; the system of Copernicus, the very theories of recent geologists, are anticipated by Da Vinci within the compass of a few pages, not perhaps in the most precise language, or on the most conclusive reasoning, but so as to strike us with something like the awe of preternatural knowledge. In an age of so much dogmatism he first laid down the grand principle of Bacon, that experiment and observation must be the guides to just theory in the investigation of nature. If any doubt could be harbored, not as to the right of Leonardo da Vinci to stand as the first name of the fifteenth century, which is beyond all doubt, but as to his originality in so many discoveries, which probably no one man, especially in such circumstances, has ever made, it must be by an hypothesis not very untenable, that some parts of physical science had already attained a height which mere books do not record."
It seems at first sight almost incomprehensible that, thus endowed as a philosopher, mechanic, inventor, discoverer, the fame of Leonardo should now rest on the works he has left as a painter. We cannot, within these limits, attempt to explain why and how it is that as the man of science he has been naturally and necessarily left behind by the onward march of intellectual progress, while as the (p. 210) poet-painter he still survives as a presence and a power. We must proceed at once to give some account of him in the character in which he exists to us and for us—that of the great artist.
Leonardo was born at Vinci, near Florence, in the Lower Val d'Arno, on the borders of the territory of Pistoia. His father, Piero da Vinci, was an advocate of Florence—not rich, but in independent circumstances, and possessed of estates in land. The singular talents of his son induced Piero to give him, from an early age, the advantage of the best instructors. As a child he distinguished himself by his proficiency in arithmetic and mathematics. Music he studied early, as a science as well as an art. He invented a species of lyre for himself, and sung his own poetical compositions to his own music, both being frequently extemporaneous. But his favorite pursuit was the art of design in all its branches; he modelled in clay or wax, or attempted to draw every object which struck his fancy. His father sent him to study under Andrea Verrocchio, famous as a sculptor, chaser in metal, and painter. Andrea, who was an excellent and correct designer, but a bad and hard colorist, was soon after engaged to paint a picture of the baptism of our Saviour. He employed Leonardo, then a youth, to execute one of the angels; this he did with so much softness and richness of color, that it far surpassed the rest of the picture; and Verrocchio from that time threw away his palette, and confined himself wholly to his works in sculpture and design, "enraged," says Vessari, "that a child should thus excel him."
The youth of Leonardo thus passed away in the pursuit of science and of art; sometimes he was deeply engaged in astronomical calculations and investigations; sometimes ardent in the study of natural history, botany, and anatomy; sometimes intent on new effects of color, light, shadow, or expression in representing objects animate or inanimate. Versatile, yet persevering, he varied his pursuits, but he never abandoned any. He was quite a young man when he conceived and demonstrated the practicability of two magnificent projects: one was to lift the whole of the church of San Giovanni, by means of immense levers, some feet higher than it now stands, and thus supply the deficient elevation; the other project was to form the Arno into a navigable canal as far as Pisa, which would have added greatly to the commercial advantages of Florence.
It happened about this time that a peasant on the estate of Piero da Vinci brought him a circular piece of wood, cut horizontally from the trunk of a very large old fig-tree, which had been lately felled, and begged to have something painted on it as an ornament for his cottage. The man being an especial favorite, Piero desired his son Leonardo to gratify his request; and Leonardo, inspired by that wildness of fancy which was one of his characteristics, took the panel into his own room, and resolved to astonish his father by a most unlooked-for proof of his art. He determined to compose something which should have an effect similar to that of the Medusa on the shield of Perseus, and almost petrify beholders. Aided by his recent studies in natural history, he collected together from the neighboring swamps and the river-mud all kinds of hideous reptiles, as adders, (p. 211) lizards, toads, serpents: insects, as moths, locusts, and other crawling and flying obscene and obnoxious things; and out of these he composed a sort of monster or chimera, which he represented as about to issue from the shield, with eyes flashing fire, and of an aspect so fearful and abominable that it seemed to infect the very air around. When finished, he led his father into the room in which it was placed, and the terror and horror of Piero proved the success of his attempt. This production, afterward known as the "Rotello del Fico," from the material on which it was painted, was sold by Piero secretly for one hundred ducats to a merchant, who carried it to Milan, and sold it to the duke for three hundred. To the poor peasant, thus cheated of his "Rotello," Piero gave a wooden shield, on which was painted a heart transfixed by a dart, a device better suited to his taste and comprehension. In the subsequent troubles of Milan, Leonardo's picture disappeared, and was probably destroyed as an object of horror by those who did not understand its value as a work of art.
During this first period of his life, which was wholly passed in Florence and its neighborhood, Leonardo painted several other pictures of a very different character, and designed some beautiful cartoons of sacred and mythological subjects, which showed that his sense of the beautiful, the elevated, and the graceful was not less a part of his mind than that eccentricity and almost perversion of fancy which made him delight in sketching ugly, exaggerated caricatures, and representing the deformed and the terrible.
Leonardo da Vinci was now about thirty years old, in the prime of his life and talents. His taste for pleasure and expense was, however, equal to his genius and indefatigable industry; and anxious to secure a certain provision for the future, as well as a wider field for the exercise of his various talents, he accepted the invitation of Ludovico Sforza il Moro, then regent, afterward Duke of Milan, to reside in his court, and to execute a colossal equestrian statue of his ancestor, Francesco Sforza. Here begins the second period of his artistic career, which includes his sojourn at Milan, that is from 1483 to 1499.
Vasari says that Leonardo was invited to the court of Milan for the Duke Ludovico's amusement, "as a musician and performer on the lyre, and as the greatest singer and improvisatore of his time;" but this is improbable. Leonardo, in his long letter to that prince, in which he recites his own qualifications for employment, dwells chiefly on his skill in engineering and fortification; and sums up his pretensions as an artist in these few brief words: "I understand the different modes of sculpture in marble, bronze, and terra-cotta. In painting, also, I may esteem myself equal to anyone, let him be who he may." Of his musical talents he makes no mention whatever, though undoubtedly these, as well as his other social accomplishments, his handsome person, his winning address, his wit and eloquence, recommended him to the notice of the prince, by whom he was greatly beloved, and in whose service he remained for about seventeen years. It is not necessary, nor would it be possible here, to give a particular account of all the works in which Leonardo was engaged for his patron, nor of the great political events in which he was involved, more by his position than (p. 212) by his inclination; for instance, the invasion of Italy by Charles VIII. of France, and the subsequent invasion of Milan by Louis XII., which ended in the destruction of the Duke Ludovico. The greatest work of all, and by far the grandest picture which, up to that time, had been executed in Italy, was the "Last Supper," painted on the wall of the refectory, or dining-room, of the Dominican convent of the Madonna delle Grazie. It occupied Leonardo about two years, from 1496 to 1498.
The moment selected by the painter is described in the 26th chapter of St. Matthew, 21st and 22d verses: "And as they did eat, he said, Verily, I say unto you, that one of you shall betray me: and they were exceeding sorrowful, and began every one of them to say unto him, Lord, is it I?" The knowledge of character displayed in the heads of the different apostles is even more wonderful than the skilful arrangement of the figures and the amazing beauty of the workmanship. The space occupied by the picture is a wall twenty-eight feet in length and the figures are larger than life.
Of this magnificent creation of art, only the mouldering remains are now visible. It has been so often repaired that almost every vestige of the original painting is annihilated; but from the multiplicity of descriptions, engravings, and copies that exist, no picture is more universally known and celebrated. Perhaps the best judgment we can now form of its merits is from the fine copy executed by one of Leonardo's best pupils, Marco Uggione, for the Certosa at Pavia, and now in London, in the collection of the Royal Academy. Eleven other copies, by various pupils of Leonardo, painted either during his lifetime or within a few years after his death, while the picture was in perfect preservation, exist in different churches and collections.
While engaged on the Cenacolo, Leonardo painted the portrait of Lucrezia Crivelli, now in the Louvre (No. 483). It has been engraved under the title of La Belle Ferronnière, but later researches leave us no doubt that it represents Lucrezia Crivelli, a beautiful favorite of Ludovico Sforza, and was painted at Milan in 1497. It is, as a work of art, of such extraordinary perfection that all critical admiration is lost in wonder.
Of the grand equestrian statue of Francesco Sforza, Leonardo never finished more than the model in clay, which was considered a masterpiece. Some years afterward (in 1499), when Milan was invaded by the French, it was used as a target by the Gascon bowmen, and completely destroyed. The profound anatomical studies which Leonardo made for this work still exist.
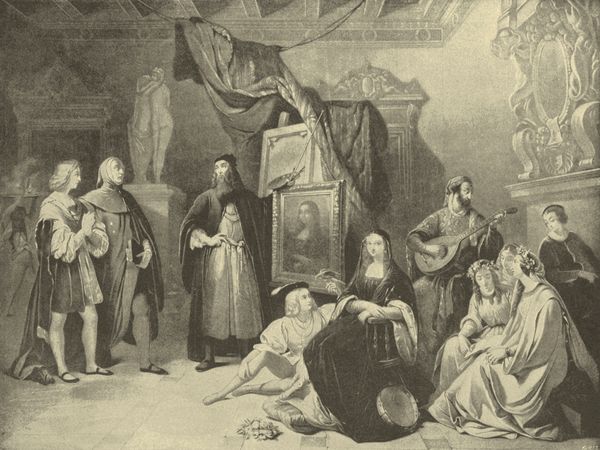

Raphael Introduced to Da Vinci.
In the year 1500, the French being in possession of Milan, his patron Ludovico in captivity, and the affairs of the state in utter confusion, Leonardo returned to his native Florence, where he hoped to re-establish his broken fortunes, and to find employment. Here begins the third period of his artistic life, from 1500 to 1513, that is, from his forty-eighth to his sixtieth year. He found the Medici family in exile, but was received by Pietro Soderini (who governed the city as "Gonfaloniêre perpetuo") with great distinction, and a pension was assigned to him as painter in the service of the republic. One of his first works (p. 213) after his return to Florence was the famous portrait of Madonna Lisa del Giocondo, called in French La Joconde, and now in the Louvre (484), which after the death of Leonardo was purchased by Francis I. for 4,000 gold crowns, equal to 45,000 francs or £1,800, an enormous sum in those days; yet who ever thought it too much?
Then began the rivalry between Leonardo and Michael Angelo, which lasted during the remainder of Leonardo's life. The difference of age (for Michael Angelo was twenty-two years younger) ought to have prevented all unseemly jealousy; but Michael Angelo was haughty and impatient of all superiority, or even equality; Leonardo, sensitive, capricious, and naturally disinclined to admit the pretensions of a rival, to whom he could say, and did say, "I was famous before you were born!" With all their admiration of each other's genius, their mutual frailties prevented any real good-will on either side.
Leonardo, during his stay at Florence, painted the portrait of Ginevra Benci, the reigning beauty of her time. We find that in 1502 he was engaged by Cæsar Borgia to visit and report on the fortifications of his territories, and in this office he was employed for two years. In 1503 he formed a plan for turning the course of the Arno, and in the following year he lost his father. In 1505 he modelled the group which we now see over the northern door of the San Giovanni, at Florence. In 1514 he was invited to Rome by Leo X., but more in his character of philosopher, mechanic, and alchemist, than as a painter. Here Raphael was at the height of his fame, and engaged in his greatest works, the frescos of the Vatican. The younger artist was introduced to the elder; and two pictures which Leonardo painted while at Rome—the "Madonna of St. Onofrio," and the "Holy Family," painted for Filiberta of Savoy, the pope's sister-in-law (which is now at St. Petersburg)—show that even this veteran in art felt the irresistible influence of the genius of his young rival. They are both Raffaelesque in the subject and treatment.
It appears that Leonardo was ill-satisfied with his sojourn at Rome. He had long been accustomed to hold the first rank as an artist wherever he resided; whereas at Rome he found himself only one among many who, if they acknowledged his greatness, affected to consider his day as past. He was conscious that many of the improvements in the arts which were now brought into use, and which enabled the painters of the day to produce such extraordinary effects, were invented or introduced by himself. If he could no longer assert that measureless superiority over all others which he had done in his younger days, it was because he himself had opened to them new paths to excellence. The arrival of his old competitor, Michael Angelo, and some slight on the part of Leo X., who was annoyed by his speculative and dilatory habits in executing the works intrusted to him, all added to his irritation and disgust. He left Rome, and set out for Pavia, where the French king, Francis I., then held his court. He was received by the young monarch with every mark of respect, loaded with favors, and a pension of 700 gold crowns settled on him for life. At the famous conference between Francis I. and Leo X., at Bologna, Leonardo attended his new patron, and was (p. 214) of essential service to him on that occasion. In the following year, 1516, he returned with Francis I. to France, and was attached to the French court as principal painter. It appears, however, that during his residence in France he did not paint a single picture. His health had begun to decline from the time he left Italy; and feeling his end approach, he prepared himself for it by religious meditation, by acts of charity, and by a most conscientious distribution by will of all his worldly possessions to his relatives and friends. At length, after protracted suffering, this great and most extraordinary man died at Cloux, near Amboise, May 2, 1519, being then in his sixty-seventh year. It is to be regretted that we cannot wholly credit the beautiful story of his dying in the arms of Francis I., who, as it is said, had come to visit him on his death-bed. It would indeed have been, as Fuseli expressed it, "an honor to the king, by which destiny would have atoned to that monarch for his future disaster at Pavia."[Back to Contents]

We have spoken of Leonardo da Vinci. Michael Angelo, the other great luminary of art, was twenty-two years younger, but the more severe and reflective cast of his mind rendered their difference of age far less in effect than in reality. It is usual to compare Michael Angelo with Raphael, but he is more aptly compared with Leonardo da Vinci. All the great artists of that time, even Raphael himself, were influenced more or less by these two extraordinary men, but they exercised no influence on each other. They started from opposite points; they pursued throughout their whole existence, and in all they planned and achieved, a course as different as their respective characters.
Michael Angelo Buonarroti was born at Setignano, near Florence, in the year 1474. He was descended from a family once noble—even among the noblest of the feudal lords of Northern Italy—the Counts of Canossa; but that branch of it represented by his father, Luigi Leonardo Buonarroti Simoni, had for some generations become poorer and poorer, until the last descendant was thankful to accept an office in the law, and had been nominated magistrate or mayor (Podesta) of Chiusi. In this situation he had limited his ambition to the prospect of seeing his eldest son a notary or advocate (p. 215) in his native city. The young Michael Angelo showed the utmost distaste for the studies allotted to him, and was continually escaping from his home and from his desk to haunt the ateliers of the painters, particularly that of Ghirlandajo who was then at the height of his reputation.
The father of Michael Angelo, who found his family increase too rapidly for his means, had destined some of his sons for commerce (it will be recollected that in Genoa and Florence the most powerful nobles were merchants or manufacturers), and others for civil or diplomatic employments; but the fine arts, as being at that time productive of little honor or emolument, he held in no esteem, and treated these tastes of his eldest son sometimes with contempt and sometimes even with harshness. Michael Angelo, however, had formed some friendships among the young painters, and particularly with Francesco Granacci, one of the best pupils of Ghirlandajo; he contrived to borrow models and drawings, and studied them in secret with such persevering assiduity and consequent improvement, that Ghirlandajo, captivated by his genius, undertook to plead his cause to his father, and at length prevailed over the old man's family pride and prejudices. At the age of fourteen Michael Angelo was received into the studio of Ghirlandajo as a regular pupil, and bound to him for three years; and such was the precocious talent of the boy, that, instead of being paid for his instruction, Ghirlandajo undertook to pay the father, Leonardo Buonarroti, for the first, second, and third years, six, eight, and twelve golden florins, as payment for the advantage he expected to derive from the labor of the son. Thus was the vocation of the young artist decided for life.
At that time Lorenzo the Magnificent reigned over Florence. He had formed in his palace and gardens a collection of antique marbles, busts, statues, fragments, which he had converted into an academy for the use of young artists, placing at the head of it as director a sculptor of some eminence, named Bertoldo. Michael Angelo was one of the first who, through the recommendation of Ghirlandajo, was received into this new academy, afterward so famous and so memorable in the history of art. The young man, then not quite sixteen, had hitherto occupied himself chiefly in drawing; but now, fired by the beauties he beheld around him, and by the example and success of a fellow-pupil, Torregiano, he set himself to model in clay, and at length to copy in marble what was before him; but, as was natural in a character and genius so steeped in individuality, his copies became not so much imitations of form as original embodyings of the leading idea. For example: his first attempt in marble, when he was about fifteen, was a copy of an antique mask of an old laughing Faun; he treated this in a manner so different from the original, and so spirited as to excite the astonishment of Lorenzo de Medici, who criticised it, however, saying, "Thou shouldst have remembered that old folks do not retain all their teeth; some of them are always wanting." The boy struck the teeth out, giving it at once the most grotesque expression; and Lorenzo, infinitely amused, sent for his father and offered to attach his son to his own particular service, and to undertake the entire care of his education. The father consented, on condition of receiving for himself an office (p. 216) under the government, and thenceforth Michael Angelo was lodged in the palace of the Medici and treated by Lorenzo as his son.
Michael Angelo continued his studies under the auspices of Lorenzo; but just as he had reached his eighteenth year he lost his generous patron, his second father, and was thenceforth thrown on his own resources. It is true that the son of Lorenzo, Piero de Medici, continued to extend his favor to the young artist, but with so little comprehension of his genius and character, that on one occasion, during the severe winter of 1494, he set him to form a statue of snow for the amusement of his guests.
Michael Angelo, while he yielded, perforce, to the caprices of his protector, turned the energies of his mind to a new study—that of anatomy—and pursued it with all that fervor which belonged to his character. His attention was at the same time directed to literature, by the counsels and conversations of a very celebrated scholar and poet then residing in the court of Piero—Angelo Poliziano; and he pursued at the same time the cultivation of his mind and the practice of his art. Engrossed by his own studies, he was scarcely aware of what was passing around him, nor of the popular intrigues which were preparing the ruin of the Medici; suddenly this powerful family were flung from sovereignty to temporary disgrace and exile; and Michael Angelo, as one of their retainers, was obliged to fly from Florence, and took refuge in the city of Bologna. During the year he spent there he found a friend, who employed him on some works of sculpture; and on his return to Florence he executed a Cupid in marble, of such beauty that it found its way into the cabinet of the Duchess of Mantua as a real antique. On the discovery that the author of this beautiful statue was a young man of two-and-twenty, the Cardinal San Giorgio invited him to Rome, and for some time lodged him in his palace. Here Michael Angelo, surrounded and inspired by the grand remains of antiquity, pursued his studies with unceasing energy; he produced a statue of Bacchus, which added to his reputation; and in 1500, at the age of five-and-twenty, he produced the famous group of the dead Christ on the knees of his Virgin Mother (called the "Pietà"), which is now in the church of St. Peter's, at Rome; this last being frequently copied and imitated, obtained him so much applause and reputation, that he was recalled to Florence, to undertake several public works, and we find him once more established in his native city in the year 1502.
In 1506 Michael Angelo was summoned to Rome by Pope Julius II., who, while living, had conceived the idea of erecting a most splendid monument to perpetuate his memory. For this work, which was never completed, Michael Angelo executed the famous statue of Moses, seated, grasping his flowing beard with one hand, and with the other sustaining the tables of the Law. While employed on this tomb, the pope commanded him to undertake also the decoration of the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel. Pope Sixtus IV. had, in the year 1473, erected this famous chapel, and summoned the best painters of that time, Signorelli, Cosimo Roselli, Perugino, and Ghirlandajo, to decorate the interior; but down to the year 1508 the ceiling remained without any ornament; and Michael (p. 217) Angelo was called upon to cover this enormous vault, a space of one hundred and fifty feet in length by fifty in breadth, with a series of subjects representing the most important events connected, either literally or typically, with the fall and redemption of mankind.
No part of Michael Angelo's long life is so interesting, so full of characteristic incident, as the history of his intercourse with Pope Julius II., which began in 1505, and ended only with the death of the pope in 1513.
Michael Angelo had at all times a lofty idea of his own dignity as an artist, and never would stoop either to flatter a patron or to conciliate a rival. Julius II., though now seventy-four, was as impatient of contradiction as fiery in temper, as full of magnificent and ambitious projects as if he had been in the prime of life; in his service was the famous architect, Bramante, who beheld with jealousy and alarm the increasing fame of Michael Angelo, and his influence with the pontiff, and set himself by indirect means to lessen both. He insinuated to Julius that it was ominous to erect his own mausoleum during his lifetime, and the pope gradually fell off in his attentions to Michael Angelo, and neglected to supply him with the necessary funds for carrying on the work. On one occasion, Michael Angelo, finding it difficult to obtain access to the pope, sent a message to him to this effect, "that henceforth, if his Holiness desired to see him, he should send to seek him elsewhere;" and the same night, leaving orders with his servants to dispose of his property, he departed for Florence. The pope despatched five couriers after him with threats, persuasions, promises—but in vain. He wrote to the Gonfaloniere Soderini, then at the head of the government of Florence, commanding him, on pain of his extreme displeasure, to send Michael Angelo back to him; but the inflexible artist absolutely refused; three months were spent in vain negotiations. Soderini, at length, fearing the pope's anger, prevailed on Michael Angelo to return, and sent with him his relation, Cardinal Soderini, to make up the quarrel between the high contending powers.
On his return to Rome, Michael Angelo wished to have resumed his work on the mausoleum; but the pope had resolved on the completion of the Sistine Chapel; he commanded Michael Angelo to undertake the decoration of the vaulted ceiling; and the artist was obliged, though reluctantly, to obey. At this time the frescos which Raphael and his pupils were painting in the chambers of the Vatican had excited the admiration of all Rome. Michael Angelo, who had never exercised himself in the mechanical part of the art of fresco, invited from Florence several painters of eminence, to execute his designs under his own superintendence; but they could not reach the grandeur of his conceptions, which became enfeebled under their hands, and one morning, in a mood of impatience, he destroyed all that they had done, closed the doors of the chapel against them, and would not thenceforth admit them to his presence. He then shut himself up, and proceeded with incredible perseverance and energy to accomplish his task alone; he even prepared his colors with his own hands. He began with the end toward the door, and in the two compartments first painted (though not first in the series), the "Deluge," and the "Vineyard of Noah;" he (p. 218) made the figures too numerous and too small to produce their full effect from below, a fault which he corrected in those executed subsequently. When almost half the work was completed, the pope insisted on viewing what was done, and the astonishment and admiration it excited rendered him more and more eager to have the whole completed at once. The progress, however, was not rapid enough to suit the impatient temper of the pontiff. On one occasion he demanded of the artist when he meant to finish it; to which Michael Angelo replied calmly, "When I can." "When thou canst!" exclaimed the fiery old pope, "thou hast a mind that I should have thee thrown from the scaffold!" At length, on the day of All Saints, 1512, the ceiling was uncovered to public view. Michael Angelo had employed on the painting only, without reckoning the time spent in preparing the cartoons, twenty-two months, and he received in payment three thousand crowns.
The collection of engravings after Michael Angelo in the British Museum is very imperfect, but it contains some fine old prints from the Prophets which should be studied by those who wish to understand the true merit of this great master, of whom Sir Joshua Reynolds said that, "to kiss the hem of his garment, to catch the slightest of his perfections, would be glory and distinction enough for an ambitious man!"
When the Sistine Chapel was completed Michael Angelo was in his thirty-ninth year; fifty years of a glorious though troubled career were still before him.
Pope Julius II. died in 1513, and was succeeded by Leo X., the son of Lorenzo the Magnificent. As a Florentine and his father's son, we might naturally have expected that he would have gloried in patronizing and employing Michael Angelo; but such was not the case. There was something in the stern, unbending character, and retired and abstemious habits of Michael Angelo, repulsive to the temper of Leo, who preferred the graceful and amiable Raphael, then in the prime of his life and genius; hence arose the memorable rivalry between Michael Angelo and Raphael, which on the part of the latter was merely generous emulation, while it must be confessed that something like scorn mingled with the feelings of Michael Angelo. The pontificate of Leo X., an interval of ten years, was the least productive period of his life. In the year 1519, when the Signoria of Florence was negotiating with Ravenna for the restoration of the remains of Dante, he petitioned the pope that he might be allowed to execute, at his own labor and expense, a monument to the "Divine Poet." He was sent to Florence to superintend the building of the church of San Lorenzo and the completion of Santa Croce; but he differed with the pope on the choice of the marble, quarrelled with the officials, and scarcely anything was accomplished. Clement VII., another Medici, was elected pope in 1523. He had conceived the idea of consecrating a chapel in the church of San Lorenzo, to receive the tombs of his ancestors and relations, and which should be adorned with all the splendor of art. Michael Angelo planned and built the chapel, and for its interior decoration designed and executed six of his greatest works in sculpture.
While Michael Angelo was engaged in these works his progress was interrupted (p. 219) by events which threw all Italy into commotion. Rome was taken and sacked by the Constable de Bourbon in 1527. The Medici were once more expelled from Florence; and Michael Angelo, in the midst of these strange vicissitudes, was employed by the republic to fortify his native city against his former patrons. Great as an engineer, as in every other department of art and science, he defended Florence for nine months. At length the city was given up by treachery, and, fearing the vengeance of the conquerors, Michael Angelo fled and concealed himself; but Clement VII. was too sensible of his merit to allow him to remain long in disgrace and exile. He was pardoned, and continued ever afterward in high favor with the pope, who employed him on the sculptures in the chapel of San Lorenzo during the remainder of his pontificate.
In the year 1531 he had completed the statues of "Night and Morning," and Clement, who heard of his incessant labors, sent him a brief commanding him, on pain of excommunication, to take care of his health, and not to accept of any other work but that which his Holiness had assigned him.
Clement VII. was succeeded by Pope Paul III., of the Farnese family, in 1534. This pope, though nearly seventy when he was elected, was as anxious to immortalize his name by great undertakings as any of his predecessors had been. His first wish was to complete the decoration of the interior of the Sistine Chapel, left unfinished by Julius II. and Leo X. He summoned Michael Angelo, who endeavored to excuse himself, pleading other engagements; but the pope would listen to no excuses which interfered with his sovereign power to dissolve all other obligations; and thus the artist found himself, after an interval of twenty years, most reluctantly forced to abandon sculpture for painting; and, as Vasari expresses it, he consented to serve Pope Paul only because he could not do otherwise.
The same Pope Paul III. had in the meantime constructed a beautiful chapel, which was called after his name the chapel Paolina, and dedicated to St. Peter and St Paul. Michael Angelo was called upon to design the decorations. He painted on one side the "Conversion of St. Paul," and on the other the "Crucifixion of St. Peter," which were completed in 1549. But these fine paintings—of which existing old engravings give a better idea than the blackened and faded remains of the original frescos—were from the first ill-disposed as to the locality, and badly lighted, and at present they excite little interest compared with the more famous works in the Sistine.
With the frescos in the Pauline Chapel ends Michael Angelo's career as a painter. He had been appointed chief architect of St. Peter's, in 1547, by Paul III. He was then in his seventy-second year, and during the remainder of his life, a period of sixteen years, we find him wholly devoted to architecture. His vast and daring genius finding ample scope in the completion of St. Peter's, he has left behind him in his capacity of architect yet greater marvels than he has achieved as painter and sculptor. Who that has seen the cupola of St. Peter's soaring into the skies, but will think almost with awe of the universal and majestic intellect of the man who reared it?
(p. 220) It appears, from the evidence of contemporary writers, that in the last years of his life the acknowledged worth and genius of Michael Angelo, his widespread fame, and his unblemished integrity, combined with his venerable age and the haughtiness and reserve of his deportment to invest him with a sort of princely dignity. It is recorded that, when he waited on Pope Julius III., to receive his commands, the pontiff rose on his approach, seated him, in spite of his excuses, on his right hand, and while a crowd of cardinals, prelates, and ambassadors, were standing round at humble distance, carried on the conference as equal with equal. When the Grand Duke Cosmo was in Rome, in 1560, he visited Michael Angelo, uncovered in his presence, and stood with his hat in his hand while speaking to him; but from the time when he made himself the tyrant of Florence he never could persuade Michael Angelo to visit, even for a day, his native city.
The arrogance imputed to Michael Angelo seems rather to have arisen from a contempt for others than from any overweening opinion of himself. He was too proud to be vain. He had placed his standard of perfection so high, that to the latest hour of his life he considered himself as striving after that ideal excellence which had been revealed to him, but to which he conceived that others were blind or indifferent. In allusion to his own imperfections, he made a drawing, since become famous, which represents an aged man in a go-cart, and underneath the words "Ancora impara" (still learning).
He continued to labor unremittingly, and with the same resolute energy of mind and purpose, till the gradual decay of his strength warned him of his approaching end. He did not suffer from any particular malady, and his mind was strong and clear to the last. He died at Rome, on February 18, 1564, in the ninetieth year of his age. A few days before his death he dictated his will in these few simple words: "I bequeath my soul to God, my body to the earth, and my possessions to my nearest relations." His nephew, Leonardo Buonarroti, who was his principal heir, by the orders of the Grand Duke Cosmo had his remains secretly conveyed out of Rome and brought to Florence; they were with due honors deposited in the church of Santa Croce, under a costly monument, on which we may see his noble bust surrounded by three very commonplace and ill-executed statues, representing the arts in which he excelled—Painting, Sculpture, and Architecture. They might have added Poetry, for Michael Angelo was so fine a poet that his productions would have given him fame, though he had never peopled the Sistine with his giant creations, nor "suspended the Pantheon in the air." The object to whom his poems are chiefly addressed, Vittoria Colonna, Marchioness of Pescara, was the widow of the celebrated commander who overcame Francis I. at the battle of Pavia; herself a poetess, and one of the most celebrated women of her time for beauty, talents, virtue, and piety. She died in 1547.[Back to Contents]
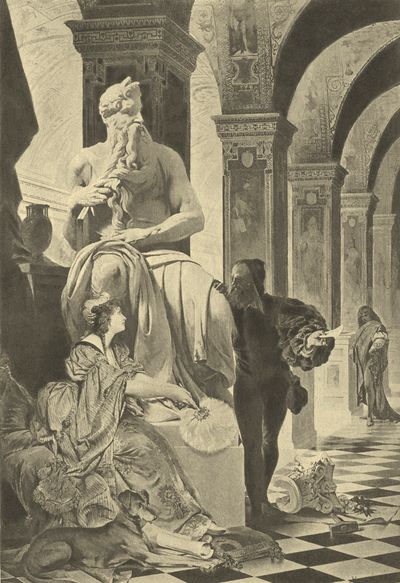

Michael Angelo and Vittoria Colonna.

The solemn and silent season of Lent had passed away; and, on the second evening of the joyful Easter, a house was seen brightly illuminated in one of the streets of Urbino. It was evident that a festival was held there on some happy occasion. The sound of music was heard, and guest after guest entered the mansion. No one, however, was more cordially welcomed than Pietro Perugino, the fellow-student of Leonardo da Vinci, at the school of the good old Andrea Verocchio.
For a moment, general gayety was suspended in honor of the guest. He was considered at that time one of the greatest painters of the age; and the host, Giovanni di Sanzio, though himself only ranking in the second or third order of limners, knew well how to prize the rare talents of his visitor.
The wife of Giovanni came forward, leading her son Raphael. Perugino had the eye of an artist: he gazed upon the mother and son with enthusiastic feeling; the striking resemblance they bore to each other, so exquisitely modulated by years and sex, was indeed a study for this minute copyist of nature.
"Benvenuto, Messer Perugino," said the hostess, with her soft musical voice and graceful Italian accent, and she placed the hand of her boy in that of the artist. Gently he laid the other on the head of the youthful Raphael, and in a solemn and tender manner pronounced a benediction.
"Your blessing is well timed, my honored friend," said Giovanni, "our festival is given to celebrate the birthday of our son."
"Is this his birthday?" inquired Perugino.
"Not so," replied the father, "he was born on April 7th, the evening of Good Friday, and it well befits us to be gay on the joyful Easter that succeeds it."
"My friend," said Perugino, "if thou wilt entrust thy boy to my care, I will take him as my pupil."
The father acceded with delight to this proposal. When the mother became acquainted with the arrangement, and found that her son was to quit his paternal dwelling at the early age of twelve, and reside wholly with Perugino, she could not restrain her tears. With hers the young Raphael's mingled, though ever and anon a bright smile darted like a sunbeam across his face.
He remained with Perugino several years. Raphael was made for affection, and fondly did his heart cling to his instructor. For a time he was content to (p. 222) follow his manner; but at length he began to dwell upon his own beau ideal; he grew impatient of imitation, and felt that his style was deficient in freshness and originality. He longed to pass the narrow bounds to which his invention had been confined.
With the approbation of Perugino and the consent of his parents, he repaired to Siena; here he was solicited to adorn the public library with fresco, and painted there with great success. But while he was busily engaged, his friend, Pinturrichio, one day entered. After looking at his friend's work very attentively, "Bravo!" he exclaimed, "thou hast done well, my Raphael—but I have just returned from Florence—oh, would that thou couldst behold the works of Leonardo da Vinci! Such horses! they paw the ground and shake the foam from their manes. Oh, my poor Raphael! thou hast never seen nature; thou art wasting time on these cartoons. Perugino is a good man and a good painter, I will not deny that—but Leonardo's horses!"
Raphael threw aside his pencil and hastily rose.
"Where now?" asked his friend; "whither art thou going so hastily?"
"To Florence," exclaimed Raphael.
"And what carries you so suddenly?"
"The horses of Leonardo," replied the young artist, sportively; "seriously, however, the desire of excellence implanted in my soul."
When he arrived at Florence he was charmed with the appearance of the city; but his whole mind was absorbed in the works of Leonardo da Vinci and of Michael Angelo, the rival artists of the age. As his stay was to be short, he did not enter upon laborious occupation. His mornings were passed in the reveries of his art; his evenings in the gay and fascinating society of Florence, where the fame of Perugino's beloved pupil had already reached. The frescos at Siena were spoken of; and the beautiful countenance and graceful deportment of Raphael won him the friendship of distinguished men. Taddeo Taddei, the learned friend of Cardinal Bembo, solicited him to reside in his house; he consented, and in return for the courtesy painted for him two pictures, in what is called his first style, that of Perugino.
One evening he retired to his couch at a late hour. He had been the hero of a fête, and love and beauty had heedlessly scattered their flowers in the path of the living Adonis. In vain he sought a few hours of slumber. He had quaffed the juice of the grape, emptying goblet after goblet, till his beating pulse and throbbing temples refused to be quieted. He started from his couch and approached the lattice; the heavens had changed their aspect, the still serenity of the evening had passed away, and the clouds were hurrying over the pale and watery moon. Nothing was heard but the low sighing of the wind, and now and then a sudden gust swept through the lattice, and threatened to extinguish the taper which was burning dimly on the table. A slight noise made him turn his eyes, and he perceived a note that the wind had displaced. He hastily took it up. It was Perugino's handwriting. He cut the silken cord that fastened it, and read:
(p. 223) "On me, my beloved Raffaello, devolves the task of informing you of the events which have taken place at Urbino. May this letter find you prepared for all the changes of life; a wise man will never suffer himself to be taken by surprise; this is true philosophy, and the only philosophy that can serve us! An epidemic has prevailed at Urbino, and has entered your paternal dwelling. Need I say more? Come to me, my son, at Perugia, for I am the only parent that remains to you. Pietro Perugino."
As he hastily arose, a crucifix which his mother had suspended to his neck at parting, fell from his bosom. Even the symbols of religion are sacred where the living principle has been early implanted in the heart. He pressed it to his lips: "Ah!" thought he, "what is the philosophy of Perugino, compared to the faith of which this is the emblem?" His thoughts went back to infancy and childhood, and his grief and remorse grew less intense. He dwelt on the deep and enduring love of his parents till he felt assured death could not extinguish it, and that he should see them again in a brighter sphere.
When morning came it found Raphael calm and composed; the lines of grief and thought were deeply marked on his youthful face; but the whirlwind and the storm had passed. He took leave of his friends, and hastened to Perugino, who received him with the fondness of a parent.
Here he remained some time, and at length collected sufficient resolution to return to Urbino, and once more enter the mansion of his desolated home.
It was necessary for him to reside at his native place for a number of months. During that time he painted several fine pictures. His heart, however, yearned for Florence, and he returned to it once more with the determination of making it his home. With far different sensations did he a second time enter the city of beauty. The freshness of his gayety was blighted; lessons of earthly disappointment were ever present to his mind, and he returned to it with the resolute purpose of devoting himself to serious occupation.
How well he fulfilled this resolution all Italy can bear witness. From this time he adopted what has been called his second manner. He painted for the Duke of Urbino the beautiful picture of the Saviour at sunrise, with the morning light cast over a face resplendent with divinity; the flowers glittering with dew, the two disciples beyond, still buried in slumber, at the time when the Saviour turns his eyes upon them with that tender and sorrowful exclamation, "Could ye not watch one hour?"
Raphael enriched the city of Florence with his works. When asked what had suggested some of the beautiful combinations of his paintings, he said, "They came to me in my sleep." At other times he called them "visions;" and then again said they were the result of "una certa idea che mi viene alla mente." It was this power of drawing from the deep wells of his own mind that gave such character, originality, and freshness to his works. He found that power within which so many seek, and seek in vain, without.
At the age of twenty-five Raphael was summoned by the pope to paint the (p. 224) chambers of the Vatican. The famous frescos of the Vatican need neither enumeration nor description; the world is their judge and their eulogist.
No artist ever consecrated his works more by his affections than Raphael. The same hallowed influence of the heart gave inexpressible charm to Correggio's, afterward. One of Raphael's friends said to him, in looking upon particular figures in his groups, "You have transmitted to posterity your own likeness."
"See you nothing beyond that?" replied the artist.
"I see," said the critic, "the deep-blue eye, and the long, fair hair parted on the forehead."
"Observe," said Raphael, "the feminine softness of expression, the beautiful harmony of thought and feeling. When I take my pencil for high and noble purposes, the spirit of my mother hovers over me. It is her countenance, not my own, of which you trace the resemblance."
This expression is always observable in his Madonnas. His portraits of the Fornarina are widely different. Raphael, in his last and most excellent style, united what was graceful and exquisite in Leonardo with the sublime and noble manner of Michael Angelo. It is the privilege and glory of genius to appropriate to itself whatever is noble and true. The region of thought is thus made a common ground for all, and one master mind becomes a reservoir for the present and future times.
When Raphael was invited to Rome by Pope Julius II., Michael Angelo was at the height of his glory; his character tended to inspire awe rather than affection; he delighted in the majestic and the terrible. In boldness of conception and grandeur of design, he surpassed Leonardo, but never could reach the sweetness and gentleness of his figures. Even his children lose something of their infantine beauty, and look mature; his women are commanding and lofty; his men of gigantic proportions. His painting, like his sculpture, is remarkable for anatomical exactness, and perfect expression of the muscles. For this union of magnificence and sublimity, it was necessary to prepare the mind; the first view was almost harsh, and it was by degrees that his mighty works produced their designed effect. Raphael, while he felt all the greatness of the Florentine, conceived that there might be something more like nature—something that should be harmonious, sweet, and flowing—that should convey the idea of intellectual rather than of external majesty. Without yielding any of the correctness of science, he avoided harshness, and imitated antiquity in uniting grace and elegance with a strict observation of science and of the rules of art.
It was with surprise that Michael Angelo beheld in the youthful Raphael a rival artist; nor did he receive this truth meekly; he treated him with coldness and distance. In the meantime Raphael went on with his works; he completed the frescos of the Vatican, and designed the cartoons. He also produced those exquisite paintings in oil which seem the perfection of human art.

Leo X. at Raphael's Bier.
Human affection is necessary to awaken the sympathy of human beings; and Raphael, in learning how to portray it, had found the way to the heart. In mere grandeur of invention he was surpassed by Michael Angelo. Titian excelled him (p. 225) in coloring, and Correggio in the beautiful gradation of tone; but Raphael knew how to paint the soul; in this he stood alone. This was the great secret of a power which seemed to operate like magic. In his paintings there is something which makes music on the chords of every heart; for they are the expression of a mind attuned to nature, and find answering sympathies in the universal soul.
While Michael Angelo was exalted with the Epic grandeur of his own Dante, Raphael presented the most finished scenes of dramatic life, and might be compared to the immortal Shakespeare—scenes of spiritual beauty, of devotion, and of pastoral simplicity, yet uniting a classic elegance which the poet does not possess. Buonarroti was the wonder of Italy, and Raphael became its idol.
Julius was so much enchanted with his paintings in the halls of the Vatican, that he ordered the frescos of former artists to be destroyed. Among them were some of Perugino's, but Raphael would not suffer these to be removed for his own; he viewed them as the relics of a beloved and honored friend, and they were consecrated by tender and grateful feelings.
Raphael collected from every part of the world medallions of intaglios and antiques to assist him in his designs. He loved splendor and conviviality, and gave offence thereby to the rigid and austere. It was said that he had a prospect of changing the graceful beretta for a cardinal's hat; but this idea might have arisen from the delay which existed in his marriage with Cardinal Bibiano's niece, whose hand her uncle had offered to him. Peremptorily to reject this proposal of the cardinal without giving offence would have been impossible, and Raphael was too gentle in his own feelings voluntarily to injure another's; but he was not one to sacrifice his affections to ambition.
Whatever were the struggles of his heart, they were early terminated. Amid the caresses of the great, the fond and devoted friendship of his equals, the enthusiastic love of his pupils, the adulation of his inferiors, while crowned with wealth, fame, and honor, and regarded as the equal of the hitherto greatest artist in the world, he was suddenly called away. He died on Good Friday, the day of his birth, at the age of thirty-seven, 1520.
We are sometimes impressed with veneration when those who have even drunk the cup of life almost to its dregs resign it with resignation and Christian faith. But Raphael calmly and firmly resigned it when it was full to the brim.
Leo X. and Cardinal Bibiano were by his bedside. The sublime picture of the "Transfiguration," the last and greatest which he painted, was placed opposite to him, by his own desire. How impressive must have been the scene! His dying eye turned from the crucifix he held in his hand to the glory of the beatified Saviour.
His contemporaries speak of him as affectionate, disinterested, modest, and sincere; encouraging humble merit, and freely giving his advice and assistance where it was needed and deserved.[Back to Contents]

Titian was born in the year 1480, at Cadore, a small place distant about five miles from the foot of the Alps; he belonged to the family of the Vecelli, which is among the most noble of those parts. Giving early proof of much intelligence, he was sent at the age of ten to an uncle in Venice, an honorable citizen, who, seeing the boy to be much inclined to painting, placed him with the excellent painter, Gian Bellino, then very famous. Under his care, the youth soon proved himself to be endowed by nature with all the gifts of judgment and genius required for the art of painting. Now, Gian Bellino and the other masters of that country, not having the habit of studying the antique, were accustomed to copy only what they saw before them, and that in a dry, hard, labored manner, which Titian also acquired; but about the year 1507, Giorgione da Castel Franco, not being satisfied with that mode of proceeding, began to give to his works an unwonted softness and relief, painting them in a very beautiful manner; yet he by no means neglected to draw from the life, or to copy nature with his colors as closely as he could; and in doing the latter he shaded with colder or warmer tints as the living object might demand, but without first making a drawing; since he held that, to paint with the colors only, without any drawing on paper, was the best mode of proceeding, and most perfectly in accord with the true principles of design.
Having seen the manner of Giorgione, Titian early resolved to abandon that of Gian Bellino, although well grounded therein. He now, therefore, devoted himself to this purpose, and in a short time so closely imitated Giorgione that his pictures were sometimes taken for those of that master, as will be related below. Increasing in age, judgment, and facility of hand, our young artist executed numerous works in fresco which cannot here be named individually, having been dispersed in various places; let it suffice to say, that they were such as to cause experienced (p. 227) men to anticipate the excellence to which he afterward attained. At the time when Titian began to adopt the manner of Giorgione, being then not more than eighteen, he took the portrait of a gentleman of the Barberigo family, who was his friend, and this was considered very beautiful, the coloring being true and natural, and the hair so distinctly painted that each one could be counted as might also the stitches in a satin doublet, painted in the same work; it was so well and carefully done, that it would have been taken for a picture by Giorgione, if Titian had not written his name on the dark ground.
Giorgione meanwhile had executed the façade of the German Exchange, when, by the intervention of Barberigo, Titian was appointed to paint certain stories in the same building and over the Merceria. After which he executed a picture with figures the size of life, which is now in the Hall of Messer Andrea Loredano, who dwells near San Marcuola; this work represents "Our Lady" in her flight into Egypt. She is in the midst of a great wood, and the landscape of this picture is well done; Titian having practised that branch of art, and keeping certain Germans, who were excellent masters therein, for several months together in his own house. Within the wood he depicted various animals, all painted from the life, and so natural as to seem almost alive. In the house of Messer Giovanni Danna, a Flemish gentleman and merchant, who was his gossip, he painted a portrait which appears to breathe, with an "Ecce Homo," comprising numerous figures which, by Titian himself, as well as others, is considered to be a very good work. The same artist executed a picture of "Our Lady," with other figures the size of life, men and children being all taken from nature, and portraits of persons belonging to the Danna family.
In the year 1507, when the Emperor Maximilian was making war on the Venetians, Titian, as he relates himself, painted the "Angel Raphael, with Tobit and a Dog," in the Church of San Marziliano. There is a distant landscape in this picture, wherein San Giovanni Battista is seen at prayer in a wood; he is looking up to heaven, and his face is illumined by a light descending thence; some believe this picture to have been done before that on the "Exchange of the Germans," mentioned above, was commenced. Now, it chanced that certain gentlemen, not knowing that Giorgione no longer worked at this façade, and that Titian was doing it (nay, had already given that part over the Merceria to public view), met the former, and began as friends to rejoice with him, declaring that he was acquitting himself better on the side of the Merceria than he had done on that of the "Grand Canal;" which remark caused Giorgione so much vexation, that he would scarcely permit himself to be seen until the whole work was completed, and Titian had become generally known as the painter; nor did he thenceforward hold any intercourse with the latter and they were no longer friends.
In the year 1508, Titian published a wood-engraving of the "Triumph of Faith;" it comprised a vast number of figures: our first Parents, the Patriarchs, the Prophets, the Sybils, the Innocents, the Martyrs, the Apostles, and Our Saviour Christ borne in triumph by the four Evangelists, and the four Doctors, followed (p. 228) by the holy Confessors; here Titian displayed much boldness, a fine manner, and improving facility. I remember that Fra Bastiano del Piombo, speaking on this subject, told me that if Titian had then gone to Rome, and seen the works of Michael Angelo, with those of Raphael and the ancients, he was convinced, the admirable facility of his coloring considered, that he would have produced works of the most astonishing perfection; seeing that, as he well deserved to be called the most perfect imitator of Nature of our times, as regards coloring, he might thus have rendered himself equal to the Urbinese or Buonarroto, as regarded the great foundation of all, design. At a later period Titian repaired to Vicenza, where he painted "The Judgment of Solomon," on the Loggetta wherein the courts of justice are held; a very beautiful work. Returning to Venice, he then depicted the façade of the Germain; at Padua he painted certain frescos in the Church of Sant' Antonio, the subjects taken from the life of that saint; and in the Church of Santo Spirito he executed a small picture of San Marco seated in the midst of other saints, whose faces are portraits painted in oil with the utmost care; this picture has been taken for a work of Giorgione.
Now, the death of Giovan Bellino had caused a story in the hall of the Great Council to remain unfinished; it was that which represents Federigo Barbarossa kneeling before Pope Alessandro III., who plants his foot on the emperor's neck. This was now finished by Titian, who altered many parts of it, introducing portraits of his friends and others. For this he received from the senate an office in the Exchange of the Germans called the Senseria, which brought him in three hundred crowns yearly, and which those Signori usually give to the most eminent painter of their city, on condition that from time to time he shall take the portrait of their doge, or prince when such shall be created, at the price of eight crowns, which the doge himself pays, the portrait being then preserved in the Palace of San Marco, as a memorial of that doge.
After the completion of these works, our artist painted, for the Church of San Rocco, a figure of Christ bearing his cross; the Saviour has a rope round his neck, and is dragged forward by a Jew; many have thought this a work of Giorgione. It has become an object of the utmost devotion in Venice, and has received more crowns as offerings than have been earned by Titian and Giorgione both, through the whole course of their lives. Now, Titian had taken the portrait of Bembo, then secretary to Pope Leo X., and was by him invited to Rome, that he might see the city, with Raffaello da Urbino and other distinguished persons; but the artist having delayed his journey until 1520, when the pope and Raffaello were both dead, put it off for that time altogether. For the Church of Santa Maria Maggiore he painted a picture of "St. John the Baptist in the wilderness;" there is an angel beside him that appears to be living; and a distant landscape, with trees on the bank of a river, which are very graceful. He took portraits of the Prince Grimani and Loredano, which were considered admirable; and not long afterward he painted the portrait of King Francis, who was then leaving Italy to return to France.

A Fête at the House of Titian.
In 1530, when the Emperor Charles V. was in Bologna, Titian, by the intervention (p. 229) of Pietro Aretino, was invited to that city by the Cardinal Ippolito de' Medici, and there he made a magnificent portrait of his majesty in full armor. This gave so much satisfaction that the artist received a present of a thousand crowns for the same. Out of these he had subsequently to give the half to Alfonso Lombardi, the sculptor, who had made a model of that monarch to be executed in marble.
Having returned to Venice, Titian there found that many gentlemen had begun to favor Pordenone, commending exceedingly the works executed by that artist in the ceiling of the Hall of the Pregai, and elsewhere. They had also procured him the commission for a small picture in the Church of San Giovanni Elemosynario, which they intended him to paint in competition with one representing that saint in his episcopal habits, which had previously been executed there by Titian. But whatever care and pains Pordenone took, he could not equal nor even approach the work of the former. Titian was then appointed to paint a picture of the Annunciation for the Church of Santa Maria degli Angeli, at Murano; but those who gave the commission for the work, not wishing to pay so much as five hundred crowns, which Titian required as its price, he sent it, by the advice of Pietro Aretino, as a gift to Charles V., who being greatly delighted with the work, made him a present of two thousand crowns. The place which the picture was to have occupied at Murano was then filled by one from the hand of Pordenone.
When the emperor, some time after this, returned with his army from Hungary, and was again at Bologna, holding a conference with Clement VII., he desired to have another portrait taken of him by Titian, who, before he departed from the city, also painted that of the Cardinal Ippolito de Medici in the Hungarian dress, with another of the same prelate fully armed, which is somewhat smaller than the first; these are both now in the Guardaroba of Duke Cosimo. He painted the portraits of Alfonso, Marquis of Davalos, and of Pietro Aretino, at the same period, and these things having made him known to Federigo Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua, he entered the service of the latter, and accompanied him to his states. At Mantua our artist made a portrait of the duke, which appears to breathe, and afterward executed that of his brother, the cardinal. These being finished, he painted twelve beautiful "Heads of the Twelve Cæsars," to decorate one of the rooms erected by Giulio Romano, and when they were done, Giulio painted a "Story from the Lives of the Emperors" beneath each head.
The productions, but more especially the portraits, of Titian are so numerous that it would be almost impossible to make the record of them all. I will, therefore, speak of the principal only, and that without order of time, seeing that it does not much signify to tell which was painted earlier and which later. He took the portrait of Charles V. several times, as we have said, and was finally invited by that monarch to his court; there he painted him as he was in those last years; and so much was that most invincible emperor pleased with the manner of Titian, that once he had been portrayed by him, he would never permit himself to be taken by any other person. Each time that Titian painted the (p. 230) emperor he received a present of a thousand crowns of gold, and the artist was made a cavalier, or knight, by his majesty, with a revenue of two hundred crowns yearly, secured on the treasury of Naples, and attached to his title.
When Titian painted Filippo, King of Spain, the son of Charles, he received another annuity of two hundred crowns; so that these four hundred, added to the three hundred from the German Exchange, make him a fixed income of seven hundred crowns, which he possesses without the necessity of exerting himself in any manner. Titian presented the portraits of Charles V. and his son Filippo to the Duke Cosimo, who has them now in his Guardaroba. He also took the portrait of Ferdinand, King of the Romans, who was afterward emperor, with those of his children, Maximilian, that is to say, now emperor, and his brother; he likewise painted the Queen Maria; and at the command of the Emperor Charles, he portrayed the Duke of Saxony, when the latter was in prison. But what a waste of time is this! when there has scarcely been a noble of high rank, scarcely a prince or lady of great name, whose portrait has not been taken by Titian, who in that branch of art is indeed an excellent painter.
All these works, with many others which I omit to avoid prolixity, have been executed up to the present age of our artist, which is above seventy-six years. Titian has been always healthy and happy; he has been favored beyond the lot of most men, and has received from Heaven only favors and blessings. In his house he has entertained whatever princes, literati, or men of distinction have gone to or dwelt in Venice; for, to say nothing of his excellence in art, he has always distinguished himself by courtesy, hospitality, and rectitude.
Titian has had some rivals in Venice, but not of any great ability, wherefore he has easily overcome them by the superiority of his art; while he has also rendered himself acceptable to the gentlemen of the city. He has gained a fair amount of wealth, his labors having always been well paid; and it would have been well if he had worked for his amusement alone during these latter years, that he might not have diminished the reputation gained in his best days by works of inferior merit, performed at a period of life when nature tends inevitably to decline, and consequent imperfection.
In the year 1566, when Vasari, the writer of the present history, was at Venice, he went to visit Titian, as one who was his friend, and found him, although then very old, still with the pencils in his hand and painting busily. Great pleasure had Vasari in beholding his works and in conversing with the master.
It may be affirmed, then, that Titian, having adorned Venice, or rather all Italy, and other parts of the world, with excellent paintings, well merits to be loved and respected by artists, and in many things to be admired and imitated also, as one who has produced, and is producing, work of infinite merit; nay, such as must endure while the memory of illustrious men shall remain.[Back to Contents]

It has been given to some men to be not only great in the domain of art by reason of that which they have themselves succeeded in producing, but by reason of that which they have inspired other men to produce. They have been not merely artists, but teachers, who by precept and example have moulded the whole current and drift of artistic thought in the ages and lands to which they have belonged. Among these lofty spirits, who live through the centuries not only in what their hands once fashioned, but still more in what they have inspired others to do, undoubtedly one of the greatest is Albert Dürer. Justly reckoned as the representative artist of Germany, he has the peculiar honor of having raised the craft of the engraver to its true position, as one of the fine arts. As a painter not unworthy to be classified with Titian and Raphael, his contemporaries upon Italian soil, he poured the wealth of his genius into woodcuts and copperplates, and taught men the practically measureless capacity of what before his day had been a rudimentary art.
Dürer was born in Nuremberg on May 21, 1471. The family was of Hungarian origin, though the name is German, and is derived from Thürer, meaning a maker of doors. The ancestral calling of the family probably was that of the carpenter. Albert Dürer, the father of the great artist, was a goldsmith, and settled about 1460 in Nuremberg, where he served as an assistant to Hieronymus Holper, a master goldsmith, whose daughter, Barbara, he married in 1468. He was at the time forty years of age, and she fifteen. As the result of the union eighteen children were born into the world, of whom Albrecht was the second. The lad, as he grew up, became a great favorite with his father, who appeared to discern in him the promise of future ability. The feeling of attachment was reciprocated in the most filial manner, and there are extant two well-authenticated portraits of the father from the facile brush of the son, one in the Uffizi at Florence, the other in the possession of the Duke of Northumberland. It was the original intention of the father of the artist that he should follow the craft of the goldsmith, but after serving a period as an apprentice in his father's (p. 232) shop, his strong predilection for the calling of the painter manifested itself to such a degree that the father reluctantly consented to allow the boy to follow his natural bent, and placed him under the tutelage of Michael Wohlgemuth, the principal painter of Nuremberg. Wohlgemuth was a representative artist of his time, who followed his calling after a mechanical fashion, having a large shop filled with apprentices who, under his direction and with his assistance, busied themselves in turning out for a small consideration altar-pieces and pictures of martyrdoms, which were in vogue as necessary parts of decoration in churches. Numerous examples of the work of Wohlgemuth and his contemporaries survive, attesting, by the wealth of crudities and unintended caricatures with which they abound, the comparatively low stage of development attained by the art of the painter in Germany at that day. According to Dürer, the period of his apprenticeship to Wohlgemuth was spent profitably, and resulted in large acquisitions of technical skill. The period of his preliminary training being ended, he set forth upon his "Wanderjahre," and travelled extensively. Just what points he visited cannot with certainty be determined. It is ascertained beyond doubt that he visited Colmar, where he was hospitably entertained by the family of Martin Schongauer, the greatest painter of his time on German soil, but who had died shortly before the visit of Dürer. He also visited Strasburg, and it is thought by many that he extended his journeyings as far as Venice. In 1494 he returned to Nuremberg, and in the month of July was married to Agnes Frey, the daughter of a prosperous merchant of the city. He was twenty-three years of age, and she somewhat younger. They lived together happily, though no children were born to them, and it has been proved that the reputation which has been given her, of being little better than a common scold, who imbittered his life by her termagancy, is the creation of the ill temper of one of the testy friends of Dürer, Willibald Pirkheimer, who, in the spirit of spitefulness, besmirched her character in a letter which unfortunately survives to this day, and in which he accuses her of having led her husband a mad and weary dance by her temper. The reason for this ebullition on the part of Pirkheimer appears to have been that, after Dürer's death, she refused to give him a pair of antlers which had belonged to her husband, and which Pirkheimer had set his heart upon having.
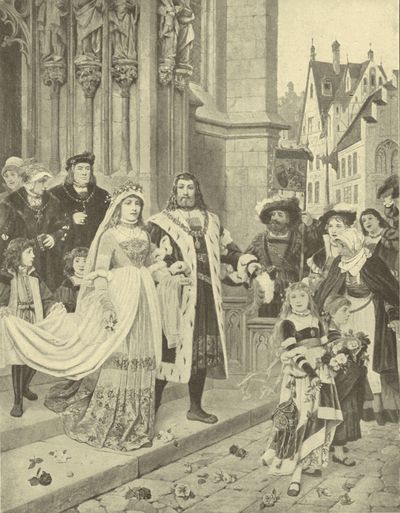

Albert Dürer's Wedding.
The first eleven years of the married life of Dürer were spent in Nuremberg, where he devoted himself with unremitting assiduity to the prosecution of his art. During these years his powers unfolded rapidly, and there are extant two notable pictures, which were undoubtedly produced at this time, the triptych in the Dresden Gallery, and an altar-piece which is in the palace of the Archbishop of Vienna, at Ober St. Veit. These compositions, while remarkable in many respects, still reveal the influence of his master, Wohlgemuth, and give evidence of having been in part executed with the assistance of apprentices. In fact, the peak-gabled house at the foot of the castle-mound in Nuremberg was a picture factory like that of Wohlgemuth, in which, however, work of a higher order than any hitherto produced in Germany was being turned out. We know the names of four or five of those who served as apprentices under Dürer at this time and (p. 233) they are stars of lesser magnitude in the constellation of German art. But Dürer was not contented simply to employ his talents in the production of painted altar-pieces, and we find him turning out a number of engravings, the most noticeable among which are his sixteen great wood-cuts illustrating the Apocalypse, which were published in 1498. The theme was one which had peculiar fascinations for all classes at the time. The breaking up of all pre-existing systems, the wonderful stirrings of a new life which were beginning to be felt everywhere with the close of the Middle Age and the dawning of the Renaissance, had filled the minds of men with wonder, and caused them to turn to the writings of the Apocalyptic Seer with keenest interest. A recent critic, commenting upon his work as represented in these engravings, says: "The energy and undismayed simplicity of his imagination enable him, in this order of creations, to touch the highest point of human achievement. The four angels keeping back the winds that they blow not, the four riders, the loosing of the angels of the Euphrates to slay the third part of men—these and others are conceptions of such force, such grave or tempestuous grandeur, in the midst of grotesqueness, as the art of no other age or hand has produced."
At this period Dürer was also engaged in experimenting upon the art of copper-plate engraving, in which he restricted himself mainly to reproducing copies of the works of other artists, among them those of Jacopo de Barbari, a painter of the Italian school, who was residing in Nuremberg, and who among other things gave the great artist instruction in plastic anatomy. The influence of his instructor is plain, when we compare engravings executed about 1504 with those published at a previous date, and especially when we examine his design of the Passion of our Lord painted in white upon a green ground, commonly known as "The Green Passion," which is treasured in the Albertina at Prague. He also during these twelve years finished seven of the twelve great wood-cuts illustrating the passion, and sixteen of the twenty cuts which compose the series known as "The Life of the Virgin." The activities of Dürer in Nuremberg were temporarily interrupted by a journey to Italy, which he undertook in the fall of the year 1505. What the immediate occasion for undertaking this journey may have been is not plain, though it seems most likely that one of his objects was to enable him to recuperate from the effects of a protracted illness, from which he had suffered during the summer of this year, and also incidentally to secure a market for his wares in Venice, the commercial relationships of which with Nuremberg were very close at this period. A German colony, composed largely of Nuremberg factors and merchants, was located at this time in Venice, and they had secured the privilege of dedicating a great painting in the church of St. Bartholomew. The commission for the execution of this painting was secured by Dürer. It represents the adoration of the Virgin, but has been commonly known under the name of "The Feast of the Rose Garlands." After having undergone many vicissitudes, it is preserved to-day in a highly mutilated condition in the monastery of Strachow, near Prague. Dürer's stay in Venice was signalized not only by the production of this painting, but of three or four (p. 234) other notable works which still exist, and which reflect the great influence upon him of the Italian school of painting, with which he had attained familiarity. His stay in Venice lasted about a year. In the fall of 1506, he returned to Nuremberg, and there remained for the next fourteen years, engaged in the practice of his art. These years were years of success and prosperity. His name and fame had spread over the whole of Europe, and the greatest artists of the day were glad to do him homage. Raphael said of him, when contemplating some of his designs, "Truly this man would have surpassed us all, if he had the masterpieces of ancient art constantly before his eyes as we have." A friendly correspondence was maintained between the immortal Italian and his German contemporary, and in his own country, all men, from the emperor to the peasant, delighted to do honor to his genius, the products of which were found alike in church and palace, and through his printed designs in the homes of the humble poor.
The proud old imperial city of Nuremberg had gathered within its battlemented walls a multitude of men who were distinguished not only for their commercial enterprise and wealth, but many of whom were the exponents of the literary and artistic culture of the time. Among the men with whom Dürer found congenial companionship were Adam Krafft, the sculptor; Veit Stoss, whose exquisite carvings in wood may reflect in some measure in the wild luxuriance of the imagination which they display, the restless, "dare-devil" spirit with which his biographers invest him; Peter Vischer, the bronze founder; and last but not least. Hans Sachs, the cobbler poet, whose quaint rhymes are a source of delight to this day, and were a mighty force in the great work of the Reformation, by which the fetters of mediæval traditions and ecclesiastical abuse were thrown off by the German people.
Of the personal appearance of Dürer at this time, we are not left in ignorance. A portrait of himself from his own hands has been preserved and is well known. His features reveal refinement and great intellectuality, united with grace, and his attire shows that he was not oblivious to matters of personal adornment. After the fashion of the time, his hair was worn in long and graceful ringlets, which fell in heavy masses about his shoulders.
The first six years which followed his return from Venice were almost wholly given to painting, and his productions give evidence of the fact that he had dismissed from his employment the retinue of assistants and apprentices, whom he had employed in his earlier years. From this period date most of his great masterpieces, which are still preserved, among them the "Adam and Eve," in the Pitti Palace; the "Ten Thousand Martyrs of Nicomedia," in the Imperial Gallery, at Vienna; the "Adoration of the Trinity," at the Belvedere, in Vienna; and "The Assumption of the Virgin," the original of which was destroyed by fire more than three hundred years ago, but of which a good copy is preserved at Frankfort. To this period belong the portraits of Charlemagne and of the Emperor Sigismund, which are preserved in the National German Museum at Nuremberg.
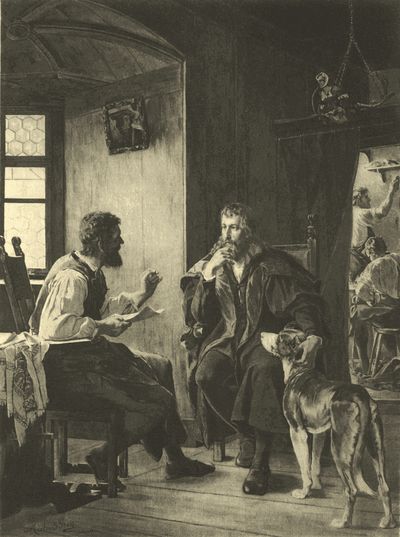

Albert Dürer visits Hans Sachs.
But while prosecuting the work of the painter, he did not neglect the art of (p. 235) the engraver, and in 1511, brought out in complete form his great book of woodcuts in folio, and began to develop that marvellous art of etching which is indissolubly connected with his name. Among the products of the etcher's needle which attest his activity in this direction are those masterpieces which have for centuries been at once the delight and the puzzle of artistic minds: the "Melancholia," "The Knight and the Devil," and "St. Jerome in his Cell." The most reasonable explanation of these weird fancies is that they were intended to represent in allegorical style the three temperaments—the melancholic, the sanguine, and the phlegmatic. The Diet of Augsburg, which was convened in 1518, gave Dürer a passing opportunity to depict the lineaments of the Emperor Maximilian, who gave him several sittings, and who manifested great interest in the painter. The death of the emperor in the following year, the outbreak of an epidemic in Nuremberg, together with the coronation of Charles V. at Aix-la-Chapelle, led Dürer to undertake a journey to the Low Countries, in which he was accompanied by his faithful wife. He was present at the coronation and was one of the distinguished civilians whose appearance added dignity to the occasion. His diary, in which he recounts his experiences upon this journey, and which is accompanied by a multitude of wayside sketches, is still preserved, and contains, besides the dry entries of his current expenditures, most entertaining allusions to the distinguished people whom he met, and who received him with the utmost cordiality. Intermingled with these narrative details are outbursts of feeling, which are provoked by passing political and ecclesiastical events, in which he took a profound interest, though he never appears to have committed himself with positive openness to the party of reform. His sympathies are, however, clearly shown by his writings, as well as by his works of art, to have been with the Reformers, and he lived on terms of intimacy with Erasmus and Melancthon, of both of whom we have portraits from his hand.
Dürer returned from the Netherlands in 1521, about the middle of July, and the remaining years of his life were spent in the prosecution of the art of the engraver, in painting, and in the effort to elucidate the sciences of perspective, geometry, and fortification, upon all of which he has left treatises.
His labors, though they had not brought with them great wealth, had secured for him a competency, and the latter years of his life were devoted more and more to labors which, while dignified, did not tend to add greatly to his already magnificent reputation. These labors were prosecuted in spite of ever-failing health. While in the Netherlands he had contracted a malarial fever, the effects of which clung to him, in spite of the best treatment which could be secured, and left him the wreck of his former self. On April 6, 1528, death suddenly overtook him. There was not even time to summon his friends to his side before his spirit had fled. The city which had been his home from childhood was filled with mourning. They took up his remains and gently laid them to rest in the burial vault of his wife's family in the graveyard of the Church of St. John, where the setting sun pours its last glowing beams at evening over the low Franconian hill-tops. The vault has since been changed and the last resting-place of the remains (p. 236) of the Raphael of the North is a lowly mound, reverently approached by all who visit the quaint imperial city, upon which is a slab, covered with a bronze tablet upon which are the words:
Quicquid Alberti Dureri Mortale
Fuit Sub Hoc Conditum Tumulo.
Emigravit VIII Idus Aprilis, MDXXVIIL
"Emigravit is the inscription on the tombstone where he lies;
Dead he is not, but departed—for the artist never dies.
Fairer seems the ancient city, and the sunshine seems more fair,
That he once has trod its pavement, that he once has breathed its air!"
[Back to Contents]


"It is just one hundred and twenty years to-day," said a young artist to his friend, as he stood in the hall of St. Mark, at Venice, contemplating the noble works of Titian. "Time, the destroyer, has here stayed his hand; the colors are as vivid and as fresh as if they were laid on but yesterday. Would that my old friend and master, Otho Venius, was here! At least I will carry back to Antwerp that in my coloring which shall prove to him that I have not played truant to the art."
"Just one hundred and twenty years," repeated he, "since Titian was born. Venice was then in its glory, but now it is all falling; its churches and palaces are crumbling to dust, its commerce interrupted. The republic continually harassed by the Porte, and obliged to call on foreign aid; depressed by her internal despotism, her council of ten, and state inquisitors; her decline, though gradual, is sure; yet the splendor of her arts remains, and the genius of Titian, her favorite son, is yet in the bloom and brilliancy of youth!"
Such was the enthusiastic exclamation of Rubens, as he contemplated those (p. 237) paintings which had brought him from Antwerp. How many gifted minds spoke to him from the noble works which were before him! The three Bellinis, the founders of the Venetian school; Giorgione, Titian, and Tintoretto. Then Paolo Veronese, who, though born at Verona, in 1537, adopted Venice as his home, and became the fellow-artist of Tintoretto, and the disciple of Titian. Pordenone, too, who viewed Titian as a rival and an enemy. Palma the young, and Palma the old, born in 1548, and the Bassanos, who died near 1627.
All these were present to the eye of Rubens, their genius embodied on the canvas in the halls of St. Mark. "These," he exclaimed, "have formed the Venetian school, and these shall be my study!"
From this time, the young artist might daily be seen with his sheets of white paper, and his pencil in his hand. A few strokes preserved the outline which his memory filled up; and by an intuitive glance, his genius understood and appropriated every signal beauty.
In Venice he became acquainted with the Archduke Albert, who introduced him to the Duke of Mantua, whither he went for the purpose of studying the works of Julio Romano. From thence he proceeded to Rome; here Raphael was his model, and Michael Angelo his wonder. He devoted himself to painting with a fervor that belongs only to genius; and he soon proved that, whatever he gained by ancient study, the originality of his own conceptions would still remain and appear. To the vivid and splendid coloring of the Venetian school, he was perhaps more indebted than to any other model. The affectionate and constant intercourse, by letters, that subsisted between Rubens and his mother, made his long residence in Italy one of pleasure. At Rome he was employed to adorn, by his paintings, the Church of Santa Croce, and also the "Chiesa Nova."
Rubens had been originally destined by his mother for one of the learned professions. His father was born at Antwerp, and held the honorable office of councillor of state. When the civil war broke out he repaired to Cologne, where his son, Peter Paul Rubens, was born. He died soon after his return to Antwerp, and left his property much diminished from losses occasioned by the civil war. The mother of Rubens put him early to the best schools, where he was initiated in learning and discovered a taste for belles-lettres; but all the intervals of necessary study were devoted to drawing. His mother perceiving it, determined to indulge his inclination, and placed him in the studio of Van Noort.
The correct taste of the scholar soon led him to perceive that he could not adopt this artist's style, and he became the pupil of Otho Venius. Similarity of thought and feeling united them closely, and it was with true disinterestedness that the master urged his pupil to quit his confined circle and repair to Italy, the great school of art.
Time flew rapidly with Rubens, while engaged in his beloved and honorable pursuit; he looked forward to the period when he might return to Antwerp and place his mother in her former affluence. Nearly seven years had passed since he took leave of her. Of late he thought her letters had been less cheerful; she spoke of her declining health, of her earnest hope that she might live to embrace (p. 238) him once more. This hint was enough for his affectionate heart. He immediately broke off all his engagements and prepared to return. Everyone knows what impatience is created when one first begins to contemplate home, after a long absence, and the heart is turned toward it. "Seven years absent?" wrote Rubens to his mother, "how is it possible I have lived so long away from you? It is too long; henceforth I will devote myself to your happiness. Antwerp shall be my future residence. I have acquired a taste for horticulture; our little garden shall be enlarged and cultivated, and our home will be a paradise."
What are human anticipations and projects! the day before he was to quit Rome he received a letter informing him that his mother was very ill, and begging him to return with all speed. With breathless haste he hurried back, without sleep or rest. When he reached the city he dared not make any inquiries. At length he stood before the paternal mansion; he saw the gloomy tiles and half-closed window-shutters. It was the fall of the trees. He observed people going in and out at the door; to speak was impossible. At length he rushed in and heard the appalling sentence, "Too late," a sentence that often strikes desolation to the human heart. His mother had expired that morning.
While he was struggling with the bitterness of sorrow, he met with Elizabeth Brants. There was something in the tone of her voice which infused tranquillity into his mind, and affection came in a new form to assuage his loss. She was the "ladye of his love," and afterward his wife. He built a magnificent house at Antwerp, with a saloon in form of a rotunda, which he ornamented and enriched with antique statues, busts, vases, and pictures by the most celebrated painters. Thus surrounded by the gems of art, he devoted himself to the execution of works which were the pride of his native country, and caused honors and wealth to be heaped upon him.
There were those found who could not endure the splendor of his success; these calumniated. There were others who tried to draw him into visionary speculations. A chemist offered him a share of his laboratory, to join in his search for the philosopher's stone. He carried the visionary to his painting-room, and said, "The offer comes too late. You see I have found out the art of making gold by my palette and pencils."
Rubens was now at the height of prosperity and happiness, a dangerous eminence, and one on which few are permitted to rest. A second time his heart was pierced with sorrow: he lost his young wife, Elizabeth, a few years after their union. Deep as was his sorrow, he had yet resolution enough to feel the necessity of exertion. He left the place which constantly reminded him of domestic enjoyment, the memory of which contrasted so sadly with the present silence and solitude, and travelled for some time in Holland. After his return, he received a commission from Mary de Medici, of France, to adorn the palace of the Luxembourg. He executed for this purpose a number of paintings at Antwerp, and instructed several pupils in his art.
At this time Rubens devoted himself wholly to painting, and scarcely allowed himself time for recreation. He considered it one of the most effectual (p. 239) means of instruction, to allow his pupils to observe his method of using his paints. He therefore had them with him while he worked on his large pictures. Teniers, Snyders, Jordaens, and Vandyke were among his pupils—all names well known.
When Rubens had executed the commission given him by Mary de Medici, wife of Henry IV., he repaired to Paris to arrange his pictures at the Luxembourg palace, and there painted two more, and likewise the galleries, representing passages of her life.
Here he became acquainted with the Duke of Buckingham, as that nobleman was on his way to Madrid with Prince Charles. On his return to Antwerp, he was summoned to the presence of the Infanta Isabella, who had, through Buckingham, become interested in his character. She thought him worthy of a political mission to the court of Madrid, where he was most graciously received by Philip. While at Madrid he painted four pictures for the convent of the Carmelites, and a fine portrait of the king on horseback, with many other pictures; for these extraordinary productions he was richly rewarded, received the honor of knighthood, and was presented with the golden key.
While in Spain, Don John, Duke of Braganza, who was afterward king of Portugal, sent and invited him to visit him at Villa Vitiosa, the place of his residence. Rubens, perhaps, might at this time have been a little dazzled with his uncommon elevation. He was now Sir Paul and celebrated all over Europe. It was proper he should make the visit as one person of high rank visits another. His preparations were great to appear in a becoming style, and not to shame his noble host. At length the morning arrived, and, attended by a numerous train of courteous friends and hired attendants, the long cavalcade began the journey. When not far distant from Villa Vitiosa, Rubens learned that Don John had sent an embassy to meet him. Such an honor had seldom been accorded to a private gentleman, and Rubens schooled himself to receive it with suitable humility and becoming dignity.
He put up at a little distance from Villa Vitiosa, awaiting the arrival of the embassy; finally it came, in the form of a single gentleman, who civilly told him that the duke, his master, had been obliged to leave home on business that could not be dispensed with, and therefore must deny himself the pleasure of the visit; but as he had probably been at some extra expense in coming so far, he begged him to accept of fifty pistoles as a remuneration.
Rubens refused the pistoles, and could not forbear adding that he had "brought two thousand along with him, which he had meant to spend at his court during the fifteen days he was to spend there."
The truth was, that when Don John was informed that Rubens was coming in the style of a prince to see him, it was wholly foreign to his plan; he was a great lover of painting, and had wished to see him as an artist. He therefore determined to prevent the visit.
The second marriage of Rubens, with Helena Forman, was, no less than the first, one of affection; she had great beauty, and became a model for his pencil. His favor with the great continued. Mary de Medici visited him at his own (p. 240) home more than once; and the Infanta Isabella was so much satisfied with his mission in Spain, that she sent him to England, to sound the disposition of the government on the subject of a peace.
Rubens disclosed in this embassy his diplomatic talents; he first appeared there in his character of artist, and insensibly won upon the confidence of Charles. The king requested him to paint the ceiling of the banqueting-house at Whitehall. While he was employed upon it, Charles frequently visited him and criticised the work. Rubens, very naturally introducing the subject, and finding, from the tenor of his conversation, that he was by no means averse to a peace with Spain, at length produced his credentials. The king received his mission most graciously, and Rubens returned to the Netherlands crowned with honors and success.
He had passed his fiftieth year when his health began to fail, and he was attacked with a severe fit of the gout. Those who have witnessed the irritation attendant upon that disorder will appreciate the perfect harmony and gentleness that existed between Rubens and his wife. With untiring tenderness she devoted herself to him, and was ingenious in devising alleviations and comforts.
The severe attacks of Rubens' disorder debilitated his frame, yet he continued painting at his easel almost to the last; and, amid suffering and sickness, never failed in giving the energy of intellect to his pictures. He died at the age of sixty-three, in the year 1640, leaving great wealth. The pomp and circumstance of funeral rite can only be of consequence as showing the estimation in which a departed citizen is held. Public funeral honors were awarded, and men of every rank were eager to manifest their respect to his memory. He was buried in the Church of St. James, at Antwerp, under the altar of his private chapel, which was decorated with one of his own noble pictures.[Back to Contents]

A heretic in art Rembrandt was to many of his Dutch contemporaries; to us, he is the master, supreme alike in genius and accomplishment. Because, as time went on, he broke completely from tradition and in his work gave full play to his originality, his pictures were looked at askance; because he chose to live his own life, indifferent to accepted conventions, he himself was misunderstood. It was his cruel fate to enjoy prosperity and popularity in his earlier years, only to meet with neglect in his old age. But this he felt probably less than other men; he was not a courtier, with Velasquez, nor vowed to worldly success, with Rubens. (p. 241) His pleasure and his reward, he found in his work. So long as easel and canvas, brushes and paints were left to him, he demanded no greater happiness.
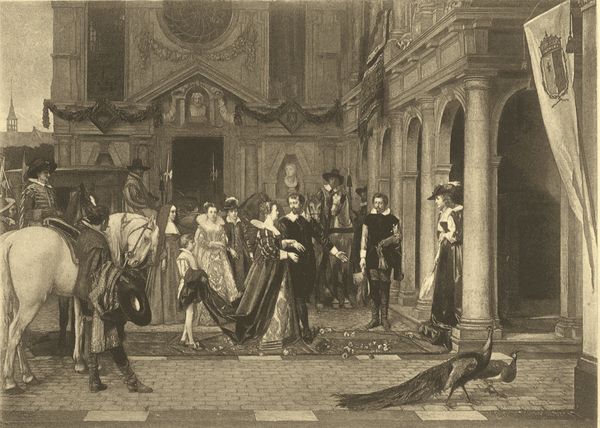

Marie De Medici at the House of Rubens.
In Leyden, a town already made famous by another master, Lucas van Leyden, Rembrandt was born in 1606; though this date has been disputed, some authorities suggesting 1607, others, 1608. His family were respectable, if not distinguished, burghers, his father, Harmen Gerritszoon, being a miller by trade, his mother, Neeltjen Willems of Zuitbroeck, the daughter of a baker. Not until early in the seventeenth century did permanent surnames become common among Dutchmen; hitherto children had been given their father's, in addition to their own Christian name; Rembrandt for many years was known as Rembrandt Harmenzoon, or the son of Harmen. But the miller, to be in the growing fashion, had called himself Van Ryn—of the Rhine—and thus, later on, Rembrandt also signed himself. Harmen was well-to-do; he owned houses in Leyden, and beyond the walls, gardens, and fields, and the mill where Rembrandt, because he once drew a mill, was supposed to have been born. But there was no reason for Neeltjen to move from a comfortable house in town into such rustic quarters, and it is more likely that Rembrandt's birthplace was the house pointed out in the Nordeinde Street. A commercial career had been chosen for his four older brothers. But Harmen, his means allowing the luxury, decided to make of his fifth son a man of letters and learning, and Rembrandt was sent to the University of Leyden. That letters, however, had small charm for him, was clear from the first. Better than his books he loved the engravings of Swanenburch, better still, the pictures of Lucas van Leyden, which he could look at to his heart's content on gala days, when the Town Hall, where they hung, was thrown open to the public. His hours of study were less profitable than his hours of recreation when he rambled in the country, through his father's estate, and, sometimes as far as the sea, a sketch-book, the chances are, for sole companion. Certainly, by the time he was fifteen, so strong were the proofs of his indifference to the classics and his love for art, that his father, sacrificing his own ambitions, allowed Rembrandt to leave the university for the studio of Van Swanenburch. From this day forth, his life's history is told in the single word—work; his indeed was the genius of industry.
Van Swanenburch had studied in Italy; but his own painting, to judge by the few examples still in existence, was entirely commonplace. Three years were more than enough to be passed under his tuition. At the end of the third, Rembrandt went to Amsterdam, and there entered the studio of Lastman. His second master also had studied in Italy, and also was a painter of mediocre talent, popular in his own times—the Apelles of the day, he was called—but remembered now chiefly because of his relations to his pupil. From the first, (p. 242) Rembrandt, even if obliged to paint the stock subjects of the day, was determined to treat them in his own way, and not to follow set forms that happened to be adopted in the schools. He used real men and women for models, and painted them as he saw them, not as he was bidden to look at them through his teacher's spectacles. In six months he had learned at least one thing, that Lastman had nothing more to teach him. The man of genius must ever be his own master, though he remain the hard-working student all his days. Back to Leyden and to his father's house, Rembrandt had not returned to lead a life of idleness. He worked tremendously in these early years. Even needed models he found in the members of his family; he has made the face of his mother as familiar as that of a friend; his own, with the heavy features, the thick, bushy hair, the small intelligent eyes, between them the vertical line, fast deepening on the fine forehead, he drew and etched and painted, again and again. More elaborate compositions he also undertook. As in his maturity, it was to the Bible he turned for suggestions: Saint Paul in prison, Samson and Delilah, the Presentation in the Temple—these were the themes then in vogue which he preferred, rendering them with the realism which distinguished his later, more famous Samsons and Abrahams and Christs, making them the motive for a fine arrangement of color, for a striking study of light and shadow. A pleasant picture one can fancy of his life at this period; he was with his own people, for whom his love was tender; busy with brush, pencil, and etching-needle; he was strengthening his powers of observation, developing and perfecting his style, occasionally producing work that won for him renown in Leyden; and, gradually, he gathered round him a small group of earnest fellow-workers, chief among them Lievens, Gerard Dou, and Van Vliet, the last two, though but slightly his juniors, looking up to him as master. These were the years of his true apprenticeship.
Leyden, however, was not the best place for a young painter who had his fortunes to make. It was essentially a university town; interest was concentrated upon letters; art was but of secondary consideration. It was different in Amsterdam, the great commercial centre of Holland. There, all was life and activity and progress; there, was money to be spent, and the liberal patron willing to lavish it upon the artist. Holland just then was in the first flush of prosperity and patriotism, following upon her virtual independence from Spain. Not a citizen but glowed with self-respect at the thought of the victory he had, in one way or another, helped to win; the state, as represented by the good burghers, was supreme in every man's mind. It was natural that individuals and corporations alike should seek to immortalize their greatness by means of the painter's art, which, in Holland, had long since ceased to be a monopoly of the church. Hence the age became essentially one of portrait-painting. Many were the painters whose portraits had already achieved distinction. De Keyser was busy in Amsterdam; a far greater genius, Franz Hals, but fifteen years Rembrandt's senior, was creating his masterpieces in The Hague and Harlem. It was as inevitable that Rembrandt should turn to portraiture, as that he should find commissions (p. 243) less numerous in Leyden than in Amsterdam. Often in the latter town his services were required; so often, indeed, that at last, about 1631, when he was just twenty-five, he settled there permanently and set up a studio of his own.
Success was his from the start. Sitter after sitter sought him out in his house on the Bloemgracht; the most distinguished men in the town hastened to patronize him. His work was liked by the burghers whom he painted, its strength was felt by artists, whose canvases soon showed its influence. Admirers crowded to his studio. He had not been in Amsterdam a twelvemonth when, before he was yet twenty-six, he was entrusted with an order of more than usual importance. This was the portrait of Dr. Tulp and his class of surgeons: the famous "Lesson in Anatomy" now in the Gallery at The Hague. The subject at the time was very popular. Many artists, De Keyser among others, had already, in painting prominent surgeons, placed them around the subject they were dissecting; indeed, this was the arrangement insisted upon by the surgeons themselves, and, as there seems to have been no limit to their vanity, "Lessons in Anatomy" were almost as plentiful in Holland as "Madonnas" in Umbria. Rembrandt in his composition was simply adhering to accepted tradition. It is true that he instilled life into a group hitherto, on other painters' canvases, stiff and perfunctory; but, though the picture was a wonderful production for a man of his years, it is not to be ranked with his greatest work.
Commissions now poured in still faster. It was at this time he painted several of his best known portraits: the "Master Shipbuilder and his Wife," at present in Buckingham Palace; that simply marvellous old woman at the National Gallery in London, made familiar to everyone by countless photographs and other reproductions; the man in ruff and woman in coif at the Brunswick Museum; and a score of others scarce less important. With increasing popularity, he was able to command his own prices, so that only a part of his time was it necessary for him to devote to the portraits which were his chief source of income. During the leisure he reserved, he painted biblical subjects, ever his delight, and made etchings and drawings, today the most prized treasures in the world's great galleries. As in Leyden, he drew about him students; a few, notably Ferdinand Bol and Christophe Paudiss, destined, in their turn, to gain name and fame. Indifferent to social claims and honors—an indifference the burghers, his patrons, found it hard to forgive, his one amusement was in collecting pictures and engravings, old stuffs and jewels, and every kind of bric-à-brac, until his house in Amsterdam was a veritable museum. This amusement later was to cost him dear.
Four years after the "Lesson in Anatomy" was painted, when he was at the height of prosperity, in 1634, he married Saskia van Uylenborch, the Saskia of so many an etching and picture. She was of a good Frisian family, and brought with her a dowry of no mean proportions. Rembrandt's marriage made small changes in his way of living. Into the society, so ready to receive him, he never went, not even now that he had a wife to introduce. It bored him, and he was no toady to waste his time fawning upon possible patrons. "When I desire to rest (p. 244) my spirit, I do not seek honors, but liberty," was his explanation. The companionship of artists he always welcomed; sometimes he visited the humbler burghers, whose ways were as simple as his own; sometimes he sought the humblest classes of all, because of their picturesqueness, and his contemporaries took him to task for his perverted taste for low company. The truth is that always he devoted himself solely and wholly to his art; the only difference, once he was married, was that, when he sat at his easel all day or over his copperplate, and sketchbook all evening, Saskia was with him. She shared all his interests, all his ambitions; she had no will but his. During his working hours, she was his model, obedient to his call. She never tired of posing for him, nor he of painting her now simply as Saskia, now as Delilah feasting with Samson, as Susanna surprised by the Elders, as the Jewish Betrothed at her toilet. Sometimes he represented her alone, sometimes with himself at her side; once, in the famous Dresden portrait, on his knee, as if to proclaim the love they bore for one another. And he, who could render faithfully the ways of the beggar, the austere black of the burgher, for himself and Saskia found no masquerading too gay or extravagant. In inventing costumes for their own portraits, he gave his exuberant fancy free play: in gorgeous embroidered robes, waving plumes, and priceless gems they arrayed themselves, until even the resources of his collection were exhausted: the same rich mantle, the same jewels appear, and reappear in picture after picture.
Rembrandt's short married years were happy, though not without their sorrows. Of Saskia's five children, four died in infancy; the fifth, Titus, was not a year old when, in 1642, the end came for Saskia, and Rembrandt, who had just reached his thirty-seventh year, was left in his great house alone with an infant son and his pupils. Her confidence in him is shown by her will, in which the inheritance of Titus is left in the father's charge, though already Rembrandt's affairs must have given signs of coming complications.

Connoisseurs at Rembrandt's Studio.
Much of his best work remained to be done, but after Saskia's death his worldly fortunes and his popularity never again touched such high-water mark. The reason for this is not far to seek. During all these years, Rembrandt's powers had matured, his methods broadened, and his individuality strengthened. With each new canvas, his originality became more conspicuous. It was not only that the world of nature, and not imagination, supplied his models. Many of the Dutch painters now were no less realists than he. It was not only that he solved certain problems of chiaro oscuro, there were men, like Lievens, who were as eager as he in the study of light and shadow. But Rembrandt brought to his every experiment an independence that startled the average man. He painted well because he saw well. If no one else saw things as he did, the loss was theirs. But he paid for his keener vision; because he did not paint like other artists, his methods were mistrusted. To be misunderstood is the penalty of genius. The picture which, of all his work, is now the most famous, marks the turn in the tide of his affairs. Shortly before Saskia's death, he had been commissioned to paint a portrait group of Banning Cock and the military company (p. 245) which he commanded. These portrait groups of the military corporations rivalled in popularity the "Lessons in Anatomy." Each member, or officer, paid to be included in the composition, and, as a rule, a stiff, formal picture, with each individual posed as for a photograph, was the result. Rembrandt, apparently, was in nowise restricted when he undertook the work for Banning Cock, and so, instead of the stupid, hackneyed arrangement, he made of the portrait of the company a picture of armed men marching forth to beating of drums and waving of banners, "The Night Watch," as it must ever be known—more accurately, "The Sortie of the Company of Banning Cock"—now in the Ryks Museum of Amsterdam. With the men for whom it was painted, it proved a failure. The grouping, the arrangement displeased them. Many of the company were left in deep shadow, which was not the privilege for which they had agreed to pay good money. Rembrandt was not the man to compromise. After this many burghers, who cared much for themselves and their own faces, and not in the least for art, were afraid to entrust their portraits to him lest their importance might be sacrificed to the painter's effects. Certain it is that six years later, in 1648, when the independence of Holland was formally recognized at the Congress of Westphalia, though Terburg and Van der Heist celebrated the event on canvas, Rembrandt's services were not secured. Good friends were left to him—men of intelligence who appreciated his strong individuality and the great originality of his work. Banning Cock himself was not among the discontented. A few leading citizens, like Dr. Tulp and the Burgomeister Six, were ever his devoted patrons. Artists still gathered about him; pupils still crowded to his studio; Nicolas Maes, De Gelder, Kneller among them. Many of his finest portraits—those of Hendrickje Stoffels, of his son, of himself in his old age, of the Burgomeister Six, above all, his masterpiece, "The Syndics of the Guild of Clothmakers," now in Amsterdam; many of his finest etchings, the little landscapes, the famous "Hundred Guilder Print," "Christ Healing the Sick," belong to this later period. There was no falling off, but rather an increase, in his powers, despite the clouds that darkened his years of middle age.
Of these clouds, the darkest was due to his financial troubles. Rembrandt had made large sums of money; Saskia's dowry had been by no means small. But he also spent lavishly. He had absolutely no business capacity. Once he was accused of miserliness; that he would at times lunch on dry bread and a herring served as reproach against him; there was a story current that his pupils would drop bits of paper painted to look like money in order to see him stoop to pick them up. Both charges are too foolish to answer seriously. When he was at work, it mattered little to him what he ate, so that he was not disturbed; who would not stoop to pick up coins apparently scattered on the floor? The money he devoted to his collection is sufficient to show how small a fancy he had for hoarding; upon it a princely fortune had been squandered. To his own people in Leyden, when times were hard, he had not been slow to hold out a generous hand. It was because he was not enough of a miser, because he gave too little heed to business matters, that difficulties at length overwhelmed him. It (p. 246) is too sad a story to tell in detail. Perhaps the beginning was when he bought a house for which he had not the ready money to pay, and borrowed a large sum for the purpose. More and more involved became his affairs. In time his creditors grew clamorous, and at length the blow fell when, in 1657, he was declared bankrupt. The collection of years, the embroidered mantles and draperies, the jewels with which Saskia had been so gayly decked, the plumes and furs and gorgeous robes in which he himself had masqueraded, the armor and plate, the engravings and pictures which had filled his house—all were sold. He, the master, had, at the age of fifty-one, to begin life anew as if he were still but the apprentice.
In the midst of his troubles and losses, Hendrickje Stoffels, whose portrait hangs in the Louvre, was the friend who cheered and comforted him. She had been his servant; afterward she lived with him as his wife, though legally they were not married. To Titus, as to her own children, she was ever a tender mother, and Titus, in return, seems to have loved her no less well. In the end, they together took Rembrandt's business interests into their own hands, the son, probably, using his inheritance in the enterprise. Renting a house in their own name, they became his print and picture dealers.
But as time went on, Rembrandt's work brought lower and lower prices, and he, himself, the last two years of his life, was almost forgotten. Though he still lived in Amsterdam, the town from which he had so seldom journeyed, and then never far, he had fallen into such obscurity, that report now established him in Stockholm as painter to the King of Sweden, now in Hull, or Yarmouth. In his own family nothing but sorrow was in store for him. Hendrickje died, probably about 1664, and he was once more alone; and next he lost Titus, who then had been married but a few short months.
Fortunately for Rembrandt, he did not long survive them. In 1669, at the age of sixty-two, his release came. He was buried in the West Church, quietly and simply. Thirteen florins his funeral cost, and even this small expense had to be met by his daughter-in-law. When an inventory of his possessions was taken, these were found to consist of nothing but his own wardrobe and his painter's tools.
But better than a mere fortune, his work he left as an heirloom for all time; his drawings, not the least among them without the stamp of his genius; his prints, still unsurpassed, though it was he who first developed the possibilities of etching; his pictures, "painted with light," as Fromentin has said. His subjects he may have borrowed from the fashions and traditions of the time; certain mannerisms of technique and arrangement his pupils may have copied. But for all that, his work belongs to no special school or group; like all the world's great masterpieces, whether produced in Spain by a Velasquez, in Venice by a Titian, in England by a Whistler, it stands alone and supreme.[Back to Contents]


"I was born," says Hogarth, in his Memoirs of himself, "in the city of London, November 10, 1697. My father's pen, like that of many authors, did not enable him to do more than put me in a way of shifting for myself. As I had naturally a good eye and a fondness for drawing, shows of all sorts gave me uncommon pleasure when an infant; and mimicry, common to all children, was remarkable in me. An early access to a neighboring painter drew my attention from play, and I was, at every possible opportunity, employed in making drawings. I picked up an acquaintance of the same turn, and soon learned to draw the alphabet with great correctness. My exercises when at school were more remarkable for the ornaments which adorned them than for the exercise itself. In the former I soon found that blockheads with better memories could much surpass me, but for the latter I was particularly distinguished."
To this account of Hogarth's childhood we have only to add that his father, an enthusiastic and laborious scholar, who, like many of his craft, owed little to the favor of fortune, consulted these indications of talent as well as his means would allow, and bound his son apprentice to a silver-plate engraver. But Hogarth aspired after something higher than drawing ciphers and coats-of-arms; and before the expiration of his indentures he had made himself a good draughtsman, and obtained considerable knowledge of coloring. It was his ambition to become distinguished as an artist; and not content with being the mere copier of other men's productions, he sought to combine the functions of the painter with those of the engraver, and to gain the power of delineating his own ideas and the fruits of his acute observation. He has himself explained the nature of his views in a passage which is worth attention:
"Many reasons led me to wish that I could find the shorter path—fix forms and characters in my mind—and instead of copying the lines, try to read the language, and, if possible, find the grammar of the art by bringing into one focus the various observations I have made, and then trying by my power on the canvas how far my plan enabled me to combine and apply them to practice. For this purpose I considered what various ways, and to what different purposes, the (p. 248) memory might be applied, and fell upon one most suitable to my situation and idle disposition; laying it down first as an axiom, that he who could by any means acquire and retain in his memory perfect ideas of the subjects he meant to draw, would have as clear a knowledge of the figure as a man who can write freely hath of the twenty-five letters of the alphabet and their infinite combinations." Acting on these principles, he improved, by constant exercise, his natural powers of observation and recollection. We find him roaming through the country, now at Yarmouth and again at Queenborough, sketching everywhere. In his rambles among the motley scenes of London he was ever on the watch for striking features or incidents; and not trusting entirely to memory, he was accustomed, when any face struck him as being peculiarly grotesque or expressive, to sketch it on his thumb-nail, to be treasured up on paper at his return home.
For some time after the expiration of his apprenticeship, Hogarth continued to practise the trade to which he was bred; and his shop-bills, coats-of-arms, engravings upon tankards, etc., have been collected with an eagerness quite disproportionate to their value. Soon he procured employment in furnishing frontispieces and designs for the booksellers. The most remarkable of these are the plates to an edition of "Hudibras," published in 1726; but even these are of no distinguished merit. About 1728 he began to seek employment as a portrait-painter. Most of his performances were small family pictures, containing several figures, which he calls "Conversation Pieces," from twelve to fifteen inches high. These for a time were very popular, and his practice was considerable, as his price was low. His life-size portraits are few; the most remarkable are that of Captain Coram, in the "Foundling Hospital," and that of Garrick as King Richard III., which is reproduced in the present volume. But his practice as a portrait-painter was not lucrative, nor his popularity lasting. Although many of his likenesses were strong and characteristic, in the representation of beauty, elegance, and high-breeding he was little skilled. The nature of the artist was as uncourtly as his pencil. When Hogarth obtained employment and eminence of another sort through his wonderful prints, he abandoned portrait-painting, with a growl at the jealousy of his professional brethren; and the vanity and blindness of the public.
March 25, 1729, Hogarth contracted a stolen marriage with the only daughter of the once fashionable painter, Sir James Thornhill. The father, for some time implacable, relented at last; and the reconciliation, it is said, was much forwarded by his admiration of the "Harlot's Progress," a series of six prints, commenced in 1731 and published in 1734. The novelty as well as merit of this series of prints won for them extraordinary popularity; and their success encouraged Hogarth to undertake a similar history of the "Rake's Progress," in eight prints, which appeared in 1735. The third, and perhaps the most popular, as it is the least objectionable of these pictorial novels, "Marriage à la Mode," was not engraved till 1745.

Hogarth sketching the Highway of Queenborough.
The merits of these prints were sufficiently intelligible to the public: their originality and boldness of design, the force and freedom of their execution, (p. 249) rough as it is, won for them an extensive popularity and a rapid and continued sale. The "Harlot's Progress" was the most eminently successful, from its novelty rather than from its superior excellence. Twelve hundred subscribers' names were entered for it; it was dramatized in several forms; and we may note, in illustration of the difference of past and present manners, that fan-mounts were engraved containing miniature copies of the six plates. The merits of the pictures were less obvious to the few who could afford to spend large sums on works of art, and Hogarth, too proud to let them go for prices much below the value which he put upon them, waited for a long time, and waited in vain, for a purchaser. At last he determined to commit them to public sale; but instead of the common method of auction, he devised a new and complex plan with the intention of excluding picture-dealers, and obliging men of rank and wealth who wished to purchase to judge and bid for themselves. The scheme failed, as might have been expected. Nineteen of Hogarth's best pictures, the "Harlot's Progress," the "Rake's Progress," the "Four Times of the Day," and "Strolling Actresses Dressing in a Barn" produced only £427 7s., not averaging £22 10s. each. The "Harlot's Progress" was purchased by Mr. Beckford at the rate of fourteen guineas a picture; five of the series perished in the fire at Fonthill. The "Rake's Progress" averaged twenty-two guineas a picture; it has passed into the possession of Sir John Soane, at the advanced price of five hundred and seventy guineas. The same eminent architect became the proprietor of the four pictures of an "Election" for the sum of £1,732. "Marriage à la Mode" was disposed of in a similar way in 1750; and on the day of the sale one bidder appeared, who became master of the six pictures, together with their frames, for £115 10s. Mr. Angerstein purchased them, in 1797, for £1,381, and they now form a striking feature in the National Gallery.
The satire of Hogarth was not often of a personal nature; but he knew his own power, and he sometimes exercised it. Two of his prints, "The Times," produced a memorable quarrel between himself, on one side, and Wilkes and Churchhill, on the other. The satire of the prints of "The Times," which were published in 1762, was directed, not against Wilkes himself, but his political friends, Pitt and Temple; nor is it so biting as to have required Wilkes, in defence of his party, to retaliate upon one with whom he had lived in familiar and friendly intercourse. He did so, however, in a number of the North Briton, containing not only abuse of the artist, but unjust and injurious mention of his wife. Hogarth was deeply wounded by this attack; he retorted by the well-known portrait of Wilkes with the cap of liberty, and he afterward represented Churchill as a bear. The quarrel was unworthy the talents either of the painter or poet. It is more to be regretted because its effects, as he himself intimates, were injurious to Hogarth's declining health. The summer of 1764 he spent at Chiswick, and the free air and exercise worked a partial renovation of his strength. The amendment, however, was but temporary, and he died suddenly, October 26th, the day after his return to his London residence in Leicester Square.[Back to Contents]

Sir Joshua Reynolds, the celebrated painter, was, on July 16, 1723, born at Plympton, a small town in Devonshire, England. His father was a minister of the parish, and also master of the grammar school; and being a man of learning and philanthropy, he was beloved and respected by all to whom he was known. Such a man, it will naturally be supposed, was assiduous in the cultivation of the minds of his children, among whom his son Joshua shone conspicuous, by displaying at a very early period a superiority of genius and the rudiments of a correct taste. Unlike other boys, who generally content themselves with giving a literal explanation of their author, regardless of his beauties or his faults, young Reynolds attended to both these, displaying a happy knowledge of what he read, and entering with ardor into the spirit of his author. He discovered likewise talents for composition, and a natural propensity to drawing, in which his friends and intimates thought him qualified to excel. Emulation was a distinguishing characteristic of his mind, which his father perceived with the delight natural to a parent; and designing him for the church, in which he hoped that his talents might raise him to eminence, he sent him to one of the universities.
Soon after this period he grew passionately fond of painting; and by the perusal of Richardson's theory of that art was determined to make it his profession through life. At his own earnest request, therefore, he was removed to London; and about the year 1742 became a pupil to Mr. Hudson, who, though not himself an eminent painter, was preceptor to many who afterward excelled in the art. One of the first advices which he gave to Mr. Reynolds was to copy carefully Guercino's drawings. This was done with such skill, that many of the copies are said to be now preserved in the cabinets of the curious as the originals of that very great master.
About the year 1749, Mr. Reynolds went to Italy under the auspices, and in the company, of the late Lord (then Commodore) Keppel, who was appointed to the command of the British squadron in the Mediterranean. In this garden of the world, this magic seat of arts, he failed not to visit the schools of the great masters, to study the productions of different ages, and to contemplate with unwearied attention the various beauties which are characteristic of each. His labor (p. 251) here, as has been observed of another painter, was "the labor of love, not the task of the hireling;" and how much he profited by it is known to all Europe.
Having remained about two years in Italy, and studied the language as well as the arts of the country with great success, he returned to England, improved by travel and refined by education. On the road to London from the port where he landed, he accidentally found in the inn where he lodged Johnson's life of Savage, and was so taken with the charms of composition, and the masterly delineation of character displayed in that work, that, having begun to read it while leaning his arm on the chimney-piece, he continued in that attitude, insensible of pain till he was hardly able to raise his hand to his head. The admiration of the work naturally led him to seek the acquaintance of its author, who continued one of his sincerest admirers and warmest friends till 1784, when they were separated by the stroke of death.
The first thing that distinguished him after his return to his native country was a full-length portrait of Commodore Keppel; which in polite circles was spoken of in terms of the highest encomium, and testified to what a degree of eminence he had arrived in his profession. This was followed by a portrait of Lord Edgecombe, and a few others, which at once introduced him to the first business in portrait-painting; and that branch of the art he cultivated with such success as will forever establish his fame with all descriptions of refined society. Having painted some of the first-rate beauties of the age, the polite world flocked to see the graces and the charms of his pencil; and he soon became the most fashionable painter not only in England, but in all Europe. He has indeed preserved the resemblance of so many illustrious characters, that we feel the less regret at his having left behind him so few historical paintings; though what he has done in that way shows him to have been qualified to excel in both departments. The only landscape, perhaps, which he ever painted, except those beautiful and chaste ones which compose the backgrounds of many of his portraits, is "A View on the Thames from Richmond," which in 1784 was exhibited by the Society for Promoting Painting and Design in Liverpool.
In 1764 Mr. Reynolds had the merit of being the first promoter of that club, which, having long existed without a name, became at last distinguished by the appellation of the Literary Club. Upon the foundation of the Royal Academy of Painting, Sculpture, and Architecture, he was appointed president; and his acknowledged excellence in his profession made the appointment acceptable to all the lovers of art. To add to the dignity of this new institution, his majesty conferred on the president the honor of knighthood; and Sir Joshua delivered his first discourse at the opening of the Academy, on January 2, 1769. The merit of that discourse has been universally admitted among painters; but it contains some directions, respecting the proper mode of prosecuting their studies, to which every student of every art would do well to pay attention. "I would chiefly recommend (says he) that an implicit obedience to the rules of art, as established by the practice of the great masters, should be exacted from the young students. That those models, which have passed through the approbation of (p. 252) ages, should be considered by them as perfect and infallible guides, as subjects for their imitation, not their criticism. I am confident that this is the only efficacious method of making a progress in the arts; and that he who sets out with doubting will find life finished before he becomes master of the rudiments. For it may be laid down as a maxim, that he who begins by presuming on his own sense, has ended his studies as soon as he has commenced them. Every opportunity, therefore, should be taken to discountenance that false and vulgar opinion, that rules are the fetters of genius. They are fetters only to men of no genius; as that armor, which upon the strong becomes an ornament and a defence, upon the weak and misshapen turns into a load, and cripples the body which it was made to protect."
Each succeeding year, on the distribution of the prizes, Sir Joshua delivered to the students a discourse of equal merit with this; and perhaps we do not hazard too much when we say, that from the whole collected, the lovers of belles-lettres and the fine arts will acquire juster notions of what is meant by taste in general, and better rules for acquiring a correct taste, than from the multitude of those volumes which have been professedly written on the subject.
In the autumn of 1785 he went to Brussels, where he expended about £1,000 on the purchase of paintings which, having been taken from the different monasteries and religious houses in Flanders and Germany, were then exposed to sale by the command of the Emperor Joseph. Gainsborough and he had engaged to paint each other's portrait; and the canvas for both being actually stretched, Sir Joshua gave one sitting to his distinguished rival; but to the regret of every admirer of the art, the unexpected death of the latter prevented all further progress.
In 1790 he was anxiously desirous to procure the vacant professorship of perspective in the academy for Mr. Bonomi, an Italian architect; but that artist not having been yet elected an associate, was, of course, no academician, and it became necessary to raise him to those positions, in order to qualify him for being a professor. Mr. Gilpin being his competitor for the associateship, the numbers on the ballot proved equal, when the president, on his casting vote, decided the election in favor of his friend, who was thereby advanced so far toward the professorship. Soon after this, an academic seat being vacant, Sir Joshua exerted all his influence to obtain it for Mr. Bonomi; but finding himself out-voted by a majority of two to one, he quitted the chair with great dissatisfaction, and next day sent to the secretary of the academy a formal resignation of the office, which for twenty-one years he had filled with honor to himself and to his country. His indignation, however, subsiding, he suffered himself to be prevailed upon to return to the chair, which, within a year and a half, he was again desirous to quit for a better reason.
Finding a disease of languor, occasioned by an enlargement of the liver, to which he had for some time been subject, increase, and daily expecting a total loss of sight, he wrote a letter to the academy, intimating his intention to resign the office of president on account of bodily infirmities, which disabled him from executing the duties of it to his own satisfaction. The academy received (p. 253) this intelligence with the respectful concern due to the talents and virtues of their president, and either then did enter, or designed to enter, into a resolution honorable to all parties, namely, that a deputation from the whole body of the academy should wait upon him, and inform him of their wish, that the authority and privileges of the office of president might be his during his life, declaring their willingness to permit the performance of any of its duties which might be irksome to him by a deputy.
From this period Sir Joshua never painted more. The last effort of his pencil was the portrait of the honorable Charles James Fox, which was executed in his best style, and shows that his fancy, his imagination, and his other great powers in the art which he professed, remained unabated to the end of his life. When the last touches were given to this picture,
"The hand of Reynolds fell, to rise no more."
On Thursday, February 23, 1792, the world was deprived of this amiable man and excellent artist, at the age of sixty-eight years; a man than whom no one, according to Johnson, had passed through life with more observations of men and manners. The following character of him is said to be the production of Mr. Burke:
"His illness was long, but borne with a mild and cheerful fortitude, without the least mixture of anything irritable or querulous, agreeably to the placid and even tenor of his whole life. He had, from the beginning of his malady, a distinct view of his dissolution, which he contemplated with that entire composure which nothing but the innocence, integrity, and usefulness of his life, and an unaffected submission to the will of Providence, could bestow. In this situation he had every consolation from family tenderness, which his tenderness to his family had always merited.
"Sir Joshua Reynolds was, on very many accounts, one of the most memorable men of his time; he was the first Englishman who added the praise of the elegant arts to the other glories of his country. In taste, in grace, in facility, in happy invention, and in richness and harmony of coloring, he was equal to the great masters of the renowned ages. In portrait he went beyond them; for he communicated to that branch of the art in which English artists are the most engaged, a variety, a fancy, and a dignity derived from the higher branches, which even those who professed them in a superior manner did not always preserve when they delineated individual nature. His portraits reminded the spectator of the invention of history and the amenity of landscape. In painting portraits he appears not to be raised upon that platform, but to descend to it from a higher sphere. His paintings illustrate his lessons, and his lessons seem to be derived from his paintings.
"He possessed the theory as perfectly as the practice of his art. To be such a painter, he was a profound and penetrating philosopher.
"In full happiness of foreign and domestic fame, admired by the expert in art, and by the learned in science, courted by the great, caressed by sovereign (p. 254) powers, and celebrated by distinguished poets, his native humility, modesty, and candor never forsook him, even on surprise or provocation; nor was the least degree of arrogance or assumption visible to the most scrutinizing eye in any part of his conduct or discourse.
"His talents of every kind—powerful from nature, and not meanly cultivated in letters—his social virtues in all the relations and all the habitudes of life, rendered him the centre of a very great and unparalleled variety of agreeable societies, which will be dissipated by his death. He had too much merit not to excite some jealousy, too much innocence to provoke any enmity. The loss of no man of his time can be felt with more sincere, general, and unmixed sorrow."[Back to Contents]

In the wilds of the new world, a century and a half ago, there was, apparently, no spot less likely to produce a famous painter than the Quaker province of Pennsylvania. And yet, when George Washington was only six years old there was born, in the little town of Springfield, Chester County, a boy whose interesting and remarkable career from infancy to old age has provided one of the most instructive lessons for students in art that America affords.
Perhaps Benjamin West's aptitude for picture-making in his infancy, while he was learning to walk and to talk, did not exceed that of hosts of other children, in like circumstances, in every generation since his time. But many curious things were remembered and told of this baby's performances after he had developed a decided talent for reproducing the beautiful objects that captivated his eye. It was in the summer of 1745, a few months before he was seven years old that his married sister came home for a visit, bringing with her an infant daughter. The next morning after her arrival, little Benjamin was left to keep the flies off the sleeping baby, while his mother and sister went to the garden for flowers. The baby smiled in its sleep, and the boy was captivated. He must catch that smile and keep it. He found some paper on the table, scrambled (p. 255) for a pen, and with red and black ink made a hasty but striking picture of the little beauty. He heard his mother returning, and conscious of having been in mischief, tried to conceal his production; but she detected and captured it, and regarded it long and lovingly, exclaiming as her daughter entered, "He has really made a likeness of little Sally!" She then caught up the boy in her arms, and kissed instead of chiding him, and he—looking up encouraged—told her he could make the flowers, too, if she would permit. The awakening of genius in Benjamin West has been distinctly traced to this incident, as the time when he first discovered that he could imitate the forms of such objects as pleased his sense of sight. And the incident itself has been aptly styled "the birth of fine arts in the New World."
The Quaker boy, in course of years, left the wilderness of America to become the president of the Royal Academy in London. His irreproachable character not less than his excellence as an artist, gave him commanding position among his contemporaries. From first to last he was distinguished for his indefatigable industry. The number of his pictures has been estimated, by a writer in Blackwood's Magazine, at three thousand; and Dunlap says that a gallery capable of holding them would be four hundred feet long, fifty feet wide, and forty feet high—or a wall a quarter of a mile long.
The parents of Benjamin West were sincere and self-respecting, and in the language of the times, well-to-do. His mother's grandfather was the intimate and confidential friend of William Penn. The family of his father claimed direct descent from the Black Prince and Lord Delaware, of the time of King Edward III. Colonel James West was the friend and companion in arms of John Hampden. When Benjamin West was at work upon his great picture of the "Institution of the Garter," the King of England was delighted when the Duke of Buckingham assured him that West had an ancestral right to a place among the warriors and knights of his own painting. The Quaker associates of the parents of the artist, the patriarchs of Pennsylvania, regarded their asylum in America as the place for affectionate intercourse—free from all the military predilections and political jealousies of Europe. The result was a state of society more contented, peaceful, and pleasing than the world had ever before exhibited. At the time of the birth of Benjamin West the interior settlements in Pennsylvania had attained considerable wealth, and unlimited hospitality formed a part of the regular economy of the principal families. Those who resided near the highways were in the habit, after supper and the religious exercises of the evening, of making a large fire in the hallway, and spreading a table with refreshments for such travellers as might pass in the night, who were expected to step in and help themselves. This was conspicuously the case in Springfield. Other acts of liberality were performed by this community, to an extent that would have beggared the munificence of the old world. Poverty was not known in this region. But whether families traced their lineage to ancient and noble sources, or otherwise, their pride was so tempered with the meekness of their faith, that it lent a singular dignity to their benevolence.
(p. 256) The Indians mingled freely with the people, and when they paid their annual visits to the plantations, raised their wigwams in the fields and orchards without asking permission, and were never molested. Shortly after Benjamin West's first efforts with pen and ink, a party of red men reached and encamped in Springfield. The boy-artist showed them his sketches of birds and flowers, which seemed to amuse them greatly. They at once proceeded to teach him how to prepare the red and yellow colors with which they decorated their ornaments. To these Mrs. West added blue, by contributing a piece of indigo. Thus the boy had three prismatic colors for his use. What could be more picturesque than the scene where the untutored Indian gave the future artist his first lesson in mixing paints! These wild men also taught him archery, that he might shoot birds for models if he wanted their bright plumage to copy.
The neighbors were attracted by the boy's drawings, and finally a relative, Mr. Pennington, a prominent merchant of Philadelphia, came to pay the family a visit. He thought the boy's crude pictures were wonderful, as he was then only entering his eighth year. When he went home he immediately sent the little fellow a box of paints, with six engravings by Grevling. John Gait, who wrote from the artist's own statements, describes the effect of this gift upon the boy. In going to bed he placed the box so near his couch, that he could hug and caress it every time he wakened. Next morning he rose early, and taking his paints and canvas to the garret, began to work. He went to breakfast, and then stole back to his post under the roof, forgetting all about school. When dinnertime came he presented himself at table, as usual, but said nothing of his occupation. He had been absent from school some days before the master called on his parents to inquire what had become of him. This led to the discovery of his secret painting, for his mother proceeded to the garret and found the truant. She was, however, so astonished with the creation upon his canvas, that she took him in her arms and kissed him with transports of affection. He had made a composition of his own out of two of the engravings—which he had colored from his ideas of the proper tints to be used—and so perfect did the picture appear to Mrs. West that, although half the canvas remained to be covered, she would not suffer the child to add another touch with his brush. Sixty-seven years afterward, Mr. Gait saw this production in the exact state in which it was left, and Mr. West himself acknowledged that in subsequent efforts he had never been able to excel some of the touches of invention in this first picture.
The first instruction in art which the artist received was from Mr. William Williams, a painter in Philadelphia. Young West's first attempt at portraiture was at Lancaster, where he painted "The Death of Socrates" for William Henry, a gunsmith. He was not yet sixteen, but other paintings followed which possessed so much genuine merit, that they have been preserved as treasures. One of these is in possession of General Meredith Reed, of Paris, France, a descendant of the signer. West returned to his home in Springfield, in 1754, to discuss the question of his future vocation. He had an inclination for military life, and volunteered as a recruit in the old French war; but military attractions vanished (p. 257) among the hardships involved, and in 1756, when eighteen years old, he established himself in Philadelphia as a portrait-painter, his price being "five guineas a head." Two years later he went to New York, where he passed eleven months, and was liberally employed by the merchants and others. He painted the portrait of Bishop Provoost, those of Gerardus Duyekinck and his wife—full length—one of Mrs. Samuel Breese, and many others, which are in the families of descendants, and characteristic examples of his early work.
In 1760 an opportunity offered for him to visit Rome, Italy. He carried letters to Cardinal Albani and other celebrities, and as he was very handsome and intelligent, and came from a far-away land about which hung the perpetual charm of tradition and romance, he soon became the lion of the day among the imaginative Italians. It was a novelty then for an American to appear in the Eternal City, and the very morning after his arrival a curious party followed his steps to observe his pursuit of art. He remained in Italy until 1763, and while there he painted, among others, his pictures of "Cimon and Iphigenia," and "Angelica and Medora." His portrait of Lord Grantham excited much interest, and that nobleman's introduction facilitated his visit to London, which proved so prolific in results. There was no great living historical painter in England just then; and at first there was no sale for West's pictures, as it was unfashionable to buy any but "old masters." But the young artist was undaunted, and presently attracted attention in high places. His picture of "Agrippina Landing with the Ashes of Germanicus," painted for Dr. Drummond, Archbishop of York, secured him the favor of George III., and the commission from his majesty to paint the "Departure of Regulus from Rome." His untiring industry and gentlemanly habits were conspicuous, and may be regarded as among the great secrets of his continual advance and public recognition. His "Parting of Hector and Andromache," and "Return of the Prodigal Son," were among his notable productions of this period. His "Death of General Wolfe" has been, says Tuckerman, "truly declared to have created an era in English art, by the successful example it initiated of the abandonment of classic costume—a reform advocated by Reynolds, who glories in the popular innovation." His characters were clad in the dress of their time. Reynolds said to the Archbishop of York: "I foresee that this picture will not only become one of the most popular, but will occasion a revolution in art." It was purchased by Lord Grosvenor. Among the long list of paintings executed by order of the king were "The Death of Chevalier Bayard;" "Edward III. Embracing his Son on the Field of Battle at Cressy;" "The Installation of the Order of the Garter;" "The Black Prince Receiving the King of France and his Son Prisoners at Poictiers," and "Queen Philippa Interceding with Edward for the Burgesses of Calais." West was one of the founders, in 1768, of the Royal Academy, and succeeded Sir Joshua Reynolds as president of the institution in 1792, which post he held almost uninterruptedly until 1815.
In the year 1780 he proposed a series of pictures on the progress of revealed religion, of which there were thirty-six subjects in all, but he never executed but (p. 258) twenty-eight of these, owing to the mental trouble which befell the king. He then commenced a new series of important works, of which "Christ Healing the Sick" was purchased by an institution in Great Britain for £3,000, and was subsequently copied for the Pennsylvania Hospital. "Penn's Treaty with the Indians" was painted for Granville Penn, the scene representing the founding of Pennsylvania. West wrote to one of his family that he had taken the liberty of introducing in this painting the likeness of his father and his brother Thomas. "That is the likeness of our brother," he says, "standing immediately behind Penn, leaning on his cane. I need not point out the picture of our father, as I believe you will find it in the print from memory." Tuckerman says that the work which, in the opinion of many critics, best illustrates the skill of West in composition, drawing, expression, and dramatic effect, is his "Death on the Pale Horse." His "Cupid," owned in Philadelphia, is one of his most effective pictures as to color.
The full-length portrait of West, by Sir Thomas Lawrence, P.R.A., represents the great artist in his character as president of the Royal Academy, delivering a lecture on "coloring" to the students. Under his right hand may be noticed, standing on an easel, a copy of Raphael's cartoon of the "Death of Ananias." The picture of West's face has been considered a perfect likeness, but the figure somewhat too large and too tall in its effects. A copy of this portrait was made by Charles R. Leslie; and Washington Allston also painted a portrait of the artist. There exists, it is said, a portrait of West from his own hand, taken apparently at about the age of forty, three-quarter length, in Quaker costume.[Back to Contents]
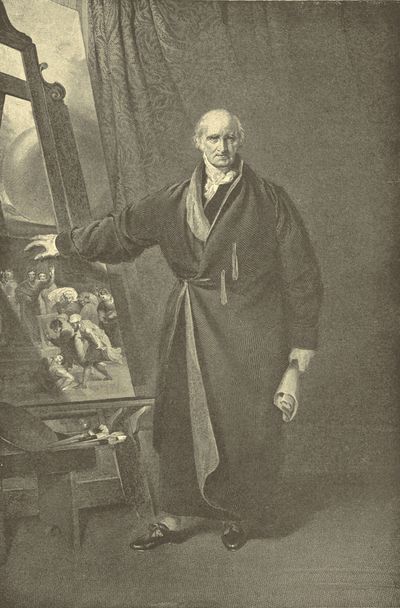

Benjamin West, President of the Royal Academy.
It was in Copenhagen, on November 19, 1770, that a carver of figures for ships' heads, by name Gottskalk Thorwaldsen, was presented by his wife, Karen Grönlund, the daughter of a clergyman in Jutland, with a son, who at his baptism received the name of Bertel, or Albert.
The father had come from Iceland, and lived in poor circumstances. They dwelt in Lille Grönnegade (Little Green Street), not far from the Academy of Arts. The moon has often peeped into their poor room; she has told us about it in "A Picture-book without Pictures":

"The father and mother slept, but their little son did not sleep; where the flowered cotton bed-curtains moved I saw the child peep out. I thought at first that he looked at the Bornholm clock, for it was finely painted with red and green, and there was a cuckoo on the top; it had heavy leaden weights, and the (p. 259) pendulum with its shining brass plate went to and fro with a 'tick! tick!' But it was not that he looked at; no, it was his mother's spinning-wheel, which stood directly under the clock; this was the dearest piece of furniture in the whole house for the boy; but he dared not touch it, for if he did, he got a rap over the fingers. While his mother spun, he would sit for hours together looking at the buzzing spindle and the revolving wheel, and then he had his own thoughts. Oh! if he only durst spin that wheel! His father and mother slept; he looked at them, he looked at the wheel, and then by degrees a little naked foot was stuck out of bed, and then another naked foot, then there came two small legs, and, with a jump, he stood on the floor. He turned round once more, to see if his parents slept; yes, they did, and so he went softly, quite softly, only in his little shirt, up to the wheel, and began to spin. The cord flew off, and the wheel then ran much quicker. His mother awoke at the same moment; the curtains moved; she looked out and thought of the brownie, or another little spectral being. 'Have mercy on us!' said she, and in her fear she struck her husband in the side; he opened his eyes, rubbed them with his hands, and looked at the busy little fellow. 'It is Bertel, woman,' said he."
What the moon relates we see here as the first picture in Thorwaldsen's life's gallery; for it is a reflection of the reality. Thorwaldsen has himself, when in familiar conversation at Nysöe, told the author almost word for word what he, in his "Picture-book," lets the moon say. It was one of his earliest remembrances, how he, in his little short shirt, sat in the moonlight and spun his mother's wheel, while she, dear soul, took him for a little spectre.
A few years ago there still lived an old ship-carpenter, who remembered the little, light-haired, blue-eyed boy, that came to his father in the carving-house at the dock-yard; he was to learn his father's trade; and as the latter felt how bad it was not to be able to draw, the boy, then eleven years of age, was sent to the drawing-school at the Academy of Arts, where he made rapid progress. Two years afterward, Bertel, or Albert, as we shall in future call him, was of great assistance to his father; nay, he even improved his work.
See the hovering ships on the wharves! The Dannebrog waves, the workmen sit in circle under the shade at their frugal breakfasts; but foremost stands the principal figure in this picture: it is a boy who cuts with a bold hand the lifelike features in the wooden image for the beak-head of the vessel. It is the ship's guardian spirit, and, as the first image from the hand of Albert Thorwaldsen, it shall wander out into the wide world. The eternally swelling sea should baptize it with its waters, and hang its wreaths of wet plants around it.
Our next picture advances a step forward. Unobserved among the other (p. 260) boys, he has now frequented the Academy's school for six years already, where, always taciturn and silent, he stood by his drawing-board. His answer was "yes" or "no," a nod or a shake of the head; but mildness shone from his features, and good-nature was in every expression. The picture shows us Albert as a candidate for confirmation. He is now seventeen years of age—not a very young age to ratify his baptismal compact; his place at the dean's house is the last among the poor boys, for his knowledge is not sufficient to place him higher. There had just at that time been an account in the newspapers, that the pupil Thorwaldsen had gained the Academy's smaller medal for a bas-relief representing a "Cupid Reposing." "Is it your brother that has gained the medal?" inquired the dean. "It is myself," said Albert, and the clergyman looked kindly on him, placed him first among all the boys, and from that time always called him Monsieur Thorwaldsen. Oh! how deeply did that "Monsieur" then sound in his mind! As he has often said since, it sounded far more powerfully than any title that kings could give him; he never afterward forgot it.
In a small house in Aabeuraa—the street where Holberg lets his poor poets dwell—lived Albert Thorwaldsen with his parents, and divided his time between the study of art and assisting his father. The Academy's lesser gold was then the prize to be obtained for sculpture. Our artist was now twenty years of age; his friends knew his abilities better than himself, and they compelled him to enter on the task. The subject proposed was, "Heliodorus Driven out of the Temple."
We are now in Charlottenburg; but the little chamber in which Thorwaldsen lately sat to make his sketch is empty, and he, chased by the demons of fear and distrust, hastens down the narrow back-stairs with the intention not to return. Nothing is accidental in the life of a great genius; an apparent insignificance is a God's guiding finger. Thorwaldsen was to complete his task. Who is it that stops him on the dark stairs? One of the professors just comes that way, speaks to him, questions, admonishes him. He returns, and in four hours the sketch is finished, and the gold medal won. This was on August 15, 1791.
Count Ditlew de Reventlow, minister of state, saw the young artist's work, and became his protector; he placed his own name at the head of a subscription that enabled Thorwaldsen to devote his time to the study of his art. Two years afterward the large gold medal was to be contended for at the Academy, the successful candidate thereby gaining the right to a travelling stipendium. Thorwaldsen was again the first; but before he entered on his travels, it was deemed necessary to extend that knowledge which an indifferent education at school had left him in want of. He read, studied, and the Academy gave him its support; acknowledgment smiled on him, a greater and more spiritual sphere lay open to him.
A portrait figure stands now before us; it is that of a Dane, the learned and severe Zoega, to whom the young artist is specially recommended, but who only sees in him a common talent; whose words are only those of censure, and whose eye sees only a servile imitation of the antique in his works. Strictly honest in his judgment, according to his own ideas, is this man, who should be Thorwaldsen's guide.
(p. 261) We let three years glide away after the arrival of Thorwaldsen, and ask Zoega what he now says of Albert, or, as the Italians call him, Alberto, and the severe man shakes his head and says: "There is much to blame, little to be satisfied with, and diligent he is not!" Yet he was diligent in a high degree; but genius is foreign to a foreign mind. "The snow had just then thawed from my eyes," he has himself often repeated. The drawings of the Danish painter Carstens formed one of those spiritual books that shed its holy baptism over that growing genius. The little atelier looked like a battle-field, for roundabout were broken statues. Genius formed them often in the midnight hours; despondency over their faults broke them in the day.
The three years, for which he had received a stipendium, were as if they had flown away, and as yet he had produced nothing. The time for his return drew nigh. One work, however, he must complete, that it might not with justice be said in Denmark, "Thorwaldsen has quite wasted his time in Rome." Doubting his genius just when it embraced him most affectionately; not expecting a victory, while he already stood on its open road, he modelled "Jason who has Gained the Golden Fleece." It was this that Thorwaldsen would have gained in the kingdom of arts, and which he now thought he must resign. The figure stood there in clay, many eyes looked carelessly on it, and—he broke it to pieces!
It was in April, 1801, that his return home was fixed, in company with Zoega. It was put off until the autumn. During this time "Jason" occupied all his thoughts. A new, a larger figure of the hero was formed, an immortal work; but it had not then been announced to the world, nor understood by it. "Here is something more than common!" was said by many. Even the man to whom all paid homage, the illustrious Canova, started, and exclaimed: "Quest' opera di quel giovane Danese è fatta in uno stilo nuovo, e grandioso!" Zoega smiled. "It is bravely done!" said he. The Danish songstress, Frederikke Brunn, was then in Rome and sang enthusiastically about Thorwaldsen's "Jason." She assisted the artist, so that he was enabled to get this figure cast in plaster; for he himself had no more money than was just sufficient for his expenses home.
The last glass of wine had been already drunk as a farewell, the boxes packed, and the vetturino's carriage was before the door at daybreak; the boxes were fastened behind. Then came a fellow-traveller—the sculptor, Hagemann, who was returning to his native city, Berlin. His passport was not ready. Their departure must be put off until the next day; and Thorwaldsen promised, although the vetturino complained and abused him, to remain so long. He stayed—stayed to win an immortal name on earth, and cast a lustre over Denmark.
Though forty years resident in Rome, rich and independent, he lived and worked with the thought of once returning home to Denmark, there to rest himself; unaccustomed to the great comforts of other rich artists in Rome, he lived a bachelor's life. Was his heart, then, no longer open to love since his first departure from Copenhagen? A thousand beautiful Cupids in marble will tell us how warmly that heart beat. Love belongs to life's mysteries.
We know that Thorwaldsen left a daughter in Rome, whose birth he acknowledged; (p. 262) we also know that more than one female of quality would willingly have given her hand to the great artist. The year before his first return to Denmark he lay ill at Naples, and was nursed by an English lady who felt the most ardent affection for him; and, from that feeling of gratitude which was awakened in him, he immediately consented to their union. When he had recovered and afterward returned to Rome, this promise preyed on his mind, he felt that he was not now formed to be a husband, acknowledged that gratitude was not love, and that they were not suited for each other; after a long combat with himself, he wrote and informed her of his determination. Thorwaldsen was never married.
The following trait is as characteristic of his heart as of his whole personality. One day, while in Rome, there came a poor countryman to him, an artisan, who had long been ill. He came to say farewell, and to thank him for the money that he and others of his countrymen had subscribed together, with which he was to reach home.
"But you will not walk the whole way?" said Thorwaldsen.
"I am obliged to do so," replied the man.
"But you are still too weak to walk—you cannot bear the fatigue, nor must you do it!" said he.
The man assured him of the necessity of doing so.
Thorwaldsen went and opened a drawer, took out a handful of scudi and gave them to him, saying, "See, now you will ride the whole way!"
The man thanked him, but assured him that his gift would not be more than sufficient to carry him to Florence.
"Well!" said Thorwaldsen, clapping him on the shoulder, as he went a second time to the drawer and took out another handful. The man was grateful in the highest degree, and was going. "Now you can ride the whole way home and be comfortable on the way," said he, as he followed the man to the door.
"I am very glad," said the man. "God bless you for it! but to ride the whole way requires a little capital."
"Well, then, tell me how great that must be," he asked, and looked earnestly at him. The man in a modest manner named the requisite sum, and Thorwaldsen went a third time to the drawer, counted out the sum, accompanied him to the door, pressed his hand, and repeated, "But now you will ride, for you have not strength to walk!"
Our artist did not belong to the class of great talkers; it was only in a small circle that he could be brought to say anything, but then it was always with humor and gayety. A few energetic exclamations of his are preserved. A well-known sculptor, expressing himself one day with much self-feeling, entered into a dispute with Thorwaldsen, and set his own works over the latter's. "You may bind my hands behind me," said Thorwaldsen, "and I will bite the marble out with my teeth better than you can carve it."
Thorwaldsen possessed specimens in plaster of all his works; these, together with the rich marble statues and bas-reliefs which he had collected of his own (p. 263) accord, without orders, and the number of paintings that he every year bought of young artists, formed a treasure that he wished to have in his proper home, Copenhagen. Therefore, when the Danish government sent vessels of war to the Mediterranean, in order to fetch the works that were ready for the palace or the churches, he always sent a number of his own things with them. Denmark was to inherit these treasures of art; and, in order to see them collected in a place worthy of them, a zeal was awakened in the nation to build a museum for their reception. A committee of his Danish admirers and friends sent out a requisition to the people, that everyone might give their mite; many a poor servant-girl and many a peasant gave theirs, so that a good sum was soon collected. Frederick VI. gave ground for the building, and the erection thereof was committed to the architect, Bindesbol.
Thorwaldsen, in 1838, had attained universal fame. The frigate Rota was dispatched to bring a cargo of his works to Copenhagen, and he was to arrive at the same time, perhaps to remain in Denmark. Close to Presto Bay, surrounded by wood-grown banks, lies Nysöe, the principal seat of the barony of Stampenborg, a place which, through Thorwaldsen, has become remarkable in Denmark. The open strand, the beautiful beech woods, even the little town seen through the orchards, at some few hundred paces from the mansion, make the place worthy of a visit on account of its truly Danish scenery. Here Thorwaldsen found his best home in Denmark; here he seemed to increase his fame, and here a series of his last beautiful bas-reliefs were produced.
Baron Stampe was one of nature's noblest-minded men; his hospitality and his lady's daughterly affection for Thorwaldsen opened a home for him here, a comfortable and good one. A great energetic power in the baroness incited his activity; she attended him with a daughter's care, elicited from him every little wish, and executed it. Directly after his first visit to Nysöe, a short tour to Moen's chalk cliffs was arranged, and during the few days that were passed there, a little atelier was erected in the garden at Nysöe, close to the canal which half encircles the principal building; here, and in a corner room of the mansion, on the first floor facing the sea, most of Thorwaldsen's works, during the last years of his life, were executed: "Christ Bearing the Cross," "The Entry into Jerusalem," "Rebecca at the Well," his own portrait-statue, Oehlenschlæger's and Holberg's busts, etc. Baroness Stampe was in faithful attendance on him, lent him a helping hand, and read aloud for him from Holberg. Driving abroad, weekly concerts, and in the evenings his fondest play, "The Lottery," were what most easily excited him, and on these occasions he would say many amusing things. He has represented the Stampe family in two bas-reliefs: in the one, representing the mother, the two daughters, and the youngest son, is the artist himself; the other exhibits the father and the two eldest sons.
All circles sought to attract Thorwaldsen; he was at every great festival, in every great society, and every evening in the theatre by the side of Oehlenschlæger. His greatness was allied to a mildness, a straightforwardness, that in the highest degree fascinated the stranger who approached him for the first (p. 264) time. His atelier in Copenhagen was visited daily; he therefore felt himself more comfortable and undisturbed at Nysöe. Baron Stampe and his family accompanied him to Italy in 1841, when he again visited that country. The whole journey, which was by way of Berlin, Dresden, Frankfort, the Rhine towns, and Munich, was a continued triumphal procession. The winter was passed in Rome, and the Danes there had a home in which they found a welcome.
The following year Thorwaldsen was again in Denmark, and at his favorite place, Nysöe. On Christmas eve he here formed his beautiful bas-relief, "Christmas Joys in Heaven," which Oehlenschlæger consecrated with a poem. The last birthday of his life was celebrated here; the performance of one of Holberg's vaudevilles was arranged, and strangers invited; yet the morning of that day was the homeliest, when only the family and the author of this memoir, who had written a merry song for the occasion, which was still wet on the paper, placed themselves outside the artist's door, each with a pair of tongs, a gong, or a bottle on which they rubbed a cork, as an accompaniment, and sung the song as a morning greeting. Thorwaldsen, in his morning gown, opened the door, laughing; he twirled his black Raphael's cap, took a pair of tongs himself, and accompanied us, while he danced round and joined the others in the loud "hurra!"
A charming bas-relief, "The Genius of Poetry," was just completed; it was the same that Thorwaldsen, on the last day of his life, bequeathed to Oehlenschlæger, and said, "It may serve as a medal for you."
On Sunday, March 24, 1844, a small party of friends were assembled at the residence of Baron Stampe, in Copenhagen. Thorwaldsen was there and was unusually lively, told stories, and spoke of a journey that he intended to make to Italy in the course of the summer. Cahn's tragedy of "Griseldis" was to be performed for the first time that evening at the theatre. Tragedy was not his favorite subject, but comedy, and particularly the comedies of Holberg; but it was something new that he was to see, and it had become a sort of habit with him to pass the evening in the theatre. About six o'clock, therefore, he went to the theatre alone. The overture had begun; on entering he shook hands with a few of his friends, took his usual seat, stood up again to allow one to pass him, sat down again, bent his head, and was no more! The music continued. Those nearest to him thought he was only in a swoon, and he was borne out; but he was numbered with the dead.
The mournful intelligence of his death soon spread through the country and through all lands; funeral dirges were sung and funeral festivals were arranged in Berlin and Rome; in the Danish theatre, whence his soul took its flight to God there was a festival; the place where he sat was decorated with crape and laurel wreaths, and a poem by Heiberg was recited, in which his greatness and his death were alluded to.
The day before Thorwaldsen's death the interior of his tomb was finished, for it was his wish that his remains might rest in the centre of the court-yard of the museum; it was then walled round, and he begged that there might be a marble edge around it, and a few rose-trees and flowers planted on it as his monument. (p. 265) The whole building, with the rich treasures which he presented to his fatherland, will be his monument; his works are to be placed in the rooms of the square building that surrounds the open court-yard, and which, both internally and externally, are painted in the Pompeian style. His arrival in the roads of Copenhagen and landing at the custom-house form the subjects depicted in the compartments under the windows of one side of the museum. Through centuries to come will nations wander to Denmark; not allured by our charming green islands, with their fresh beech-woods alone—no, but to see these works and this tomb.
There is, however, one place more that the stranger will visit, the little spot at Nysöe where his atelier stands, and where the tree bends its branches over the canal to the solitary swan which he fed. The name of Thorwaldsen will be remembered in England by his statues of Jason and Byron; in Switzerland, by his "recumbent lion;" in Roeskilde, by his figure of Christian the Fourth. It will live in every breast in which a love of art is enkindled.[Back to Contents]

We read that on one occasion, when a picture by some Dutch artist, representing peasants at their sports, was shown to Louis XIV., he angrily exclaimed, "Take away those vermin!" Such subjects had never been chosen by French artists, nor indeed had they been seen anywhere in Europe before the Dutch artists began to paint them in the seventeenth century. The Italian painters of the early and the later Renaissance, working almost exclusively for the churches, or for the palaces of pleasure-loving princes, did not consider the peasant or the laboring man, by himself, a proper subject for his art. If he were introduced at any time into picture or bas-relief, it was only as a necessary actor in some religious story, such as "The Adoration of the Shepherds," or in the representations of the months or the seasons, as in the Fountain of the Public Square at Perugia, where we see the peasant engaged in the labors of the farm or vineyard: cutting the wheat, gathering in the grapes, and treading out the wine, and, in the later season, dressing (p. 266) the hog he has been killing; for in those less sophisticated times, Art, no more than Poetry, despised the ruder side of rustic life.
The German artists of the sixteenth century introduced peasants and peasant-life into their designs whenever the subject admitted. Albert Dürer was especially given to this, and it often gives a particular savor, sometimes a half-humorous expression, to his treatment of even religious subjects; as where, in his design, "The Repose in Egypt," he shows Joseph, the foster-father of Jesus, making a water-trough out of a huge log, and a bevy of cherub-urchins about him gathering up the chips. Mary, meanwhile, as the peasant mother, sits by, spinning and rocking the cradle of the Holy Child with her foot.
But these examples only serve to make clearer the fact that in the earlier times there was no place found in art for the representation of the laboring man, whether in the field or in the shop, except as an illustration of some allegorical or religious theme. Nor in the Dutch pictures that Louis XIV. despised, and that our own time finds so valuable for their artistic qualities, was there anything outside of their beauty or richness of tone or color to redeem their coarseness and vulgarity. There was no poetry in the treatment, nor any sympathy with anything higher than the grossest guzzling, fighting, and horseplay. The great monarch, who, according to his lights, was a man of delicacy and refinement, was certainly right in contemning such subjects, and it is perhaps to his credit that he did not care enough for "Art for Art's sake" to excuse the brutality of the theme for the sake of the beauty of the painting.
The next appearance of the peasant in art was of a very different sort, and represented a very different state of social feeling from the "peasants" of the Dutch painters. In the Salon of 1850 there appeared a picture called "The Sower" and representing a young peasant sowing grain. There was nothing in the subject to connect it particularly with any religious symbolism—not even with the Parable of the Sower who went forth to sow; nor with any series of personifications of the months. This was a simple peasant of the Norman coast, in his red blouse and blue trousers, his legs wrapped in straw, and his weather-beaten hat, full of holes. He marches with the rhythmic step made necessary by his task, over the downs that top the high cliffs, followed by a cloud of crows that pounce upon the grain as he sows it. At first sight there would seem to be nothing in this picture to call for particular notice; but the public, the artists, the critics, were with one accord strongly drawn to it. Something in the picture appealed to feelings deeper than mere curiosity, and an interest was excited such as did not naturally belong to a picture of a man sowing a field of grain. The secret was this: that a man born and bred in the midst of laboring people, struggling with the hard necessities of life—himself a laborer, and one who knew by experience all the lights and shades of the laborer's life—had painted this picture out of his own deep sympathy with his fellows, and to please himself by reproducing the most significant and poetical act in the life of the farmer.
The painter of this picture, the first man of our time to give the laborer in the fields and on the farm a place in art, and to set people to thinking about him, (p. 267) as a man, not merely as an illustration of some sacred text, or an image in a book of allegories, was Jean-François Millet, known as the peasant painter of peasants.
He was born at Gruchy, a small hamlet on the coast of Normandy, where his family, well known in the region for several generations, lived by the labor of their hands, cultivating their fields and exercising the simple virtues of that pastoral life, without ambition and without desire for change. This content was a part of the religion of the country and must not be looked upon as arguing a low state of intelligence or of manners. Of their neighbors we have no account, but the Millet household contained many of the elements that go to sustain the intellectual no less than the spiritual life. If there was plain living, there was high thinking; there were books and of the best, and more than one member of the circle valued learning for its own sake. Millet owed much to his grandmother, a woman of great strength of character and of a deeply religious nature. As his godmother she gave him his name, calling him Jean, after his father, and François, after Saint Francis of Assisi. As is usual in Catholic countries, the boy was called after the name of his patron saint, and in the case of Millet, Saint Francis, the ardent lover of nature, the friend of the birds and of all the animate creation, was well chosen as the guardian of one who was to prove himself, all his life, the passionate lover of nature.
The boyhood of Millet was passed at home. He had no schooling except some small instruction in Latin from the village priest and from a neighboring curate, but he made good use of what he learned. He worked on the farm with his father and his men, ploughing, harrowing, sowing, reaping, mowing, winnowing—in a word, sharing actively and contentedly in all the work that belongs to the farmer's life. And in the long winter evenings or in the few hours of rest that the day afforded, he would hungrily devour the books that were at hand—the "Lives of the Saints," the "Confessions of Saint Augustine," the "Life of Saint Jerome," and especially his letters, which he read and re-read all his life. These and the philosophers of Port Royal, with Bossuet, and Fénelon, with the Bible and Virgil, were his mental food. Virgil and the Bible he read always in the Latin; he was so familiar with them both that, when a man, his biographer, Sensier, says he never met a more eloquent translator of these two books. When the time came, therefore, for Millet to go up to Paris, he was not, as has been said by some writer, an ignorant peasant, but a well-taught man who had read much and digested what he had read, and knew good books from bad. The needs of his narrow life absorbed him so seriously that the seeds of art that lay hid in his nature found a way to the light with difficulty. But his master-passion was soon to assert itself, and, as in all such cases, in an unexpected manner.
Millet's attempts at drawing had hitherto been confined to studies made in hours stolen from rest. He had copied the engravings found in an old family Bible, and he had drawn, from his window, the garden, the stable, the field running down to the edge of the high cliff, and with the sea in the horizon, and he (p. 268) had sometimes tried his hand at sketching the cows and sheep in the pasture. But he was now to take a step in advance. Coming home one day from church, he walked behind an old man bent with age and feebleness, painfully making his way. The foreshortening and the movement of the man's figure struck the boy forcibly, and in a flash he discovered the secret of perspective and the mystery of planes. He ran quickly home, got a pencil and drew from memory a picture of the old man, so lively in its resemblance that as soon as his parents saw it, they recognized it and fell a-laughing. Talk with his boy revealed to the father his son's strong desire to be an artist; but before such a serious step could be taken, it was necessary to consult with some person better able to judge than any one in the Millet household. Cherbourg, the nearest large town, was the natural place where to seek advice; thither Millet and his father repaired, the boy with two drawings under his arm that he had made for the occasion, and these were submitted to the critical eye of Mouchel, an old pupil of David, who eked out the scanty living he got by painting by giving lessons in drawing. When the two drawings made by young Millet were shown him he refused to believe they were the work of the lad of fifteen. The very subjects chosen by the boy showed something out of the common. One was a sort of home idyl: two shepherds were in a little orchard close, one playing on the flute, the other listening; some sheep were browsing near. The men wore the blouse and wooden shoes of Millet's country; the orchard was one that belonged to his father. The other drawing showed a starry night. A man was coming from the house with loaves of bread in his hand which he gave to another man who eagerly received them. Underneath, in Latin, were the words from St. Luke: "Though he will not rise and give him because he is his friend, yet because of his importunity he will rise and give him as many as he needeth." A friend of Millet's, who saw these drawings thirty years after, said they were the work of a man who already knew the great significance of art, the effects it was capable of, and what were its resources.
Mouchel consented to receive Millet as a pupil, but, as it proved, he could do little for him in the way of direct teaching. He left the boy free to follow his own devices. He said to him: "Do whatever you wish; choose whatever model you find in my studio that pleases you, and study in the Museum." This might not be the course to follow with every boy, but Mouchel had the artist's penetration and knew with whom he had to deal.
The death of Millet's father interrupted his studies and he returned home for awhile to help his mother on the farm. But it was thought best that he should keep on with the work he had begun. The grandmother urged his return: "My François," she said, "we must accept the will of God. Thy father, my son, Jean-Louis, said that you were to be a painter; obey him, and go back to Cherbourg."
Millet did not need persuasion from his family. Friends in Cherbourg urged him to come back, promised him commissions, and assured him a place in the studio of Langlois, a painter of a higher grade than Mouchel, who had recently set up his easel in the town. Once more established at Cherbourg Millet continued (p. 269) his studies after the same easy fashion with Langlois as with his former master. Langlois, who was as much impressed by his pupil's talent as Mouchel had been and willing to serve him, made a personal appeal to the mayor and council, asking that Millet, as a promising young artist and one likely to do credit to the town, might be assisted in going to Paris to study under better advantages than he could enjoy at home.
On the strength of this appeal, the council of Cherbourg agreed to allow Millet an annuity of four hundred francs, equal to eighty dollars. With this small sum, and the addition of two hundred francs given him at parting by his mother and grandmother, making one hundred and twenty dollars in all, Millet left his quiet life in Normandy behind him and set out for Paris, where, as his biographer, Sensier, says, he was to pass as a captive the richest years of his life.
Millet was twenty-two years old when he went first to Paris and he remained there, with occasional visits to Gruchy and Cherbourg, for the next thirteen years. Paris was, from the first, more than distasteful to him. He was thoroughly unhappy there. Outside the Louvre and the studios of a few artist-friends, he found nothing that appealed to what was deepest in him. His first experiences were unusually bitter. The struggle with poverty was hard to bear, but perhaps a more serious drawback was his want of an aim in art, of a substantial reason, so to speak, for the profession he had chosen, leading him to one false move after another in search of a subject. Unformed and unrecognized in his mind lay the desire to express in art the life he had left behind him in Normandy; but it was long before he arrived at the knowledge of himself and of his true vocation. He seems to have had no one in Paris to guide or direct him, and he rather stumbled into the studio of Delaroche, than entered it deliberately. He made but a brief stay there, and although he won the respect of his master, who would willingly have retained him as pupil and assistant, he was conscious that he learned nothing from Delaroche; and accordingly, in company with another pupil, Marolles, who had taken a great liking to him, he left the studio without much ceremony; and the two friends improvised a studio and a lodging for themselves in a garret in a poor quarter of the city, and began their search for a means of pleasing the public. But the way was not opened to either of them; they could not sell what they painted, and they were reduced to serious straits. It was not the fault of the public. Marolles was but an indifferent painter at any time, and Millet would not have blamed the public for its indifference to subjects in which he himself took no real interest.
Millet was at a loss what to do for bread. His mind ran back continually to his rural life at Gruchy. "What if I should paint men mowing or winnowing?" he said to Marolles; "their movements are picturesque!" "You could not sell them," replied his friend. "Well, then, what do you say to fauns and dryads?" "Who in Paris cares for fauns and dryads?" "What shall I do, then?" said Millet in despair. "What does the public like?" "It likes Boucher's Cupids, Watteau's Pastorals, nudities, anecdotes, and copies of the past." It was hard for Millet, but hunger drove him. He would not appeal to his (p. 270) family, life was as difficult for them as for him. But before yielding he would make one more trial, painting something from his own fancy. He made a small picture representing "Charity"—a sad-faced woman cherishing three children in her arms. He carried it to the dealers: not one of them would buy it. He came back to Marolles. "Give me a subject," he said, "and I will paint it."
To this time belong the pictures for which Millet has been much criticised by people who did not appreciate his position. Some of them recall Watteau, others Boucher, but they have a charm, a grace of their own; they are far from being copies of these men. Others were fanciful subjects to which Marolles gave names likely to attract the notice of picture-buyers in search of a subject. But all was in vain. The dealers were obstinate: the public unsympathetic. The highest price that was offered was never above twenty francs, or five dollars. Yet with this in his pocket, Millet deemed himself already on the high road to fortune, and saw the day not distant when he could paint at his pleasure the rustic subjects, memories of his home, that had always been in his mind.
Several times in the course of this hard novitiate, Millet had escaped from Paris for a visit to his own country. At one time he had remained for a year at Cherbourg, where he painted portraits for such small sums as he could get, and here he and one of his sitters, a young girl of Cherbourg, falling in love with one another, were married. The marriage only added, as might have been foreseen, to Millet's troubles: his wife's health was always delicate; after her marriage it became worse, and she died four years after in Paris. Not long after her death Millet married again, and this proved a fortunate venture. His wife came with him to Paris, and the struggle with life began anew. The turning-point in the long period of Millet's uncertainties and disappointments with himself came in 1849, when the political troubles of the time, and the visit of the cholera, combined to drive him and his family from Paris. They took refuge at Barbizon, a small hamlet on the outskirts of the Forest of Fontainebleau, and here, in the place that was to be forever associated with his name and work, Millet passed, with few interruptions, the remaining years of his life.
The phrase so often heard to-day, "The Barbizon School," is rather wider than a strict interpretation would warrant, since Millet and Rousseau were the only ones of the group who lived in the village. Corot was not acquainted with Millet. Decamps was never in Millet's house except as a rare visitor to his studio. Diaz lived in Paris. Jacque, the painter of sheep, was a friend of Millet, and for a time at least lived at Barbizon in the house where he lodged before he procured a home of his own. The artistic relationship between these artists is slight, except in the case of Rousseau and Diaz, and even there it is only occasionally to be detected. All these men, with Dupré, Courbet and Delacroix, were counted heretics in art by the Academy and the official critics, and as Millet was the most marked figure in the group and was greatly admired and respected by all who composed it, it was perhaps natural that they should be considered by the public as disciples of the peasant painter of Barbizon.
Here, then, at Barbizon, Millet lived for the remaining twenty-seven years of (p. 271) his life, dividing his day between the labors of his farm in the morning hours, painting in his studio in the afternoon—he always preferred the half-light for painting—and in the evening enjoying the society of his wife and children and of such friends as might join the circle. Occasional visits to Paris, to the galleries, and to the studios of his artist-circle, kept him in touch with the world to which he belonged. His books, too, were his unfailing companions, though he never cared to stray far beyond the circle of his youthful friendships, Homer, and Virgil, and especially the Bible, which he looked upon as the book of painters, the inexhaustible source of the noblest and most touching subjects, capable of expression in the grandest forms.
But it was in the rural life about him, the life in which he actively shared, that he found the world wherein he could pour all his thoughts, feelings, and experiences with the certainty of seeing them emerge in forms answering to his conception. It was not until he came to Barbizon that he began truly to live the artist-life as he understood it, where the work is a faithful reflection of the only things a man really cares for—the things he knows by heart. In the pictures painted at Barbizon, and in the multitude of slight sketches for subjects never painted, with finished drawings and pastels, Millet has composed a series of moral eclogues well worthy of a place with those of Virgil and Theocritus. All the world knows them; all the world loves them: the "Mother Feeding Her Children," "The Peasant Grafting," "The First Step," "Going to Work," "The Sower," "The Gleaners," "The Sheep-Shearing," "The Angelus"—even to name them would carry us far beyond our limits. They made the fame of Millet while he still lived, although the pecuniary reward of his labors was not what they deserved nor what it would have been had he earlier found his true way or had his life been prolonged to the normal limit. He died in 1875 at the age of sixty-one. Since his death more than one of his pictures has been sold at a price exceeding all that he earned during his whole lifetime. Seen from the world's side, there was much in his life that was sad and discouraging, but from the spiritual side there was far more to cheer and uplift. His private life was honorable and happy, his friends were many and among the chosen ones of the time, and he had the happiness of seeing his work accepted and rated at something like its true worth before he left it.[Back to Contents]

Among the many beautiful paintings collected in the Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York, there is one that always attracts a crowd, on the free-days and holidays when the general public finds admission. This is the picture called simply, "Friedland: 1807," and representing the soldiers of Napoleon saluting the emperor at the battle of Friedland. It was painted by Jean Louis Meissonier for the late A. T. Stewart, of New York, who paid for it what seemed a very large sum, $60,000; but when Mr. Stewart died, and his pictures were sold at auction, this painting brought the still larger sum of $66,000, showing that a great many people admired the work, and were willing to pay a good price for it. The picture was bought by Judge Hilton, of New York, and was presented by him to the Metropolitan Museum as a memorial of the long friendship that had existed between himself and Mr. Stewart. No doubt the facts of the high price paid for the picture, and that a gift of such value should be made to the Museum, have caused a great many people to look at the painting with more interest than they would, had the circumstances been less uncommon. But a great many more people find this picture interesting for its own sake; they are moved rather by the spirited way in which it tells its story, and find their curiosity excited by the studious accuracy shown by the artist in the painting of every detail.
The scene of the action is a field that has been planted with grain which now lies trampled under the feet of men and horses. The turning-point in the battle has been reached, and in the joy of coming victory, the body-guard of the emperor, spurring their jaded horses to the hillock where he sits on his white charger surrounded by his mounted staff, salute him with loud cries as they rush madly by him. Napoleon, calm and self-possessed, returns the salute, but it is plain his thoughts are busier with the battle that is raging in the distance than with these demonstrations of his body-guard's loyalty. This picture was the favorite work of the artist; he calls it, "the life and joy of my studio," and he is said to have worked on it at intervals during fifteen years.
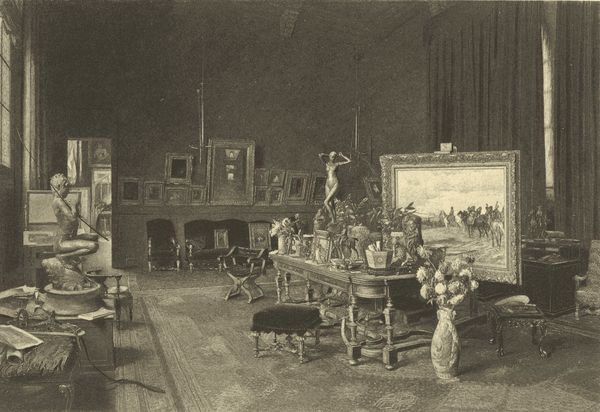

Meissonier's Atelier.
Somebody has said that "genius" means nothing but "taking pains." In that case, Meissonier must have been a man of genius, for, with whatever he painted, (p. 273) were it small or great, he took infinite pains, never content until he had done everything in his power to show things exactly as they were. Thus, in the picture we have just been describing, we may be sure that we know, from looking at it, exactly how Napoleon was dressed on the day of Friedland, and also how each member of his military staff was dressed; not a button, nor a strap, nor any smallest detail but has been faithfully copied from the thing itself, while every head in the group is a trustworthy portrait. When it was not possible to get the actual dress worn by the person he was painting, Meissonier spared no pains nor money to obtain an exact copy. How it was in the case of the "Friedland," we do not know, but when he painted the "March to Paris," Meissonier borrowed from the Museum, in Paris, where relics of all the kings of France are kept (the Musée des Souverains), the famous "little gray riding-coat" worn by Napoleon at the battle of the Pyramids and in other engagements. This coat, Meissonier had copied by a tailor, with the minutest accuracy, and it was then worn by the model while he was painting the picture. The same pains were taken with the cuirassiers who are dashing across the front of the picture in the "Friedland." As will be seen on looking closely, one model served for all the men in the front rank, but as the uniform was the same it was only necessary to vary the attitude. The uniform and all the accoutrements were carefully reproduced by workmen from originals of the time, borrowed by Meissonier for the purpose, and the model was then mounted on a jointed wooden horse and made to take the attitude required: the action of the horse was as carefully studied from that of the living animal. By the time that Meissonier came to paint this picture, he was so famous an artist, and had gained such a place in the world, that he could have almost anything he asked for to aid him in his work. So, when, with the same desire for accuracy that he had shown in painting other parts of the picture, he came to paint the trampled grain, the Government, or so we are told, bought the use of a field of ripe grain and lent Meissonier the services of a company of cuirassiers who were set to dashing about in it until they had got it into proper condition. We can see that the cost of all this accuracy would, in the end, amount to a considerable sum, and when we reckon the time of an artist so distinguished as Meissonier, it is not so surprising as it may have appeared at first, that his picture should have brought so much money.
Of course, Meissonier did not come all at once to fame and prosperity. The rewards he gained were such as are earned only by hard and constant labor. When he came to Paris about the year 1832, from Lyons, where he was born, he was about nineteen years old. His parents were in humble circumstances, and would seem to have been able to do nothing to advance the lad, who arrived in Paris with little money in his pocket, and with no friends at hand. He had, however, the materials out of which friends and money are made: health, a generous spirit, energy, and a clear purpose, and with these he went to work. We do not hear much about his early life in Paris. When he first appears in sight, he is working in the same studio with Daubigny, the landscape-painter, the two painting pictures for a dollar the square yard, religious pictures probably, and (p. 274) probably also copies, to be sent into the country and hung up in the parish churches. Although this may have seemed like hardship at the time, yet there is no doubt it was good practice, for among artists we are told it is an accepted doctrine that in order to paint on a small scale really well, you must be able to paint on a larger. And it is said that Meissonier was in the habit all his life of making life-size studies in order to keep his style from falling into pettiness. So, after all, the painting of these big pictures may have been a useful ordeal for the artist who for the next sixty years was to reap fame by painting small ones.
While he was earning a scanty living by this hack-work, Meissonier found time to paint two pictures which he sent to the Salon of 1836. One of these attracted the attention of a clever artist, Tony Johannot, who introduced him to Léon Cogniet, with whom he studied for a time, but from whom he learned but little. The mechanism of his art he had pretty well mastered already, as was shown by the Salon accepting his early pictures, and the chief advantage he gained from his stay in Cogniet's studio was a wider acquaintance with the world of artists; for Cogniet was a favorite teacher, and had a great many pupils, not a few of whom became distinguished painters. But his style of painting was not one to attract Meissonier, who was ambitious to paint like the old Dutch artists, Terburg, Metzu, Mieris, and others, who have the charm that their pictures are finished with the most exquisite minuteness, and yet treated in such a large way that, after awhile, we forget the microscopic wonder of the performance and think only of the skill the artist has shown in painting character. Meissonier was the first artist to bring back into favor the Dutch school of painting of the seventeenth century. Louis XIV., who set the fashion in everything in his day, had set the fashion of despising the Dutch painters, and the French people had never unlearned the lesson. It was Meissonier who brought back the taste, and taught the public to admire these small panels where interest in the subject is for the most part lost in the exquisite beauty of the painting and where the Dutch painters of similar subjects are successfully met on their own ground and equalled in every respect except in the charm of color.
There is an old saying: "Imitation is the sincerest mode of flattery;" and Meissonier's immediate success with the public was the signal for a bevy of imitators to try to win a like success by like methods. Some of these artists were very clever, but an imitator is but an imitator after all, and is more apt to call attention to his model than to himself. It must be admitted that Meissonier himself has suffered somewhat in the same way: the evident fact that his methods of painting were inspired by the study of the Dutch masters has led to his being called an imitator, and his pictures are often compared, and not to their advantage, with those of his models. Meissonier is, however, very much more than an imitator; he was inspired by the Dutch painters, but he soon found a way of his own, and he has put so much of himself into his work, that the charge of imitation long since ceased to be brought against him.
While he was still not much known to the public, the Duke of Orleans bought of him, for six hundred francs, a picture that to-day is worth thirty thousand (p. 275) francs. As is usual in such affairs, the purchase was made, not by the duke in person, but by an agent: in this case, it was his secretary, M. Adaline, who bought the picture from Meissonier, who as an acknowledgment of the service gave the secretary a water-color drawing which, to-day, like everything coming from the hand of Meissonier, would bring the owner a good round sum if offered for sale.
In 1865, Meissonier's son Charles, himself a very good painter, went to a costume-ball dressed like a Fleming of the seventeenth century and looking as if he had stepped out of a picture by Terburg. The costume had been made with the greatest accuracy, and Meissonier was so pleased with his son's appearance that he made a study and sold it for two thousand francs. Twenty years after, in 1884, hearing that it was to be sold at auction, and desiring, out of affection for his son, to have the study back again, he asked his friend, M. Petit, to buy it for him, at whatever cost. A rich Parisian, M. Secretan, who had a collection of pictures since become famous—it was to him that Millet's "L'Angelus" belonged—and who had such an admiration for Meissonier and his work that he had paid no less than four hundred thousand francs for his picture "Les Cuirassiers," hearing from M. Petit of Meissonier's desire for the portrait of his son, bought the picture for twenty-five thousand francs and presented it to the artist. These stories are told only as illustrations of the growth of Meissonier's reputation and of the increased number of people who desire to have an example of his work. The rise in value of a small sketch of a single figure, from $500 to $5,000, in fifteen years, is no greater in proportion than has happened in the case of every one of Meissonier's pictures, drawings, studies, and even his slight sketches, on some of which originally he would have placed no value at all. Yet everything he left behind him, even unconsidered trifles, are found to be of value, and the sale of the contents of his studio just ended in Paris brought nearly five hundred thousand francs, although the collection contained not a single finished picture of importance, but was made up almost entirely of unfinished studies and of sketches.
Meissonier's industry was constant and untiring. It is told of him that he rarely had the pencil or the brush out of his hand when in the house, and that when he called at a friend's house and was kept waiting he used the spare minutes in sketching upon the first piece of paper that he found at hand. One of his friends, who knew of this habit, collected in the course of many visits he received from the artist enough of these scraps to fill a small album; while it is told of another of his friends that he instructed his servant to put beside Meissonier's coffee-cup after dinner a number of bits of paper of the size of cigarette-papers but of better quality on which Meissonier in his absent way would fall to drawing as he chatted with his companions. After dinner these jottings remained as a valuable memorial of his visit. Perhaps if they were all collected, these slight affairs might bring enough at auction to pay for all the dinners to which the prudent host had invited the artist.
The world of subjects included in Meissonier's art was a very narrow one, and (p. 276) was not calculated to interest men and women in general. The nearest that he came to striking the popular note was in his Napoleon subjects, and beside the excellence of the painting, these pictures really make a valuable series of historical documents by reason of their accuracy. But the greater number of the pictures which he left behind him are chiefly interesting from the beautiful way in which they are painted: we accept the subject for the sake of the art. The world rewarded him for all this patient labor, this exquisite workmanship, by an immense fortune that enabled him to live in splendor, and to be generous without stint. From the humble lodgings of his youth in the Rue des Ecouffes, he passed, in time, to the palace in the Place Malsherbes where he spent the latter half of his long life in luxurious surroundings: pictures and statues, rich furniture, tapestries and armor and curiosities of art from every land. But the visitor, after passing through all this splendor, came upon the artist in a studio, ample and well lighted indeed, but furnished only for work, where, to the end of his life, he pursued his industrious calling with all the energy and ardor of youth. He died in 1891, and was buried by the government with all the honors that befitted one of her most illustrious citizens.[Back to Contents]
A girl of something over ten, of sturdy build, with a dark complexion, deep blue eyes, and strong features crowned by a head of clustering curls, is sitting in the window of a plainly furnished room, high up in an apartment-house in Paris. In a cage at her side is a parrot, which, with its head on one side, is gravely calling out the letters of the alphabet, while the child as gravely repeats them, interrupting the lesson every now and then by a visit to the other side of the room, where a pet lamb greets its young mistress with a friendly bleat.
This is our first glimpse of Rosalie, known now to all the world as Rosa Bonheur, the painter of "The Horse Fair" and of many another picture, which have earned for her the distinction of the best animal-painter of her time.
Her father's family belonged to Bordeaux. Raymond Bonheur had gone up as a youth to Paris to study art. After the usual apprenticeship to privation which art exacts from her servants, he had become moderately successful, when the condition of his parents, now old and poorly-off, moved him to return to Bordeaux (p. 277) and do what he could to make their life easier. As the chances for a professional artist were small, he adopted the modest employment of drawing-teacher. His skill soon brought him pupils; among them a young lady from Altona, between whom and her teacher a mutual interest sprang up which led to their marriage. Raymond Bonheur brought his wife home to his father's house, where she was welcomed as a daughter, and for the brief term of her life all went well. What the husband earned by his drawing-lessons, the wife supplemented by her lessons in music; but this happiness was not to last. The parents of Raymond Bonheur died, and then, after not more than twelve years of marriage, the wife died, leaving behind her four children, Rosalie, Francois-Auguste, Jules-Isidore, and Juliette.

Rosalie is the best known of these four children of Raymond Bonheur; but each of them has honorably connected his name with the art of modern France. Francois-Auguste has a reputation as an animal-painter almost equal to that of his sister Rosa. A fine picture painted by him, "Cattle in the Forest of Fontainebleau," was once the property of the late A. T. Stewart. His merit secured him the Cross of the Legion of Honor in 1867. He died in 1880. The other brother, Jules-Isidore, has gained distinction as a sculptor of animals; most of his work is on a small scale, but he has designed some large pieces that decorate his sister's château near Fontainebleau. Juliette Bonheur married a M. Peyrol, and joining her family-name to his, is known in the art-world as Mme. Peyrol Bonheur. It is thus she signs her pictures, mostly still-life and animal subjects, which have gained for her a good position among the minor artists of France.
Rosa, the eldest of the family, born in 1822, was ten years old when her mother died. Not long after, Raymond Bonheur decided to leave Bordeaux and to return to Paris, where the chances for professional success were better than in a provincial town, and where there were greater opportunities for the education of his young children. The change proved very distasteful, however, to the little ones. Accustomed to the comparative freedom of the town in which they had been brought up, and where their family had been so long rooted that their circle of friends and relatives gave them playmates and companions in plenty, they found themselves very lonely in Paris, where they were reduced for a good part of the time to such amusement as they could find in the narrow quarters of their rooms on the sixth floor of an apartment-house. It is not the custom in Paris for the children, even of the poor, to make a playground of the street, and our (p. 278) little ones had nobody to walk out with them but an old servant who had come with them from Bordeaux, and who was ill-fitted, for all her virtues, to take a mother's place to the children. She was honest and faithful, but like all of her class, she liked routine and order, and she could make no allowances for the restlessness of her bright-minded charge. Rosa was her especial torment; the black sheep of the brood. Household tasks she despised, and study, as it was pursued in the successive schools to which her despairing father sent her, had no charms for her. Her best playmates were animals; the horses and dogs she saw in the streets and which she fearlessly accosted; the sheep that found itself queerly lodged on the top floor of a city house; and the parrot which, as we have seen, was not only her playmate but her schoolmaster.
There came a time when the charge of such a child, so averse to rules and so given to strange ways of passing her time, became too much for the old servant with her orthodox views of life, and she persuaded Rosa's father to put her as a day-scholar with the nuns at Chaillot, a small suburb of Paris. How it happened that she was allowed to go back and forth alone, between home and school, we do not know; but it is not to be wondered at if she were irregular in her hours; if, one day, she set the nuns wondering why she did not appear at school-opening, and another day put the old servant into a twitter because she did not come home in season. The truth was, she had found that there was something better in Paris than streets and shops and tall houses; she had discovered a wood there, a veritable forest, with trees, and pools of water, and birds, and wild flowers, and though this enchanted spot which citizens called the Bois de Boulogne—not then a formal park as it is to-day—was off the road to Chaillot, yet it was not so far that she need fear getting lost in going there or in coming back. No wonder, then, if, once this way discovered of escape from tiresome school duties, it was travelled so often by Rosalie, and that her school-work became in consequence so unsatisfactory that at length the patient nuns remonstrated. They advised Rosa's father, since she neither would nor could learn anything from books, that it would be better to put her to some useful trade by which she might earn her living; and the good sisters suggested—dressmaking! The wisdom of these ladies, who could not see that they were dealing with the last woman in the world to whom dressmaking could be interesting, was matched by that of the father, who showed himself so blind to the character of his daughter that he resolved to act at once upon the advice of the nuns; and without consulting the wishes of poor Rosalie he apprenticed her straightway to a Parisian dressmaker. The docile girl allowed the yoke to be slipped over her head without complaint, but the confinement wore upon her health and spirits, and after a short trial the experiment had to be abandoned. Her father yielded to her entreaties and took her home.

Rosa Bonheur.
The girl was long in coming to a knowledge of herself. Although she was to be, in time, a famous artist, the familiar legend of the biographers is wanting in her case; we read nothing about scribbled books or walls defaced by childish sketches, nor does she appear to have handled a pencil or a brush until she was (p. 279) a girl well grown. Her father's means were not sufficient to give Rosa or his other children an education such as he could wish; but an expedient suggested itself in his perplexity over this latest experiment in providing for his eldest daughter: he proposed to the principal of a young ladies' school where he taught drawing, that his services should be accepted in payment of Rosa's education. The offer was accepted, and in the regular course of study Rosa became a member of her father's drawing-class. It was not long before she surpassed all her school-fellows in that department, and found herself for the first time in her life in possession of the key to that happiness which consists in knowing what we can do, and feeling the strength within us to do it. Some of the biographers of Rosa's life speak of unhappy days at this school: the richer girls made sport of the dress of the drawing-master's daughter, and of her independent, awkward ways. Her progress in drawing, too, was counterbalanced by her slowness in her other studies; in fact her new accomplishment was such a delight to her, that in her devotion to it she became less and less interested in her books; and as for dress—that it should be clean and suited both to her means and to the work she was doing, was all that concerned her, then or since!
At the end of her first year in school, Rosa obtained her father's permission to give up her other studies and to enter his studio as pupil and assistant. From that time, though as yet she had not found the reason of her vocation, yet her true life had begun. She worked diligently under the direction of a master she loved, and her father, in his turn, delighted at the discovery of a talent so long hid, redoubled his efforts to advance his pupil and to make up for lost time.
Rosa worked for some months at copying in the Louvre, but though she worked with such diligence and skill as to win the praise of the director, she came, after a time, to feel that the mere copying of the works of other men, however great, was not the goal she was striving after; so one day she took a sudden determination, left the Louvre, packed up her painting materials, and started off for one of the rural suburbs of Paris, where she sat herself down to sketch from nature. Her love of animals, hitherto an aimless pleasure, now took on a new phase as she saw her beloved cows and sheep in their place in nature giving life and animation to the landscape.
In the winter season, when work out-of-doors was no longer pleasant or profitable, Rosa made what use she could of the few opportunities Paris had to offer for the study of animals. She spent what time she could spare from work at the horse-market; she visited the slaughter-houses, and the suburban fairs where cattle and horses, sheep and pigs compete for prizes, and in these places she filled her portfolios with sketches.
In 1840 she sent her first picture to the Salon, and as it was accepted and well received, she continued to send her work every year; but, up to 1849, her pictures were small, and had little more interest than belongs to simple studies from nature; 1849 was a memorable year to her, as it was to France. In this year her father died of cholera, just as he had been appointed director of the School of Design for Young Girls. Rosa was appointed to succeed him with the (p. 280) title of Honorary Directress, and her sister Juliette was made a teacher in the school. In the same year she exhibited the picture that may be said to have made her reputation with the artists and amateurs, as well as with the general public. This was her "Oxen of Cantal," a picture that combined with no little feeling for landscape the most admirable painting of cattle in repose. Its high qualities were immediately recognized. Horace Vernet, in the name of the Provisional Government, presented her with a handsome vase of Sèvres porcelain, and the gold medal for painting. In 1851, the jury selected for exhibition at the World's Fair in London another picture by Rosa, "Ploughing in the Nivernais," which made the artist's name known to England, where the national love of animals secured for her no end of praise and of substantial reward. In 1856 Rosa painted her most popular picture, "The Horse Fair," now in the Metropolitan Museum. This painting went from Paris to London, where it was bought for rising £1,500, and created such an interest in the artist's personality as would have turned the head of any ordinary woman; but Rosa Bonheur's whole life proves her no ordinary woman.
For many years Mlle. Bonheur lived in Paris in a house surrounded by a large garden where she kept a number of animals, partly for the pleasure of their companionship, partly for the opportunity it gave her of studying their habits, and using them as models. She now resides in the Château By, near Fontainebleau, where she leads the same industrious life in her advancing years that she did in the beginning of her career. She rises early, and works at her painting all day, and often spends the evening in drawing: for she takes but little interest in what is called society, and cares only for the companionship of her intimate friends, which she can enjoy without disarranging her life, or neglecting the studies she loves. She dresses with great simplicity at all times, and even when she accepts invitations, makes no concessions to the caprices of fashion. In her student-days, when visiting the abattoirs, markets, and fairs, she accustomed herself to wear such a modification of man's dress as would permit her to move about among rough men without compromising her sex. But, beside that her dignity was always safe in her own keeping, she bears testimony to the good manners and the good dispositions of the men she came in contact with. Rosa Bonheur has always been an honor to art and an honor to her sex. At seventy-two she finds herself in the enjoyment of many things that go to make a happy life. She has a well-earned fame as an artist; an abundant fortune gained by her own industry and used as honorably as it has been gained; and she has troops of friends drawn to her by her solid worth of character.
Of the great number of pictures Rosa Bonheur has painted, by far the most are of subjects found in France, but a few of the best were painted in Scotland. She has received many public honors in medals and decorations. In 1856, after painting the "Horse Fair," the Empress Eugénie visited her at her studio and bestowed upon her the Cross of the Legion of Honor, fastening the decoration to the artist's dress with her own hands. When the invading army of Prussia reached Paris, the Crown Prince gave orders that the studio of Rosa Bonheur (p. 281) should be respected. But though she, no doubt, holds all these honors at their worth, yet she holds still more dear the art to which she owes, not only these, but all that has made her life a treasury of happy remembrances.[Back to Contents]

In the Paris Salon of 1847, a small picture appeared, representing a Greek boy and girl stirring up two game-cocks to fight. Although it was the work of an unknown painter, and had to contend with an unusually brilliant display of pictures, many of them by men already famous, yet it strongly attracted the general public, partly by the novelty of the subject, and partly by the careful and finished manner of the painting. It delighted the critics as well, and one of the most distinguished of them, Théophile Gautier, wrote: "A new Greek is born to us, and his name is Gérôme!"
This picture, which was to prove the first leaf in a laurel-crown to be awarded the painter in his lifetime, and not, as is so often the case, by the tardy hand of Death, was the work of Jean-Léon Gérôme, a young man of twenty-three. He had been for six years under the teaching of Paul Delaroche, part of the time in Italy, but most of it in Paris. He was born at Vesoul, a small, dull town in the Department of Haute-Saône, in 1824. His father was a goldsmith, who, like most French fathers in his rank of life, had hoped to bring up his son to succeed him in his business. The boy did for a time, we believe, work in his father's shop, but he had a stronger natural bent for painting; something perhaps in the occupation fostered, or even created, this taste—for not a few distinguished painters have been apprenticed to the goldsmith's trade—and his father, like a wise man, instead of opposing his son's wishes, did what he could to further them. He bought him painting-materials; and instead of sending him to a "school of design," or putting him under the tutelage of some third-rate drawing-master, such as is commonly found in country towns, he bought him a picture by Decamps, an artist since become famous, but then just in the dawn of his fame, and put it before his son as a model. Young Gérôme made a copy of this picture, and an artist from Paris, who happened to be passing through Vesoul, saw (p. 282) it, and discerning the boy's talent, gave him a letter to Paul Delaroche, encouraging him to go to Paris and there to take up the study of art as a profession. At seventeen years of age, with his father's consent and $250 in his pocket, Gérôme went up to Paris, and presenting his letter to Delaroche, was well received by him, and entered the School of Fine Arts (École des Beaux-Arts) as his pupil.
He had been with Delaroche three years and had proved himself one of the most loyal and diligent of his pupils, when an event occurred, insignificant in itself, but which was to have an important influence upon his life and give a new direction to his talent.
French studios are not as a rule very orderly places. The young men who frequent them are left pretty much to themselves, with no one to govern them or to oversee them. The artist they are studying under makes, at the most, a brief daily visit, going the round of the easels, saying a word or two to each pupil, although it often happens that he says nothing, and then departs for his proper work, leaving his pupils to their own devices. The students are for the most part like young men everywhere, a turbulent set, full of animal spirits, which sometimes carry them beyond reasonable bounds. It was a boisterous outbreak of this sort, but far wilder than common, that occurred in the studio of Delaroche, and which brought about the crisis in Gérôme's life to which we have alluded. Fortunately for him, the incident took place while Gérôme was on a visit to his parents at Vesoul, so that he was in no way implicated in the affair. He came back to find the studio closed; Delaroche, deeply disturbed, had dismissed all his pupils and announced his intention to visit Italy. His studio was to be taken during his absence, by Gleyre, and he advised those of his pupils in whom he took a personal interest, to continue their studies under his successor. Gérôme was one of those to whom he gave this advice, but Gérôme was too much attached to his master to leave him for another, and bluntly announced his purpose of following him to Rome. A few of the other pupils of Delaroche were of the same mind, and they all set out for Italy together. Arrived in Rome, Gérôme, always a hard worker, threw himself energetically into his studies; drawing the ancient buildings, the Capitol, the Colosseum; sketching in the Forum and on the Campagna; copying the pictures and the statues, saturating his mind in the spirit of antique art, and schooling his hand in its forms, until he had laid up a rich store of material for use in future pictures. On his return to Paris he worked for a while in Gleyre's studio, but when Delaroche came back from Italy, Gérôme again joined him and renewed his old relation as pupil and assistant—working, among other tasks, on the painting of "Charlemagne Crossing the Alps," a commission given to Delaroche by the Government, for the Grande Galerie des Batailles at Versailles: a vast apartment lined with pictures of all the victories of the French from Soissons to Solferino.
Such work as this, however, had little interest for Gérôme. His mind at this time was full of the Greeks and Romans; his enthusiasm for Napoleon, which later was to give birth to so many pictures, had not yet awakened; nor did he (p. 283) care for the subjects from the histories of France and England in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, that had provided his master, Delaroche, with so many tragic themes for his pencil: "The Death of the Duke of Guise," "The Children of Edward," the "Death of Queen Elizabeth," "The Execution of Lady Jane Grey," "Cromwell at the Coffin of Charles I.," and others of the same strain.
Gérôme's visit to Italy had awakened in him a strong interest in the life of the antique world, and this would naturally be strengthened by all that he would hear and see of the growing interest of the public in the same subject: an interest kindled by the discoveries of archaeologists in classic soil: in Greece and Italy, in Assyria and Egypt. These discoveries had filled the museums and the cabinets of private collectors with beautiful and interesting fragments illustrating the external life of the past, and illuminating its poetry; and it is no wonder that some of the younger artists rejoiced in the new world of anecdote and story that opened so richly before them.
However it came about—whether his own interest in the antique life communicated itself to his fellows, or whether they, all together, simply shared in the interest taken in the subject by the world about them—Gérôme and some of his companions in Delaroche's studio showed such a predilection for classic themes, that they were nicknamed by the critics "The New Greeks." Among Gérôme's fellow-pupils were two young men, Hamon and Aubert, who later gained no small applause by their playful and familiar way of treating classic themes. They are well known to us by engravings from their pictures, which are in all our shops. Hamon's "My Sister is not at home," and Aubert's various pretty fancies of nymphs and cupids, while they are not great works of art, are reasonably sure of a long life, due to their innocent freshness and simplicity.
Delaroche's pupils were working all together in friendly competition for the grand Roman prize which was to give the fortunate one the right to four years' study in Rome at the expense of the state. Gérôme's studio was shared by his friends Picou and Hamon. Hamon, writing in later years about his youthful days, says: "Companions and rivals at the same time, we were all working together for the Grand Prix de Rome. Gérôme inspired us all with the love of hard work, and of hard work to the accompaniment of singing and laughing."
But in the intervals of his hard work for the prize, Gérôme was also working on a picture which he hoped to have accepted for the Salon. This was the picture we spoke of in the beginning of this notice: "Two Young Greeks stirring-up Game-cocks to fight." When it was finished Gérôme showed it to his master with many misgivings; but Delaroche encouraged him to send it to the Salon. It was accepted, and as we have seen, won for Gérôme a great success with the public. The next year, 1848, he again exhibited, but the impression he made was less marked than on the first occasion. His former picture had a subject such as it was, of his own devising. The "Cock-fight" was not an illustration of any passage in Greek poetry, and in spite of its antique setting, it had a modern air, and to this, no doubt, its popularity was largely due. But in 1848 he essayed an illustration of the Greek poet, Anacreon, translating into picture the (p. 284) poem that tells how, one winter evening, sitting by his fire, the old poet was surprised by a sound of weeping outside his door, and opening it, found Cupid wet and shivering and begging for a shelter from the cold. The man takes the pretty, dimpled mischief to his bosom, warms his feet and hands at the fire, dries his bow and arrows, and lets him sip wine from his cup. Then, when Cupid is refreshed and warmed, he tries his arrows, now here, now there, and at last aims one straight at his benefactor's heart, and laughing at the jest, flies out at the open door. Gérôme's picture was in three panels. The first showed the poet opening the door to the sobbing Cupid, with his bedraggled wings and dripping curls; in the next, the rosy ingrate wounds his benefactor; in the third, the poet sits disconsolate by his hearth, musing over the days when Love was his guest, if but for an hour. As the story was an old one, so many an artist before Gérôme had played with it as a subject for a picture. Jean-François Millet himself, another pupil of Delaroche, though earlier than Gérôme, had tried his hand at illustrating Anacreon's fable before he found his proper field of work in portraying the occupations of the men and women about him, the peasants among whom he was born and bred.
Gérôme's picture did nothing to advance his fortunes with the public. 1848 was a stormy time in France and in all Europe, and people were not in the mood to be amused with such trifles as Anacreon and his Cupid. The pictures in that year's Salon that drew the public in crowds about them were Couture's "The Romans of the Decline of the Empire," in which all Paris saw, or thought it saw, the handwriting-on-the-wall for the government of Louis-Philippe; and the "Shipwrecked Sailors in a Bark," of Delacroix, a wild and stormy scene of terror that seemed to echo the prophecies of evil days at hand for France with which the time was rife.
Gérôme's next picture, however, was to bring him once more before the public, and to carry his name beyond his native France even as far as America. Leaving for the nonce his chosen field of antiquity, where yet he was to distinguish himself, he looked for a subject in the Paris of his own day. "The Duel after the Masquerade" opens for us a corner of the Bois de Boulogne—the fashionable park on the outskirts of Paris—where in the still dawn of a winter's day, a group of men are met to witness a duel between two of their companions who have quarrelled at a masked ball. The ground is covered with a light fall of snow; the bare branches of the trees weave their network across the gray sky, and in the distance we see the carriages that have brought the disputants to the field. The duel is over. One of the men, dressed in the costume of Pierrot, the loose white trousers and slippers, the baggy white shirt, and white skull-cap, falls, mortally wounded, into the arms of his second: the pallor of coming death masked by the white-painted face. The other combatant, a Mohawk Indian (once a staple character at every masked-ball in Paris: curious survival of the popularity of Cooper's novels), is led wounded off the field by a friend dressed as Harlequin. Gérôme in this striking picture showed for the first time that talent as a story-teller to which he is so largely indebted for his reputation. Whatever (p. 285) his subject may be, it is always set forth in the clearest manner, so that everyone may understand the story without the need of an interpreter.
Leaving out of view the few pictures he painted illustrating passages in Napoleon's career, it may be said that Gérôme's taste led him away from scenes of modern life; for even his many oriental subjects so relate to forms of life belonging in reality to the past, that they make no exception to the statement. He did not therefore follow up "The Duel" with other comments on the follies of modern society—for in the temper of that time this picture, like Couture's "Roman Orgie" and Millet's "Man with the Hoe," was looked upon as a satire and a warning, and owed its popularity as much to this conviction on the part of the public as to its pictorial merits—but returned to antique times, and showed in his treatment of themes from that source an equal, if not a greater power to interest the public.
Gérôme's two pictures, the "Ave Cæsar! Morituri te Salutant," "Hail, Cæsar! Those about to die, salute Thee," and "The Gladiators," are so universally known as to need no description. Whatever criticism may be made upon them, they will always remain interesting to the world at large; from their subject, from the way in which the discoveries of archæology are made familiar, and, not least, from the impression they make of the artist's own strong interest in what he had to say. In both pictures he succeeded in showing the Colosseum as no longer a ruin, but as, so to speak, a living place peopled by the swarm of the Roman populace, with the emperor and his court, and the College of the Vestal Virgins, and, for chief actors, the hapless wretches who are "butchered to make a Roman holiday." Another picture that greatly increased Gérôme's reputation, was his "Death of Julius Cæsar," though it must be confessed there was a touch of the stage in the arrangement of the scene, and in the action of the body of senators and conspirators leaving the hall with brandished swords and as if singing in chorus, that was absent from the pictures of the amphitheatre. There was also less material for the curiosity of the lovers of archæology; no such striking point, for instance, as the reproduction of the gladiators' helmets and armor recently discovered in Herculaneum; but the body of the dead Cæsar lying "even at the base of Pompey's statue" with his face muffled in his toga, was a masterly performance; some critic, moved by the grandeur of the lines, said it was not a mere piece of foreshortening, it was "a perspective." Gérôme made a life-size painting of the Cæsar in this picture. It is in the Corcoran Gallery at Washington.
Gérôme painted several other pictures from classic subjects, but none of them had the interest for the general public of those we have described. In 1854 he exhibited a huge canvas, called "The Age of Augustus," a picture suggested, perhaps, by the "Hemicycle" of his master Delaroche, on which he himself had painted. It represented heroes, poets, sages, of the Augustan age, grouped about the cradle of the infant Christ; it procured for Gérôme the red ribbon of the Legion of Honor, and is now, as the artist himself jestingly says, "the 'greatest' picture in the Museum of Amiens." In the same year Gérôme went (p. 286) to Egypt for the first time; since then he has more than once visited it, but it is doubtful if he could renew the pleasure of his youthful experience. "I set out," he says, "with my friends, I the fifth, all of us lightly furnished with money, but full of youthful enthusiasm. Life was then easy in Egypt; we lived at a very moderate rate; we hired a boat and lived four months upon the Nile, hunting, painting, fishing by turns, from Damietta to Philæ. We returned to Cairo and remained there four months longer in a house in the older part of the town, belonging to Soleman Pasha. As Frenchmen, he treated us with cordial hospitality. Happy period of youth, of freedom from care! Hope and the future opened bright before us; the sky was blue!"
Gérôme's pictures of Eastern life make a gallery by themselves. A few of them are historic, such as his "Cleopatra visiting Cæsar," but the most of them are simply scenes and incidents drawn from the daily life of the modern inhabitants of Cairo and the desert, illustrating their manners and customs. The mere titles would fill up a large part of our space. Many of the best of them are owned in this country, and all have been reproduced by engraving or by photography.
In another field Gérôme won great distinction, painting scenes from the history of France in the reign of Louis XIV.; subjects drawn from what may be called the high comedy of court-life, and treated by Gérôme with remarkable refinement and distinction. Among these pictures the best known are: "Molière Breakfasting with Louis XIV.," illustrating the story of the king's rebuke to his courtiers who affected to despise the man of genius; "Père Joseph," the priest who under the guise of humility and self-abnegation reduces the greatest nobles to the state of lackeys; "Louis XIV. Receiving the Great Condé," and "Collaboration," two poets of Louis XIV.'s time working together over a play. Among his accomplishments as an artist we must not forget the talent that Gérôme has shown as a sculptor. He has modelled several figures from his own pictures, with such admirable skill as to prove that he might easily have made sculpture a profession had he not chosen to devote himself to painting.[Back to Contents]

Those whose privilege it was to meet the late Mr. Gabriel Rossetti, at once in the plenitude of his powers and in the freshness of their own impressions, will not expect to be moved again through life by so magnetic a presence. In his dealings with those much younger than himself, his tact and influence were unequalled; he received a shy but ardent youth with such a noble courtesy, with so much sympathy yet with no condescension, with so grand an air and yet so warm a welcome, that his new acquaintance was enslaved at the first sentence. This seems to me to have been in a certain sense the key-note of the man. He was essentially a point of fire; not a peripatetic in any sense, not a person of wide circumference, but a nucleus of pure imagination that never stirred or shifted, but scintillated in all directions. The function of Gabriel Rossetti, or at least his most obvious function, was to sit in isolation, and to have vaguely glimmering spirits presented to him for complete illumination. He was the most prompt in suggestion, the most regal in giving, the most sympathetic in response, of the men I have known or seen; and this without a single touch of the prophetic manner, the air of such professional seers as Coleridge or Carlyle. What he had to give was not mystical or abstract; it was purely concrete. His mind was full of practical artistic schemes, only a few of which were suited to his own practice in painting or poetry; the rest were at the service of whoever would come in a friendly spirit and take them. I find among his letters to me, which I have just been reading once again, a paper of delightful suggestions about the cover of a book of verse; the next youth who waited upon him would perhaps be a painter, and would find that the great genius and master did not disdain the (p. 288) discussion of picture-frames. This was but the undercurrent of his influence; as we shall see more and more every year as the central decades of this century become history, its main stream directed the two great arts of painting and poetry into new channels, and set a score of diverse talents in motion.
But, as far as anything can be seen plainly about Rossetti at present, to me the fact of his immovability, his self-support, his curious reserve, seems to be the most interesting. He held in all things to the essential and not to the accidental; he preferred the dry grain of musk to a diluted flood of perfume. An Italian by birth and deeply moved by all things Italian, he never visited Italy; a lover of ritual and a sympathizer with all the mysteries of the Roman creed, he never joined the Catholic Church; a poet whose form and substance alike influenced almost all the men of his generation, he was more than forty years of age before he gave his verse to the public; a painter who considered the attitude of the past with more ardor and faith than almost any artist of his time, he never chose to visit the churches or galleries of Europe. It has been said, among the many absurd things which his death has provoked, that he shrank from publicity from timidity, or spurned it from ill-temper. One brilliant journalist has described him as sulking like Hector in his tent. It used to be Achilles who sulked when I was at school; but it certainly never was Gabriel Rossetti. Those who only knew him, after his constitution had passed under the yoke of the drug which killed him, cannot judge of his natural reserve from that artificial and morbid reserve which embittered the last years of his life. The former was not connected with any objection to new faces or dislike of cordial society, but with the indomitable characteristic of the man, which made him give out the treasures of the spirit, and never need to receive them. So far from disliking society, it is my impression that he craved it as a necessity, although he chose to select its constituents and narrow its range.
He was born in 1828. The story of his parentage is well known, and has been told in full detail since his death. He was born in London and christened Gabriel Charles Rossetti; it was not, I am told, until he was of age to appreciate the value of the name that he took upon himself the cognomen which his father had borne, the Dante by which the world, though not his friends, have known him. Living with his father in Charlotte street, with two sisters and a brother no less ardently trained in letters than himself, he seems to have been turned to poetry, as he was afterward sustained in it, by the interior flame. The household has been described to me by one who saw it in 1847: the father, titular professor of Italian literature, but with no professional duties, seated the livelong day, with a shade over his eyes, writing devotional or patriotic poetry in his native tongue; the girls reading Dante aloud with their rich maiden voices; Gabriel buried here in his writing, or darting round the corner of the street to the studio where he painted. From this seclusion he wrote to the friend who has kindly helped me in preparing these notes, and whose memories of the poet extend over a longer period than those of any survivor not related to him.
Mr. W. B. Scott, now so well known in more arts than one, had then but (p. 289) just published his first book, his mystical and transcendental poem of "The Year of the World." This seems to have fallen under Rossetti's notice, for on November 25, 1847, he wrote to the author, a perfect stranger to himself, a letter of warm sympathy and acknowledgment. Mr. Scott was living in Newcastle, and, instead of meeting, the young poets at first made acquaintance with each other by correspondence. Rossetti soon mentioned, of course, his own schemes and ambitions, and he sent, as a sample of his powers, his poems of "The Blessed Damozel," and "My Sister's Sleep," which he had written about eighteen months before.
Mr. Scott tells me that his first feeling on receiving these poems, written in English by an Italian boy of eighteen, was one of amazement. I cannot wonder at it. If the "Blessed Damozel," when it was published a quarter of a century later, seemed a masterpiece to those who had, in the meanwhile, read so much that was vaguely inspired by it, what must it have been in 1846? Certain pieces in Tennyson's "Poems," of 1842, and a few fragments of Browning's "Bells and Pomegranates" were the only English poems which can be supposed to have given it birth, even indirectly. In its interpretation of mystical thoughts by concrete images, in its mediæval fervor and consistence of fancy, in its peculiar metrical facility, it was distinctly new—original as few poems except those by the acknowledged masters of the craft can ever be.
"The sun was gone now; the curled moon
Was like a little feather
Fluttering far down the gulf; and now
She spoke through the clear weather.
Her voice was like the voice the stars
Had when they sang together."
This was a strange accent in 1846. Miss Barrett and Mr. Tennyson were then the most accepted poets. Mr. Browning spoke fluently and persistently, but only to a very little circle; Mr. Horne's "Orion" and Mr. Bailey's "Festus" were the recent outcomes of Keats and Goethe; the Spasmodic School, to be presently born of much unwise study of "Festus," was still unknown; Mr. Clough, Mr. Matthew Arnold, and Mr. Patmore were quite unapparent, taking form and voice in solitude; and here was a new singer, utterly unlike them all, pouring out his first notes with the precision and independence of the new-fledged thrush in the woodland chorus.
In painting, the process was somewhat different. In this art, no less than in poetry, Rossetti understood at once what it was that he wished to do himself, and what he desired to see others doing; but the difficulties of technique were in his way. He had begun to write in childhood, but he had taken up design late in his youth, and he had undergone no discipline in it. At the present day, when every student has to pass a somewhat stringent examination in design, Rossetti, at eighteen, could not have entered the schools of the Royal Academy. He did so, however, yet without ever advancing to the Life School. The soul of (p. 290) art, at this early period, interested him far more than the body, especially such a substance as he found under the presidency of Sir Martin Shee and the keepership of George Jones. Let us not forget, meanwhile, that it is easy to sneer at the incompetence of mannered old artists, and yet hard to over-estimate the value of discipline in a school, however conventional. Rossetti was too impatient to learn to draw, and this he lived to regret. His immediate associates, the young men whom he began to lead and impress, were better draughtsmen than he. His first oil picture, I believe, was a portrait of his father, now in possession of the family. But, as far as can be now made out, he did not begin to paint seriously till about January, 1848, when he persuaded another Royal Academy student, W. Holman Hunt, to take a large room close to the paternal house in Charlotte street, and make it their studio. Here Mr. Scott visited them in the early spring of that year; he describes to me the large pictures they were struggling upon, Hunt, on his "Oath of Rienzi," and Rossetti, on his "Girlhood of Mary Virgin." The latter was evidently at present but poorly equipped; the painting was timid and boyish, pale in tone, and with no hint or promise of that radiant color which afterward became Rossetti's main characteristic. But the feeling was identical with that in his far more accomplished early poems. The very pulse and throb of mediæval adoration pervaded the whole conception of the picture, and Mr. Scott's first impression was that, in this marvellous poet and possible painter, the new Tractarian movement had found its expositor in art. Yet this surely was no such feeble or sentimental echo as had inspired the declared Tractarian poets of eight or nine years earlier; there was nothing here that recalled such a book as the "Cherwell Water Lily" of Father Faber. This contained the genuine fleshly mysticism, bodily presentment of a spiritual idea, and intimate knowledge of mediæval sentiment without which the new religious fervor had no intellectual basis. This strong instinct for the forms of the Catholic religion, combined with no attendance on the rites of that church, fostered by no study of ecclesiastical literature or association with teachers or proselytes, but original to himself and self-supported, was at that time without doubt the feature in Rossetti's intellectual character which demands our closest attention. Nor do I believe that this passion for the physical presentation of a mystical idea was ever entirely supplanted by those other views of life and art which came to occupy his maturer mind. In his latest poems—in "Rose Mary," for instance—I see this first impulse returning upon him with more than its early fascination. In his youth, however, the mysticism was very naïve and straightforward. It was fostered by one of the very few excursions which Rossetti ever took—a tour in Belgium in October, 1849. I am told that he and the painter-friend who accompanied him were so purely devoted to the mediæval aspect of all they saw, that, in walking through the galleries, they turned away their heads in approaching modern pictures, and carefully closed their eyes while they were passing Rubens's "Descent from the Cross." In Belgium, or as the result of his tour there, Rossetti wrote several curious poems, which were so harsh and forced that he omitted them from his collection when he first published his "Poems," in 1870.
(p. 291) The effort in these early pieces is too marked. I remember once hearing Rossetti say that he did not mind what people called him, if only they would not call him "quaint." But the fact was that, if quaintness be defined as the inability to conceal the labor of an art, there is no doubt that both his poems and his designs occasionally deserved this epithet. He was so excessively sincere an artist, so determined not to permit anything like trickiness of effect or meaningless smoothness to conceal the direct statement of an idea, that his lack of initial discipline sometimes made itself felt in a curious angular hardness.
And now it would be necessary, if I were attempting a complete study of Gabriel Rossetti's intellectual career, to diverge into a description of what has so much exercised popular curiosity, the pre-Raphaelite movement of 1848. But there is no reason why, in a few notes on character, I should repeat from hearsay what several of the seven brothers have reported from authoritative memory. It is admitted, by them and by all who have understood the movement, that Gabriel Rossetti was the founder and, in the Shakespearian sense, "begetter" of all that was done by this earnest band of young artists. One of them, Mr. Millais, was already distinguished; two others, Mr. Holman Hunt and Mr. Woolner, had at that time more training and technical power than he; but he was, nevertheless, the brain and soul of the enterprise. What these young men proposed was excellently propounded in the sonnet by "W. M. R.," which they prefixed to their little literary venture, the "Germ," in 1850. Plainly to think even a little thought, to express it in natural words which are native to the speaker, to paint even an insignificant object as it is, and not as the old masters or the new masters have said it should be painted, to persevere in looking at truth and at nature without the smallest prejudice for tradition, this was the whole mystery and cabal of the P. R. B. They called themselves "preraphaelite," because they found in the wings of Lippi's angels, and the columbines of Perugino's gardens that loving and exact study of minute things which gave to them a sense of sincerity, and which they missed in the breadth and ease of later work. They had no ambition to "splash as no one splashed before since great Caldasi Polidore;" but they did wish to draw a flower or a cloud so that it should be a portrait of that cloud or flower. In this ambition it would be curious to know, and I do not think that I have ever heard it stated, how far they were influenced by Mr. Ruskin and his "Modern Painters." I should not expect to find Rossetti influenced by any outside force in this any more than in other instances, but at all events Mr. Ruskin eagerly accepted the brotherhood as practical exponents of the theories he had pronounced. None of them, I think, knew him personally when he wrote the famous letter to the Times in 1851, defending Mr. Millais and Mr. Holman Hunt from the abuse of ignorant critics, who, he said, had failed to perceive the very principles on which these "two young men" were proceeding. Somebody wrote to him to explain that there were "three young men," and Mr. Ruskin wrote a note to Gabriel Rossetti, desiring to see his work, and thus the acquaintance of these two remarkable men commenced.
Meanwhile, although the more vigorous members of the brotherhood had (p. 292) shown no special sympathy for Rossetti's religious mysticism, a feebler artist, himself one of the original seven, had taken it up with embarrassing effusion. This was the late James Collinson, whose principal picture, "St. Elizabeth of Hungary," finished in 1851, produced a sort of crisis in Rossetti's career. This painting out-mystified the mystic himself; it was simply maudlin and hysterical, though drawn with some feeling for grace, and in a very earnest spirit. Rossetti, with his strong good sense, recognized that it would be impossible ever to reach the public with art of this unmanly character, and from this time forth he began to abandon the practice of directly sacred art.
For some little time after abandoning the directly sacred field in painting, Rossetti seems to have passed through a disconsolate and dubious period. I am told that he worked for many months over a large picture called "Kate the Queen," from some well-known words by Browning. He made no progress with this, seemed dissatisfied with his own media, felt the weight of his lack of training, and passed, in short, through one of those downcast moods, which Shakespeare has so marvellously described in "Tired with all these," and which are incident, sooner or later, to every man of genius. While his touch in poetry grew constantly more sure and masterly, his power as a draughtsman threatened to leave him altogether. He was to have drawn one of the frontispieces in the "Germ," but, although he toiled with a design, he could not make it "come right." At last a happy accident put him on the true track, and revealed his proper genius to himself. He began to make small drawings of poetical subjects in water-colors—most of those which I have seen are not more than twenty inches by twelve—over which he labored, and into which he poured his exquisite sense of color, inspired without doubt by the glass of mediæval church windows. He travelled so very little, that I do not know whether he ever saw the treasures of radiant jewel-work which fret the gloom of Chartres or of Bourges; but if he never saw them, he divined them, and these are the only pieces of color which in the least degree suggest the drawings of this, Rossetti's second period. As far as one can gather, his method was, first, to become interpenetrated with the sentiment of some ballad or passage of emotional poetry, then to meditate on the scene till he saw it clearly before him; then—and this seems to have always been the difficult and tedious part—to draw in the design, and then with triumphant ease to fill in the outlines with radiant color. He had an almost insuperable difficulty in keeping his composition within the confines of the paper upon which he worked, and at last was content to have a purely accidental limit to the design, no matter what limbs of the dramatis personæ were sheered away by the frame. It would not be the act of a true friend to Rossetti's memory to pretend that these drawings, of which for the next ten or fifteen years he continued to produce a great number, were without faults of a nature which any coxcomb could perceive, or without eccentricities which an untrained eye might easily mistake for faults; but this does not in the least militate against the fact that in two great departments of the painter's faculty, in imaginative sentiment and in wealth of color, they have never been surpassed. They have rarely, indeed, been equalled (p. 293) in the history of painting. A Rossetti drawing of this class hung with specimens of other art, ancient or modern, simply destroys them. I do not mean that it is better or worse than they are, but that it kills them as the electric light puts out a glow-worm. No other man's color will bear these points of ruby-crimson, these expanses of deep turquoise-blue, these flagrant scarlets and thunderous purples. He paints the sleeve of a trumpeter; it is such an orange as the eye can scarce endure to look at. He paints the tiles of a chimney-corner; they are as green as the peacock's eyes in the sunshine.
The world is seldom ready to receive any new thing. These drawings of Rossetti's were scarcely noticed even by those who are habitually on the watch for fresh developments in art. But when the painter next emerges into something like publicity we find him attended by a brilliant company of younger men, all more or less influenced by his teaching and attracted by his gifts. The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood had been a very ephemeral institution; in three years, or four at the most, it had ceased to exist; but its principles and the energy of its founder had left their mark on the whole world of art. In 1849 Rossetti had exhibited his picture, "The Girlhood of Mary Virgin," at the Portland Gallery, an exhibition in rivalry of the Royal Academy, which existed but a very short time. As far as I can discover, he did not exhibit again in London until 1856, when he and his friends opened a collection of their pictures at 4 Russell Place, Fitzroy Square. We would rather have seen that little gallery than see most of the show-exhibitions of Europe. In it the fine art of the Anglo-Saxon race was seen dawning again after its long and dark night. Rossetti himself was the principal exhibitor, but his two earliest colleagues, now famous painters, Mr. Millais and Mr. Holman Hunt, also contributed. And here were all the new talents whom Rossetti had attracted around him during the last seven years: Mr. Madox Brown, with his fine genius for history; Mr. J. D. Watson, with his strong mediæval affinities; Mr. Boyce, with his delicate portraiture of rustic scenes; Mr. Brett, the finest of our students of the sea; Mr. W. B. Scott himself; besides one or two others, Mr. Charles Collins, Mr. Campbell, Mr. Halliday, Mr. Martineau, whom death or adverse fortune removed before they had quite fulfilled their promise. Gabriel Rossetti contributed to this interesting and historic exhibition five or six of those marvellous drawings of which mention has just been made. "Dante's Dream," the famous vision of June 9, 1290, with its counterpart, "The Anniversary of the Dream," in 1291, were the most prominent of these. A "Mary Magdalene" was perhaps the most moving and exciting. This extremely original design showed the Magdalene pursued by her lovers, but turning away from them all to seek Jesus in the house of Simon the Pharisee. The architecture in this drawing was almost childish; the wall of Simon's house is not three inches thick, and there is not room for a grown-up person on the stairs that lead to it; but the tender imagination of the whole, the sweet persuasiveness of Christ, who looks out of a window, the passion of the awakened sinner, who tears the roses out of her hair, the curious novelty of treatment in the heads and draperies, all these combine to make it one of those (p. 294) works, the moral force and directness of which appeal to the heart at once. Perhaps the most brilliant piece of color at the Russell Place Gallery may have been Rossetti's "Blue Closet," a picture which either illustrated or, as I should rather suppose, suggested Mr. Morris's wonderful poem published two years later.
The same year that displayed him to the public already surrounded by a brilliant phalanx of painter-friends, discovered him also, to the judicious, as a centre of poetic light and heat. The circumstances connected with Rossetti's visit to Oxford a little earlier than this are too recent, are fresh in the memories of too many living persons of distinction, to be discussed with propriety by one who was not present. But certain facts are public, and may be mentioned. The Oxford Union still shows around the interior of its cupola strange, shadowy frescoes, melting into nothingness, which are the work of six men, of whom Rossetti was the leader. These youths had enjoyed no practical training in that particularly artificial branch of art, mural painting, and yet it seems strange that Rossetti himself, at least, should not have understood that a vehicle, such as yolk of egg mixed with vinegar, was absolutely necessary to tempera, or that it was proper, in fresco-painting, to prepare the walls, and paint in the fresh wet mortar. They used no vehicle, they fixed their colors in no coat of plaster, but they threw their ineffectual dry paint on the naked brick. The result has been that their interesting boyish efforts are now decayed beyond any chance of restoration. It is impossible, however, to ascend the gallery of the Oxford Union and examine the ghostly frescoes that are fading there, without great interest and even emotion. Of the young men who painted there under Gabriel Rossetti's eye, all have become greatly distinguished. Mr. Edward Burne-Jones, Mr. William Morris, and Mr. Spencer Stanhope were undergraduates at Oxford. Mr. Valentine Prinsep and Mr. Arthur Hughes, I believe, were Royal Academy students who were invited down by Rossetti. Their work was naïve and queer to the last degree. It is perhaps not fair to say which one of them found so much difficulty in painting the legs of his figures that he drew an impenetrable covert of sunflowers right across his picture, and only showed the faces of his heroes and heroines between the golden disks.
The Oxford and Cambridge Magazine, which also dates from the year 1856, is a still more notable expression of budding genius than the dome of the Oxford Union. It was edited by Mr. Godfrey Lushington, all its articles were anonymous, and it contrived to exist through twelve consecutive monthly numbers. A complete set is now rare, and the periodical itself is much less known than befits such a receptacle of pure literature. It contains three or four of Rossetti's finest poems; a great many of those extraordinary pieces, steeped in mediæval coloring, which Mr. William Morris was to collect in 1858 into his bewitching volume, called "The Defence of Guenevere;" several delightful prose stories of life in the Middle Ages, also by Mr. Morris, which, like certain prose romances by Mr. Burne-Jones, have never been publicly claimed or reprinted by their author; and not a little else that was as new as it was notable. A little later Mr. William Morris's first book was dedicated "To my Friend Dante Gabriel (p. 295) Rossetti, Painter," and in 1860 Mr. Swinburne followed with a like inscription of his first-fruits, his tragic drama of "The Queen-Mother." Thus in the course of a little more than ten years, Rossetti had become the centre and sun of a galaxy of talent in poetry and painting, more brilliant perhaps than any which has ever acknowledged the beneficent sway of any one Englishman of genius.
But all this while the world outside knew nothing of the matter. One by one the younger men stepped forward on the public stage and secured the plaudits of the discerning, and ascended the slow incline of general reputation. But Rossetti remained obstinately recluse, far preferring to be the priest and confessor of genius to acting himself a public part. To this determination several outward things engaged him still further. He married quite early in life; and his wife, who was herself an artist of rare, if somewhat wild and untrained talent, bore him a son who died at birth, and then shortly after died herself. During his brief married months Rossetti had collected the MSS. of his poems, and thought to publish them; but when he lost his wife, in a paroxysm of grief he placed the sheets of his poems in her coffin, and would hear no more a suggestion of publication. In 1861 he presented the world with a very learned and beautiful anthology of early Italian poetry, and proposed as early as that year to print his original poems. It was his scheme to name the little volume "Dante in Verona, and other Poems;" but it came to nothing. About 1867 the scheme of publication again took possession of him. I have been told that a sudden sentiment of middle age, the fact that he found himself in his fortieth year, led him to conquer his scruples, and finally arrange his pieces. But he was singularly fastidious; the arrangement would never please him; the cover must be cut in brass, the paper at the sides must bear a special design. These niceties were rarer twelve years ago than they are now, and the printers fatigued him with their persistent obstinacy. It was not till early in 1870 that the "Poems" in stately form first appeared, and were hailed with a shout of admiration which was practically universal.
It was about Christmas in that same year, 1870, that he who writes these lines was first presented to Gabriel Rossetti. The impression on my mental eye is as fresh as if it had been made yesterday, instead of twelve years ago. He was a man of average height, commonly loosely clad in black, so as to give one something of the notion of an abbé; the head very full, and domed like that of Shakespeare, as it was then usual to say—to my thinking more like that of Chaucer—in any case a head surcharged with imagination and power, strongly Italian in color and cast. The eyes were exceedingly deep set, in cavernous sockets; they were large, and black, and full of a restless brilliance, a piercing quality which consoled the shy novice by not being stationary. Lastly, a voice of bell-like tone and sonority, a voice capable of expressing without effort every shade of emotion from rage and terror to the most sublime tenderness. I have never heard a voice so fitted for poetical effect, so purely imaginative, and yet, in its absence of rhetoric, so clear and various, as that of Gabriel Rossetti. I retain one special memory of his reading in his own studio the unfinished MS. of (p. 296) "Rose Mary," in 1873, which surpassed in this direction any pleasure which it has been my lot to enjoy; and on various occasions I have listened to his reading of sonnets, his own and those of others, with a sense that his intonation revealed a beauty in the form of that species of verse which it had never been seen to possess before. I have already spoken of his wonderful courtliness to a new acquaintance, his bewitching air of sympathy; on a closer intimacy this stately manner would break up into wild fits of mirth, and any sketch of Rossetti would be incomplete that did not describe his loud and infectious laughter. He lived very much apart from the every-day life of mankind, not ostentatiously, but from a genuine lack of interest in passing events. An old friend tells me that during the French Revolution he burst into Rossetti's studio with the incredible news, "Louis-Philippe has landed in England!" "Has he?" said Rossetti, calmly. "What has he come for?" That certain political events, in which he saw a great symbolic significance, could move him deeply, is easily proved by such sonnets as the noble "On the Refusal of Aid between Nations," and "Czar Alexander II." But such glances out of window into the living street were rare, and formed no characteristic part of his scheme of life.
As a poet in these great years he possessed rare gifts of passionate utterance, and harmony of vision and expression. Mr. Swinburne has characterized these qualities in words which leave no later commentator the chance of distinguishing himself. But it would be totally unjust, even in so cursory and personal a sketch as this, to allow the impression to go undisputed that Rossetti preferred the external form to the inward substance of poetry. This charge was brought against him, as it has always been brought against earnest students of poetic art. I will rather quote a few words from a letter of Rossetti to me, written in 1873, when he was composing his own magnum opus of "Rose Mary." I have always felt them to be very salutary, none the less because it is obvious that the writer did not at all times contrive, or perhaps desire, to make them true in his own work:
"It seems to me that all poetry, to be really enduring, is bound to be as amusing (however trivial the word may sound) as any other class of literature; and I do not think that enough amusement to keep it alive can ever be got out of incidents not amounting to events, or out of travelling experiences of an ordinary kind however agreeably, observantly, or even thoughtfully treated. I would eschew in writing all themes that are not so trenchantly individualized as to leave no margin for discursiveness."
During the last eight years of his life, Rossetti's whole being was clouded by the terrible curse of an excitable temperament—sleeplessness. To overcome this enemy, which interfered with his powers of work and concentration of thought, he accepted the treacherous aid of the new drug, chloral, which was then vaunted as perfectly harmless in its effect upon the health. The doses of chloral became more and more necessary to him, and I am told that at last they became so frequent and excessive that no case has been recorded in the annals of medicine in which one patient has taken so much, or even half so much, chloral as Rossetti took. Under this unwholesome drug his constitution, originally a magnificent (p. 297) one, slipped unconsciously into decay, the more stealthily that the poison seemed to have no effect whatever on the powers of the victim's intellect. He painted until physical force failed him; he wrote brilliantly to the very last, and two sonnets dictated by him on his death-bed are described to me as being entirely worthy of his mature powers. There is something almost melancholy in such a proof of the superior vitality of the brain. If the mind had shared the weakness of the body, the insidious enemy might perhaps have been routed in time to secure the elastic rebound of both. But when the chloral was stoutly met at last, it was too late.
So at the age of fifty-four we have lost a man whom we should have retained, in the nature of things, for twenty years longer in the plentitude of his powers, but for a mistake in hygiene—a medical experiment. His work of inspiring the young, of projecting his fiery originality along the veins of others, was perhaps completed; it is doubtful whether this can ever be continued with advantage through more than two generations. The prophet is apt at last to become a tyrant, and from this ill apotheosis Rossetti was spared. But there was no reason why he should not, for at least a score of years, have produced noble pictures and have written gorgeous poems, emphasizing a personal success which he would have extended, though he hardly could have raised it. Yet he was always a melancholy man; of late years he had become almost a solitary man. Like Charles of Austria, he had disbanded his body-guard, and had retired to the cloister. Perhaps a longer life would not have brought much enjoyment with it. But these are idle speculations, and we have rather to call to our remembrance the fact that one of the brightest and most distinguished of our race, a man whose very existence was a protest against narrowness of aim and feebleness of purpose, one of the great torch-bearers in the procession of English art, has been called from us in the prime of life, before the full significance of his genius had been properly felt. He was the contemporary of some mighty names older than his, yet there scarcely was to be found among them all a spirit more thoroughly original; and surely, when the paltry conflicts of passing taste are laid to rest forever, it will be found that this man has written his signature indelibly on one of the principal pages of the register of our intellectual history.[Back to Contents]


It is now eleven years since Gustave Doré died. He was an officer of the Legion of Honor, had attained considerable wealth, and was probably more widely known than any other artist of his day. His name was a household word in two continents. Yet he died a disappointed and embittered man, and is proclaimed by his friends as a neglected and misunderstood genius. He was known the world over as the most astonishingly prolific illustrator of books that has ever lived; he wished to be known in France as a great painter and a great sculptor, and because the artists and critics of France never seriously recognized his claims to this glory, he seems to have become a victim of the mania of persecution, and his naturally sunny nature was over-clouded with moroseness and suspicion. Hailed by some as the emulator and equal of the great names of the Italian Renaissance, and considered a great moral force—a "preacher painter"—by others he has been denounced as "designer in chief to the devil," and described as a man wallowing in all foulness and horror, a sort of demon of frightful power. Both these extreme judgments are English. The late Blanchard Jerrold, an intimate friend and collaborator of the artist, takes the first view. Mr. Ruskin and Mr. Hamerton have taken the second. Doré's own countrymen have never accepted either. Just where, between them, the truth lies, as we see it, we shall endeavor to show in this article.
The main facts of Doré's life may be dismissed very briefly. He was born with a caul on January 6, 1832, in the Rue Bleue at Strasbourg, near the Cathedral. About 1841 his father removed to Bourg, in the Department of Ain, where he was chief government engineer of the department. These two residences of the young artist are supposed to account for the mastery of Gothic (p. 299) architecture and of mountain scenery which his admirers find in his mature work. He showed very early in life a passion for drawing, and, as a small child, had always a pencil in his hand, which he begged to have "sharpened at both ends," that he might work longer without interruption. His father intended him for an engineer, but he was determined from the first to be an artist. He was of a gay and jovial disposition, given to pranks and practical jokes, and of an athletic temperament. Théophile Gautier afterward called him a "gamin de génie." In 1847, when he was fifteen years old, being in Paris with his parents, he called upon Phillippon, the publisher, and showed him some of his sketches. M. Phillippon looked at them, and sent a letter to Doré's parents, persuading them to allow the boy to remain in Paris, and promising them to begin using his work at once and to pay for it. Thus, without any study of art whatever, he began his career, and in a few years had produced a prodigious quantity of work, and was a celebrated man before he was twenty. No one knows how many drawings he made. He "lived like an Arab," worked early and late, and with astonishing rapidity made thousands of drawings for the comic papers, besides early beginning the publication of independent books. One estimate, which Mr. Jerrold thinks excessive, credits him with having published forty thousand drawings before he was forty! Mr. Jerrold himself reckons two hundred and sixty-six drawings done in one year. His "Labors of Hercules" was brought out in 1848, when he was sixteen, and before he was twenty-seven he had published his "Holy Russia," his "Wandering Jew," his illustrations to Balzac's "Contes Drôlatiques," to Rabelais, and many other authors. His best work was done at an age when most artists are painfully acquiring the rudiments of their art. We all know the books that followed.
Meanwhile he was determined to be known as a great painter, and, while flooding the market with his countless illustrations, was working at great canvases of Biblical subjects, which, though the French would not accept them, were hugely admired in the Doré Gallery of London. Later he tried sculpture also, and his last work was a monument to Alexandre Dumas, which he made at his own expense, and presented to the city of Paris. He died in the beginning of the year 1883, worn out with excessive production—a great name, but an unsatisfied man.
Mr. Jerrold has divided his book into two parts, dealing first with Doré the illustrator, and then with Doré the painter and sculptor. It is an eminently natural arrangement, and, in our effort to arrive at Doré's true position in art, we cannot do better than to follow it.
Doré's earliest work was frankly that of a caricaturist. He had a quick eye, no training, and a certain extravagant imagination, and caricature was his inevitable field. He was, however, as Mr. Jerrold himself remarks, "a caricaturist who seldom raises a laugh." Not hearty fun, still less delicate humor, was his. In the higher qualities of caricature his contemporaries, Daumier and Gavarni, were vastly his superiors. An exuberance of grotesque fancy and a recklessness of exaggeration were his dominant notes. His earlier work, up to and including (p. 300) the Rabelais, is not really funny—to many minds it is even painful—but it is unmistakably caricature of a dashing, savage sort. To our mind it remains his best work, and that by which he is most likely to live. At least it is the work that formed him and fixed his characteristics, and an understanding of it is essential to any judgment of him. The qualities and the defects of his later work—that which is most praised and most blamed in his production—are inherent in the work of this period, and are best explained by a reference to the latter.
Take, for instance, what has been denounced as his love of horrors and of foulness, his delight in blood and massacre. He is scored for this as if he were one of that modern French school, beginning, perhaps, with Regnault, who have revelled in the realistic presentation of executions and battles, and have sought to effect by sheer sensationalism what they could not by gentler means. It is surprising that his critics have not seen that Doré's battles are always, even to the end, the battles of a caricaturist. His decapitated trunks, cloven heads, smoking hearts, arms still fighting though severed from their bodies, are simply a debauch of grim humor. There is never the slightest attempt to realize carnage—only to convey, by the caricaturist's exaggeration, an idea of colossally impossible bloodthirstiness. One may not enjoy this kind of fun, but to take it seriously, as the emanation of a gloomy and diabolic genius, is absurd.
The same test is equally destructive of much of the praise Doré has received. He is constantly spoken of, even by severe critics of his painting, as a great illustrator who identified himself with the minds of one great writer after another. But Doré identified himself with no one; he was always Doré. Even in these early drawings he cannot keep to the spirit of the text, though the subjects suited him much better than many he tried later. There is a great deal of broad gayety and "Gallic wit" in the "Contes Drôlatiques," but it was not broad enough for Doré, and he has converted its most human characters into impossible grotesques.
Another thing for which Doré is praised is his wonderful memory. Mr. Jerrold repeats more than once Doré's phrase, "I have lots of collodion in my head," and recounts how he could scarcely be induced to make sketches from nature, but relied upon his memory. He also speaks of Doré's system of dividing and subdividing a subject, and noting the details in their places, so that he could reproduce the whole afterward. This question of work from memory is one of the most vital for an understanding of Doré, and one of general interest in all matters of art, and is worth attention. Of course, a man who made hundreds of drawings every year could not work much from nature, and came to rely upon his memory. But what is the nature of artistic memory, and how does it perform its task? We think the truth is, that the artist who habitually works from memory, fills in his details, not from memory of the object, but from memory of the way he has formerly drawn similar objects. He reverts to a series of formulæ that he has gradually accumulated. This man must have a cloak. This is the way a cloak is done. A hand? Nothing can be easier; the hand formula is ready. The stock in trade of the professional illustrator and caricaturist is (p. 301) made up of a thousand such formulæ—methods of expression that convey the idea readily enough to the spectator, but have little relation to fact. So it is that Doré never learned, in the true sense, to draw. He had made for himself a sort of artistic shorthand, which enabled him to convey his superabundant ideas quickly and certainly to his public, but his drawing is what is called mannered in the extreme. It is not representation of nature at all, but pure formula and chic. He is said to be a master of drapery, but he never drew a single fold correctly. He is said to show great knowledge of Gothic architecture, but he never drew well a single column or finial. In his later years he studied anatomy with great perseverance, and advocated the necessity of dissection, saying, "Il faut fourrer la main dedans" (You must stick your hand in it); but the manner was formed, and he never drew a leg with a bone in it.
With this equipment he illustrated Don Quixote, Dante, the Bible. Is it strange that he shows no sympathy with the grand simplicity of Dante, or the subtle humor of Cervantes, and that we can only be thankful that he never completed his projected illustrations to Shakespeare? Doré, the illustrator, was fecund beyond precedent, possessed a certain strange drollery, had a wonderful flow of ideas, but was superficial, theatrical, and mannered, and as far from expressing real horror as from expressing real fun. What shall we say of Doré the painter and sculptor?
Mr. Jerrold reports a discussion between Doré and Théophile Gautier, in which the roles of artist and man of letters are strangely reversed. "Gautier and Doré," he says, "disagreed fundamentally on the aims and methods of art. Gautier loved correctness, perfect form—the technique, in short, of art; whereas Doré contended that art which said nothing, which conveyed no idea, albeit perfect in form and color, missed the highest quality and raison d'être of art." What is plain from this is, that Gautier was an artist and cared first of all for art, while Doré was never an artist, properly speaking, at all, and never understood the artist's passion for perfection. To Doré, what was necessary was to express himself anyhow—who cared if the style was defective, the drawing bad, the color crude? The idea was the thing. His admirers can defend him only on this ground, and they adopt of necessity the Philistine point of view. The artists of Doré's time and country were very clear in their opinion. "The painters," says Mr. Jerrold, "said he could not paint."
The sculptors admitted that he had ideas in his groups, but he was not sculpturesque. His friends protest against this judgment, and attribute it, ad nauseam, to "malevolence" and "envy." What if his technique was less brilliant than that of Hals, they say; what if his shadows are less transparent than those of Rembrandt (and they will make no meaner comparison)? He is "teeming with noble thoughts," and these will put his work "on a level with the masterpieces of the Italian masters of the sixteenth century." It is the conception, the creation—not the perfect painting of legs and arms and heads, the harmonious grouping, the happy and delicate combination of color—by which the observer is held spell bound. All these qualities, which his admirers grudgingly admit that Doré had (p. 302) not, are classed as "mere dexterity," and are not considered worth a second thought.
This is the true literary gospel of art, but it is one that no artist, and no critic who has any true feeling of art, has ever accepted or will ever accept. Thoughts, ideas, conceptions, may enhance the value of a work of art, provided it is first of all a piece of beautiful art in itself, but they have never preserved, and never will preserve from oblivion bad painting or bad sculpture. The style is the artist, if not the man; and of the two, beautiful painting with no idea at all (granting, for the sake of argument, that it exists), will ever be infinitely more valuable to the world than the lame expression of the noblest thoughts. What may be the real value of Doré's thoughts is therefore a question with which we have no concern. As painter and sculptor, his lack of education and his great technical imperfections—his bad drawing, false light and shade, and crude color—relegate him forever to a rank far below mediocrity. Such reputation as he has is the result of the admiration of those altogether ignorant of art, but possessed of enough literary ability to trumpet abroad their praises of "great conceptions," and will as surely fade away to nothing as the reputation of such simple painters as Van Der Meer or Chardin will continue to grow, while painting as an art is loved and understood.[Back to Contents]
George Frederick Handel, of whom Haydn once reverently said, "He is the master of us all," was born at Halle, in Lower Saxony, on February 23, 1685. His father was a surgeon, and sixty-three years of age at the time of his birth—a terribly severe old man, who, almost before his son was born, had determined that he should be a lawyer. The little child knew nothing of the fate before him, he only found that he was never allowed to go near a musical instrument, much as he wanted to hear its sweet sounds, and the obstinate father even took him away from the public day-school for the simple reason that the musical gamut was taught there in addition to ordinary reading, writing, and arithmetic.
But love always "finds out the way," and his mother or nurse managed to procure for him the forbidden delights; a small clavichord, or dumb spinet, with the strings covered with strips of cloth to deaden the sound, was found for the (p. 303) child, and this he used to keep hidden in the garret, creeping away to play it in the night-time, when everyone was asleep, or whenever his father was away from home doctoring his patients.

But, at last, when George Frederick was seven years of age, the old man was compelled to change his views. It happened in this way. He set out one day on a visit to the court of the Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels, where another son by a former marriage was a page. George Frederick had been teasing his father to let him go with him to see his elder brother, whom he had not yet met, but this was refused. When old Handel started by the stagecoach the next morning, the persistent little fellow was on the watch; he began running after it, and at length the father was constrained to stop the coach and take the boy in. So, though at the expense of a severe scolding, the child had his way and was allowed to go on to Saxe-Weissenfels. When there, the chapel, with the beautiful organ, was the great attraction, and George Frederick, as indomitable then as he was in after-life, found his way into the organ loft, and when the regular service was over, contrived to take the organist's place, and began a performance of his own; and strange to say, though he had not had the slightest training, a melody with chords and the correct harmonies was heard. The duke had not left the chapel, and noticing the difference in style from that of the ordinary organist, inquired as to the player, and when the little boy was brought to him he soon discovered, by the questions he put, the great passion for music which possessed the child. The duke, a sensible man, told the father it would be wrong to oppose the inclination of a boy who already displayed such extraordinary genius; and old Handel, either convinced, or at any rate submitting to the duke's advice, promised to procure for his son regular musical instruments. Handel never afterward forgot the debt of gratitude he owed to the Duke of Saxe-Weissenfels for this intercession.
On his return to Halle he became the pupil of Zachau, the organist of the cathedral there. This man was an excellent teacher and a sound musician. Before the pupil was nine years old his instructor used to set him to write fugues and motets as exercises, and before long the boy was allowed to play the organ at the cathedral services on Sunday, whenever the elder musician was inclined to linger over his breakfast or to take a holiday. At last, when young Handel was nine years old, the master honestly confessed that his pupil knew more music than he himself did, and advised that he should be sent to Berlin for a course of further study there. Thither he accordingly went in the year 1696.
In Berlin the boy of eleven years was soon recognized as a prodigy. There he met two Italian composers of established reputation, Bononcini and Attilio Ariosti, both of whom he was to encounter in after-life, though under very different circumstances, in London. Bononcini, who was of a sour and jealous disposition, soon conceived a dislike for the gifted little fellow, and attempted to (p. 304) injure him by composing a piece for the harpsichord full of the most extraordinary difficulties, and then asking him to play it at sight. The boy, however, at once executed it without a mistake, and thus the malicious schemer was foiled by his own device. Attilio was of a different disposition; he praised the young musician to the skies, and was never weary of sitting by his side at the organ or harpsichord, and hearing him improvise for hours. The Elector of Brandenburg also conceived a great admiration for the boy's talents, and offered to send him to Italy. On old Handel being consulted, however, he pleaded that he was now an old man, and wished his son to remain near him. In consequence of this, probably much to the boy's disappointment, he was brought back to Halle, and there set to work again under his old master, Zachau.
Soon after this return his father died, in 1697, leaving hardly anything for his family, and young Handel had now to seriously bestir himself to make a living. With this object he went to Hamburg, where he obtained a place as second violin in the Opera-house. Soon after arriving there, the post of organist at Lübeck became vacant, and Handel was a candidate for it. But a peculiar condition was attached to the acceptance of the office; the new organist must marry the daughter of the old one! And, as Handel either did not approve of the lady, or of matrimony generally (and in fact he never was married), he promptly retired from the competition. At first, no one suspected the youth's talents, for he amused himself by pretending to be an ignoramus, until one day the accompanyist on the harpsichord (then the most important instrument in an orchestra) was absent, and young Handel took his place, astonishing everybody by his masterly touch. Probably this discovery aroused the jealousy of some of his brother-artists, for soon afterward a duel took place between him and Matheson, a clever composer and singer, who one night, in the midst of a quarrel on leaving the theatre, gave him a box on the ear; swords were drawn, and the duel took place there and then under the portico of the theatre. Fortunately Matheson's weapon was shivered by coming in contact with a metal button on his opponent's coat. Explanations were then offered, and the two adversaries became friends—indeed, close friends—afterward. "Almira, Queen of Castile," Handel's first opera, was brought out in Hamburg in 1705, and was followed by two others, "Nero," and "Daphne," all received with great favor, and frequently performed.
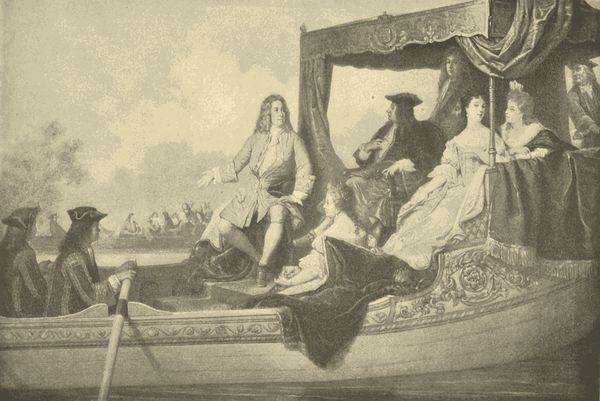

Handel's River-Concert for George I.
But the young musician determined to visit Italy as soon as possible, and after staying in Hamburg three years, and having, besides the money he sent his mother, saved two hundred ducats for travelling expenses, he was able to set off on the journey, then one of the great events in a musician's lifetime. He visited Florence, Venice, Rome, and Naples, in almost every city writing operas, which we are told were produced with the most brilliant success. At Venice an opera was sought for from him, and in three weeks he had written "Agrippina." When produced, the people received it with frantic enthusiasm, the theatre resounding with shouts of "Viva il caro Sassone!" (Long live the dear Saxon!) The following story illustrates the extraordinary fame he so quickly acquired in Italy. He (p. 305) arrived at Venice during the middle of the carnival, and was taken to a masked ball, and there played the harpsichord, still keeping on his mask. Domenico Scarlatti, the most famous harpsichord player of his age, on hearing him, exclaimed, "Why, it's the devil, or else the Saxon whom everyone is talking about!" In 1709 he returned to Hanover, and was appointed by the Elector George of Brunswick, afterward King George I., of England, his Court Capellmeister.
Handel's wanderings next led him to England, where he was treated with so much honor that he showed no great hurry to return to Hanover, and, in fact, he remained in England and coolly ignored his engagement as Capellmeister. But an awkward piece of retribution was at hand. The Elector of Hanover, on the death of Queen Anne, came to England as the new king, and Handel, his delinquent Capellmeister, could hardly expect to receive any share of the royal favor in future. With the help of a friend of his, Baron Kilmanseck, he determined, however, to make an attempt to conciliate the king, and accordingly he wrote twenty-five short concerted pieces of music, and made arrangements for these to be performed by musicians in a boat following the royal barge on the Thames, one day when the king went on an excursion up the river for a picnic. The king recognized the composer at once by his style, and spoke in terms of approbation of the music, and the news was quickly conveyed by his friend to the anxious musician. This is the story of the origin of the famous "Water Music." Soon afterward the king allowed Handel to appear before him to play the harpsichord accompaniments to some sonatas executed by Geminiani, a celebrated Italian violinist, and finally peace was made between them, Handel being appointed music-master to the royal children, and receiving an additional pension of £200. In 1726 a private Act of Parliament was passed, making George Frederick Handel a naturalized Englishman.
In the year 1720 a number of noblemen formed themselves into a company for the purpose of reviving Italian opera in London, at the Haymarket Theatre, and subscribed a capital of £50,000. The king himself subscribed £1,000, and allowed the society to take the name of the Royal Academy of Music, and at first everything seemed to promise the most brilliant success. Handel was appointed director of the music. Bononcini and Attilio Ariosti, his old acquaintances in Berlin, were also attracted by this new operatic venture to London, and their arrival was followed by a competition of a very novel character. The libretto of a new opera, "Muzio Scævola," was divided between the three composers. Attilio was to put the first act to music, Bononcini the second, and Handel the third. We need hardly wonder that the victory is said to have rested with the last and youngest of the trio, although at this time the cabals against him, which afterward were to do him such grievous harm, had already commenced.
Handel still clung to the operatic speculation; and when he had to leave the Haymarket Theatre, which was given up to another Italian company with the famous Farinelli, from Lincoln's Inn Fields, undauntedly he changed to the Lincoln's Inn Fields Theatre, and there commenced again. More operas were produced, with the one unvarying tale of fiasco, and at last, in 1737, having lost the (p. 306) whole of his hardly earned money, Handel was compelled to close the theatre, and, worse than all, to suspend payment for a time. Happily he now turned his thoughts to oratorio. "Saul" and "Israel in Egypt" were composed in quick succession; the last gigantic work being written in the almost incredibly short space of twenty-seven days. How great it is everyone now knows, but, at the time the colossal choruses were actually considered a great deal too heavy and monotonous; and Handel, always quick in resource, at the second performance introduced a number of operatic songs to make them go down better, and after the third performance the piece was withdrawn altogether. Fortunately, opinions have changed since then. These works were followed by his fine setting of Dryden's "Ode on St. Cecilia's Day," and Milton's "L'Allegro" and "Il Penseroso;" but it cannot be said that his pecuniary affairs were materially improved by their production.
The first performance of his greatest oratorio, the "Messiah," took place at Neale's Music Hall, in Dublin, on April 18, 1742, at mid-day, and, apropos of the absurdities of fashion, it may be noticed that the announcements contained the following request: "That ladies who honor this performance with their presence, will be pleased to come without hoops, as it will greatly increase the charity by making room for more company." The work was gloriously successful, and £400 were obtained the first day for the Dublin charities. Handel seems always to have had a special feeling with regard to this masterpiece of his—as if it were too sacred to be merely used for making money by, like his other works. He very frequently assisted at its performance for the benefit of the Foundling Hospital, and he left the score as a precious gift to the governor of that institution. This work alone brought no less a sum than £10,299 to the funds of the hospital. In this connection a fine saying of his may be repeated. Lord Kinnoul had complimented him on the noble "entertainment" which by the "Messiah" he had lately given the town. "My Lord," said Handel, "I should be sorry if I only entertained them—I wish to make them better." And when someone questioned him on his feelings when composing the "Hallelujah Chorus," he replied in his peculiar English, "I did think I did see all heaven before me, and the great God himself." What a fine saying that was of poor old George III., in describing the "pastoral symphony" in this oratorio—"I could see the stars shining through it!"
The now constant custom of the audience to rise and remain standing during the performance of this chorus, is said to have originated in the following manner: On the first production of the work in London, "the audience were exceedingly struck and affected by the music in general; but when that chorus struck up, 'For the Lord God Omnipotent' in the 'Hallelujah,' they were so transported that they all together, with the king (who happened to be present), started up and remained standing till the chorus ended." "This anecdote I had from Lord Kinnoul." So says Dr. Beattie, the once famous poet, in one of his letters.
The "Messiah" was commenced on August 22, 1741, finished on September (p. 307) 12th, and the orchestration filled up two days afterward—the whole work thus being completed in twenty-three days. Handel was fifty-six years old at the time.
The next ten years of the life of the "Goliath of Music," as he has been called, are marked by some of the most splendid achievements of his genius. "Samson," the "Dettingen Te Deum," "Joseph," "Belshazzar," "The Occasional Oratorio," "Judas Maccabeus," "Joshua," "Solomon," and, "Theodora," being composed by him during this time, when, already an old man, it might have been thought that he would have taken some repose after the labors of so toilsome and troubled a life. But, oak-like, he was one of those who mature late; like Milton, his greatest works were those of his old age.
But a terrible misfortune was approaching—his eyesight was failing. The "drop serene," of which Milton speaks so pathetically, had fallen on his eyes, and at the time when, in February, 1752, he was composing his last work, "Jephtha" (the one containing "Deeper and Deeper Still," and "Waft her, Angels"), the effort in tracing the lines is, in the original MS., very painfully apparent. Soon afterward he submitted to three operations, but they were in vain, and henceforth all was to be dark to him. His sole remaining work was now to improvise on the organ, and to play at performances of his oratorios. There is a pathetic story told of an incident that occurred on one occasion, when "Samson" was given. While the magnificent air,
Total eclipse! no sun, no moon!
All dark, amidst the blaze of noon.
O glorious light! no cheering ray
To glad my eyes with welcome day.
Why thus deprived thy prime decree?
Sun, moon, and stars are dark to me—
was being sung by Beard, the tenor, the blind old man, seated at the organ, was seen to tremble and grow pale, and then, when he was led forward to the audience to receive their applause, tears were in the eyes of nearly everyone present at the sight. It was like the scene that is described in Beethoven's life on the occasion of that composer's appearance, when almost totally deaf, to conduct his great Choral Symphony at Vienna.
One night, on returning home from a performance of the "Messiah" at Covent Garden, Handel was seized with sudden weakness and retired hurriedly to bed, from which he was never to rise again. He prayed that he might breathe his last on Good Friday, "in hope of meeting his God, his sweet Lord and Saviour on the day of his resurrection." And strangely enough his wish was granted, for on Good Friday, April 13, 1759, he quietly passed away from this life, being then seventy-four years of age. His remains were laid in Poets' Corner in Westminster Abbey, and the place is marked by a statue by Roubilliac, representing him leaning over a table covered with musical instruments, his hand holding a pen, and before him is laid the "Messiah," open at the words, "I know that my Redeemer liveth."[Back to Contents]

Leopold Mozart was a violinist in the band of Archbishop Sigismund, the reigning Prince of Salzburg, and it was probably in compliment to his master that he bestowed on the youngest of his seven children the name of Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Sigismundus. Born on January 27, 1756, this child was destined to make the name of Mozart famous wherever music is known; and surely no more beautiful life—beautiful in itself and in the works of immortal beauty which in its short course were produced—has ever been lived by anyone of those to whom the crown of inspired singers and an enduring monument in the temple of art has been given. "Look around," was the epitaph on a great architect. "Listen," is the most fitting tribute to the wonderful genius of a Mozart.
Infant prodigies very often turn out to be nobodies in after-life. But Mozart was an exception; and though he might well have been called "the marvellous boy," his latest works—and he died at the early age of thirty-five—were undoubtedly his grandest and most perfect. He began very early to compose. One of these first attempts was a concerto so difficult that no one could play it; but the child undauntedly said, "Why, that's the very reason why it is called a concerto; people must practise it before they can play it perfectly."
Wolfgang and his sister, Nannerl, as he used to call her, had been taken by their father, in 1762, to Vienna, where the children played the piano before the Empress Maria Theresa and her husband. Little Wolfgang was here, as everywhere, perfectly at his ease, with a simplicity and childish grace that won every heart. When he had been playing for some time, he jumped without ceremony on the lap of the empress, and kissed her heartily for being so good to him. Little Marie Antoinette, her daughter, afterward the ill-fated wife of Louis XVI., and then about the same age as Wolfgang, he treated in almost the same way. He had slipped on the polished floor, to which he was unaccustomed, and the little princess had hurried forward to raise him up, on which he promptly said, "You are good; I will marry you." The empress asked why he wished this, to which he answered, "Out of gratitude; she was kind, while her sister took no notice of me" (she had not come forward to help him). After returning (p. 309) to Salzburg, Leopold Mozart, in the spring of 1763, took his children on a more lengthy tour to Munich, Paris, London, and The Hague, and everywhere their playing, especially Wolfgang's performances on the organ, which he had now learned, were listened to with delight and astonishment. At Heidelberg the priest of the Church of the Holy Ghost engraved on the organ the boy's name and the date of his visit, in remembrance of "this wonder of God," as he called the child. At London, old Mozart says, they were received, on April 27th, by King George III. and Queen Caroline, at the palace, and remained from six to nine o'clock. The king placed before the boy compositions of Bach and Handel, all of which he played at sight perfectly; he had also the honor of accompanying the queen in a song. "On leaving the palace," the careful father says, "we received a present of 24 guineas."
A great delight was now before him, for his father had resolved on a journey to Italy, then far more than now the land of music. How much this visit did for the young maestro it is impossible to say; he has not, like Mendelssohn, left us an "Italian Symphony," recording the impressions which that sunny spot of classic beauty had made upon him, but there can be little doubt of the great influence it had on the whole of his after-life. There are some significant words which he wrote eight years later to his father from Paris: "You must faithfully promise to let me see Italy again in order to refresh my life. I do entreat of you to confer this happiness upon me." In Mantua, Milan, Bologna (where he had the good fortune to meet the learned Padre Martini, one of the soundest musicians of his age, and for whom he ever afterward maintained a warm attachment), Florence, Rome, and Naples, the young genius was received everywhere with enthusiasm by the crowds who came to hear him. In Naples the superstitious people believed that there was magic in his playing, and pointed to a ring on his left hand as the cause of his wonderful dexterity; and it was only when he had taken this off, and gone on playing just the same, that they had to acknowledge it was simply the perfection of art.
There is something sad in contrasting these brilliant early days with the anxious times that came later on, when the great Mozart was compelled to wait in the ante-chambers of the great, dine with their lacqueys, give lessons to stupid young countesses, and write begging letters to his friends; yet, in reality, those later days, when "Don Giovanni," "Die Zauberflöte," and the "Requiem," were composed, were the truly brilliant ones. And it may be that the very greatness came, in some measure, from the sorrow and pain; that Mozart, like so many others of the world's great singers, "learnt in suffering what he taught in song."
On his return to Munich, after composing a comic opera in the Italian style, "La Finta Giardiniera," which had a great success, young Mozart, who had been very shabbily treated by Archbishop Hieronymus—of whose spiteful conduct we shall hear more hereafter—the successor of Sigismund, determined to resign his situation in the court band, and to set out on his travels again, giving concerts from place to place, and everywhere looking out for some suitable appointment that might afford him a permanent income. This time his father was refused (p. 310) permission to travel, and, as on his exertions depended the support of the whole family, he remained behind, while Frau Mozart, the mother, accompanied young Wolfgang. In 1777, now a young man of twenty-one, he set out upon his second great artistic tour, buoyant with hope, and with all the beautiful audacity of young genius determined to conquer the world. This time it was not the infant prodigy whom men listened to, but the matured musician and the composer of melodies sweeter than men had ever listened to before. But the tale is changed now. True, there are triumphs to be spoken of, flattery from the great, and presents sent in recompense for his marvellous playing (he tells one day of his chagrin in receiving from a certain prince a gold watch, instead of money that he sorely wanted—and, besides, he had five watches already!); but rebuffs, intrigues, and all sorts of petty machinations against him, make the tale a sadder one; and so it continued to be to the end.
From Munich—where it had been hoped that the elector would have given him an appointment at court, but he was only told to go to Italy and become famous, "it was too early yet to think about becoming a Capellmeister"—he went to Augsburg, spending some pleasant days there in the society of a cousin, Marianne, nicknamed by him Bäsle, a merry, open-hearted girl of nineteen.
Thence, he went on to Mannheim, a town that is memorable as the place where he first met the Webers, and made the acquaintance of Herr Cannabich, the director of the music at the elector's court, and one who proved a stanch friend through everything to the young composer. Cannabich had a daughter named Rosa, a girl of thirteen, exceedingly pretty and clever, and Wolfgang appears to have admired her very much, and perhaps for a time to have flirted and been in love with her. He wrote her a sonata, and was delighted with the way in which she played it; the andante, he said, he had composed to represent her, and when it was finished he vowed she was just what the andante was. But this little love affair, if it existed, soon was forgotten in a more serious one with Aloysia Weber. Her father was a theatre copyist in poor circumstances. There were a number of children, and she was a beautiful girl of fifteen, with a magnificent voice. She was cousin, by the way, to Weber, afterward composer of the "Freischütz." Mozart was so charmed with her voice that he undertook to give her lessons, and we soon hear of him composing airs for her and meditating a concert tour in Italy in company with her, and her father and sister. In writing of it to his own father he sets out the advantages to be gained by co-partnership, and very prosaically says: "Should we stay long anywhere, the eldest daughter [Josepha, afterward Frau Hofer, for whom Mozart wrote the part of Astrafiammente in the "Zauberflöte"] would be of the greatest use to us; for we could have our own ménage, as she understands cooking." But papa Mozart decidedly objected. "Your proposal to travel about with Herr Weber—N. B., two daughters—has driven me nearly wild," and he straightway orders his son off to Paris, whither, with a parting present of a pair of mittens knitted for him by Mlle. Weber, he reluctantly sets out in company with his mother.
His stay in Paris during the next year was not very eventful, and a symphony (p. 311) produced at the Concerts Spirituels seems to have been his most successful work at this time. It was clever and lively, full of striking effects, and was most warmly applauded. He says: "The moment the symphony was over I went off in my joy to the Palais Royal, where I took a good ice, told my beads, as I had vowed, and went home, where I am happiest and always shall be happiest." A great sorrow came to him here in the death of his mother. Owing to the great expense of living in Paris, they had been compelled to live together in a small, dark room, so cramped for space that there was not even room for the indispensable piano. Here she was taken ill, and though for fourteen days Wolfgang most devotedly attended to her wants, she died in his arms. The letters in which he breaks the news to his father and sister are full of the most beautiful tenderness and forgetfulness of his own grief in solicitude for theirs. Things did not indeed prosper with him in Paris; he tried to give lessons, but the ladies whom he taught paid him very shabbily, and the labor of getting from one part of the city to another to teach was so great that he found it difficult to give the time he wished to composition.
Music in Paris, just then, was at a low ebb. Vapidly pretty Italian operas were in fashion, and Piccinni was the favorite composer. It was some years afterward that the great contest between the Piccinnists and Gluckists culminated in the victory of the latter, though "Alceste," had already been produced, and "Iphigenia" was soon to follow. Mozart was a fervent admirer of Gluck, and the music of the older master had evidently an important influence on that of the younger and more gifted composer.
Once more his thoughts were turned to Salzburg, for two of the leading musicians there having died, the Archbishop Hieronymus offered their posts to the Mozarts, father and son, at a salary of a thousand florins for the two. The father anxiously entreated his son to return and accept this offer, mentioning as a further bait, that Aloysia Weber would probably be engaged to sing in Salzburg. Much as Wolfgang hated Salzburg, or rather the people living there, his love for his father and sister prevailed over his aversion; and though with no pleasure at all in the prospect of seeing the hateful archbishop again, he set out from Paris, travelling to Salzburg in very leisurely fashion via Strasbourg, Mannheim, and Munich. At Strasbourg he was induced to give several concerts, but they were not pecuniary successes, and he did not make by any one more than three louis d'or. But how the artist peeps out in every line of the letters in which he describes these! After saying how few were present, and how cold it was, he proceeds: "But I soon warmed myself, to show the Strasbourg gentlemen how little I cared, and played to them a long time for my own amusement, giving a concerto more than I had promised, and at the close extemporizing. It is now over, but at all events I gained honor and fame."
At Munich a great shock awaited him. He visited the Webers, and being in mourning for his mother, wore, after the French fashion, a red coat with black buttons. When he appeared, Aloysia hardly seemed to recognize him, and her coldness was so marked, that Mozart quietly seated himself at the piano, and (p. 312) sang in a loud voice, "Ich lass das Mädchen gern das mich nicht will" (I gladly give up the girl who slights me). It was all over, and he had to bear the loss of the fickle girl as best he might. There is a significant line in one of his letters at this time to his father: "In my whole life I never wrote worse than I do to-day, but I really am unfit for anything; my heart is so full of tears." After two years' absence he returned home to Salzburg, where he was warmly welcomed back. Here he remained for a little while, and wrote his first serious opera, "Idomeneo," to the text of an Abbe Varesco, a Salzburger. This opera Beethoven thought the finest of all that Mozart wrote. It was brought out at Munich in January, 1781, and was brilliantly successful. In the March following, an order was received from the archbishop to follow him to Vienna, where he wished to appear with all the full pomp and brilliant retinue of a prince of the church; and as one of this retinue Mozart had to follow him, little thinking at the time that he should never return to Salzburg, but that Vienna henceforth was to be his home.
In Vienna he found that he had to live in the archbishop's house, and was looked upon there as one of the ordinary servants. He says, "We dine at eleven o'clock in the forenoon, unluckily rather too early an hour for me. Our party consists of the two valets, the comptroller, Herr Zetti, the confectioner, the two cooks, Cecarilli, Brunetti (two singers), and my insignificant self. N. B.—The two valets sit at the head of the table. I have, at all events, the honor to be placed above the cooks; I almost believe I am back to Salzburg."
Mozart was a true gentleman, with no foolish false pride, but with the honorable self-respect that every gentleman must possess, and it was very galling to him to have to suffer such odious treatment from the mean-spirited archbishop. Indeed, it was only for his father's sake that he submitted to the continued contumely and petty slights to which the archbishop delighted in subjecting him. At last the open rupture came. The archbishop called him a knave and dissolute fellow, and told him to be off; and when Mozart waited upon Count Arco, the principal official, to obtain the regular dismissal that was necessary, the fellow poured abuse upon him, and actually kicked him out of the room. Poor Mozart was in a state of violent excitement after this outrage, and for some days was so ill that he could not continue his ordinary work. But now at least he was free, and though his father, like a timid, prudent old man, bewailed the loss of the stipend which his son had been receiving, Mozart himself knew that the release was entirely for the best.
In 1782 appeared "Die Entführung aus dem Serail," his first really important opera, full of beautiful airs, which at once became enormously popular with the Viennese. The Emperor Joseph II. knew very little about music, but, as frequently happens in such cases, considered that he possessed prodigious taste. On hearing it he said, "Much too fine for our ears, dear Mozart; and what a quantity of notes!"
The bold reply to this was, "Just as many notes as are necessary, your Majesty."
(p. 313) Much of the delight which Mozart felt in the success of the opera arose from the fact that it enabled him seriously to contemplate marriage. Aloysia Weber had been faithless to him, but there was another sister—with no special beauty save that of bright eyes, a comely figure, and a cheerful, amiable disposition—Constanze, whom he now hoped to make his wife. His father objected to all of the Weber family, and there was some difficulty in obtaining the paternal consent; but at last the marriage took place, on August 4, 1782. How truly he loved his wife from first to last, his letters abundantly show; her frequent illnesses were afterward a great and almost constant source of expense to him, but he never ceased to write to her with the passionate ardor of a young lover. He says: "I found that I never prayed so fervently, or confessed so piously, as by her side; she felt the same." And now for some time everything went smoothly in the modest little ménage in Vienna. Mozart had plenty of lessons to give, but none of the commissions for operas which he would have wished.
Passing over a visit to Leipsic—where he studied with the keenest delight a number of the unpublished works of the great Sebastian Bach—and to Berlin, he returned to Vienna, and at once set to work upon some quartets which the King of Prussia had ordered from him. "Cosi fan tutte," a comic opera, with the beautifully flowing music that only Mozart could write, but with a stupid plot that has prevented its frequent repetition in later times; and the glorious "Zauberflöte," written to assist a theatrical manager, Schikaneder, were his next works. At this time a strange melancholy began to show itself in his letters—it may be that already his overwrought brain was conscious that the end was not far distant. Such lines as these, pathetic and sad in their simple and almost childlike expression, occur in a letter he wrote during a short absence from his wife, at Frankfort, in 1790: "I am as happy as a child at the thought of returning to you. If people could see into my heart I should almost feel ashamed—all there is cold, cold as ice. Were you with me, I should possibly take more pleasure in the kindness of those I meet here, but all seems to me so empty." On his return to Vienna pecuniary want was rather pressingly felt; his silver plate had to be pawned, and a perfidious friend, Stadler, made away with the tickets, and the silver was never redeemed. On one occasion Joseph Deiner, the landlord of the "Silberne Schlange," chanced to call upon him, and was surprised to find Mozart and his wife Constanze dancing round the room. The laughing explanation was that they had no firewood in the house, and so were trying to warm themselves with dancing. Deiner at once offered to send in firewood, Mozart promising to pay as soon as he could.
That grand work, the "Zauberflöte," had just been completed when a strange commission was given him. One day a tall, haggard-looking man, dressed in gray, with a very sombre expression of countenance, called upon Mozart, bringing with him an anonymous letter. This letter contained an inquiry as to the sum for which he would write a mass for the dead, and in how short a time this could be completed. Mozart consulted his wife, and the sum of fifty ducats was mentioned. The stranger departed, and soon returned with the money, promising Mozart a further sum on completion, and also mentioned that he might as (p. 314) well spare the trouble of finding out who had given this commission, for it would be entirely useless. We now know that the commission had really been given by Count Walsegg, a foolish nobleman, whose wife had died, and who wanted, by transcribing Mozart's score, to pass it off as his own composition—and this he actually did after the composer's death. Poor Mozart, in the weak state of health in which he now was, with nerves unstrung and over-excited brain, was strangely impressed by this visit, and soon the fancy took firm possession of him that the messenger had arrived with a mandate from the unseen world, and that the "Requiem" he was to write was for himself. Not the less did he ardently set to work on it. Hardly, however, was it commenced than he was compelled to write another opera, "La Clemenza di Tito," for which a commission had been given him by the Bohemian Estates, for production on the occasion of the Emperor Leopold's coronation in their capital. This was accomplished in the short space of eighteen days, and though it does not contain the best music, yet the overture and several of the numbers are full of a piquant beauty and liveliness well suiting the festival of a people's rejoicing. But a far greater work, the "Zauberflöte," was produced in Vienna shortly afterward. It did not take very well at first, but subsequent performances went better.
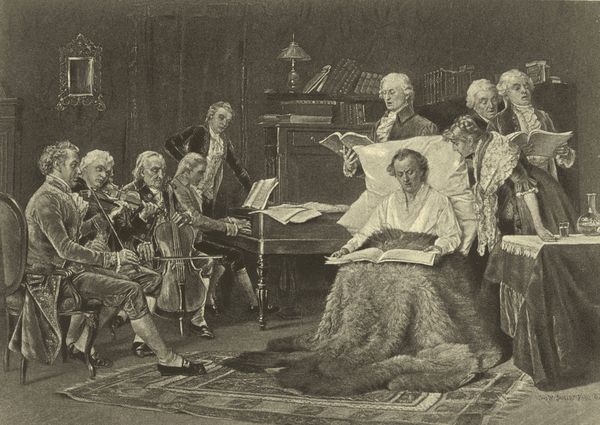

Mozart singing his Requiem.
His labors in bringing out the "Zauberflöte" over, Mozart returned to the "Requiem" he had already commenced, but while writing he often had to sink back in his chair, being seized with short swoons. Too plainly was his strength exhausted, but he persisted in his solemn work. One bright November morning he was walking with Constanze in the Prater, and sadly pointing out to her the falling leaves, and speaking of death, with tears in his eyes, he added; "I well know I am writing this 'Requiem' for myself. My own feelings tell me that I shall not last long. No doubt some one has given me poison—I cannot get rid of this thought." With these gloomy fancies haunting his mind, he rapidly grew worse, and soon could not leave his room. The performances of the "Zauberflöte" were still going on, and extraordinarily successful. He took the greatest interest in hearing of them, and at night would take out his watch and note the time—"Now the first act is over, now is the time for the great Queen of Night." The day before his death he said to his wife, "Oh, that I could only once more hear my 'Flauto Magico!'" humming, in scarcely audible voice, the lively bird-catcher song. The same day, at two o'clock in the afternoon, he called his friends together, and asked for the score of his nearly completed "Requiem" to be laid on his bed. Benedict Schack sang the soprano; his brother-in-law, Hofer, the tenor; Gerl, the bass; and Mozart himself took the alto in a weak but delicately clear voice. They had got through the various parts till they came to the "Lacrymosa," when Mozart burst into tears, and laid the score aside. The next day (Sunday), he was worse, and said to Sophie, his sister-in-law, "I have the taste of death on my tongue, I smell the grave, and who can comfort my Constanze, if you don't stay here?" In her account of his last moments, she says: "I found Süssmayer sitting by Mozart's bed. The well-known 'Requiem' was lying on the coverlet, and Mozart was explaining to Süssmayer the (p. 315) mode in which he wished him to complete it after his death. He further requested his wife to keep his death secret until she had informed Albrechtsberger of it, 'for the situation of assistant organist at the Stephen Church ought to be his before God and the world.' The doctor came and ordered cold applications on Mozart's burning head.... The last movement of his lips was an endeavor to indicate where the kettledrums should be used in the 'Requiem.' I think I still hear the sound."[Back to Contents]

No composer has ever given greater or purer pleasure by his compositions than is given by "papa" Haydn; there is an unceasing flow of cheerfulness and lively tone in his music, even in the most solemn pieces, as in his Masses, the predominant feeling is that of gladness; as he once said to Carpani: "At the thought of God my heart leaps for joy, and I cannot help my music doing the same." But it is not alone as the writer of graceful and beautiful music that Haydn has a claim on our remembrance; he has been truly called the "father of the symphony." Mozart once said: "It was from Haydn that I first learned the true way to compose quartettes;" and "The Creation," which must ever be counted one of the masterpieces of oratorio music, was his work.
His family were of the people, his father being a master wheelwright at Rohrau, a small Austrian village on the borders of Lower Austria and Hungary and his mother having been employed as a cook in the castle of Count Harrach, the principal lord of the district. Joseph Haydn was born on March 31, 1732 the second child of his parents; and as ten brothers and sisters afterward came into the world, it can easily be understood that his lot was not a very luxurious one. His parents were simple, honest people of the laboring class, very ignorant, but, like most German peasants, with a certain love for and facility in music, not quite so common in this country. Haydn's father had a good voice, and could sing well, accompanying himself on the harp, though he did not know a single note of written music. Then there was the village schoolmaster, who could actually play the violin, and whom little Joseph watched with wondering eyes, extracting (p. 316) those marvellously sweet sounds from his wooden instrument, until, with the child's spirit of imitation, as his parents sang their "Volkslieder," the little fellow, perched on a stone bench, gravely handled two pieces of wood of his own as if they were bow and fiddle, keeping exact time, and flourishing the bow in the approved fashion of the schoolmaster. From this very little incident came an important change in his life; for a relation, Johann Mathias Frankh, of Hainburg, happened to be present on one occasion, and, thinking he saw an aptitude for music in the boy, offered to take him into his own school at Hainburg, where accordingly young Haydn went at the age of six years.
There he remained for two years, making rapid progress in singing and in playing all sorts of instruments, among others the clavier, violin, organ, and drum. He said afterward, with the unaffected piety, far removed from cant, that was characteristic of him: "Almighty God, to whom I render thanks for all his unnumbered mercies, gave me such facility in music that, by the time I was six years old, I stood up like a man and sang masses in the church choir, and could play a little on the clavier and violin." Of Frankh, a very strict, but thorough and most painstaking teacher, he also said afterward: "I shall be grateful to that man as long as I live for keeping me so hard at work, though I used to get more flogging than food;" and in Haydn's will he remembered Frankh's family, leaving his daughter a sum of money and a portrait of Frankh himself, "my first instructor in music."
For some years he seems to have lived a miserable, struggling life, giving lessons, playing the organ in churches, and studying when and where he could. He had a few pupils at the moderate remuneration of two florins a month, and he had contrived to obtain possession of an old worm-eaten clavier, on which he used diligently to practise in the garret in the Kohlmarkt, where he lived. A pitiable description is given of the lodging he then occupied. It was on the sixth story, in a room without stove or window. In winter his breath froze on his thin coverlet, and the water, that in the morning he had to fetch himself from the spring for washing, was frequently changed into a lump of ice before his arrival in that elevated region. Life was indeed hard; but he was constantly at work, and, having made a precious "find" on an old bookstall one day of Fux's "Gradus ad Parnassum," in a very dilapidated condition, but very cheap, he was ardently preparing himself for the life—he now vowed should be his—of a composer.
About this time Haydn received a commission from Felix Kurz, a comic actor of the Stadt-Theatre, to put a farce of his, "Der neue krumme Teufel," to music. This farce, of which the words still remain, though the music has been lost, was very successful, and was played in Vienna, Prague, Berlin, and a number of other towns. The well-known story of Haydn's "Tempest Music" is connected with this. In one part of this piece a terrible storm was supposed to be raging, and the accompanying music must of course be suitably descriptive; but the difficulty was that Haydn had never seen the sea: therefore had not the slightest notion of what a storm at sea was like. Kurz tries to describe the (p. 317) waves running mountains high, the pitching and tossing, the roll of thunder, and the howling of the wind; and Haydn produces all sorts of ugly, jerky, and noisy music, but none of it is in the remotest degree like a storm at sea, or anywhere else. At last, after Kurz had become hoarse with his nautical disquisitions, and Haydn's fingers were tired of scrambling all over the piano, the little musician in a rage crashed his hands down on the two extremes of the instrument, exclaiming: "Let's have done with this tempest!"
"Why, that's it; that's the very thing!" shouted the clown, jumping up and embracing him; and with this crash and a run of semitones to the centre of the piano this troublesome tempest was most satisfactorily represented.
When, many years afterward, Haydn was crossing the Straits of Dover to England, amid his sufferings he could not help laughing at the ludicrous recollections of this early experience of his.
Things still went on improving, and Haydn, who was always lucky in the patrons he secured (at least according to the notion about patrons that then prevailed), was invited to the country-house of Herr von Fürnberg, a wealthy amateur, to stay there and compose quartettes for him—a style of music for which von Fürnberg had an especial liking. To his prompting it is that we owe the lovely series of quartettes which Haydn wrote—still as fresh and full of serene beauty as when first tried over by the virtuosi of Weinzirl. The next piece of good fortune was Haydn's appointment as director of the band and composer to Count Ferdinand Morzin at Lukaver near Pilsen; and here, in 1759, his first symphony was written. His salary was very small, only 200 florins a year (or £20), with board and lodgings; but on the strength of it he unfortunately determined on the serious step of embarking in matrimony. A barber, named Keller, is said to have been very kind to him in the days of his poverty, and out of gratitude Haydn gave music-lessons to his daughters. One of them, the youngest, was very pretty, and Haydn fell in love with her. But she became a nun; and the father then prevailed upon Haydn to marry the elder one, who was three years older than he—a sour-tempered, bigoted, and abominably selfish woman, who contributed little to the happiness of his life, and was always bringing priests and friars to the house and worrying her good-tempered husband to compose masses and other church music for these men.
Count Morzin was compelled to give up his band in 1761; but Haydn did not remain long without employment, as Prince Esterhazy, who had heard his symphonies at Morzin's house, engaged him to assist Werner, his Capellmeister. As director of Prince Esterhazy's band, Haydn was fated to remain for many years living at Esterház, the prince's country-seat, composing there nearly all his operas and songs, and many of his symphonies.
In 1785 Haydn received a commission which showed the wide reputation he had then gained. The Chapter of Cadiz Cathedral requested him to write some instrumental music for performance on Good Friday. "The Seven Words of our Saviour on the Cross" was in consequence written by him.
Several invitations had been sent from England for Haydn to pay a visit (p. 318) there; but it was only after Prince Esterhazy was dead that he was prevailed on by Salomon to cross the sea. A characteristic conversation between him and Mozart—which took place before he undertook this, in those days, really formidable journey—is recorded.
"Papa," said Mozart, "you have no training for the great world, and you speak too few languages."
Haydn replied: "My language is understood by all the world."
He set out on December 15, 1790, and did not return to Vienna till July, 1792. In London, where he wrote and conducted a number of symphonies for Salomon, he was the "lion" of the season, being in constant request for conducting concerts and paying visits to the nobility. Of these symphonies Salomon once said to him: "I am strongly of opinion that you never will surpass this music."
"I never mean to try," was the answer.
But this must not be taken to mean that Haydn had given up striving after the truest perfection in his art, and it probably meant no more than that for the time he was satisfied with his work. Far more like the genuine expression of the feeling of the great artist was his utterance, just before he died, to Kalkbrenner: "I have only just learned in my old age how to use the wind-instruments; and now that I do understand them, I must leave the world."

Haydn composing his "Creation."
Great as the work accomplished in his youth and early manhood unquestionably was, it remained for his old age to accomplish his greatest work, and that by which he is best known—the oratorio of "The Creation." It is said that the first ideas for this came to him when, in crossing the English Channel, he encountered a terrific storm. Soon after his leaving London, where the words had been given him by Salomon, Haydn set about composing the music. "Never," he says, "was I so pious as when composing 'The Creation.' I knelt down every day and prayed God to strengthen me for my work." It was first produced on March 31, 1799, his 67th birthday, at the National Theatre, Vienna, and was at once accorded an extraordinary share of popular favor. There is a pathetic story of the last performance of the work, at which Haydn, in extreme old age, in 1808, was present, when Salieri conducted. He was carried in an arm-chair into the hall, and received there with the warmest greeting by the audience. At the sublime passage, "And there was light!" Haydn, quite overcome, raised his hand, pointing upward and saying, "It came from thence." Soon after this his agitation increased so much that it was thought better to take him home at the end of the first part. The people crowded round him to take leave, and Beethoven is said to have reverently kissed his hand and forehead. After composing "The Creation," Haydn was prevailed upon to write another work, of somewhat similar character, to words adapted from Thomson's poem, and entitled "The Seasons." This, though containing some fine descriptive music and several choruses of great beauty, is not at all equal to the earlier work, though at the time its success was quite as complete. But the exertion of writing two such great works, almost without rest between them, was too great, and he himself (p. 319) said: "'The Seasons' gave me the finishing stroke." The bombardment of Vienna by the French in 1809 greatly disturbed the poor old man. He still retained some of his old humor, and during the thunder of the cannons called out to his servants: "Children, don't be frightened; no harm can happen to you while Haydn is by!" He was now no longer able to compose, and to his last unfinished quartette he added a few bars of "Der Greis," as a conclusion:
"Hin ist alle meine Kraft:
Alt und schwach bin ich.
—Joseph Haydn."
"Gone is all my strength: old and weak am I." And these lines he caused to be engraved, and sent on a card to the friends who visited him. The end was indeed now near. On May 26, 1809, he had his servants gathered round him for the last adieus; then, by his desire, he was carried to the piano, where he played three times over the "Emperor's Hymn," composed by him. Then he was taken to his bed, where five days afterward he died.[Back to Contents]

In one of his letters to Frau von Streicher, at Baden, Beethoven writes: "When you visit the ancient ruins, do not forget that Beethoven has often lingered there; when you stray through the silent pine-forests, do not forget that Beethoven often wrote poetry there, or, as it is termed, composed." He was always fond of claiming the title "Ton-dichter, poet in music;" and surely of all the great geniuses who have walked the earth, to none can the glorious name of "poet" more truly be given than to Ludwig von Beethoven.
He was born at Bonn, on December 17, 1770. His father, Johann von Beethoven, was a tenor singer in the Electoral Chapel of the Archbishop of Cologne, at Bonn, and his mother, Maria Magdalena, was a daughter of the head cook at the castle of Ehrenbreitstein. The Beethoven family originally came from Louvain, in Belgium; but the composer's grandfather had settled in Bonn, first as a singer, and afterward as Capellmeister to the court. Musicians were not held of much account in those days, and the (p. 320) marriage of a singer with the daughter of a cook was not at all considered a mésalliance. Johann was a sad drunken scapegrace, and his poor wife, in bringing up her family upon the small portion of his earnings which she could save from being squandered at the tavern, had a pitiably hard and long struggling life of it.
Johann soon discovered the extraordinary musical endowments of his child and at once set to work to make a "prodigy" of him, as Handel, Bach, and Mozart had been before; for in this way the father hoped to secure a mine of wealth and lazy competence for himself. So the boy, when only a few years old, was kept for long weary hours practising the piano, and one of the earliest stories of his life is of the five-year-old little child made to stand on a bench before the piano laboring over the notes, while the tears flowed fast down his cheeks at the cold and aching pain, from which his hard taskmaster would not release him. Besides his father, a clever musician who lodged in the house, Pfeiffer, an oboist at the theatre, gave him lessons. Beethoven used afterward to say that he had learnt more from this Pfeiffer than from any one else; but he was too ready to abet the father in his tyranny, and many a time, when the two came reeling home late at night from drinking bouts at the tavern, they would arouse the little fellow from his sleep and set him to work at the piano till daybreak.
His next instructor was Neefe, the organist of the Archbishop's private chapel, a really skilful and learned musician, who predicted that the boy would become a second Mozart. Under him Beethoven studied for several years, and in 1782, when he was hardly twelve years old, we find him acting as organist in Neefe's place during the absence of the latter on a journey. The next year three sonatas composed by young Beethoven, and dedicated to the Elector in fulsome language, which was probably his father's production, were printed. Soon afterward the boy obtained the appointment of assistant-organist to the Elector, with a salary of a hundred thalers, no inconsiderable addition to the resources of his poor mother, who, with her family of three children, Ludwig, Carl, and Johann, and the more and more frequent visits of her ne'er-do-well of a husband to the tavern, was often grievously hard put to it for money. Young Ludwig had little play time in his life, and little opportunity for education; but amid his hard work some indications of a mischievous boyish spirit are to be found.
In the year 1791, the Elector, as head of the Teutonic Order, had to be present at a grand conclave at Mergentheim, and thither he resolved to take his musical and theatrical staff. Two ships were chartered to convey these gentlemen down the Rhine and Maine, and a very pleasant excursion, with all sorts of frolics and high revellings, they had of it. Lux, a celebrated actor, was chosen king of the expedition, and we find Beethoven figuring among the scullions.
In the autumn of the year following, a visit was paid by Haydn to Bonn on his return from his second journey to London. The musicians of the town gave a breakfast at Godesberg in his honor, and here Beethoven summoned up courage to show the veteran musician a cantata which he had recently composed. This was warmly praised by Haydn, and probably about this time arrangements were made for Beethoven to be received as a pupil by the older master. It is (p. 321) in this period that we must place a well-known anecdote. The young musician, already famous in his own neighborhood, was composing, as his custom was, in the wood outside the city, when a funeral cortége passed him. The priest, seeing him, instantly checked the dirge which was being chanted, and the procession passed in solemn silence, "for fear of disturbing him." In the beginning of November, 1792, the young musician left Bonn for Vienna, and, as it happened, he never afterward returned to the familiar scenes of his birthplace.
Beethoven was never a very easy man to get on with, and his intercourse with Haydn, who used to call him the "Great Mogul," does not seem to have been the most friendly. He was dissatisfied with the instruction given him, and suspicions were awakened in his mind that the elder musician was jealous of him, and did not wish him to improve. These thoughts were strengthened by the result of a chance meeting one day, as he was walking home with his portfolio under his arm, with Johann Schenk, a scientific and thoroughly accomplished musician. Beethoven complained to him of the little advance he was making in counterpoint, and that Haydn never corrected his exercises or taught him anything. Schenk asked to look through the portfolio, and see the last work that Haydn had revised, and on examining it he was astonished to find a number of mistakes that had not been pointed out. It is difficult to understand Haydn's conduct in this matter, for the perfidious treatment suspected by Beethoven is quite at variance with the ordinarily accepted character of the old man, and I cannot help fancying that the only foundation for Beethoven's suspicion was that Haydn did not quite understand the erratic genius of the youth till some time afterward. Beethoven dedicated his three pianoforte sonatas, Op. II., to Haydn, and when the latter suggested that he should add on the title page "Pupil of Haydn," the "Great Mogul" refused, bluntly saying "that he had never learnt anything from him." After Haydn, Albrechtsberger and Salieri were for a time his teachers, but Beethoven got on no better with them, and Albrechtsberger said, "Have nothing to do with him; he has learnt nothing, and will never do anything in decent style." Perhaps not in your pedant's style, O great contrapuntist!
Beethoven cannot be said to have been unfortunate in his friends. He had many true and faithful ones throughout his life, and though he suffered from pecuniary troubles, caused by the conduct of his brothers, he was never in such a state of grinding poverty as some other artists, such as Schubert, have been—never compelled to waste precious years of his life in producing "pot-boilers"—working not for art so much as for mere food and shelter. In 1794 Prince Karl Lichnowski, who had been a pupil of Mozart, and who, as well as his wife Christiane, was fanatico per la musica, proposed that Beethoven should come and live at his palace. They had no children; a suite of rooms was placed at the musician's disposal; no terms were proposed; the offer was the most delicate and friendly imaginable, and was accepted by Beethoven in the spirit in which it was made. For ten years he resided with the Lichnowskis, and these were probably the years of purest happiness in the great composer's life, although early in their (p. 322) course the terrible affliction of deafness began to be felt by him. He at this time freely frequented the salons of the Viennese nobility, many of whom were accomplished virtuosi themselves, and were able to appreciate the great genius of the new-comer, rough and bearish as oftentimes he must have appeared to them—a great contrast to the courtly Haydn and Salieri, who might be seen sitting side by side on the sofa in some grandee's music-room, with their swords, wigs, ruffles, silk stockings, and snuff-boxes, while the insignificant-looking and meanly dressed Beethoven used to stand unnoticed in a corner. Here is a description of his appearance given by a Frau von Bernhard: "When he visited us, he generally put his head in at the door before entering, to see if there were any one present he did not like. He was short and insignificant-looking, with a red face covered with pock-marks. His hair was quite dark. His dress was very common, quite a contrast to the elegant attire customary in those days, especially in our circles.... He was very proud, and I have known him refuse to play, even when Countess Thun, the mother of Princess Lichnowski, had fallen on her knees before him as he lay on the sofa to beg him to. The Countess was a very eccentric person.... At the Lichnowskis' I saw Haydn and Salieri, who were then very famous, while Beethoven excited no interest."
It was in the year 1800 that Beethoven at last was compelled to acknowledge to himself the terrible calamity of almost total deafness that had befallen him. He writes to his friend Wegeler, "If I had not read somewhere that man must not of his own free will depart this life, I should long ere this have been no more and that through my own act.... What is to be the result of this the good God alone knows. I beg of you not to mention my state to any one, not even to Lorchen [Wegeler's wife]. But," he continues, "I live only in my music, and no sooner is one thing completed than another is begun. In fact, as at present, I am often engaged on three or four compositions at one time."

An Anecdote about Beethoven.
But at first all was not gloom; for Beethoven was in love—not the love of fleeting fancy that, like other poets, he may have experienced before, but deeply, tragically, in love; and it seems that, for a time at least, this love was returned. The lady was the Countess Julia Guicciardi; but his dream did not last long, for in the year 1801 she married a Count Gallenberg. Hardly anything is known of this love affair of Beethoven's. A few letters full of passionate tenderness, and with a certain very pathetic simple trustfulness in her love running through them all—on which her marriage shortly afterward is a strange comment; the "Moonlight Sonata," vibrating, as it is throughout, with a lover's supremest ecstasy of devotion, these are the only records of that one blissful epoch in the poor composer's life; but how much it affected his after life, how it mingled in the dreams from which his loveliest creations of later years arose, it is impossible now to say. In a letter to Wegeler, dated November 16, 1801, he says, "You can hardly realize what a miserable, desolate life mine has been for the last two years; my defective hearing everywhere pursuing me like a spectre, making me fly from every one, and appear a misanthrope; and yet no one in reality is less so! This change [to a happier life] has been brought about by a lovely and fascinating (p. 323) girl who loves me and whom I love. After the lapse of two years I have again enjoyed some blissful moments, and now for the first time I feel that marriage can bestow happiness; but alas! she is not in the same rank of life as myself.... You shall see me as happy as I am destined to be here below, but not unhappy. No, that I could not bear. I will grasp Fate by the throat; it shall not utterly crush me. Oh, it is so glorious to live one's life a thousand times!" No misanthropy this, surely; he could not always speak the speech of common men, or care for the tawdry bravery of titles or fine clothes in which they strutted, but what a heart there was in the man, what a wondrous insight into all the beauty of the world, visible and invisible, around him! The most glorious lovesong ever composed, "Adelaide," was written by him; but Julia Guicciardi preferred a Count Gallenberg, keeper of the royal archives in Vienna, and Beethoven, to the end of his days, went on his way alone.
It was at this time that he composed his oratorio, "The Mount of Olives," which can hardly be reckoned among his finest works; and his one opera—but such an opera—"Fidelio." The greater part of these works was composed during his stay, in the summer months, at Hetzendorf, a pretty, secluded little village near Schönbrunn. He spent his days wandering alone through the quiet, shady alleys of the imperial park there, and his favorite seat was between two boughs of a venerable oak, at a height of about two feet from the ground. For some time he had apartments at a residence of Baron Pronay's, near this village; but he suddenly left, "because the baron would persist in making him profound bows every time that he met him." Like a true poet, he delighted in the country. "No man on earth," he writes, "loves the country more. Woods, trees, and rock give the response which man requires. Every tree seems to say, 'Holy, holy.'"
In 1804 the magnificent "Eroica" symphony was completed. This had originally been commenced in honor of Napoleon Bonaparte, then First Consul, who, Beethoven—throughout his life an ardent Republican—then believed was about to bring liberty to all the nations of Europe. When the news of the empire came the dream departed, and Beethoven, in a passionate rage, tore the title page of the symphony in two, and, with a torrent of imprecations against the tyrant, stamped on the torn fragments.
"My hero—a tyrant!" he shrieked, as he trampled on the poor page. On this page the inscription had been simply, "Bonaparte—Luigi v. Beethoven". For some years he refused to publish the work, and, when at last this was done, the inscription read as follows: "Sinfonia Eroica per festigiari il sovvenire d'un grand' uomo" (Heroic symphony, to celebrate the memory of a great man). When Napoleon died, in 1821, Beethoven said, "Seventeen years before I composed the music for this occasion;" and surely no grander music than that of the "Funeral March" was ever composed for the obsequies of a fallen hero. This is not the place to enter into a description of the marvellous succession of colossal works—symphonies, concertos, sonatas, trios, quartets, etc., culminating in the "Choral Symphony," his ninth, and last—which, through those long years of a (p. 324) silent life, imprisoned within himself, the great master put forth. His deafness prevented his appearing in public to conduct, although, with the natural desire of a composer to be present at the production of his own work, he long struggled to take his part in the first performances of symphonies and concertos.
When the great choral symphony was first performed he attempted to conduct, but in reality another conductor was stationed near him to give the right time to the band. After the majestic instrumental movements had been played came the final one, concluding with Schiller's "Hymn to Joy." The chorus breaks forth, thundering out in concert with all the instruments. At the words "Seid umschlunger, Millionen," the audience could no longer restrain their excited delight, and burst into tremendous applause, drowning the voices of singers and the sounds of strings and brass. The last notes are heard, but still Beethoven stands there absorbed in thought—he does not know that the music is ended. This was the first time that the people realized the full deprivation of hearing from which he suffered. Fraulein Unger, the soprano, gently takes his arm and turns him round to front the acclaiming multitude. There are few in that crowd who, while they cheer, do not feel the tears stealing down their cheeks at the sight of the poor lonely man who, from the prison-house of his affliction, has brought to them the gladness of thought so divine. Unmoved, he bowed his acknowledgment, and quietly left the building.
His later years were embittered with troubles about his nephew Carl, a youth to whom he was fondly attached, but who shamefully repaid the love of the desolate old man. Letters like the following, to the teacher in whose house the boy lived, show the constant thought and affection given to this boy: "Your estimable lady is politely requested to let the undersigned know as soon as possible (that I may not be obliged to keep it all in my head) how many pairs of stockings, trousers, shoes, and drawers are required, and how many yards of kerseymere to make a pair of black trousers for my tall nephew."
His death was the result of a cold which produced inflammation of the lungs. On the morning of March 24, 1827, he took the sacrament and when the clergyman was gone and his friends stood round his bed, he muttered. "Plaudite amici, comedia finita est." He then fell into an agony so intense that he could no longer articulate, and thus continued until the evening of the 26th. A violent thunder-storm arose; one of his friends, watching by his bedside when the thunder was rolling and a vivid flash of lightning lit up the room, saw him suddenly open his eyes, lift his right hand upward for some seconds—as if in defiance of the powers of evil—with clenched fist and a stern, solemn expression on his face; and then he sank back and died.[Back to Contents]

Nicolo Paganini, whose European fame as a violinist entitles him to a notice here, was born at Genoa in 1784. His father, a commission-broker, played on the mandolin; but fully aware of the inferiority of an instrument so limited in power, he put a violin into his son's hands, and initiated him in the principles of music. The child succeeded so well under parental tuition, that at eight years of age he played three times a week in the church, as well as in the public saloons. At the same period he composed a sonata. In his ninth year he was placed under the instruction of Costa, first violoncellist of Genoa; then had lessons of Rolla, a famous performer and composer; and finally studied counterpoint at Parma under Ghiretti and the celebrated maestro Paer. He now took an engagement at Lucca, where he chiefly associated with persons who at the gaming-table stripped him of his gains as quickly as he acquired them. He there received the appointment of director of orchestra to the court, at which the Princess Elisa Bacciochi, sister of Napoleon I., presided, and thither invited, to the full extent of her means, superior talent of every kind. In 1813 he performed at Milan; five years after, at Turin; and subsequently at Florence and Naples. In 1828 he visited Vienna, where a very popular violinist and composer, Mayseder, asked him how he produced such new effects. His reply was characteristic of a selfish mind: "Chacun a ses secrets" In that capital, it is affirmed, he was imprisoned, being accused of having murdered his wife. He challenged proofs of his ever having been married, which could not be produced. Then he was charged with having poignarded his mistress. This he also publicly refuted. The fact is that he knew better how to make money than friends, and he raised up enemies wherever his thirst for gold led him. Avarice was his master-passion; and, second to this, gross sensuality.
The year 1831 found Paganini in Paris, in which excitable capital he produced a sensation not inferior to that created by the visit of Rossini. Even this renowned composer was so carried away, either by the actual genius of the violinist or by the current of popular enthusiasm, that he is said to have wept on hearing Paganini for the first time. He arrived in England in 1831, and immediately announced a concert at the Italian Opera House, at a price which, if acceded to, would have yielded £3,391 per night; but the attempt was too audacious, and he was compelled to abate his demands, though he succeeded in (p. 326) drawing audiences fifteen nights in that season at the ordinary high prices of the King's Theatre. He also gave concerts in other parts of London, and performed at benefits, always taking at these a large proportion of the proceeds. He visited most of the great towns, where his good fortune still attended him. He was asked to play at the Commemoration Festival at Oxford, in 1834, and demanded 1,000 guineas for his assistance at three concerts. His terms were of course rejected.
Paganini died at Nice, in 1840, of a diseased larynx ("phthisie laryngée"). By his will, dated 1837, he gave his two sisters legacies of 60,000 and 70,000 francs; his mother a pension of 1,200; the mother of his son Achillino (a Jewess of Milan) a similar pension; and the rest of his fortune, amounting to 4,000,000 francs, devolved on his son. These and other facts before related, we give on the authority of the "Biographie Universelle."
Paganini certainly was a man of genius and a great performer, but sacrificed his art to his avarice. His mastery over the violin was almost marvellous, though he made an ignoble use of his power by employing it to captivate the mob of pretended amateurs by feats little better than sleight-of-hand. His performance on a single string, and the perfection of his harmonics, were very extraordinary; but why, as was asked at the time, be confined to one string when there are four at command that would answer every musical purpose so much better? His tone was pure, though not strong, his strings having been of smaller diameter than usual, to enable him to strain them at pleasure; for he tuned his instrument most capriciously. He could be a very expressive player; we have heard him produce effects deeply pathetic. His arpeggios evinced his knowledge of harmony, and some of his compositions exhibit many original and beautiful traits.[Back to Contents]
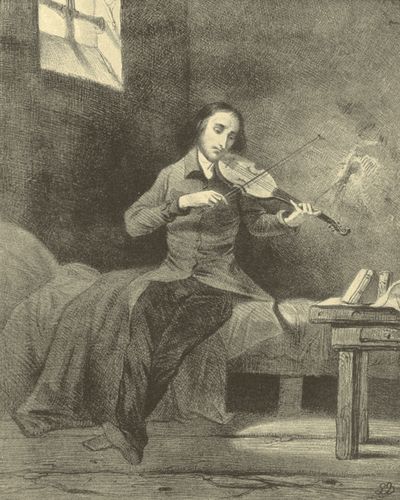

Paganini in Prison
Mendelssohn's lot in life was strikingly different from that of all the musicians of whom I have hitherto written; he never knew, like Schubert, what grinding poverty was, or suffered the long worries that Mozart had to endure for lack of money. His father was a Jewish banker in Berlin, the son of Moses Mendelssohn, a philosopher whose writings had already made the name celebrated throughout Europe. The composer's father used to say, with a very natural pride, after his own son had grown up, "Formerly I was the son of my father, and now I am the father of my son!"
Felix Mendelssohn-Bartholdy was born on February 3, 1809. His parents (p. 327) were neither of them trained musicians, though both appreciated and loved music, and it was from his mother that young Felix received his first music-lessons. When he had made some advance, Ludwig Berger became his tutor for the piano, and Zelter, a very learned and severe theorist, for counterpoint. At the age of nine years Felix had attained such proficiency that we find him taking the pianoforte part in a trio at a public concert of a Herr Gugel's, and when twelve years old he began to compose, and actually wrote a trio, some sonatas, a cantata, and several organ pieces. His home life was in the highest degree favorable to his musical development. On alternate Sundays musical performances were regularly given with a small orchestra in the large dining-room, Felix or his sister Fanny, who also possessed remarkable musical gifts, taking the pianoforte part, and new compositions by Felix were always included in the programme. Many friends, musicians and others, used to be present, Zelter regularly among their number, and the pieces were always freely commented on, Felix receiving then, as indeed he did all his life, the criticisms expressed, with the utmost good-natured readiness.

In 1824 Moscheles, at that time a celebrated pianist, and residing in London, visited Berlin, and was asked to give Felix music-lessons. This is the testimony of Moscheles, an excellent and kind-hearted man, and a thoroughly skilled musician, after spending nearly every day for six weeks with the family: "It is a family such as I have never known before; Felix, a mature artist, and yet but fifteen; Fanny, extraordinarily gifted, playing Bach's fugues by heart and with astonishing correctness—in fact, a thorough musician. The parents give me the impression of people of the highest cultivation;" and on the subject of lessons he says: "Felix has no need of lessons; if he wishes to take a hint from me as to anything new, he can easily do so." But it is very pleasant to find Mendelssohn afterward referring to these lessons as having urged him on to enthusiasm, and, in the days in London when his own fame had far outstripped that of the older musician, acknowledging himself as "Moscheles's pupil." The elder Mendelssohn was by no means carried away by the applause which the boy's playing and compositions had gained, and in 1825 he took his son to Paris to obtain Cherubini's opinion as to his musical abilities, with a view to the choice of a profession; for he had by no means made up his mind that Felix should spend his whole life as a musician. However, the surly old Florentine, who was not always civil or appreciative of budding genius (teste Berlioz), gave a decidedly favorable judgment on the compositions submitted to him, and urged the father to (p. 328) devote his son to a musical career. And, indeed, on listening to the pieces which were dated this year, especially a beautiful quartet in B minor, an octet for strings, the music to an opera in two acts, "Camacho's Wedding," and numerous pianoforte pieces, it is difficult to realize that the composer was then only sixteen years of age, or that anyone could question the artistic vocation that claimed him. But the next year a work was written, the score of which is marked "Berlin, August 6, 1826," when it must be remembered that he was seventeen years of age, which of itself was sufficient to rank him among the immortals—the overture to the "Midsummer Night's Dream." Full of lovely imaginings, with a wonderful fairy grace all its own, and a bewitching beauty, revealing not only the soul of the true poet, but also the musician profoundly skilled in all the art of orchestral effect, it is hard to believe that it is the work of a boy under twenty, written in the bright summer days of 1826, in his father's garden at Berlin.
Passing over the intermediate years with a simple reference to the "Meeresstille," "Calm Sea and Prosperous Voyage," which was then composed, and a fine performance of Bach's "Passion Music," for which he had been long drilling the members of the Berlin Singakademie, the next event is a visit to England in 1829, where he was received with extraordinary warmth, playing at the Philharmonic Concerts, conducting his C minor Symphony, which he dedicated to the Philharmonic Society, they in their turn electing him one of their honorary members; going to dinners, balls, and the House of Commons, and enjoying himself most hugely. His letters from England at this time are brimming over with fun and graphic description; there is one especially amusing, in which he describes himself with two friends going home from a late dinner at the German Ambassador's, and on the way buying three German sausages, going down a quiet street to devour them, with all the while joyous laughter and snatches of part songs. There is also a little incident of this time showing the wonderful memory he possessed. After a concert on "Midsummer Night," when the "Midsummer Night's Dream" had very appropriately been played, it was found that the score had been lost in a hackney-coach as the party were returning to Mr. Attwood's. "Never mind," said Mendelssohn, "I will make another," which he did, and on comparison with the separate parts not a single difference was found in it.
At the beginning of December he was at home again, and that winter he wrote the "Reformation Symphony," intended to be produced at the tercentenary festival of the "Augsburg Confession" in the following June. This symphony, with which Mendelssohn was not entirely satisfied, was only once performed during his lifetime, but since his death it has frequently been performed, and though not one of his most perfect works, is recognized as a noble monument in honor of a great event. The next spring he again set out on his travels, this time southward to Italy.
In 1833 Mendelssohn accepted an official post offered him by the authorities of Düsseldorf, by which the entire musical arrangements of the town, church, theatre, and singing societies were put under his care. Immermann, the celebrated (p. 329) poet, being associated with him in the direction of the theatre. Things, however, did not go on very smoothly there. Mendelssohn found all the many worries of theatrical management—the engagement of singers and musicians, the dissensions to be arranged, the many tastes to be conciliated—too irksome, and he did not long retain this appointment; but the life among his friends at Düsseldorf was most delightful, and the letters written at this time are exceedingly lively and gay. It was here that he received the commission from the Cæcilia-Verein of Frankfort for, and commenced, his grand oratorio "St. Paul." The words for this, as also for the "Elijah" and "Hymn of Praise" afterward, he selected himself with the help of his friend Schubung, and they are entirely from the Bible—as he said, "The Bible is always the best of all." Circumstances prevented the oratorio being then produced at Frankfort, and the first public performance took place at the Lower Rhine Festival at Düsseldorf, in May, 1836.
But his visits to Frankfort had a very important result in another way. Mendelssohn there met Mademoiselle Cécile Jeanrenaud, the daughter of a pastor of the French Reformed Church, and, though he had frequently indulged in the admiration of beautiful and clever women—which is allowable, and indeed an absolute necessity for a poet!—now for the first time he fell furiously in plain unmistakable and downright love. But it is more characteristic of the staid Teuton than the impulsive musician, that before plighting his troth to her he went away for a month's bathing at Scheveningen, in Holland, for the purpose of testing the strength of his affection by this absence. On his return, finding his amatory pulse still beating satisfactorily, he proposed to the young lady, and, as it must be presumed that she had already made up her own mind without any testing, he was accepted. On March 28, 1837, they were married, and the wedded life that then began was one of pure, unclouded happiness to the very end. Cécile Mendelssohn was a beautiful, gentle-hearted, and loving wife, just the one to give a weary and nervous artist in the home-life, with herself and the children near him, the blessed solace of rest and calm that he so needed. It is thus that Edward Devrient, the great German actor, and one of Mendelssohn's most intimate friends, describes her: "Cécile was one of those sweet womanly natures whose gentle simplicity, whose mere presence, soothed and pleased. She was slight, with features of striking beauty and delicacy; her hair was between brown and gold, but the transcendent lustre of her great blue eyes, and the brilliant roses of her cheeks, were sad harbingers of early death. She spoke little, and never with animation, in a low, soft voice. Shakespeare's words, "My gracious silence," applied to her no less than to the wife of Coriolanus."
After giving up his official position at Düsseldorf, in 1835, Mendelssohn was invited to become the conductor of the now famous Gewandhaus concerts at Leipsic, a post which he gladly accepted, and which, retained by him for many years, was to be one of the greatest delights of his artistic life. Not only was he loved and appreciated in Leipsic—far more than in Berlin, his own city—but he had here an opportunity of assisting many composers and virtuosi, who otherwise would have sought in vain for a hearing. Thus, after Liszt, when visiting the (p. 330) town, had been first of all received with great coldness, owing to the usual prices of admission to the concerts having been raised, Mendelssohn set everything straight by having a soirée in his honor at the Gewandhaus, where there were three hundred and fifty people, orchestra, chorus, punch, pastry, Meeresstille Psalm, Bach's Triple Concerto, choruses from St. Paul, Fantasia on Lucia, the Erl King, the Devil and his Grandmother, the latter probably a mild satirical reference to Liszt's stormy and often incoherent playing. It is also pleasant to find how cordially Mendelssohn received Berlioz there, as told in the "Memoirs" of the latter, spending ungrudgingly long days in aiding in rehearsals for his "Romeo et Juliette," though Mendelssohn never sympathized much with Berlioz's eccentric muse.
The "Lobgesang," or "Hymn of Praise," a "symphonie-cantata," as he called it, was his next great work, composed in 1840, together with other music, at the request of the Leipsic Town-Council, for a festival held in that town in commemoration of the invention of printing, on June 25th. None who have heard this work can forget the first impression produced when the grand instrumental movements with which it commences are merged in the majestic chorus, "All men, all things, praise ye the Lord," or the intensely dramatic effect of the repeated tenor cry, "Watchman, will the night soon pass?" answered at last by the clear soprano message of glad tidings, "The night is departing, the day is at hand!" This "watchman" episode was added some time afterward, and, as he told a friend, was suggested to the composer during the weary hours of a long sleepless night, when the words, "Will the night soon pass?" again and again seemed to be repeated to him. But a greater work even than this was now in progress; the "Elijah" had been begun.
In 1841 began a troublesome and harassing connection with Berlin, a city where, except in his home life, Mendelssohn never seems to have been very fortunate. At the urgent entreaty of the king, he went to reside there as head of the new Musical Academy. But disagreements arose, and he did not long take an active part in the management. The king, however, was very anxious to retain his services, and a sort of general office seems to have been created for him, the duties of which were to supply music for any dramatic works which the king took it into his head to have so embellished. And, though it is to this that we owe the noble "Antigone," "Œdipus," "Athalie," "Midsummer Night's Dream," and other music, this work to dictation was very worrying, and one cannot think without impatience of the annoyances to which he was subjected. The king could not understand why he shrank from writing music to the choruses of Æschylus's "Eumenides." Other composers would do it by the yard, why not he?
Passing rapidly over the intervening years filled with busy work, both in composition and as one of the principals of a newly started Conservatorium in Leipsic, we come to 1846, when his great work "Elijah" was at last completed and performed. On August 26th, at the Birmingham Festival, the performance went splendidly. Staudigl took the part of the prophet, and a young tenor, Lockey, sang the air, "Then shall the righteous," in the last part, as Mendelssohn (p. 331) says, "so very beautifully, that I was obliged to collect myself to prevent my being overcome, and to enable me to beat time steadily." Rarely, indeed, has a composer so truly realized his own conception as Mendelssohn did in the great tone-picture which he drew of the Prophet of Carmel and the wilderness.
"I figured to myself," he says, "Elijah as a grand, mighty prophet, such as might again reappear in our own day, energetic and zealous, stern, wrathful, and gloomy, a striking contrast to the court myrmidons and popular rabble—in fact, in opposition to the whole world, and yet borne on angel's wings!" Nothing can be finer than this, with that exquisite touch in the last words, "in opposition to the whole world, and yet borne on angel's wings."
After returning to Germany he was soon busily employed in recasting some portions of "Elijah" with which he was not satisfied; he had also another oratorio on even a grander scale, "Christus," already commenced; and at last, after all his life-long seeking in vain for a good libretto for an opera, he had begun to set one written by Geibel, the German poet, "Loreley," to music. But his friends now noticed how worn and weary he used oftentimes to look, and how strangely irritable he frequently was, and there can hardly be a doubt that some form of the cerebral disease from which his father and several of his relations had died, was already, deep-seated and obscure, disquieting him. The sudden announcement of the death of his sister, Fanny Hensel, herself a musical genius, to whom he was very fondly attached, on his return to Frankfort from his last visit to England in May, 1847, terribly affected him. He fell to the ground with a loud shriek, and it was long before he recovered consciousness.
Indeed, it may be said that he never really recovered from this shock. In the summer he went with his wife and children, and in company with his brother Paul and his family, on a tour in Switzerland, where he hoped that complete idleness as regards music, life in the open air, sketching, and intercourse with chosen friends, might once more give strength to his enfeebled nerves. And for a time the beauty of the mountains and the lakes seemed to bring him rest, and again he began to work at his oratorio "Christus;" but still his friends continued anxious about him. He looked broken down and aged, a constant agitation seemed to possess him, and the least thing would often strangely affect and upset him.
In September he returned to Leipsic; he was then more cheerful, and able to talk about music and to write, although he could not resume the conductorship of the Gewandhaus concerts. He again had projects in view. Jenny Lind was to sing in his "Elijah," at Vienna, whither he would go and conduct, and he was about to publish some new songs. One day in October he went to call upon his friend, Madame Frege, a gifted lady who, he said, sang his songs better than anyone else, to consult her about some new songs. She sang them over to him several times, and then, as it was getting dark, she went out of the room for a few minutes to order lights. When she returned he was lying on the sofa, shivering with cold, and in agonizing pain. Leeches were applied, and he partially recovered; but another attack followed, and this was the last.[Back to Contents]

Franz Liszt was born in 1811. He had the hot Hungarian blood of his father, the fervid German spirit of his mother, and he inherited the lofty independence, with none of the class prejudices, of the old Hungarian nobility from which he sprang. Liszt's father, Adam, earned a modest livelihood as agent and accountant in the house of Count Esterhazy. In that great musical family, inseparably associated with the names of Haydn and Schubert, Adam Liszt had frequent opportunities of meeting distinguished musicians. The prince's private band had risen to public fame under the instruction of the venerable Haydn himself. The Liszts, father and son, often went to Eisenstadt, where the count lived; there they rubbed elbows with Cherubini and Hummel, a pupil of Mozart.
Franz took to music from his earliest childhood. When about five years old he was asked what he would like to do. "Learn the piano," said the little fellow. Soon afterward his father asked him what he would like to be; the child pointed to a print of Beethoven hanging on the wall, and said, "Like him." Long before his feet could reach the pedals or his fingers stretch an octave, the boy spent all his spare time strumming, making what he called "clangs," chords and modulations. He mastered scales and exercises without difficulty.
Czerny at once took to Liszt, but refused to take anything for his instruction. Salieri was also fascinated, and instructed him in harmony; and fortunate it was that Liszt began his course under two strict mentors. He soon began to resent Czerny's method—thought he knew better and needed not those dry studies of Clementi and that irksome fingering by rule—he could finger anything in a half-a-dozen different ways. There was a moment when it seemed that master and pupil would have to part, but timely concessions to genius paved the way to dutiful submission, and years afterward the great master dedicated to the rigid disciplinarian of his boyhood his "Vingt-quatre Grandes Études" in affectionate remembrance.
Such a light as Liszt's could not be long hid; all Vienna, in 1822, was talking of the wonderful boy. "Est deus in nobis," wrote the papers, profanely. The "little Hercules," the "young giant," the boy "virtuoso from the clouds," were among the epithets coined to celebrate his marvellous renderings of Hummel's "Concerto in A," and a free "Fantasia" of his own. The Vienna Concert Hall was crowded to hear him, and the other illustrious artists—then, as (p. 333) indeed they have been ever since forced to do wherever Liszt appeared—effaced themselves with as good a grace as they could.
It is a remarkable tribute to the generous nature as well as to the consummate ability of Liszt, that, while opposing partisans have fought bitterly over him—Thalbergites, Herzites, Mendelssohnites versus Lisztites—yet few of the great artists who have, one after another, had to yield to him in popularity have denied to him their admiration, while most of them have given him their friendship.
Liszt early wooed, and early won Vienna. He spoke ever of his dear Viennese, and their resounding city. A concert tour on his way to Paris brought him before the critical public of Stuttgart and Munich. Hummel, an old man, and Moscheles, then in his prime, heard him and declared that his playing was equal to theirs. But Liszt was bent upon completing his studies in the celebrated school of the French capital, and at the feet of the old musical dictator, Cherubini. The Erards, who were destined to owe so much to Liszt, and to whom Liszt throughout his career owed so much, at once provided him with a magnificent piano; but Cherubini put in force a certain by-law of the Conservatoire excluding foreigners, and excluded Franz Liszt.
This was a bitter pill to the eager student. He hardly knew how little he required such patronage. In a very short time "le petit Liszt" was the great Paris sensation. The old noblesse tried to spoil him with flattery, the Duchesse de Berri drugged him with bonbons, the Duke of Orleans called him the "little Mozart." He gave private concerts, at which Herz, Moscheles, Lafont, and De Beriot, assisted. Rossini would sit by his side at the piano, and applaud. He was a "miracle." The company never tired of extolling his "nerve, fougue et originalité," while the ladies who petted and caressed him after each performance, were delighted at his simple and graceful carriage, the elegance of his language, and the perfect breeding and propriety of his demeanor.
He was only twelve when he played for the first time at the Italian Opera, and one of those singular incidents which remind one of Paganini's triumphs occurred. At the close of a bravura cadenza, the band forgot to come in, so absorbed were the musicians in watching the young prodigy. Their failure was worth a dozen successes to Liszt. The ball of the marvellous was fairly set rolling. Gall, the inventor of phrenology, took a cast of the little Liszt's skull; Talma, the tragedian, embraced him openly with effusion; and the misanthropic Marquis de Noailles became his mentor, and initiated him into the art of painting.
In 1824 Liszt, then thirteen years old, came with his father to England; his mother returned to Austria. He went down to Windsor to see George IV., who was delighted with him, and Liszt, speaking of him to me, said: "I was very young at the time, but I remember the king very well—a fine, pompous-looking gentleman." George IV. went to Drury Lane on purpose to hear the boy, and commanded an encore. Liszt was also heard in the theatre at Manchester, and in several private houses.
On his return to France, people noticed a change in him. He was now fourteen, (p. 334) grave, serious, often pre-occupied, already a little tired of praise, and excessively tired of being called "le petit Liszt." His vision began to take a wider sweep. The relation between art and religion exercised him. His mind was naturally devout. Thomas à Kempis was his constant companion. "Rejoice in nothing but a good deed;" "Through labor to rest, through combat to victory;" "The glory which men give and take is transitory," these and like phrases were already deeply engraven on the fleshly tablets of his heart. Amid all his glowing triumphs he was developing a curious disinclination to appear in public; he seemed to yearn for solitude and meditation.
In 1827 he again hurried to England for a short time, but his father's sudden illness drove them to Boulogne, where, in his forty-seventh year, died Adam Liszt, leaving the young Franz for the first time in his life, at the early age of sixteen, unprotected and alone. Rousing himself from the bodily prostration and torpor of grief into which he had been thrown by the death of his father, Franz, with admirable energy and that high sense of honor which always distinguished him, began to set his house in order. He called in all his debts, sold his magnificent grand "Erard," and left Boulogne for Paris with a heavy heart and a light pocket, but not owing a sou.
He sent for his mother, and for the next twelve years, 1828-1840, the two lived together, chiefly in Paris. There, as a child, he had been a nine days' wonder, but the solidity of his reputation was now destined to go hand in hand with his stormy and interrupted mental and moral development. Such a plant could not come to maturity all at once. No drawing-room or concert-room success satisfied a heart for which the world of human emotion seemed too small, and an intellect piercing with intuitive intelligence into the "clear-obscure" depths of religion and philosophy.
But Franz was young, and Franz was poor, and his mother had to be supported. She was his first care. Systematically, he labored to put by a sum which would assure her of a competency, and often with his tender genial smile he would remind her of his own childish words, "God will help me to repay you for all that you have done for me." Still he labored, often woefully against the grain. "Poverty," he writes, "that old mediator between man and evil, tore me from my solitude devoted to meditation, and placed me before a public on whom not only my own but my own mother's existence depended. Young and over-strained, I suffered painfully under the contact with external things which my vocation as a musician brought with it, and which wounded me all the more intensely that my heart at this time was filled entirely with the mystical feelings of love and religion."

Franz Liszt.
Of course the gifted young pianist's connection grew rapidly. He got his twenty francs a lesson at the best houses; he was naturally a welcome guest, and from the first seemed to have the run of high Parisian society. His life was feverish, his activity irregular, his health far from strong; but the vulgar temptations of the gay capital seemed to have little attraction for his noble nature. His heart remained unspoiled. He was most generous to those who could not (p. 335) afford to pay for his lessons, most pitiful to the poor, most dutiful and affectionate to his mother. Coming home late from some grand entertainment, he would sit outside on the staircase till morning, sooner than awaken, or perhaps alarm, her by letting himself in. But in losing his father he seemed to have lost a certain method and order. His meals were irregular, so were his lessons; more so were the hours devoted to sleep.
At this time he was hardly twenty; we are not surprised anon to hear in his own words, of "a female form chaste, and pure as the alabaster of holy vessel," but he adds: "Such was the sacrifice which I offered with tears to the God of Christians!"
I will explain. Mlle. Caroline St. Cricq was just seventeen, lithe, slender, and of "angelic" beauty, with a complexion like a lily flushed with roses, open, "impressionable to beauty, to the world, to religion, to God." The countess, her mother, appears to have been a charming woman, very partial to Liszt, whom she engaged to instruct Mademoiselle in music. The lessons went not by time, but by inclination. The young man's eloquence, varied knowledge, ardent love of literature, and flashing genius won both the mother and daughter. Not one of them seemed to suspect the whirlpool of grief and death to which they were hurrying. The countess fell ill and died, but not before she had recommended Liszt to the Count St. Cricq as a possible suitor for the hand of Mademoiselle.
The haughty diplomat, St. Cricq, at once put his foot down. The funeral over, Liszt's movements were watched. They were innocent enough. He was already an enfant de la maison, but one night he lingered reading aloud some favorite author to Mademoiselle a little too late. He was reported by the servants, and received his polite dismissal as music master. In an interview with the count his own pride was deeply wounded. "Difference of rank!" said the count. That was quite enough for Liszt. He rose, pale as death, with quivering lip, but uttered not a word. As a man of honor he had but one course. He and Caroline parted forever. She contracted later an uncongenial marriage; he seems to have turned with intense ardor to religion. His good mother used to complain to those who came to inquire for him that he was all day long in church, and had ceased to occupy himself, as he should, with music.
It was toward the close of 1831 that Liszt met Chopin in Paris. From the first, these two men, so different, became fast friends. Chopin's delicate, retiring soul found a singular delight in Liszt's strong and imposing personality. Liszt's exquisite perception enabled him perfectly to live in the strange dreamland of Chopin's fancies, while his own vigor inspired Chopin with nerve to conceive those mighty Polonaises that he could never properly play himself, and which he so gladly committed to the keeping of his prodigious friend. Liszt undertook the task of interpreting Chopin to the mixed crowds which he revelled in subduing, but from which his fastidious and delicately strung friend shrank with something like aversion.
From Chopin, Liszt and all the world after him got that tempo rubato, that playing with the duration of notes without breaking the time, and those arabesque (p. 336) ornaments which are woven like fine embroidery all about the pages of Chopin's nocturnes, and lift what in others are mere casual flourishes into the dignity of interpretative phrases and poetic commentaries on the text.
People were fond of comparing the two young men who so often appeared in the same salons together—Liszt with his finely shaped, long, oval head and profil d'ivoire, set proudly on his shoulders, his stiff hair of dark blonde thrown back from the forehead without a parting, and cut in a straight line, his aplomb, his magnificent and courtly bearing, his ready tongue, his flashing wit and fine irony, his genial bonhomie and irresistibly winning smile; and Chopin, also, with dark blonde hair, but soft as silk, parted on one side, to use Liszt's own words, "An angel of fair countenance, with brown eyes from which intellect beamed rather than burned; a gentle, refined smile, slightly aquiline nose; a delicious, clear, almost diaphanous complexion, all bearing witness to the harmony of a soul which required no commentary beyond itself."
Nothing can be more generous or more true than Liszt's recognition of Chopin's independent support. "To our endeavors," he says, "to our struggles, just then so much needing certainty, he lent us the support of a calm, unshakable conviction, equally armed against apathy and cajolery." There was only one picture on the walls of Chopin's room; it hung just above his piano. It was a head of Liszt.
It is no part of my present scheme to describe the battle which romanticism in music waged against the prevalent conventionalities. We know the general outcome of the struggle culminating, after the most prodigious artistic convulsions, in the musical supremacy of Richard Wagner, who certainly marks firmly and broadly enough the greatest stride in musical development made since Beethoven.
In 1842 Liszt visited Weimar, Berlin, and then went to Paris; he was meditating a tour in Russia. Pressing invitations reached him from St. Petersburg and Moscow. The most fabulous accounts of his virtuosity had raised expectation to its highest pitch. He was as legendary even among the common people as Paganini. His first concert at St. Petersburg realized the then unheard-of sum of £2,000. The roads were crowded to see him pass, and the corridors and approaches to the Grand Opera blocked to catch a glimpse of him. The same scenes were repeated at Moscow, where he gave six concerts without exhausting the popular excitement.
On his return to Weimar he accepted the post of Capellmeister to the Grand Duke. It provided him with that settled abode, and above all with an orchestra, which he now felt so indispensable to meet his growing passion for orchestral composition. But the time of rest had not yet come.
In 1844 and 1845 he was received in Spain and Portugal with incredible enthusiasm, after which he returned to Bonn to assist at the inauguration of Beethoven's statue. With boundless liberality, he had subscribed more money than all the princes and people of Germany put together, to make the statue worthy of the occasion and the occasion worthy of the statue.
The golden river which poured into him from all the capitals of Europe now (p. 337) freely found a new vent in boundless generosity. Hospitals, poor and needy, patriotic celebrations, the dignity and interests of art, were all subsidized from his private purse. His transcendent virtuosity was only equalled by his splendid munificence; but he found—what others have so often experienced—that great personal gifts and prodigious éclat cannot possibly escape the poison of envy and detraction. He was attacked by calumny; his gifts denied and ridiculed; his munificence ascribed to vainglory, and his charity to pride and ostentation; yet none will ever know the extent of his private charities, and no one who knows anything of Liszt can be ignorant of the simple, unaffected goodness of heart which prompted them.
Still he was wounded by ingratitude and abuse. It seemed to check and paralyze for the moment his generous nature. Fétis saw him at Coblenz soon after the Bonn festival, at which he had expended such vast sums. He was sitting alone, dejected and out of health. He said he was sick of everything, tired of life, and nearly ruined. But that mood never lasted long with Liszt; he soon arose and shook himself like a lion. His detractors slunk away into their holes, and he walked forth victorious to refill his empty purse and reap new laurels.
His career was interrupted by the stormy events of 1848. He settled down for a time at Weimar, and it was then that he began to take that warm interest in Richard Wagner which ended in the closest and most enduring of friendships.
He labored incessantly to get a hearing for the "Lohengrin" and "Tannhäuser." He forced Wagner's compositions on the band, on the grand-duke; he breasted public opposition and fought nobly for the eccentric and obscure person who was chiefly known as a political outlaw and an inventor of extravagant compositions which it was impossible to play or sing, and odiously unpleasant to listen to. But years of faithful service, mainly the service and immense prestige and authority of Liszt, procured Wagner a hearing, and paved the way for his glorious triumphs at Bayreuth in 1876, 1882, and 1883.
I have preferred to confine myself in this article to the personality of Liszt, and have made no allusion to his orchestral works and oratorio compositions. The "Symphonic Poems" speak for themselves—magnificent renderings of the inner life of spontaneous emotion—but subject-matter which calls for a special article can find no place at the fag-end of this, and at all times it is better to hear music than to describe it. As it would be impossible to describe Liszt's orchestration intelligibly to those who have not heard it, and unnecessary to those who have, I will simply leave it alone.
I saw Liszt but six times, and then only between the years 1876 and 1881. I heard him play upon two occasions only, and then he played certain pieces of Chopin at my request and a new composition by himself. I have heard Mme Schumann, Bülow, Rubenstein, Menter, and Esipoff, but I can understand that saying of Tausig, himself one of the greatest masters of technique whom Germany has ever produced: "No mortal can measure himself with Liszt. He dwells alone upon a solitary height."[Back to Contents]

Richard Wagner's personality has been so overshadowed by and almost merged in the great controversy which his schemes of reform in opera raised, that his life and character are often now sorely misjudged—just as his music long was—by those who have not the time, the inclination, or the ability to understand the facts and the issues. Before briefly stating then the theories he propounded and their development, as shown in successive music dramas, it will be well to summarize the story of a life (1813-83) during which he was called to endure so much vicissitude, trial and temptation, suffering and defeat.
Born in Leipsic, on May 22, 1813, the youngest of nine children, Wilhelm Richard was only five months old when his father died. His mother's second marriage entailed a removal to Dresden, where, at the Kreuzschule, young Wagner received an excellent liberal education. At the age of thirteen the bent of his taste, as well as his diligence, was shown by his translation (out of school hours) of the first twelve books of the "Odyssey." In the following year his passion for poetry found expression in a grand tragedy. "It was a mixture," he says, "of Hamlet and Lear. Forty-two persons died in the course of the play, and, for want of more characters, I had to make some of them reappear as ghosts in the last act." Weber, who was then conductor of the Dresden opera, seems to have attracted the boy both by his personality and by his music; but it was Beethoven's music which gave him his real inspiration. From 1830 to 1833 many compositions after standard models are evidence of hard and systematic work and in 1833 he began his long career as an operatic composer with "Die Feen" which, however, never reached the dignity of performance till 1888—five years after Wagner's death. After some time spent in very unremunerative routine work in Heidelberg, Königsberg, and Riga (where in 1836 he married), he resolved, in 1839, to try his fortune in Paris with "Rienzi," a new opera, written on the lines of the Paris Grand Opera and with all its great resources in view. From the month's terrific storm in the North Sea, through which the vessel struggled to its haven, till the spring of 1842, when Wagner left Paris with "Rienzi" unperformed, heartsick with hope deferred, his lot was a hard and bitter one. Berlioz, in similar straits, supported himself by singing in the chorus of a second-rate theatre. Wagner was refused even that humble post. In 1842 "Rienzi" was accepted at Dresden, and its signal success led to his appointment (p. 339) as Capellmeister there (January, 1843). In the following year the "Flying Dutchman" was not so enthusiastically received, but it has since easily distanced the earlier work in popular favor. The story was suggested to his mind during the stormy voyage from Riga; and it is a remarkable fact that the wonderful tone-picture of Norway's storm-beaten shore was painted by one who, till that voyage, had never set eyes on the sea. In 1845 his new opera, "Tannhäuser," proved at first a comparative failure. The subject, one which had been proposed to Weber in 1814, attracted Wagner while he was in Paris, and during his studies for the libretto he found also the first suggestions of "Lohengrin" and "Parsifal." The temporary failure of the opera led him to the consideration and self-examination which resulted in the elaborate exposition of his ideal (in "Opera and Drama," and many other essays). "I saw a single possibility before me," he writes, "to induce the public to understand and participate in my aims as an artist." "Lohengrin" was finished early in 1848, and also the poem of "Siegfried's Tod," the result of Wagner's studies in the old Nibelungen Lied; but a too warm sympathy with some of the aims of the revolutionary party (which reigned for two short days behind the street barricades in Dresden, May, 1849) rendered his absence from Saxony advisable, and a few days later news reached him in Weimar that a warrant was issued for his arrest. With a passport procured by Liszt he fled across the frontier, and for nearly twelve years the bitterness of exile was added to the hardships of poverty. It is this period which is mainly responsible for Wagner's polemical writings, so biting in their sarcasm, and often unfair in their attacks. He was a good hater; one of the most fiendish pamphlets in existence is the "Capitulation" (1871), in which Wagner, safe from poverty (thanks to the kindness of Liszt and the munificence of Ludwig II., of Bavaria), and nearing the summit of his ambition, but remembering only his misfortunes and his slights, gloated in public over the horrors which were making a hell of the fairest city on earth. There is excuse at least, if not justification, to be found for his attacks on Meyerbeer and others; there are considerations to be taken into account while one reads with humiliation and pity the correspondence between Wagner and his benefactor, Liszt; but it is sad that an affectionate, humane, intensely human, to say nothing of an artistic, nature, could so blaspheme against the first principles of humanity.
In 1852 the poem of the "Nibelungen Ring Trilogy" was finished. In 1854 "Rheingold" (the introduction of "Vorabend") was ready, and "Die Walküre" (Part I.) in 1856. But "tired," as he said, "of heaping one silent score upon another," he left "Siegfried" unfinished, and turned to the story of "Tristan." The poem was completed in 1857, and the music two years later. At last, in 1861, he received permission to return to Germany, and in Vienna he had the first opportunity of hearing his own "Lohengrin." For three years the struggle with fortune seems to have been harder than ever before, and Wagner, in broken health, had practically determined to give up the unequal contest, when an invitation was sent him by Ludwig II., the young King of Bavaria—"Come here and finish your work." Here at last was salvation for Wagner, and the rest of his life was (p. 340) comparatively smooth. In 1865 "Tristan und Isolde" was performed at Munich, and was followed three years later by a comic opera, "Die Meistersinger," the first sketches of which date from 1845. "Siegfried" ("Nibelungen Ring," Part II.) was completed in 1869, and in the following year Wagner married Cosima, the daughter of Liszt, and formerly the wife of Von Bülow. His first wife, from whom he had been separated in 1861, died at Dresden in 1866.
A theatre built somewhere off the main lines of traffic, and specially constructed for the performance of Wagner's later works, must have seemed the most impracticable and visionary of proposals in 1870; and yet, chiefly through the unwearying exertions of Carl Tausig (and, after his death, of the various Wagner societies), the foundation-stone of the Baireuth Theatre was laid in 1872, and in 1876, two years after the completion of the "Götterdämmerung" ("Nibelungen Ring," Part III.), it became an accomplished fact. The first work given was the entire "Trilogy;" and in July, 1882, Wagner's long and stormy career was magnificently crowned there by the first performance of "Parsifal." A few weeks later his health showed signs of giving way, and he resolved to spend the winter at Venice. There he died suddenly, February 13, 1883, and was buried in the garden of his own house, Wahnfried, at Baireuth.[12]
Wagner's life and his individuality are of unusual importance in rightly estimating his work, because, unlike the other great masters, he not only devoted all his genius to one branch of music—the opera—but he gradually evolved a theory and an ideal which he consciously formulated and adopted, and perseveringly followed. It may be asked whether Wagner's premises were sound and his conclusions right; and also whether his genius was great enough to be the worthy champion of a cause involving such revolutions. Unless Wagner's operas, considered solely as music, are not only more advanced in style, but worthy in themselves to stand at least on a level with the greatest efforts of his predecessors, no amount of proof that these were wrong and he right will give his name the place his admirers claim for it. It is now universally acknowledged that Wagner can only be compared with the greatest names in music. His instrumentation has the advantage in being the inheritor of the enormous development of the orchestra from Haydn to Berlioz, his harmony is as daring and original as Bach's, and his melody is as beautiful as it is different from Beethoven's or Mozart's. (These names are used not in order to institute profitless comparisons, but as convenient standards; therefore even a qualification of the statement will not invalidate the case.)
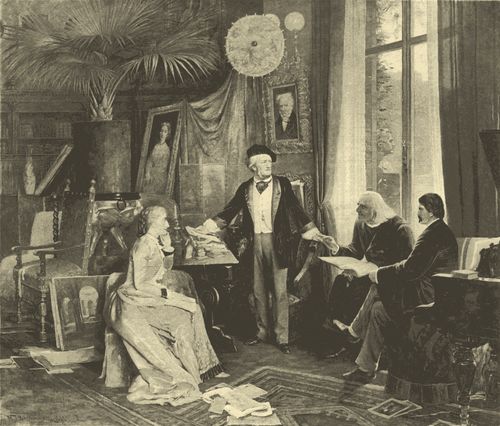

Wagner and his Friends.
His aim (stated very generally) was to reform the whole structure of opera, using the last or "Beethoven" development of instrumental music as a basis, and freeing it from the fetters which conventionality had imposed, in the shape of set forms, accepted arrangements, and traditional concessions to a style of singing now happily almost extinct. The one canon was to be dramatic fitness. In this "Art Work of the Future," as he called it, the interest of the drama is to depend (p. 341) not entirely on the music, but also on the poem and on the acting and staging as well. It will be seen that Wagner's theory is not new. All or most of it is contained in the theories of Gluck and others, who at various periods in the development of opera consciously strove after an ideal music drama. But the times were not ripe, and therefore such music could not exert its proper influence. The twin arts of music and poetry, dissociated by the rapid advance of literature and the slow development of music, pursued their several paths alone. The attempt to reunite them in the end of the sixteenth century was futile, and only led to opera which never needed, and therefore did not employ, great poetry. In Germany music was developed along instrumental lines until the school arrived at its culmination in Beethoven; and when an opera composer stopped to think on the eternal verities, the result must always have been such a prophecy of Wagner's work as we find in Mozart's letters:
"October, 1781.—Verse indeed is indispensable for music, but rhyme is bad in its very nature.... It would be by far the best if a good composer, understanding the theatre and knowing how to produce a piece, and a clever poet, could be united in one...."
Other but comparatively unimportant features in the Wagner music drama are, e.g., the use of the Leitmotiv, or leading motive—found occasionally in Gluck, Mozart, Weber, etc., but here first adopted with a definite purpose, and the contention for mythological rather than historical subjects—now largely admitted. But all Wagner's principles would have been useless without the energy and perseverance which directed his work, the loving study which stored his memory with all the great works of his predecessors, and, above all, the genius which commands the admiration of the musical world.
Wagner's works show a remarkable and progressive development. "Rienzi" is quite in the grand opera style of Meyerbeer, Spontini, etc. The "Flying Dutchman" is a deliberate departure from that style, and in romantic opera strikes out for itself a new line, which, followed still further in "Tannhäuser," reaches its stage of perfection in "Lohengrin." From this time dates the music drama, of which "Tristan" is the most uncompromising type, and by virtue of wonderful orchestration, and the intense pathos of the beautifully written poem, the most fascinating of all. The "Trilogy" ("Walküre," "Siegfried," "Götterdämmerung," with the "Rheingold" as introduction) is a very unequal work. It is full of Wagner's most inspired writing and most marvellous orchestration; but it is too long and too diffuse. The plot also is strangely confused and uninteresting, and fails alike as a story and as a vehicle of theories, morals, or religion. "Parsifal," with its sacred allegory, its lofty nobility of tone, and its pure mysticism, stands on a platform by itself, and is almost above criticism, or praise, or blame. The libretto alone might have won Wagner immortality, so original is it and perfect in intention; and the music seems to be no longer a mere accessory to the effect, but the very essence and fragrance of the great conception.[Back to Contents]

Giuseppe Verdi, the last and most widely successful of the school of Italian opera proper, was born at Roncole, near Busseto, October 9, 1813. At ten years he was organist of the small church in his native village, the salary being raised after a year from £1 8s. 10d. to £1 12s. per annum. At the age of sixteen he was provided with funds to prosecute his studies at the Conservatorium at Milan; but at the entrance examination he showed so little evidence of musical talent that the authorities declined to enroll him. Nothing daunted, he pursued his studies with ardor under Lavigna, from 1831 to 1833, when, according to agreement, he returned to Busseto to take the place of his old teacher Provesi, now deceased.
After five unhappy years in a town where he was little appreciated, Verdi returned to Milan. His first opera, "Oberto," is chiefly indebted to Bellini, and the next, "Un Giorno di Regno" (which fulfilled its own title, as it was only once performed), has been styled "Un Bazar de Reminiscences." Poor Verdi had just lost his wife and two children within a few days of each other, so it is hardly to be wondered at that a comic opera was not a very congenial work, nor successfully accomplished.
"Nabucodonosor" (1842) was his first hit, and in the next year "I Lombardi" was even more successful—partly owing to the revolutionary feeling which in no small degree was to help him to his future high position. Indeed, his name was a useful acrostic to the revolutionary party, who shouted "Viva Verdi," when they meant "Viva Vittorio Emanuele Re D' Italia." "Ernani," produced at Venice in 1844, also scored a success, owing to the republican sentiment in the libretto, which was adapted from Victor Hugo's "Hernani." Many works followed in quick succession, each arousing the enthusiasm of the audiences, chiefly when an opportunity was afforded them of expressing their feelings against the Austrian rule. Only with his sixteenth opera did Verdi win the supremacy when there were no longer any living competitors; and "Rigoletto" (1851), "Il Trovatore," and "La Traviata" (1853) must be called the best, as they are the last of (p. 343) the Italian opera school. "I Vespri Siciliani" (1855) and "Simon Boccanegra" (1857) were not so successful as "Un Ballo in Maschera" (1859); and none of them, any more than "La Forza del Destino" (1862) or "Don Carlos" (1867), added anything to the fame of the composer of "Il Trovatore."
Only now begins the interest which the student of musical history finds in Verdi's life. Hitherto he had proved a good man, struggling with adversity and poverty, a successful composer ambitious to succeed to the vacant throne of Italian opera. But the keen insight into dramatic necessity which had gradually developed and had given such force to otherwise unimportant scenes in earlier operas, also showed him the insufficiency of the means hitherto at the disposal of Italian composers, and from time to time he had tried to learn the lessons taught in the French Grand Opera School, but with poor success. Now a longer interval seemed to promise a more careful, a more ambitious work, and when "Aïda" was produced at Cairo (1871), it was at once acknowledged that a revolution had taken place in Verdi's mind and method, which might produce still greater results. The influence of Wagner and the music-drama is distinctly to be felt.
But Verdi was apparently not yet satisfied. For sixteen years the successful composer maintained absolute silence in opera, when whispers of a great music-drama roused the expectation of musical Europe to an extraordinary pitch; nor were the highest expectations disappointed when "Otello" was produced at Milan in 1887. The surrender of Italian opera was complete, and Verdi took his right place at the head of the vigorous new school which has arisen in Italy, and which promises to regain for the "Land of Song" some of her ancient preeminence in music. A comic opera by Verdi, "Falstaff," was announced in 1892: it has well sustained his previous reputation.[Back to Contents]
This celebrated actor was the son of Peter Garrick, who had a captain's commission in the army, but who generally resided at Lichfield. He was born at Hereford, when his father was on a recruiting party there, and was baptized in the Church of All-Saints, in that city, on February 20, 1716. Young Garrick received part of his education at the grammar school there, but he did not apply himself to his books with much assiduity. He had conceived a very early passion for theatrical (p. 344) representation, from which nothing could turn him aside. When he was a little more than eleven years of age, he formed the project of getting a play acted by young gentlemen and ladies. After he had made some trial of his own and his companions' abilities, and prevailed upon the parents to give their consent, he pitched upon the "Recruiting Officer," for the play. He assembled his little company in a large room, the destined place of representation. There we may suppose our young boy distributed the several characters according to the merits of the performer. He prevailed on one of his sisters to play the part of the chambermaid. Sergeant Kite, a character of busy intrigue and bold humor, he chose for himself.

The play was acted in a manner so far above the expectation of the audience, that it gave general satisfaction, and was much applauded. The ease, vivacity, and humor of Kite are still remembered with pleasure at Lichfield. The first stage attempt of our English Roscius was in 1727.
Not long after, he was invited to Lisbon by an uncle, who was a considerable wine merchant in that city, but his stay there was very short, for he returned to Lichfield the year following. It is imagined that the gay disposition of the young gentleman was not very suitable to the old man's temper, which was, perhaps, too grave and austere to relish the vivacities of his nephew.
However, during his short stay at Lisbon, young Garrick made himself agreeable to all who knew him, particularly to the English merchants who resided there, with whom he often dined. After dinner they usually diverted themselves by placing him upon the table, and calling upon him to repeat verses and speeches from plays, which he did with great readiness, and much to the satisfaction of the hearers. Some Portuguese young gentlemen of the highest rank, who were of his own age, were also much delighted with his conversation.
He afterward returned to Lichfield, and in 1737 came up to town in company with Samuel Johnson, who was to make so conspicuous a figure in the literary world, and of whose life we have already given an account.
Soon after his arrival in London, Garrick entered himself at Lincoln's Inn, and he also put himself under the tuition of Mr. Colson, an eminent mathematician at Rochester. But as he applied himself little to the study of the law, his proficiency in mathematics and philosophy was not extensive. His mind was theatrically led, and nothing could divert his thoughts from the study of that to (p. 345) which his genius so powerfully prompted him. He had £1,000 left him by his uncle at Lisbon, and he engaged for a short time in the wine trade, in partnership with his brother, Mr. Peter Garrick; they hired vaults in Durham Yard, for the purpose of carrying on the business. The union between the brothers was of no long date. Peter was calm, sedate, and methodical; David was gay, volatile, impetuous, and perhaps not so confined to regularity as his partner could have wished. To prevent the continuance of fruitless and daily altercation, by the interposition of friends the partnership was amicably dissolved. And now Garrick prepared himself in earnest for that employment which he so ardently loved, and in which nature designed he should eminently excel.
He was frequently in the company of the most eminent actors; he got himself introduced to the managers of the theatres, and tried his talent in the recitation of some particular and favorite portions of plays. Now and then he indulged himself in the practice of mimicry, a talent which, however inferior, is never willingly resigned by him who excels in it. Sometimes he wrote criticisms upon the action and elocution of the players, and published them in the prints. These sudden effusions of his mind generally comprehended judicious observations and shrewd remarks, unmixed with that illiberality which often disgraces the instructions of stage critics.
Garrick's diffidence withheld him from trying his strength at first upon a London theatre. He thought the hazard was too great, and embraced the advantage of commencing his noviciate in acting with a company of players then ready to set out for Ipswich, under the direction of Mr. William Gifford and Mr. Dunstall, in the summer of 1741.
The first effort of his theatrical talents was exerted as Aboan, in the play of "Oroonoko," a part in which his features could not be easily discerned. Under the disguise of a black countenance, he hoped to escape being known, should it be his misfortune not to please. Though Aboan is not a first-rate character, yet the scenes of pathetic persuasion and affecting distress in which that character is involved, will always command the attention of the audience when represented by a judicious actor. Our young player's applause was equal to his most sanguine desires. Under the assumed name of Lyddal, he not only acted a variety of characters in plays, particularly Chamont, in the "Orphan;" Captain Brazen, in the "Recruiting Officer;" and Sir Harry Wildair; but he likewise gave such delight to the audience, that they gratified him with constant and loud proofs of their approbation. The town of Ipswich will long boast of having first seen and encouraged so great a genius as Garrick.
His first appearance as an actor in London, was on October 19, 1741, when he performed the part of Richard III., at the playhouse in Goodman's Fields. His easy and familiar, yet forcible, style in speaking and acting, at first threw the critics into some hesitation concerning the novelty, as well as propriety, of his manner. They had been long accustomed to an elevation of the voice, with a sudden mechanical depression of its tones, calculated to excite admiration, and to intrap applause. To the just modulation of the words, and concurring (p. 346) expression of the features from the genuine works of nature, they had been strangers, at least for some time. But after he had gone through a variety of scenes, in which he gave evident proofs of consummate art and perfect knowledge of character, their doubts were turned into surprise and astonishment, from which they relieved themselves by loud and reiterated applause. They were more especially charmed when the actor, after having thrown aside the hypocrite and politician, assumed the warrior and the hero. When news was brought to Richard that the Duke of Buckingham was taken, Garrick's look and action, when he pronounced the words
"——Off with his head!
So much for Buckingham!"
were so magnificent and important, from his visible enjoyment of the incident, that several loud shouts of approbation proclaimed the triumph of the actor and satisfaction of the audience. Richard's dream before the battle, and his death, were accompanied with the loudest gratulations of applause.
Such was the universal approbation which followed our young actor, that the more established theatres of Drury Lane and Covent Garden were deserted. Garrick drew after him the inhabitants of the most polite parts of the town: Goodman's Fields were full of the splendor of St. James' and Grosvenor Square; the coaches of the nobility filled up the space from Temple Bar to Whitechapel. He had so perfectly convinced the public of his superior accomplishments in acting, that not to admire him would not only have argued an absence of taste, but the grossest stupidity. Those who had seen and been delighted with the most admired of the old actors, confessed that he had excelled the ablest of them in the variety of the exhibitions, and equalled them all in their must applauded characters.
Alexander Pope was persuaded by Lord Orrery to see him in the first dawn of his fame. That great man, who had often seen and admired Betterton, was struck with the propriety and beauty of Mr. Garrick's action; and as a convincing proof that he had a good opinion of his merit, he told Lord Orrery that he was afraid the young man would be spoiled, for he would have no competitor.
Mr. Garrick shone forth like a theatrical Newton; he threw new light on elocution and action; he banished ranting, bombast, and grimace; and restored nature, ease, simplicity, and genuine humor.
In 1742 he entered into stated agreements with Fleetwood, patentee of Drury Lane, for the annual income of £500. His fame continued to increase at the royal theatre, and soon became so extended that a deputation was sent from Ireland, to invite him to act in Dublin during the months of June, July, and August, upon very profitable conditions. These he embraced, and crossed the seas to the metropolis of Ireland in June, 1742, accompanied by Mrs. Woffington.
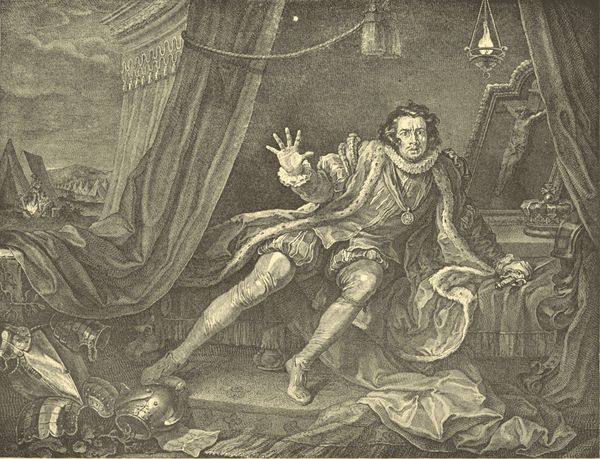

Garrick as Richard III.
His success at Dublin exceeded all imagination, though much was expected from him; he was caressed by all ranks of people as a prodigy of theatrical accomplishment. During the hottest days in the year the play-house was crowded (p. 347) with persons of fashion and rank, who were never tired with seeing and applauding the various essays of his skill.
The excessive heat became prejudicial to the frequenters of the theatre; and the epidemical distemper, which seized and carried off great numbers, was nicknamed the Garrick fever. Satisfied with the emoluments arising from the summer campaign, and delighted with the generous encouragement and kind countenance which the nobility and gentry of Ireland had given him, and of which he always spoke in the strongest terms of acknowledgment and gratitude, he set out for London, to renew his labors and to receive the applause of the most critical, as well as most candid, audience in Europe.
Such an actor as Garrick, whose name when announced in the play-bill operated like a charm and drew multitudes to the theatre, of consequence considerably augmented the profits of the patentee. But at the time when all without doors was apparently gay and splendid, and the theatre of Drury Lane seemed to be in the most flourishing condition, by the strange and absurd conduct of the manager the whole fabric was absolutely running into certain destruction.
His behavior brought on a revolt of the principal actors, with Mr. Garrick and Mr. Macklin at their head, and for some time they seceded from the theatre. They endeavored to procure a patent for a new theatre, but without success; and Garrick at length accommodated his dispute with the manager, Mr. Fleetwood, by engaging to play again for a salary of six or seven hundred pounds.
In 1744, Garrick made a second voyage to Dublin, and became joint-manager of the theatre there with Mr. Sheridan. They met with great success; and Garrick returned again to London, in May, 1746, having considerably added to his stock of money. In 1747 he became joint-patentee of Drury Lane Theatre with Mr. Lacy. Mr. Garrick and Mr. Lacy divided the business of the theatre in such a manner as not to encroach upon each other's province. Mr. Lacy took upon himself the care of the wardrobe, the scenes, and the economy of the household; while Garrick regulated the more important business of treating with authors, hiring actors, distributing parts in plays, superintending of rehearsals, etc. Besides the profits accruing from his half-share, he was allowed an income of £500 for his acting, and some particular emoluments for altering plays, farces, etc.
In 1749, Mr. Garrick was married to Mademoiselle Violetti, a young lady who (as Mr. Davies says), to great elegance of form and many polite accomplishments, joined the more amiable virtues of the mind. In 1763, 1764, and 1765, he made a journey to France and Italy, accompanied by Mrs. Garrick, who, from the day of her marriage till the death of her husband, was never separated from him for twenty-four hours. During his stay abroad his company was desired by many foreigners of high birth and great merit. He was sometimes invited to give the company a taste of that art in which he was known so greatly to excel. Such a request he very readily consented to, for indeed his compliance cost him nothing. He could, without the least preparation, transform himself into any character tragic or comic, and seize instantaneously upon any passion of the human mind. He could make a sudden transition from violent rage, and even (p. 348) madness, to the extremes of levity and humor, and go through the whole circle of theatric evolution with the most surprising velocity.
On the death of Mr. Lacy, joint patentee of Drury Lane with Mr. Garrick, in 1773, the whole management of that theatre devolved on Mr. Garrick. But in 1776, being about sixty years of age, he sold his share of the patent, and formed a resolution of quitting the stage. He was, however, determined, before he left the theatre, to give the public proofs of his abilities to delight them as highly as he had ever done in the flower and vigor of his life. To this end he presented them with some of the most capital and trying characters of Shakespeare; with Hamlet, Richard, and Lear, besides other parts which were less fatiguing. Hamlet and Lear were repeated; Richard he acted once only, and by the king's command. His Majesty was much surprised to see him, at an age so advanced, run about the field of battle with so much fire, force, and agility.
He finished his dramatic race with one of his favorite parts, with Felix, in "The Wonder a Woman Keeps a Secret." When the play was ended, Mr. Garrick advanced toward the audience, with much palpitation of mind, and visible emotion in his countenance. No premeditation whatever could prepare him for this affecting scene. He bowed—he paused—the spectators were all attention. After a short struggle of nature, he recovered from the shock he had felt, and addressed his auditors in the following words:
"Ladies and Gentlemen: It has been customary with persons under my circumstances to address you in a farewell epilogue. I had the same intention, and turned my thoughts that way; but indeed, I found myself then as incapable of writing such an epilogue, as I should be now of speaking it.
"The jingle of rhyme and the language of fiction would but ill suit my present feelings. This is to me a very awful moment; it is no less than parting forever with those from whom I have received the greatest kindness and favors, and upon the spot where that kindness and those favors were enjoyed." [Here he was unable to proceed till he was relieved by a shower of tears.]
"Whatever may be the changes of my future life, the deepest impression of your kindness will always remain here" (putting his hand on his breast) "fixed and unalterable. I will very readily agree to my successors having more skill and ability for their station than I have; but I defy them all to take more sincere, and more uninterrupted pains for your favor, or to be more truly sensible of it, than is your humble servant."
After a profound obeisance, he retired, amid the tears and acclamations of a most crowded and brilliant audience.
He died on Wednesday morning, January 20, 1779, at eight o'clock, without a groan. The disease was pronounced to be a palsy in the kidneys. On Monday, February 1st, the body of David Garrick was conveyed from his own house in the Adelphi, and most magnificently interred in Westminster Abbey, under the monument of his beloved Shakespeare. He was attended to the grave by persons of the first rank; by men illustrious for genius, and famous for science; by those who loved him living, and lamented his death.[Back to Contents]

Edwin Forrest was born in the city of Philadelphia, March 9, 1806, his father, a Scotchman, having emigrated to America during the last year of the preceding century. The boy, like many others of his profession, was designed for the ministry, and before the age of eleven the future Channing had attracted admiring listeners by the music of his voice and the aptness of his mimicry. His memory was remarkable, and he would recite whole passages of his preceptor's sermons. Perched upon a chair or stool, and crowned with the proud approval of family and friends, the young mimic filled the hearts of his listeners with fervent hopes of his coming success in the fold of their beloved church. These hopes were destined to be met with disappointment. The bias of the future leader of the American stage was only faintly outlined as yet; his hour of development was still to come.
He must have learned early the road to the theatre, permitted to go by the family, or going, perhaps, without the knowledge or consent of his seniors in the overworked household; for, before he had passed his tenth year, our young sermonizer was a member of a Thespian club, and before he was eleven he had made his appearance at one of the regular theatres in a female character, but with most disastrous results. He soon outgrew the ignominy of his first failure, however, and again and again sought to overcome its disgrace by a fresh appearance. To his appeals the irate manager lent a deaf ear. The sacred portal that leads to the enchanted ground of the stage was closed against young Forrest, the warden being instructed not to let the importunate boy pass the door. At last, in desperation, he resolved to storm the citadel, to beat down the faithful guard and to carry war into the enemy's camp. One night he dashed past the astonished guardian of the stage entrance just as the curtain fell upon one of the acts of a play. He emerged before the footlights, eluding all pursuit, dressed as a harlequin, and, before the audience had recovered from its astonishment at this (p. 350) scene not set down in the bills, the baffled, but not subdued, aspirant had delivered the lines of an epilogue in rhyme with so much effect that, before he could be seized by the astounded stage-manager and hurled from the theatre, he had attracted public notice, successfully won his surprised audience, and not only secured immunity from punishment for his temerity, but actually gained that respect in the manager's estimation which he had so long and so vainly striven to acquire.
At last Forrest was promised an appearance at the Walnut Street house, then one of the leading theatres of the country. He selected Young Norval in Home's tragedy of "Douglas," and on November 27, 1820, the future master of the American stage, then fourteen years of age—a boy in years, a man in character—announced as "A Young Gentleman of this City," surrounded by a group of veteran actors who had for many years shared the favor of the public, began a career which was as auspicious at its opening as it was splendid in its maturity. At his entrance he won the vast audience at once by the grace of his figure and the modest bearing that was natural to him. Something of that magnetism which he exercised so effectively in late years now attracted all who heard him, and made friends even before he spoke.
He was allowed to reappear as Frederick in "Lovers' Vows," repeating his first success; and on January 8, 1821, he benefited as Octavian in the "Mountaineers," a play associated with the early glories of Edmund Kean. In this year, also, he made his first and only venture as a manager, boldly taking the Prune Street Theatre, Philadelphia, and giving a successful performance of "Richard III.," which not only pleased the audience, but brought him a few dollars of profit. He made many attempts to secure a regular engagement in one of the Western circuits, where experience could be gained; and at last, after many denials, he was employed by Collins and Jones to play leading juvenile parts in their theatres in Pittsburgh, Cincinnati, and Lexington. Thus, at the age of sixteen or eighteen, Edwin Forrest enrolled himself as a regular member of a theatrical company, and broke loose from trade forever.
Of his professional progress here we have but poor accounts. He seems to have been very popular, and to have had an experience larger than he had heretofore enjoyed. He played with the elder Conway, and was affected by the grandeur of that actor's Othello, a study which served Forrest well when in late years he inherited the character.
Jane Placide, who inspired the first love of Edwin Forrest, was an actress who combined talent, beauty, and goodness. Her character would have softened the asperities of his, and led him by a calmer path to those grand elevations toward which Providence had directed his footsteps. Baffled in love, however, and believing Caldwell to be his rival and enemy, he challenged him; but was rebuked by the silent contempt of his manager, whom the impulsive and disappointed lover "posted."
The hard novitiate of Edwin Forrest was now drawing near its close. Securing a stock engagement with Charles Gilfert, manager of the Albany Theatre, he (p. 351) opened there in the early fall, and played for the first time with Edmund Kean, then on his second visit to America. The meeting with this extraordinary man and the attention he received from him were foremost among the directing influences of Forrest's life. To his last hour he never wearied of singing the praises of Kean, whose genius filled the English-speaking world with admiration. Two men more unlike in mind and body can scarcely be imagined. Until now Forrest had seen no actor who represented in perfection the impassioned school of which Kean was the master. He could not have known Cooke, even in the decline of that great tragedian's power, and the little giant was indeed a revelation. He played Iago to Kean's Othello, Titus to his Brutus, and Richmond to his Richard III.
In the interval which preceded the opening of the Bowery Theatre, New York, Forrest appeared at the Park for the benefit of Woodhull, playing Othello. He made a pronounced success, his old manager sitting in front, profanely exclaiming, "By God, the boy has made a hit!" This was a great event, as the Park was then the leading theatre of America, and its actors were the most famous and exclusive.
He opened at the Bowery Theatre in November, 1826, as Othello, and made a brilliant impression. His salary was raised from $28 to $40 per week. From this success may be traced the first absolute hold made by Edwin Forrest upon the attention of cultivated auditors and intelligent critics. The Bowery was then a very different theatre from what it afterward became, when the newsboys took forcible possession of its pit and the fire-laddies were the arbiters of public taste in its neighborhood.
An instance of Forrest's moral integrity may be told here. He had been approached by a rival manager, after his first success, and urged to secede from the Bowery and join the other house at a much larger salary. He scornfully refused to break his word, although his own interests he knew must suffer. His popularity at this time was so great that, when his contract for the season had expired, he was instantly engaged for eight nights, at a salary of two hundred dollars a night.
The success which had greeted Forrest on his first appearance in New York, was renewed in every city in the land. Fortune attended fame, and filled his pockets, as the breath of adulation filled his heart. He had paid the last penny of debt left by his father, and had seen a firm shelter raised over the head of his living family. With a patriotic feeling for all things American, Forrest, about this time, formed a plan for the encouragement or development of an American drama, which resulted in heavy money losses to himself, but produced such contributions to our stage literature as the "Gladiator," "Jack Cade," and "Metamora."[14] After five years of constant labor he felt that he had earned the right to a holiday, and he formed his plans for a two years' absence in Europe. A (p. 352) farewell banquet was tendered him by the citizens of New York, and a medal was struck in honor of the occasion. Bryant, Halleck, Leggett, Ingraham and other distinguished men were present. This was an honor which had never before been paid to an American actor.
He had been absent about two years when he landed in New York in September, 1836. On his appearance at the Walnut Street Theatre, Philadelphia, he was received with unprecedented enthusiasm. He gave six performances only, on this occasion, and each saw a repetition of the scene at the beginning of the engagement. The receipts were the largest ever known in that house.
On September 19, 1836, Forrest embarked once more for the mother country, this time with serious purpose. After a speedy and uneventful passage he reached England, and at once set about the preliminary business of his British engagement, which began October 17, 1836. He was the first really great American actor who had appeared in London as a rival of the English tragedians; for Cooper was born in England, though always regarded as belonging to the younger country. His opening part was Spartacus in the "Gladiator." The play was condemned, the actor applauded. In Othello, in Lear, and in Macbeth, he achieved instant success. He began his engagement October 17th and closed December 19th, having acted Macbeth seven times, Othello nine, and King Lear eight. A dinner at the Garrick Club was offered and accepted. Here he sat down with Charles Kemble and Macready; Sergeant Talfourd was in the chair.
It was during this engagement he met his future wife, Miss Catherine Sinclair. In the latter part of June, 1837, the marriage took place in St. Paul's Church, Covent Garden. Mr. and Mrs. Forrest soon after embarked for America. The tragedian resumed his American engagements November 15, 1837, at the old Chestnut Street Theatre, Philadelphia. Presented to his friends, his wife at once made a deep and lasting impression. Her native delicacy of mind and refinement of manners enchanted those who hoped for some such influence to be exerted in softening the rough vigor and democratic downrightness of the man. Domestic discord came too soon, however, and in an evil hour for himself, in an evil hour for his art and for the struggling drama in America, Edwin Forrest threw open the doors of his home to the scrutiny of the world, and appealed to the courts to remove the skeleton which was hidden in his closet. With the proceedings of that trial, which resulted in divorce, alimony, and separation, this memoir has nothing to do.

Forrest as Metamora.
Edwin Forrest, leaving the court-room a defeated man, was instantly raised to a popularity with the masses beyond anything even he had before experienced. He began an engagement soon after at the Broadway Theatre, opening as Damon. The house was crowded to suffocation. The engagement of sixty nights was unparalleled in the history of the American drama for length and profit. But despite the flattering applause of the multitude, life never again had for him the smiling aspect it had so often worn before. The applause which filled his ears, the wealth which flowed in upon him could not improve that temper which had never been amiable, and all the hard stories of his life belong to this period.
(p. 353) On September 20, 1852, he reappeared at the Broadway Theatre, New York. In February, 1853, "Macbeth" was produced in grand style, with new scenery and appointments. The tragedy was played on twenty consecutive nights, then by far the longest run of any Shakespearean play in America. The cast was very strong. It included Conway, Duff, Davenport, Pope, Davidge, Barry, and Madame Ponisi.
On September 17, 1860, after an absence of nearly four years, Edwin Forrest appeared again on the stage. He was engaged by James Nixon, and began his contract of one hundred nights at Niblo's Garden, New York, in the character of Hamlet. The long retirement only increased the curious interest which centred round his historic name. Upon his opening night the seats were sold at auction. His success in Philadelphia rivalled that of New York. In Boston the vast auditorium of the grandest theatre in America was found too small to contain the crowds he drew.
Severe attacks of gout were beginning to tell upon that herculean form, sapping and undermining it; and in 1865, while playing Damon at the Holiday Street Theatre, in Baltimore, the weather being very cold and the theatre open to draughts, he was seized with a sudden illness, which was followed by very serious results. Suffering the most intense agony, he was able to get to the end of the part; but when his robes were laid aside and physicians summoned, it was found to his horror that he had suffered a partial paralysis of the sciatic nerve. In an instant the sturdy gait, the proud tread of the herculean actor was forever gone; for he never regained complete control of his limb, a perceptible hobble being the legacy of the dreadful visitation. His right hand was almost powerless, and he could not hold his sword.
In 1866 he went to California, urged by the manager in San Francisco. His last engagement in New York took place in February, 1871. He played Lear and Richelieu, his two greatest parts. On the night of March 25, 1872, Forrest opened in "Lear" at the Globe Theatre, Boston. "Lear" was played six nights. During the second week he was announced for Richelieu and Virginius; but he caught a violent cold on Sunday, and labored sorely on Monday evening through the part of Richelieu. On Tuesday he repeated the performance, against the advice of friends and physicians. Rare bursts of his old power lighted up the play, but he labored piteously on against his illness and threatened pneumonia. When stimulants were offered he rejected them, declaring "that if he died to-night, he should still be his old royal self."
Announced for Virginius the following evening, he was unable to appear. A severe attack of pneumonia developed itself. He was carried to his hotel, and his last engagement was brought to an abrupt and melancholy end. As soon as he was able to move, he left Boston for his home in Philadelphia, resting on his way only a day in New York. As the summer passed away, the desire for work grew stronger and stronger, and he decided to re-enter public life, but simply as a reader of the great plays in which he had as an actor been so successful. The result was a disappointment. On December 11, 1872, he wrote to Oakes his (p. 354) last letter, saying sadly, but fondly: "God bless you ever, my dear and much-beloved friend."
When the morning of December 12th came, his servant, hearing no sound in his chamber at his general hour of rising, became alarmed, opened his master's door, and found there, cold in death upon his bed, the form of the great tragedian. His arms were crossed upon his bosom, and he seemed to be at rest. The stroke had come suddenly. With little warning, and without pain, he had passed away.
The dead man's will was found to contain several bequests to old friends and servants, and an elaborate scheme by which his fortune, in the hands of trustees, was to be applied to the erection and support of a retreat for aged actors, to be called "The Edwin Forrest Home." The idea had been long in his mind, and careful directions were drawn up for its practical working; but the trustees found themselves powerless to realize fully the hopes and wishes of the testator. A settlement had to be made to the divorced wife, who acted liberally toward the estate; but the amount withdrawn seriously crippled it, as it was deprived at once of a large sum of ready money. Other legal difficulties arose. And thus the great ambition of the tragedian to be a benefactor to his profession was destined to come almost to naught. Of this happily little he recks now. He has parted with all the cares of life, and has at last found rest.
Forrest's greatest Shakespearean parts were Lear, Othello, and Coriolanus. The first grew mellow and rich as the actor grew in years, while it still retained much of its earlier force. His Othello suffered with the decline of his faculties, although his clear conception of all he did was apparent to the end in the acting of every one of his parts. Coriolanus died with him, the last of all the Romans. He was greatest, however, in such parts as Virginius, William Tell, and Spartacus. Here his mannerisms of gait and utterance were less noticeable than in his Shakespearean characters, or were overlooked in the rugged massiveness of the creation. Hamlet, Richard, and Macbeth were out of his temperament, and added nothing to his fame; but Richelieu is said to have been one of his noblest and most impressive performances. He was in all things marked and distinctive. His obtrusive personality often destroyed the harmony of the portrait he was painting; but in his inspired moments, which were many, his touches were sublime. He passed over quiet scenes with little elaboration, and dwelt strongly upon the grand features of the characters he represented. His Lear, in the great scenes, rose to a majestic height, but fell in places almost to mediocrity. His art was unequal to his natural gifts. He was totally unlike his great contemporary and rival, Macready, whose attention to detail gave to every performance the harmony of perfect work.
This memoir may fitly close with an illustrative anecdote of the great actor. Toward the end of his professional career he was playing an engagement at St. Louis. He was very feeble in health, and his lameness was a source of great anxiety to him. Sitting at a late supper in his hotel one evening, after a performance of "King Lear," with his friend J. B. McCullough, of the Globe-Democrat, (p. 355) that gentleman remarked to him: "Mr. Forrest, I never in my life saw you play Lear so well as you did to-night." Whereupon the veteran almost indignantly replied, rising slowly and laboriously from his chair to his full height: "Play Lear! What do you mean, sir? I do not play Lear! I play Hamlet, Richard, Shylock, Virginius, if you please, but by God, sir, I am Lear!"
Nor was this wholly imaginative. Ingratitude of the basest kind had rent his soul. Old friends were gone from him; new friends were but half-hearted. His hearthstone was desolate. The public, to whom he had given his best years, was becoming impatient of his infirmities. The royalty of his powers he saw by degrees torn from his decaying form. Other kings had arisen on the stage, to whom his old subjects now showed a reverence once all his own. The mockery of his diadem only remained. A wreck of the once proud man who had despised all weakness, and had ruled his kingdom with imperial sway, he now stood alone. Broken in health and in spirit, deserted, forgotten, unkinged, he might well exclaim, "I am Lear!"[Back to Contents]

The Pilgrim Fathers figure in American pedigrees almost as frequently and persistently as Norman William and his followers appear at the trunk of our family-trees. Certainly, the Mayflower must have carried very many heads of houses across the Atlantic. It was not in the Mayflower, however, but in the Fortune, a smaller vessel, of fifty-five tons, that Robert Cushman, Nonconformist, the founder of the Cushman family in America, sailed from England, for the better enjoyment of liberty of conscience and freedom of religion. In the seventh generation from Robert Cushman appeared Elkanah Cushman, who took to wife Mary Eliza, daughter of Erasmus Babbit, Jr., lawyer, musician, and captain in the army. Of this marriage was born Charlotte Saunders Cushman, in Richmond Street, Boston, July 23, 1816, and other children.
Charlotte Cushman says of herself: "I was born a tom-boy." She had a passion for climbing trees and for breaking open dolls' heads. She could not (p. 356) make dolls' clothes, but she could manufacture their furniture—could do anything with tools. "I was very destructive to toys and clothes, tyrannical to brothers and sister, but very social, and a great favorite with other children. Imitation was a prevailing trait." The first play she ever saw was "Coriolanus," with Macready in the leading part; her second play was "The Gamester." She became noted in her school for her skill in reading aloud. Her competitors grumbled: "No wonder she can read; she goes to the theatre!" Until then she had been shy and reserved, not to say stupid, about reading aloud in school, afraid of the sound of her own voice, and unwilling to trust it; but acquaintance with the theatre loosened her tongue, as she describes it, and gave opportunity and expression to a faculty which became the ruling passion of her life. At home, as a child, she took part in an operetta founded upon the story of "Bluebeard," and played Selim, the lover, with great applause, in a large attic chamber of her father's house before an enthusiastic audience of young people.
Elkanah Cushman had been for some years a successful merchant, a member of the firm of Topliffe & Cushman, Long Wharf, Boston. But failure befell him, "attributable," writes Charlotte Cushman's biographer, Miss Stebbins, "to the infidelity of those whom he trusted as supercargoes." The family removed from Boston to Charlestown. Charlotte was placed at a public school, remaining there until she was thirteen only. Elkanah Cushman died, leaving his widow and five children with very slender means. Mrs. Cushman opened a boarding-house in Boston, and struggled hard to ward off further misfortune. It was discovered that Charlotte possessed a noble voice of almost two registers, "a full contralto and almost a full soprano; but the low voice was the natural one." The fortunes of the family seemed to rest upon the due cultivation of Charlotte's voice and upon her future as a singer. "My mother," she writes, "at great self-sacrifice gave me what opportunities for instruction she could obtain for me; and then my father's friend, Mr. R. D. Shepherd, of Shepherdstown, Va., gave me two years of the best culture that could be obtained in Boston at that time, under John Paddon, an English organist and teacher of singing." When the English singer, Mrs. Wood—better known, perhaps, as Miss Paton—visited Boston in 1835 or 1836, she needed the support of a contralto voice. Charlotte Cushman was sent for, and rehearsed duets with Mrs. Wood. The young beginner was advised to prepare herself for the operatic stage; she was assured that such a voice would "lead her to any height of fortune she coveted." She became the articled pupil of Mr. Maeder, the husband of Clara Fisher, actress and vocalist, and the musical director of Mr. and Mrs. Wood. Instructed by Maeder, Miss Cushman undertook the parts of the Countess in "The Marriage of Figaro" and Lucy Bertram in the opera of "Guy Mannering." These were her first appearances upon the stage.
Mrs. Maeder's voice was a contralto; it became necessary, therefore, to assign soprano parts to Miss Cushman. Undue stress was thus laid upon her upper notes. She was very young, and she felt the change of climate when she went on with the Maeders to New Orleans. It is likely that her powers as a singer (p. 357) had been tried too soon and too severely; her operatic career was brought to a sudden close. Her voice failed her; her upper notes departed, never to return; she was left with a weakened and limited contralto register. Alarmed and wretched, she sought counsel of Mr. Caldwell, the manager of the chief New Orleans theatre. "You ought to be an actress, and not a singer," he said, and advised her to take lessons of Mr. Barton, his leading tragedian. Her articles of apprenticeship to Maeder were cancelled. Soon she was ready to appear as Lady Macbeth on the occasion of Barton's benefit.
The season ended, she sailed for Philadelphia on her way to New York. Presently she had entered into a three years' engagement with Mr. Hamblin, the manager of the Bowery Theatre, at a salary of twenty-five dollars a week for the first year, thirty-five for the second year, and forty-five for the third. Mr. Hamblin had received excellent accounts of the actress from his friend, Mr. Barton, of New Orleans, and had heard her rehearse scenes from "Macbeth," "Jane Shore," "Venice Preserved," "The Stranger," etc. To enable her to obtain a suitable wardrobe, he became security for her with his tradespeople, deducting five dollars a week from her salary until the debt was satisfied. All promised well; independence seemed secure at last. Mrs. Cushman was sent for from Boston; she gave up her boarding-house and hastened to her daughter. Miss Cushman writes: "I got a situation for my eldest brother in a store in New York. I left my only sister in charge of a half-sister in Boston, and I took my youngest brother with me." But rheumatic fever seized the actress; she was able to act for a few nights only, and her dream of good fortune came to a disastrous close. "The Bowery Theatre was burned to the ground, with all my wardrobe, all my debt upon it, and my three years' contract ending in smoke." Grievously distressed, but not disheartened, with her family dependent upon her exertions, she accepted an engagement at the principal theatre in Albany, where she remained five months, acting all the leading characters. In September, 1837, she entered into an engagement, which endured for three years, with the manager of the Park Theatre, New York. She was required to fulfil the duties of "walking lady" and "general utility" at a salary of twenty dollars a week.
During this period of her career she performed very many characters, and toiled assiduously at her profession. It was then the custom to afford the public a great variety of performances, to change the plays nightly, and to present two and sometimes three plays upon the same evening. The actors were forever busy studying new parts, and, when they were not performing, they were rehearsing. "It was a time of hard work," writes Miss Stebbins, "of ceaseless activity, and of hard-won and scantily accorded appreciation." Miss Cushman had no choice of parts; she was not the chief actress of the company; she sustained without question all the characters the management assigned to her. Her appearance as Meg Merrilies (she acquired subsequently great favor by her performance of this character) was due to an incident—the illness of Mrs. Chippendale, the actress who usually supported the part. It was in the year 1840; the veteran Braham was to appear as Henry Bertram. A Meg Merrilies had to be (p. 358) improvised. The obscure "utility" actress was called upon to take Mrs. Chippendale's place. She might read the part if she could not commit it to memory but personate Meg Merrilies after some sort she must. She had never especially noticed the part; but as she stood at the side scene, book in hand, awaiting her moment of entrance, her ear caught the dialogue going on upon the stage between two of the gypsies, "conveying the impression that Meg was no longer to be feared or respected—that she was no longer in her right mind." This furnished her with a clew to the character, and led her to present it upon the stage as the weird and startling figure which afterward became so famous. Of course, the first performance was but a sketch of her later portrayals of Meg Merrilies, yet she made a profound impression. "I had not thought that I had done anything remarkable," she wrote, "and when a knock came at my dressing-room door, and I heard Braham's voice, my first thought was, 'Now what have I done? He is surely displeased with me about something.' Imagine my gratification, when Mr. Braham said, 'Miss Cushman, I have come to thank you for the most veritable sensation I have experienced for a long time. I give you my word, when I saw you in that first scene I felt a cold chill run all over me. Where have you learned to do anything like that?'"
During her visits to England, Miss Cushman personated Meg Merrilies more often than any other character. In America she was also famous for her performance of Nancy, in a melodrama founded upon "Oliver Twist;" but this part she did not bring with her across the Atlantic. She had first played Nancy during her "general utility" days at the Park Theatre, when the energy and pathos of her acting powerfully affected her audience, and the tradition of her success in the part long "lingered in the memory of managers, and caused them, ever and anon, as their business interests prompted, to bring great pressure to bear upon her for a reproduction of it." Mr. George Vandenhoff describes Nancy as Miss Cushman's "greatest part; fearfully natural, dreadfully intense, horribly real."
In the winter of 1842 Miss Cushman undertook the management of the Walnut Street Theatre, Philadelphia, which was then in rather a fallen state. Under her energetic rule, however, the establishment recovered its popularity. "She displayed at that day," writes Mr. George Vandenhoff—who "starred at the Walnut Street Theatre for six nights to small audiences"—"a rude, strong, uncultivated talent. It was not till after she had seen and acted with Mr. Macready—which she did the next season—that she really brought artistic study and finish to her performances." Macready arrived in New York in the autumn of 1843. He notes: "The Miss Cushman, who acted Lady Macbeth, interested me much. She has to learn her art, but she showed mind and sympathy with me—a novelty so refreshing to me on the stage." She discerned the opportunity for study and improvement presented by Macready's visit, and underwent the fatigue of acting on alternate nights in Philadelphia and New York during the term of his engagement at the Park Theatre. Her own success was very great. She wrote to her mother of her great reception: of her being called out after the play; of the (p. 359) "hats and handkerchiefs waved to me; flowers sent to me," etc. In October, 1844, she sailed for England in the packet-ship Garrick. She had little money with her. A farewell benefit taken in Boston, her native city, had not proved very productive, and she had been obliged "to make arrangements for the maintenance of her family during her absence." And with characteristic prudence she left behind her a certain sum, to be in readiness for her, in case failure in England should drive her promptly back to America.
No engagement in London had been offered her; but she received, upon her arrival, a letter from Macready, proposing that she should join a company then being formed to give representations in Paris. She thought it prudent to decline this proposal, however, so as to avoid entering into anything like rivalry with Miss Helen Faucit, the leading actress of the troupe. She visited Paris for a few days, but only to sit with the audience of the best French theatres. She returned to her dull lodgings in Covent Garden, "awaiting her destiny." She was fond, in after years, of referring to the struggles and poverty, the hopes and the despair, of her first sojourn in London. Her means were nearly exhausted. Sally, the dresser, used to relate: "Miss Cushman lived on a mutton-chop a day, and I always bought the baker's dozen of muffins for the sake of the extra one, and we ate them all, no matter how stale they were, and we never suffered from want of appetite in those days." She found herself reduced to her last sovereign, when Mr. Maddox, the manager of the Princess's Theatre, came to her with a proposal. The watchful Sally reported that he had been walking up and down the street for some time early in the morning, too early for a visit. "He is anxious," said Miss Cushman. "I can make my own terms." He wished her to appear with Forrest, the American tragedian, then visiting the London stage for the second and last time. She stipulated that she should have her opportunity first, and "alone." If successful, she was willing to appear in support of Forrest. So it was agreed.
Her first appearance upon the English stage was made on February 14, 1845; she assumed the character of Bianca, in Dean Milman's rather dull tragedy of "Fazio." Her triumph was indisputable. Her intensity and vehemence completely carried away the house. As the pit rose at Kean's Shylock, so it rose at Charlotte Cushman's Bianca. She wrote to her mother in America: "All my success put together, since I have been upon the stage, would not come near my success in London." The critics described, as the crowning effort of her performance, the energy and pathos and abandonment of her appeal to Aldabella, when the wife sacrifices her pride, and sinks, "huddled into a heap," at the feet of her rival, imploring her to save the life of Fazio. Miss Cushman, speaking of her first performance in London, was wont to relate how she was so completely overcome, not only by the excitement of the scene, but by the nervous agitation of the occasion, that she lost for the moment her self-command, and was especially grateful for the long-continued applause which gave her time to recover herself. When she slowly rose at last and faced the house again, the spectacle of its enthusiasm thrilled and impressed her in a manner she could never (p. 360) forget. The audience were standing; some had mounted on the benches; there was wild waving of hats and handkerchiefs, a storm of cheering, great showering of bouquets.
Her second character in London was Lady Macbeth, to the Macbeth of Edwin Forrest; but the American actor failed to please, and the audience gave free expression to their discontent. Greatly disgusted, Forrest withdrew, deluding himself with the belief that he was the victim of a conspiracy. Miss Cushman's success knew no abatement. She played a round of parts, assisted by James Wallack, Leigh Murray, and Mrs. Stirling, appearing now as Rosalind, now as Juliana in "The Honeymoon," as Mrs. Haller, as Beatrice, as Julia in "The Hunchback." Her second season was even more successful than her first. After a long provincial tour she appeared in December, 1845, as Romeo at the Haymarket Theatre, then under the management of Mr. Webster, her sister Susan assuming the character of Juliet. She had sent for her family to share her prosperity, and had established them in a furnished house at Bayswater.
Her success as Romeo was very great. The tragedy was played for eighty nights. Her performance won applause even from those most opposed to the representation of Shakespeare's hero by a woman. For a time her intense earnestness of speech and manner, the passion of her interviews with Juliet, the fury of her combat with Tybalt, the despair of her closing scenes, bore down all opposition, silenced criticism, and excited her audience to an extraordinary degree. She appeared afterward, but not in London, as Hamlet, following an unfortunate example set by Mrs. Siddons; and as Ion in Talfourd's tragedy of that name.
In America, toward the close of her career, she even ventured to appear as Cardinal Wolsey, obtaining great applause by her exertions in the character, and the skill and force of her impersonation. But histrionic feats of this kind trespass against good taste, do violence to the intentions of the dramatists, and are, in truth, departures from the purpose of playing. Miss Cushman had for excuse—in the first instance, at any rate—her anxiety to forward the professional interests of her sister, who, in truth, had little qualification for the stage, apart from her good looks and her graces of manner. The sisters had played together in Philadelphia in "The Genoese"—a drama written by a young American—when, to give support and encouragement to Susan in her personation of the heroine, Charlotte undertook the part of her lover. Their success prompted them to appear in "Romeo and Juliet." Other plays, in which both could appear, were afterward selected—such, for instance, as "Twelfth Night," in which Charlotte played Viola to the Olivia of Susan—so that the engagement of one might compel the engagement of the other. Susan, however, quitted the stage in 1847, to become the wife of Dr. Sheridan Muspratt, of Liverpool.

Charlotte Cushman as Mrs. Haller.
Charlotte Cushman called few new plays into being. Dramas, entitled "Infatuation," by James Kenny, in 1845, and "Duchess Elinour," by the late H. F. Chorley, in 1854, were produced for her, but were summarily condemned by the audience, being scarcely permitted indeed a second performance in either case. (p. 361) Otherwise, she did not add to her repertory. For many years she led the life of a "star," fulfilling brief engagements here and there, appearing now for a term in London, and now travelling through the provinces, playing some half a dozen characters over and over again. Of these Lady Macbeth, Queen Katherine and Meg Merrilies were perhaps the most frequently demanded. Her fame and fortune she always dated from the immediate recognition she obtained upon her first performance in London. But she made frequent visits to America; indeed, she crossed the Atlantic "upward of sixteen times," says her biographer. In 1854 she took a house in Bolton Row, Mayfair, "where for some years she dispensed the most charming and genial hospitality," and, notably, entertained Ristori on her first visit to England in 1856. Several winters she passed in Rome, occupying apartments in the Via Gregoriana, where she cordially received a host of friends and visitors of all nations. In 1859 she was called to England by her sister's fatal illness; in 1866 she was again summoned to England to attend the death-bed of her mother. In 1860 she was playing in all the chief cities of America. Three years later she again visited America, her chief object being to act for the benefit of the Sanitary Commission, and aid the sick and wounded victims of the civil war. During the late years of her life she appeared before the public more as a dramatic reader than as an actress. There were long intervals between her theatrical engagements; she seemed to quit her profession only to return to it after an interval with renewed appetite, and she incurred reproaches because of the frequency of her farewells, and the doubt that prevailed as to whether her "last appearances" were really to be the "very last." It was not until 1874, however, that she took final leave of the New York stage, amid extraordinary enthusiasm, with many poetic and other ceremonies. She was the subject of addresses in prose and verse. Mr. Bryant, after an eloquent speech, tendered her a laurel wreath bound with white ribbon resting upon a purple velvet cushion, with a suitable inscription embroidered in golden letters; a torchbearers' procession escorted her from the theatre to her hotel; she was serenaded at midnight, and in her honor Fifth Avenue blazed with fireworks. After this came farewells to Philadelphia, Boston and other cities, and to these succeeded readings all over the country. It is to be said, however, that incessant work had become a necessity with her, not because of its pecuniary results, but as a means of obtaining mental relief or comparative forgetfulness for a season. During the last five or six years of her life she was afflicted with an incurable and agonizing malady. Under most painful conditions she toiled unceasingly, moving rapidly from place to place, and passing days and nights in railway journeys. In a letter to a friend, she writes: "I do get so dreadfully depressed about myself, and all things seem so hopeless to me at those times, that I pray God to take me quickly at any moment, so that I may not torture those I love by letting them see my pain. But when the dark hour passes, and I try to forget by constant occupation that I have such a load near my heart, then it is not so bad." She died almost painlessly at last on February 18, 1876.
Charlotte Cushman may assuredly be accounted an actress of genius in right (p. 362) of her originality, her vivid power of depicting emotion, the vehemence and intensity of her histrionic manner. Her best successes were obtained in tragedy, although she possessed a keen sense of humor, and could deliver the witty speeches of Rosalind or of Beatrice with excellent point and effect. Her Meg Merrilies will probably be remembered as her most impressive achievement. It was really, as she played it, a character of her own invention; but, in truth, it taxed her intellectual resources far less than her Bianca, her Queen Katherine, or her Lady Macbeth. Her physical peculiarities no doubt limited the range of her efforts, hindered her advance as an actress, or urged her toward exceptional impersonations. Her performances lacked femininity, to use Coleridge's word; but in power to stir an audience, to touch their sympathies, to kindle their enthusiasm, and to compel their applause, she takes rank among the finest players. It only remains to add that Miss Stebbins' fervid and affecting biography of her friend admirably demonstrates that the woman was not less estimable than the actress; that Charlotte Cushman was of noble character, intellectual, large and tenderhearted, of exemplary conduct in every respect. The simple, direct earnestness of her manner upon the mimic scene, characterized her proceedings in real life. She was at once the slave and the benefactress of her family; she was devotedly fond of children; she was of liberal and generous nature; she was happiest when conferring kindness upon others; her career abounded in self-sacrifice. She pretended to few accomplishments, to little cultivation of a literary sort; but she could write, as Miss Stebbins proves, excellent letters, now grave, now gay, now reflective, now descriptive, always interesting, and altogether remarkable for sound sense and for force and skill of expression. Her death was regarded in America almost as a national catastrophe. As Miss Stebbins writes, "The press of the entire country bore witness to her greatness, and laid their tributes upon her tomb."
The following letter of good counsel from Miss Cushman to young Mr. Barton is reprinted, by permission of Messrs. Houghton, Mifflin & Co., from the "Life and Letters of Charlotte Cushman."
"I think if you have to wait for a while it will do you no harm. You seem to me quite frantic for immediate work; but teach yourself quiet and repose in the time you are waiting. With half your strength I could bear to wait and labor with myself to conquer fretting. The greatest power in the world is shown in conquest over self. More life will be worked out of you by fretting than all the stage-playing in the world. God bless you, my poor child. You have indeed trouble enough; but you have a strong and earnest spirit, and you have the true religion of labor in your heart. Therefore I have no fears for you let what will come. Let me hear from you at your leisure, and be sure you have no warmer friend than I am and wish to be."[Back to Contents]

It is told that Rachel Felix was born on March 24, 1821, at Munf, near the town of Aarau, in the Canton of Aargau, Switzerland; the burgomaster of the district simply noting in his books that upon the day stated, at the little village inn, the wife of a poor pedler had given birth to a female child. The entry included no mention of family, name, or religion, and otherwise the event was not registered in any civil or religious record. The father and mother were Abraham Felix, a Jew, born in Metz, but of German origin, and Esther Haya, his wife. They had wandered about the continent during many years, seeking a living and scarcely finding it. Several children were born to them by the wayside, as it were, on their journeyings hither and thither: Sarah in Germany, Rebecca in Lyons, Dinah in Paris, Rachel in Switzerland; and there were other infants who did not long survive their birth, succumbing to the austerities of the state of life to which they had been called. For a time, perhaps because of their numerous progeny, M. and Madame Felix settled in Lyons. Madame Felix opened a small shop and dealt in second-hand clothes; M. Felix gave lessons in German to the very few pupils he could obtain. About 1830 the family moved to Paris. They were still miserably poor. The children Sarah and Rachel, usually carrying a smaller child in their arms or wheeling it with them in a wooden cart, were sent into the streets to earn money by singing at the doors of cafes and estaminets. A musical amateur, one M. Morin, noticed the girls, questioned them, interested himself about them, and finally obtained their admission into the Government School of Sacred Music in the Rue Vaugirard. Rachel's voice did not promise much, however; as she confessed, she could not sing—she could only recite. She had received but the scantiest and meanest education; she read with difficulty; she (p. 364) was teaching herself writing by copying the manuscript of others. Presently she was studying elocution under M. St. Aulaire, an old actor retired from the Français, who took pains with the child, instructing her gratuitously and calling her "ma petite diablesse." The performances of M. St. Aulaire's pupil were occasionally witnessed by the established players, among them Monval of the Gymnase and Samson of the Comédie. Monval approved and encouraged the young actress, and upon the recommendation of Samson she entered the classes of the Conservatoire, over which he presided, with Michelot and Provost as his co-professors.
At the Conservatoire Rachel made little progress. All her efforts failed to win the good opinion of her preceptors. In despair she resolved to abandon altogether the institution, its classes and performances. She felt herself neglected, aggrieved, insulted. "Tartuffe" had been announced for representation by the pupils; she had been assigned the mute part of Flipote, the serving-maid, who simply appears upon the scene in the first act that her ears may be soundly boxed by Madame Pernelle. To this humiliation she would not submit. She hurried to her old friend, St. Aulaire, who consulted Monval, who commended her to his manager, M. Poirson. She entered into an engagement to serve the Gymnase for a term of three years upon a salary of 3,000 francs. M. Poirson was quick to perceive that she was not as so many other beginners were; that there was something new and startling about the young actress. He obtained for her first appearance, from M. Paul Duport, a little melodrama in two acts. It was called "La Vendéenne," and owed its more striking scenes to "The Heart of Midlothian." After the manner of Jeanie Deans, Géneviève, the heroine of the play, footsore and travel-stained, seeks the presence of the Empress Josephine to implore the pardon of a Vendéan peasant condemned to death for following George Cadoudal. "La Vendéenne," produced on April 24, 1837, and received with great applause, was played on sixty successive nights, but not to very crowded audiences. The press scarcely noticed the new actress. The critic of the Journal des Débats, however, while rashly affirming that Rachel was not a phenomenon and would never be extolled as a wonder, carefully noted certain of the merits and characteristics of her performance. "She was an unskilled child, but she possessed heart, soul, intellect. There was something bold, abrupt, uncouth about her aspect, gait, and manner. She was dressed simply and truthfully in the coarse woollen gown of a peasant-girl; her hands were red; her voice was harsh and untrained, but powerful; she acted without effort or exaggeration; she did not scream or gesticulate unduly; she seemed to perceive intuitively the feeling she was required to express, and could interest the audience greatly, moving them to tears. She was not pretty, but she pleased," etc. Bouffé, who witnessed this representation, observed: "What an odd little girl! Assuredly there is something in her. But her place is not here." So judged Samson also, becoming more and more aware of the merits of his former pupil. She was transferred to the Français to play the leading characters in tragedy, at a salary of 4,000 francs a year. M. Poirson did not hesitate to cancel her agreement (p. 365) with him. Indeed, he had been troubled with thinking how he could employ his new actress. She was not an ingénue of the ordinary type; she could not be classed among soubrettes. There were no parts suited to her in the light comedies of Scribe and his compeers, which constituted the chief repertory of the Gymnase.
It was on June 12, 1838, that Rachel, as Camille, in "Horace," made her first appearance upon the stage of the Théâtre Français. The receipts were but seven hundred and fifty francs; it was an unfashionable period of the year; Paris was out of town; the weather was most sultry. There were many Jews in the house, it was said, resolute to support the daughter of Israel, and her success was unequivocal; nevertheless, a large share of the applause of the night was confessedly carried off by the veteran Joanny, who played Horace. On June 16th Rachel made her second appearance, personating Emilie in the "Cinna," of Corneille. The receipts fell to five hundred and fifty francs. She repeated her performance of Camille on the 23d; the receipts were only three hundred francs! the poorest house, perhaps, she ever played to in Paris. She afterward appeared as Hermione in "Andromaque," Aménaide in "Tancrède," Eriphile in "Iphigénie," Monime in "Mithridate," and Roxane in "Bajazet," the receipts now gradually rising, until, in October, when she played Hermione for the tenth time, six thousand francs were taken at the doors, an equal amount being received in November, when, for the sixth time, she appeared as Camille. Paris was now at her feet. In 1839, called upon to play two or three times per week, she essayed but one new part, Esther, in Racine's tragedy of that name. The public was quite content that she should assume again and again the characters in which she had already triumphed. In 1840 she added to her list of impersonations Laodie and Pauline in Corneille's "Nicomède" and "Polyeucte," and Marie Stuart in Lebrun's tragedy. In 1841 she played no new parts. In 1842 she first appeared as Chimène in "Le Cid," as Ariane, and as Frédégonde in a wretched tragedy by Le Mercier.
Rachel had saved the Théâtre Français, had given back to the stage the masterpieces of the French classical drama. It was very well for Thackeray to write from Paris in 1839 that the actress had "only galvanized the corpse, not revivified.... Racine will never come to life again and cause audiences to weep as of yore." He predicted: "Ancient French tragedy, red-heeled, patched, and beperiwigged, lies in the grave, and it is only the ghost of it that the fair Jewess has raised." But it was something more than a galvanized animation that Rachel had imparted to the old drama of France. During her career of twenty years, her performances of Racine and Corneille filled the coffers of the Français, and it may be traced to her influence and example that the classic plays still keep their place upon the stage and stir the ambition of the players. But now the committee of the Français had to reckon with their leading actress, and pay the price of the prosperity she had brought them. They cancelled her engagement and offered her terms such as seemed to them liberal beyond all precedent. But the more they offered, so much the more was demanded. In the first instance, the actress being a minor, negotiations were carried on with her father, the committee (p. 366) denouncing in the bitterest terms the avarice and rapacity of M. Felix. But when Rachel became competent to deal on her own behalf, she proved herself every whit as exacting as her sire. She became a sociétaire in 1843, entitled to one of the twenty-four shares into which the profits of the institution were divided. She was rewarded, moreover, with a salary of forty-two thousand francs per annum; and it was estimated that by her performances during her congé of three or four months every year she earned a further annual income of thirty thousand francs. She met with extraordinary success upon her provincial tours; enormous profits resulted from her repeated visits to Holland and Belgium, Germany, Russia, and England. But, from first to last, Rachel's connection with the Français was an incessant quarrel. She was capricious, ungrateful, unscrupulous, extortionate. She struggled to evade her duties, to do as little as she possibly could in return for the large sums she received from the committee. She pretended to be too ill to play in Paris, the while she was always well enough to hurry away and obtain great rewards by her performances in the provinces. She wore herself out by her endless wanderings hither and thither, her continuous efforts upon the scene. She denied herself all rest, or slept in a travelling carriage to save time in her passage from one country theatre to another. Her company complained that they fell asleep as they acted, her engagements denying them proper opportunities of repose. The newspapers at one time set forth the acrimonious letters she had interchanged with the committee of the Français. Finally she tended her resignation of the position she occupied as sociétaire; the committee took legal proceedings to compel her to return to her duties; some concessions were made on either side, however, and a reconciliation was patched up.
The new tragedies, "Judith" and "Cléopatre," written for the actress by Madame de Girardin, failed to please, nor did success attend the production of M. Romand's "Catherine II.," M. Soumet's "Jeanne d'Arc," in which, to the indignation of the critics, the heroine was seen at last surrounded by real flames! or "Le Vieux de la Montagne" of M. Latour de St. Ybars. With better fortune Rachel appeared in the same author's "Virginie," and in the "Lucrèce" of Ponsard. Voltaire's "Oreste" was revived for her in 1845 that she might play Electre. She personated Racine's "Athalie" in 1847, assuming long white locks, painting furrows on her face, and disguising herself beyond recognition, in her determination to seem completely the character she had undertaken. In 1848 she played Agrippine in the "Britannicus" of Racine, and dressed in plain white muslin, and clasping the tri-colored flag to her heart, she delivered the "Marseillaise" to please the Revolutionists, lending the air strange meaning and passion by the intensity of her manner, as she half chanted, half recited the words, her voice now shrill and harsh, now deep, hollow, and reverberating—her enraptured auditors likening it in effect to distant thunder.
To the dramatists who sought to supply her with new parts, Rachel was the occasion of much chagrin and perplexity. After accepting Scribe's "Adrienne Lecouvreur" she rejected it absolutely only to resume it eagerly, however, when she learned that the leading character was to be undertaken by Mademoiselle (p. 367) Rose Chéri. His "Chandelier" having met with success, Rachel applied to De Musset for a play. She was offered, it seems, "Les Caprices de Marianne," but meantime the poet's "Bettine" failed, and the actress distrustfully turned away from him. An undertaking to appear in the "Medea" of Legouvé landed her in a protracted lawsuit. The courts condemned her in damages to the amount of two hundred francs for every day she delayed playing the part of Medea after the date fixed upon by the management for the commencement of the rehearsals of the tragedy. She paid nothing, however, for the management failed to fix any such date. M. Legouvé was only avenged in the success his play obtained, in a translated form, at the hands of Madame Ristori. In lieu of "Medea" Rachel produced "Rosemonde," a tragedy by M. Latour de St. Ybars, which failed completely. Other plays written for her were the "Valéria" of MM. Lacroix and Maquet, in which she personated two characters—the Empress Messalina and her half sister, Lysisca, a courtesan; the "Diane," of M. Augier, an imitation of Victor Hugo's "Marion Delorme;" "Lady Tartuffe," a comedy by Madame de Girardin; and "La Czarine," by M. Scribe. She appeared also in certain of the characters originally contrived for Mademoiselle Mais, such as La Tisbe in Victor Hugo's "Angelo," and the heroines of Dumas's "Mademoiselle de Belle Isle" and of "Louise de Lignerolles" by MM. Legouvé and Dinaux.
The classical drama of France has not found much favor in England and America. We are all, perhaps, apt to think with Thackeray disrespectfully of the "old tragedies—well-nigh dead, and full time too—in which half a dozen characters appear and shout sonorous Alexandrines for half a dozen hours;" or we are disposed to agree with Mr. Matthew Arnold, that their drama, being fundamentally insufficient both in substance and in form, the French, with all their gifts, have not, as we have, an adequate form for poetry of the highest class. Those who remember Rachel, however, can testify that she breathed the most ardent life into the frigid remains of Racine and Corneille, relumed them with Promethean heat, and showed them to be instinct with the truest and intensest passion—When she occupied the scene, there could be no thought of the old artificial times of hair powder and rouge, periwigs and patches, in connection with the characters she represented. Phèdre and Hermione, Pauline and Camille, interpreted by her genius, became as real and natural, warm and palpitating, as Constance or Lady Macbeth could have been when played by Mrs. Siddons, or as Juliet when impersonated by Miss O'Neill. Before Rachel came, it had been thought that the new romantic drama of MM. Hugo and Dumas, because of its greater truth to nature, had given the coup de grâce to the old classic plays; but the public, at her bidding, turned gladly from the spasms and the rant of "Angelo" and "Angèle," "Antony" and "Hernani," to the old-world stories, the formal tragedies of the seventeenth century poet-dramatists of France. The actress fairly witched her public. There was something of magic in her very presence upon the scene.
None could fail to be impressed by the aspect of the slight, pallid woman who (p. 368) seemed to gain height by reason of her slenderness, who moved toward her audience with such simple natural majesty, who wore and conducted her fluent classical draperies with such admirable and perfect grace. It was as though she had lived always so attired in tunic, peplum, and pallium—had known no other dress—not that she was of modern times playing at antiquity, she was the muse of Greek tragedy in person. The physical traditions of her race found expression or incarnation in her. Her face was of refined Judaical character—the thin nose slightly curved, the lower lip a trifle full, but the mouth exquisitely shaped, and the teeth small, white, and even. The profuse black-brown hair was smoothed and braided from the broad, low, white, somewhat over-hanging brow, beneath which in shadow the keen black eyes flashed out their lightnings, or glowed luridly like coals at a red heat. Her gestures were remarkable for their dignity and appropriateness; the long, slight arms lent themselves surprisingly to gracefulness; the beautifully formed hands, with the thin tapering fingers and the pink filbert nails, seemed always tremblingly on the alert to add significance or accent to her speeches. But there was eloquence in her very silence and complete repose. She could relate a whole history by her changes of facial expression. She possessed special powers of self-control; she was under subjection to both art and nature when she seemed to abandon herself the most absolutely to the whirlwind of her passion. There were no undue excesses of posture, movement, or tone. Her attitudes, it was once said, were those of "a Pythoness cast in bronze." Her voice thrilled and awed at its first note: it was so strangely deep, so solemnly melodious, until, stirred by passion as it were, it became thick and husky in certain of its tones; but it was always audible, articulate, and telling, whether sunk to a whisper or raised clamorously. Her declamation was superb, if, as critics reported, there had been decline in this matter during those later years of her life, to which my own acquaintance with Rachel's acting is confined. I saw her first at the Français in 1849, and I was present at her last performance at the St. James' Theatre in 1853, having in the interval witnessed her assumption of certain of her most admired characters. And it may be true, too, that, like Kean, she was more and more disposed, as the years passed, to make "points," to slur over the less important scenes, and reserve herself for a grand outburst or a vehement climax, sacrificing thus many of the subtler graces, refinements, and graduations of elocution, for which she had once been famous. To English ears, it was hardly an offence that she broke up the sing-song of the rhymed tirades of the old plays and gave them a more natural sound, regardless of the traditional methods of speech of Clairon, Le Kain, and others of the great French players of the past.

Rachel as the Muse of Greek Tragedy.
Less success than had been looked for attended Rachel's invasion of the repertory of Mlle. Mars, an actress so idolized by the Parisians that her sixty years and great portliness of form were not thought hindrances to her personation of the youthful heroines of modern comedy and drama. But Rachel's fittest occupation and her greatest triumphs were found in the classical poetic plays. She, perhaps, intellectualized too much the creations of Hugo, Dumas, and (p. 369) Scribe; gave them excess of majesty. Her histrionic style was too exalted an ideal for the conventional characters of the drama of her own time; it was even said of her that she could not speak its prose properly or tolerably. She disliked the hair-powder necessary to Adrienne Lecouvreur and Gabrielle de Belle Isle, although her beauty, for all its severity, did not lose picturesqueness in the costumes of the time of Louis XV. As Gabrielle she was more girlish and gentle, pathetic, and tender, than was her wont, while the signal fervor of her speech addressed to Richelieu, beginning, "Vous mentez, Monsieur le Duc," stirred the audience to the most excited applause.
Rachel was seen upon the stage for the last time at Charleston on December 17, 1856. She played Adrienne Lecouvreur. She had been tempted to America by the prospect of extravagant profits. It had been dinned into her ears that Jenny Lind, by thirty-eight performances in America, had realized seventeen hundred thousand francs. Why might not she, Rachel, receive as much? And then, she was eager to quit Paris. There had been strange worship there of Madame Ristori, even in the rejected part of Medea. But already Rachel's health was in a deplorable state. Her constitution, never very strong, had suffered severely from the cruel fatigues, the incessant exertions, she had undergone. It may be, too, that the deprivations and sufferings of her childhood now made themselves felt as over-due claims that could be no longer denied or deferred. She forced herself to play, in fulfilment of her engagement, but she was languid, weak, emaciated; she coughed incessantly, her strength was gone; she was dying slowly but certainly of phthisis. And she appeared before an audience that applauded her, it is true, but cared nothing for Racine and Corneille, knew little of the French language, and were urgent that she should sing the "Marseillaise" as she had sung it in 1848! It was forgotten, or it was not known in America, that the actress had long since renounced revolutionary sentiments to espouse the cause of the Second Empire. She performed all her more important characters, however, at New York, Philadelphia, and Boston. Nor was the undertaking commercially disappointing, if it did not wholly satisfy expectation. She returned to France possessed of nearly three hundred thousand francs as her share of the profits of her forty-two performances in the United States; but she returned to die. The winter of 1856 she passed at Cairo. She returned to France in the spring of 1857, but her physicians forbade her to remain long in Paris. In September she moved again to the South, finding her last retreat in the villa Sardou, at Cannet, a little village in the environs of Cannes. She lingered to January 3, 1858. The Théâtre Français closed its doors when news arrived of her death, and again on the day of her funeral. The body was embalmed and brought to Paris for interment in the cemetery of Père la Chaise, the obsequies being performed in accordance with the Jewish rites. The most eminent of the authors and actors of France were present, and funeral orations were delivered by MM. Jules Janin, Bataille, and Auguste Maquet. Victor Hugo was in exile; or, as Janin announced, the author of "Angelo" would not have withheld the tribute of his eulogy upon the sad occasion.[Back to Contents]

The great actor who has lately left the world furnished, in his own remarkable character and shining career, a striking exception to the popular tradition that men of genius are the fathers of ordinary sons. The father of Edwin Booth was in his time one of the glories of the English and American stage; but, even in his case the strict rule wavered, for his father, though not a genius, was yet a man of exceptional character; one who marked out a clear path for himself in the world, and walked in it to the end.
How far back the line of the family can be traced, or what was its origin, we do not know; but it has lately been said that the family was of Hebrew extraction, and came into England from Spain, where it had been known by the Spanish name, Cabana. The branch of the family that left Spain to live in England translated the name into the language of their new home, and from "Cabana," a shepherd's cabin, made the English equivalent, Booth.
However it may have been in this case, it was quite in the order of things that this change of name should be made. It has been done everywhere in Europe since very early times, and is doing to-day in this country by new comers from all parts of the old world.
The first of the Booths we read of in England was a silversmith, living in Bloomsbury, London, in the latter half of the last century. He had a son, Richard, who was bred to the law, but who was so imbued with the republican ideas rife at the time that he actually came to America to fight in the cause of Independence! He was taken prisoner, and carried back to England, where, not without some struggles, he again applied himself to the practice of the law, and in time made a fortune. He did not, however, forget America, and we are told that he had, hanging in his house, a portrait of Washington, which he expected all his visitors to salute.
One of the ways in which the republicans of that time showed where their sympathies lay, was in naming their children after the heroes of Greece and Rome; and accordingly we find Richard Booth calling his eldest son, Junius Brutus (p. 371) Booth, after the Roman patriot. This son was born in London, in 1796. His father was a man of scholarly tastes, and gave the boy a classical education, but it was long before he showed a marked inclination for any particular walk in life. He tried his hand at painting, sculpture, and poetry; and for a while studied law with his father. But, when the time came to choose, he gave his voice for the navy, and would have joined the brig Boxer, then fitting out for Nova Scotia. But, as war threatened between England and America, he was induced, by the strong persuasions of his father, not to run the risk of being forced to fight against America. He then decided to go upon the stage, and, in spite of his father's remonstrances, carried out his purpose. After some unimportant essays he at last succeeded in attracting public attention, and before long showed such unmistakable ability in dealing with difficult parts, that the public, till that time undivided in its enthusiasm for Kean, awoke to the fact that a dangerous rival threatened the security of their idol's throne. In the midst of his successes, however, Booth married and left England with his wife for a honeymoon trip to the West Indies. He had intended to return at once to England, but he was persuaded to prolong his journey and to visit New York. After playing a successful engagement there he went to Richmond, where he was no less prosperous. He next visited New Orleans and acquired such facility in speaking French that he played parts in French plays more than acceptably, and distinguished himself by acting Orestes in Racine's "Andromaque," to the delight of the French-speaking population. His accent is said to have been remarkable for its purity. Returning to New York, he acted Othello to Forrest's Iago; but, in the midst of his successes, the death of two of his children produced a temporary insanity, and this was made worse by the news of the death of his favorite son, Henry Byron, in London, of small-pox. This grievous loss was, however, to be made up to him by his son, Edwin, in whom he was to find the counterpart of himself, softened, refined, ennobled, while between father and son was to grow a strong attachment, a bond of mutual affection to last as long as life should endure.
Edwin Thomas Booth was born at Bel Air, Maryland, November 12, 1833. He was named Edwin, after his father's friend, Edwin Forrest, and Thomas, after Thomas Flynn, the actor, whom the elder Booth had known intimately in London. His son dropped the name of Thomas, later in life, and was only known to the public by the name of Edwin Booth. Owing to his father's wandering life Edwin had few advantages of education, but he made the most of his opportunities, and indeed was a student of good letters all his life, turning the light of all he learned from books and experience upon his art. His youth is described as reticent, and marked by a strong individuality, with a deep sympathy for his father, early manifested; his father, a much enduring, suffering man, strongly in need of sympathy, knowing to repay it, too, in kind.
Edwin Booth made his first appearance on the stage in 1849 at the Boston Museum in the youthful part of Tressil, in Colley Cibber's version of Shakespeare's "Richard III." It had been against his father's wishes that he had adopted the stage as a profession; but, as his father had done in a like case before him (p. 372) he persevered, and soon had the satisfaction of convincing his parent that he had decided wisely. He did not at once come to New York after his success in Boston, but went to Providence and to Philadelphia, acting Cassio in "Othello," and Wilford in the "Iron Chest," a part he soon made his own and in which he made his first appearance in New York, playing at the National Theatre in Chatham Street, in 1850. The next year he played Richard III. for the first time, taking the part unexpectedly to fill the place of his father, who was suddenly ill. In 1852 he went out with his father to San Francisco, where his brother, Junius Brutus Booth, Jr., was the manager of a theatre; and the father and his two sons acted together. At Sacramento, we are told that the incident occurred which led Edwin Booth to think of acting Hamlet, a part which was to become as closely associated with his name as that of Richard III. was with his father. He was dressed for the part of Jaffier in Otway's play, "Venice Preserved," when some one said to him "You look like Hamlet, why not play it?" It was, however, some time before he ventured to assume the part. In October, 1852, the father and son parted, not to meet again. The elder Booth went to New Orleans, and after playing for a week took passage in a steamboat on the Mississippi, and catching a severe cold succumbed after a few days' illness and died. For a while after his father's death Edwin suffered greatly from poverty and from the hardships of his precarious life, unsustained as he now was by the affection and encouragement of a father who, with all his faults, and in all the misfortunes brought on by serious ill-health and some aberrations that were the effect of ill-health had always been an affectionate and true friend. But a talent such as Edwin Booth possessed, united to a high character, and to a dauntless spirit, could not long be hid, and in a short time his name began to be heard of as that of one destined to great ends. In 1854 he went to Australia as a member of Laura Keene's company. He had made a deep impression in California, acting such parts as Richard III., Shylock, Macbeth, and Hamlet, and on returning there from Australia that first impression was greatly strengthened. On leaving San Francisco he received various testimonials showing the high esteem in which his acting was held by the educated part of the community; but throughout Edwin Booth's career, the interest he excited in the vast audiences that followed him was by no means confined to the self-styled "best people." Though he never "played to the gallery," the heart of the gallery was as much with him as the heart of the boxes, and he knew the value of its rapt silence as well as of its stormy voices.
In Boston, in 1857, he played Sir Giles Overreach, in Massinger's "A New Way to Pay Old Debts," and the profound impression he made in it confirmed him in his purpose to devote himself to tragic acting. The story of an actor's life is seldom eventful, and Mr. Booth's history, after his first assured success, is the record of a long line of triumphs without a failure. The most remarkable of these triumphs was at the Winter Garden Theatre in New York, where he acted Hamlet to large and ever-increasing audiences for over one hundred successive nights, that is, from November 21, 1864, to March 24, 1865. On this (p. 373) occasion a gold medal was presented to the actor by friends and admirers in New York; the list of subscribers including the names of many well-known citizens. The Winter Garden Theatre was managed by Booth and his brother-in-law, the clever actor, J. S. Clarke, until Booth bought out Clarke and assumed the entire management himself. In 1865 the terrible tragedy occurred which blighted Booth's whole after-life, and for a time drove him from the stage. He did not act again until 1866; in 1867 the theatre was destroyed by fire, and in 1868 the corner-stone of a new building, to be known as Booth's Theatre, was laid, and in a short time New York was in possession, for the first time, of a thoroughly appointed, comfortable, and handsome theatre. This building was made famous by a number of Shakespearian revivals that for beauty, magnificence, and scenic poetry have, we believe, never been equalled. We doubt if "Hamlet," "Julius Cæsar," or "Romeo and Juliet," have ever been presented with more satisfying completeness to the eye and to the imagination than in this theatre by Mr. Booth and his company. Although the theatre was in existence for thirteen years, from 1868 to 1882, when it was finally closed, Mr. Booth's management lasted only about half that time. The speculation was not a fortunate one for the actor; the expenses ate up all the profits, and Mr. Booth was bankrupted by his venture. He paid all his debts, however, and went bravely to work to build up a new fortune. He made a tour of the South, which was one long ovation, and in a season of eight weeks in San Francisco he took in $96,000.
In 1880 he went to England and remained there two years. In 1882 he visited Germany, acting in both countries with great success, and in 1883 he returned home and made a tour of America, repeating everywhere his old triumphs, and winning golden opinions from all classes of his countrymen.
Edwin Booth died in New York, June 7, 1893, at the Players' Club, where he had lived for the last few years of his life. This was a building erected by his own munificence, fitted up with luxurious completeness, and presented to a society of his professional brethren for the use and behoof of his fellow-artists, reserving for himself only the modest apartment where he chose to live, in sympathetic touch with those who still pursued the noble art he had relinquished.
Mr. Booth was twice married. By his first wife, Miss Mary Devlin, who died in 1863, he had one child, a daughter; by the second, Miss McVicker, he had no children. She died in 1881.[Back to Contents]

Joseph Jefferson, distinguished, among his other brilliant successes as an actor, as the creator for this generation of the character of Rip Van Winkle in the play dramatized from the story in Washington Irving's "Sketch Book," was the third of his name in a family of actors. The first of the three was born at Plymouth, England, in 1774. He was the son of Thomas Jefferson, a comedian of merit, the contemporary and friend of Garrick, and came to this country in 1795, making his first appearance in New York on February 10, 1796, in the part of Squire Richard in "The Provoked Husband." Dunlap says that, young as he was, he was already an artist, and that among the men of the company he held the first place. He lived in this country for thirty-six years, admired as an actor and respected as a man. He died at Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, in 1832.
Joseph Jefferson, the second, was born in Philadelphia in 1804. He inherited the laughing blue eyes and sunny disposition of his father, but he had not his talent as an actor; he is said to have been best in old men's parts. His taste, however, led him to scene-painting rather than to acting; yet his skill in either direction was not enough to win success, and, in spite of well-meant efforts, he lived and died a poor man: ill luck pursuing him to the end of his days, when he was carried off by yellow fever at Mobile in 1842, just as his unprosperous skies were brightening a little. His son bears affectionate witness to the upright character of the man and to his indomitable cheerfulness in the most adverse circumstances. He spared no pains in bringing up his children in good ways, and he was earnestly seconded by his wife, a heroic figure in her humble sphere, whose tact and courage not seldom saved the family bark when it was drifting in shoal water. Mrs. Jefferson came of French parents, and was a Mrs. Burke, a widow with one child, a son, when she married Mr. Jefferson. Her son tells us that she had been one of the most attractive stars in America, the leading prima donna of the country; but she bore her changed fortune, as the wife of an unsuccessful actor and manager, with no less dignity on the stage of real life, where no applause was to be had but what came from those who loved her as mother, wife, and friend.
This, then, was the family circle in which our Joseph Jefferson passed his (p. 375) earliest years, the formative period of his life. There were the kind-hearted, easy-going father, the practical, energetic mother, a sister, and the half-brother, Charles Burke, whose after-reputation as an actor lives in the pages of Jefferson's autobiography enshrined in words of warm but judicious appreciation. "Although only a half-brother," says Jefferson, "he seemed like a father to me, and there was a deep and strange affection between us." Nor must mention be forgotten of one other member of the family: Mary, his foster-mother, as Jefferson affectionately calls her, "a faithful, loving, truthful friend, rather than a servant, with no ambition or thought for herself, living only for us, and totally unconscious of her own existence."
Joseph Jefferson, the third of the name, and in whom the talent of his grandfather was to reappear enriched with added graces of his own, was born in Philadelphia in 1829. He tells us that his earliest recollections are connected with a theatre in Washington. This was a rickety, old, frame-building adjoining the house in which his father lived as manager, the door at the end of the hall-way opening directly upon the stage; and as a toddling little chap in a short frock he was allowed full run of the place. Thus "behind the scenes" was his first playground; and here, "in this huge and dusty toy-shop made for children of a larger growth," he got his first experience. He was early accustomed to face an audience; for, being the son of the manager and almost living in the theatre, he was always pressed into the service whenever a small child was wanted, and "often went on the stage in long clothes as a property infant in groups of happy peasantry." His first dim recollection of such a public appearance is as the "child," in Kotzebue's play, "Pizarro," who is carried across the bridge by Rolla. His next appearance was in a new entertainment, called "Living Statues," where he struck attitudes as "Ajax Defying the Lightning," or "The Dying Gladiator." At four years of age he made a hit by accompanying T. D. Rice, the original "Jim Crow," as a miniature copy of that once famous character, and the first money he earned was the sum of $24 thrown upon the stage in silver from pit and gallery, to reward his childish dancing and singing on that occasion.
Thus early wedded to the stage, Jefferson followed the fortunes of his family, and led with them a wandering life for many years, growing, by slow degrees and constant, varied practice, to the perfection of his prime. In 1838 his father led the flock to Chicago, just then grown from an Indian village to a thriving place of two thousand inhabitants, where he was to join his brother in the management of a new theatre, then building. Jefferson's account of the journey is a striking picture, at once amusing and pathetic, of the changes that have been wrought by fifty years. The real privations and hardships of the trip are veiled in the actor's story by his quiet humor and his disposition to see everything in a cheerful light. Always quizzing his own youthful follies, he cannot conceal from us by any mischievous anecdotes his essential goodness of nature, his merry helpfulness, his unselfish devotion to the welfare of the others, or the pluck with which he met the accidents of this itinerant life. From Chicago, where their success was not brilliant, the family went by stage to Springfield, where, by a singular (p. 376) chance, they were rescued from the danger that threatened them in the closing of the theatre by a municipal law trumped up in the interest of religious revivalists, by the adroitness of a young lawyer, who proved to be none other than Abraham Lincoln. In Memphis, when bad business had closed the theatre, young Jefferson's pluck and ready wit saved the family purse from absolute collapse. A city ordinance had been passed, requiring that all carts, drays, and public vehicles should be numbered; and the boy, hearing of this, called at the mayor's office, and, explaining the situation that had obliged his father to exchange acting for sign-painting, applied in his name for the contract for painting the numbers—and obtained it! The new industry furnished father and son with a month's work, and some jobs at sign-painting helped still further to make life easier.
From Memphis the family went to Mobile, where they hoped to rest after their long wanderings, and where it was also hoped the children, Joseph and his sister, might be put to school. But the yellow fever was raging in Mobile, and they had been in the city only a fortnight when Mr. Jefferson was attacked by the disease and died. In Mobile, too, the good Mary died, and Mrs. Jefferson was left alone to care for herself and her children as she could. She had no longer a heart for acting, and she decided to open a boarding-house for actors, while Joseph and his sister earned a small stipend by variety work in the theatre.
More years of hardship followed—the trio of mother and children wandering over the country, south and west: in Mississippi and Mexico, seeing life in all its phases of ill luck and disappointment, with faint gleams of success here and there, but meeting all with a spirit of such cheerful bravery as makes the darkest experience yield a pleasure in the telling. Surely, it might soften the heart of the sourest enemy of the stage to read the spirit in which this family met the long-continued crosses of their professional life.

Joe Jefferson as Bob Acres.
Joseph Jefferson tells the story of his career so modestly, that it is hard to discover just when it was that success first began to turn a smiling face upon his efforts. Yet it would seem as if, for himself, the day broke when he created the part of Asa Trenchard in "Our American Cousin." He says that up to 1858, when he acted that part, he had been always more or less a "legitimate" actor, that is, one who has his place with others in a stock company, and never thinks of himself as an individual and single attraction—a star, as it is called. While engaged with this part, it suddenly occurred to him that in acting Asa Trenchard he had, for the first time in his life on the stage, spoken a pathetic speech; up to that time all with him had been pure comedy. Now he had found a part in which he could move his audience to tears as well as smiles. This was to him a delightful discovery, and he looked about for a new part in which he could repeat the experiment. One day in summer, as he lay in the loft of a barn reading in a book he well calls delightful, Pierre Irving's "Life and Letters of Washington Irving," he learned that the great writer had seen him act the part of Goldfinch, in Holcroft's "Road to Ruin," and that he reminded him of his grandfather, Joseph Jefferson, "in look, gesture, size, and make." Naturally pleased to find (p. 377) himself remembered and written of by such a man, he lay musing on the compliment, when the "Sketch Book" and the story of Rip van Winkle came suddenly into his mind. "There was to me," he writes, "magic in the sound of the name as I repeated it. Why was not this the very character I wanted? An American story by an American author was surely just the thing suited to an American actor."
There had been three or four plays founded on this story, but Jefferson says that none of them were good. His father and his half-brother had acted the part before him, but nothing that he remembered gave him any hope that he could make a good play out of existing material. He therefore went to work to construct a play for himself, and his story of how he did it, told in two pages of his book, and with the most unconscious air in the world, reveals the whole secret of Jefferson's acting: its humor and pathos subtly mingled, its deep humanity, its pure poetry—the assemblage of qualities, in fine, that make it the most perfect as well as the most original product of the American stage.
Yet the play, even in the form he gave it, did not satisfy him, nor did it make the impression in America that he desired. It was not until five years later that Dion Boucicault, in London, remade it for Jefferson; and it was in that city it first saw the light in its new form, September 5, 1865. It was at once successful, and had a run of one hundred and seventy-five nights.
With his Asa Trenchard and his Rip van Winkle will ever be associated in the loving memory of play-goers his Bob Acres in Sheridan's "Rivals," thought by many to be his capital part—a personification where all the foibles of the would-be man-of-the-world: his self-conceit, his brag, his cowardice, are transformed into virtues and captivate our hearts, dissolved in the brimming humor which yet never overflows the just measure, so degenerating into farce.
Between the two productions of Rip van Winkle in New York and in London, Jefferson had had many strange experiences. His wife died in 1861, and he broke up his household in New York, and leaving three of his children at school in that city, he left home with his eldest son and went to California. After acting in San Francisco, he sailed for Australia, where he was warmly received; thence went to the other British colonies in that region, touched on his return at Lima and Callao and Panama, at which place he took a sailing-packet for London, and after his great success in that city returned to America in 1866. In 1867 he married, in Chicago, Miss Sarah Warren, and since that time his life has flowed on in an even stream, happy in all its relations, private and public, crowned with honors, not of a gaudy or brilliant kind, but solid and enduring. His art is henceforth part and parcel of the rich treasure of the American stage.[Back to Contents]

A consensus of opinion places this distinguished artiste at the head of all her compeers, for it may be truly said that she is the brightest star which has dazzled the musical firmament during the past half century, and, is still in the very zenith of her noonday splendor.
Regardful of the transcendent beauty of her voice, enhanced as this is by her other natural and attractive attributes, one might almost believe that nightingales have surrounded the cradle presided over by Euterpe, for never has bird sung so sweetly as the gifted subject of my memoir, and while the Fates smiled on the birth of their favorite, destined to become the unrivalled Queen of Song throughout the civilized world, fanciful natures might conceive a poetical vision, and behold Melpomene with her sad, grave eyes breathing into her the spirit of tragedy, and Thalia, with her laughing smile, welcoming a gifted disciple by whose genius her fire was to be rekindled in the far future.
In the year 1861 there arrived in England a young singer who, accompanied by her brother-in-law, took apartments in Norfolk Street, Strand. The young lady, then only seventeen, sought Mr. Frederick Gye, who was the lessee of the Royal Italian Opera, for his permission to sing at his theatre, volunteering to do so for nothing. The offer was at first absolutely declined, but subsequently the young artiste succeeded, and made her first appearance on May 14, 1861, as Amina in Bellini's opera of "La Sonnambula." Unheralded by any previous notice, she was then totally unknown to the English public. Not a syllable had reached that country of her antecedents or fame. I remember being present on the occasion when this youthful cantatrice tripped lightly on to the centre of the stage. Not a single hand was raised to greet her, nor a sound of welcome extended to encourage the young artiste. The audience of Covent Garden, usually reserved, except to old-established favorites, seemed wrapped in more than their conventional coldness on that particular evening. Ere long, however, indeed before she had finished the opening aria, a change manifested itself in the feelings of all present. The habitués looked round in astonishment, and people near me almost held their breath in amazement. The second act followed, and to surprise quickly succeeded delight, for when in the third act she threw all her vocal and dramatic power into the melodious wailing of "Ah non credea," with its brilliant sequel, "Ah non giunge," the enthusiasm of the audience forgot all restriction, and burst into a spontaneous shout of applause, the (p. 379) pent-up fervor of the assembly exploding in a ringing cheer of acclamation rarely heard within the walls of the Royal Italian Opera House. The heroine of the evening was Adelina Patti, who thenceforward became the idol of the musical world. When I left the theatre that evening, I became conscious that a course of fascination had commenced of a most unwonted nature; one that neither time nor change has modified, but which three decades have served only to enhance and intensify.
At the conclusion of the performance, Mr. Gye went on to the stage full of the excitement which prevailed in the theatre, and he immediately concluded an engagement with Mlle. Patti on the terms which had been previously agreed between them; these being that Mlle. Patti was to receive at the rate of £150 a month for three years, appearing twice each week during the season, or at the rate of about £17 for each performance. Mr. Gye also offered her the sum of £200 if she would consent to sing exclusively at Covent Garden.
Patti repeated her performance of Amina eight times during the season, and subsequently confirmed her success by her assumption of Lucia, Violetta, Zerlina, Martha, and Rosina.
Having met with such unprecedented success throughout the London season, Mlle. Patti was offered an engagement to sing at the Italian Opera in Paris, where unusual curiosity was awakened concerning her. Everyone is aware that the Parisians do not admit an artist to be a celebrity until they have themselves acknowledged it. At Paris, after the first act, the sensation was indescribable, musicians, ministers, poets, and fashionable beauties all concurring in the general chorus of acclamation; while the genial Auber, the composer of so many delightful operas, and one of the greatest authorities, by his experience and judgment, on all musical matters, was so enchanted that he declared she had made him young again, and for several days he could scarcely talk on any other subject but Adelina Patti and opera. The conquest she had achieved with the English public was thus triumphantly ratified by the exacting and critical members of musical society in Paris.
Adèle Juan Maria Patti, according to her own statement, which she related to the Queen Isabella of Spain, was born at Madrid, on February 19, 1843, and is the youngest daughter of two famous Italian singers, Signor Salvatore Patti and Signora Patti-Barili. The signor having placed her two sisters—Amalia, who subsequently married Maurice Strakosch, the well-known impresario, and Carlotta, also a vocalist of remarkable powers—in a boarding-school at Milan, went to New York with his wife and daughter, where they remained until Adelina reached sixteen.
Adelina Patti had barely reached the age of three years when she was heard humming and singing the airs her mother sang.
The child's voice was naturally so flexible that executive difficulties were always easy to her, and, before she had attained her ninth year she could execute a prolonged shake with fluency. Her father not being prosperous at the time, it became a necessity for him to look for support to his little Adelina, who had shown (p. 380) such remarkable promise; and, accordingly, she began to take singing lessons—not, as is stated in Grove's "Dictionary of Musicians," from Maurice Strakosch, but from a French lady, subsequently studying with her step-brother, Ettore Barili, who was a famous baritone singer; but nature had been so prodigal of her gifts to the child that she never undertook a serious course of study, but, as she herself says, her real master was "le bon Dieu." At a very early age she would sing and play the part of Norma, and knew the whole of the words and music of Rosina, the heroine of Rossini's immortal "Il Barbiere di Seviglia." She sang at various concerts in different cities, until she reached the age of twelve and a half, when her career was temporarily interrupted, for Maurice Strakosch, observing the ruinous effect the continuous strain upon her delicate voice was working, insisted upon her discontinuing singing altogether, which advice she happily followed. After this interval of two years' silence, and having emerged from the wonder-child to the young artiste, she recommenced her studies under M. Strakosch, and very soon afterward was engaged to sing on a regular stage. Strakosch travelled with her and Gottschalk, the pianist, through the United States, during the tour giving a number of concerts with varying financial results; ultimately returning to New York in 1859, where she appeared at a concert of which The New York Herald of November 28th gives the following notice: "One of the most remarkable events in the operatic history of the metropolis, or even of the world, has taken place during the last week at the Academy of Music. Mlle. Patti sang the mad scene from Lucia in such a superb manner as to stir up the audience to the heartiest demonstrations of delight. The success of this artiste, educated and reared among us, has made everybody talk of her." In the following year, Strakosch considered the time had arrived for her to appear in Europe. He accordingly brought his young protégée to England, with the result I have already attempted to describe.
After singing in London and Paris, Patti was engaged to appear at Berlin, Brussels, Moscow, and St. Petersburg, at which latter city enthusiasm reached its climax, when on one occasion she was called before the curtain no fewer than forty times. One who was with her there during her last visit, writes: "Having been witness of Adelina's many triumphs and of outbursts of enthusiasm bordering upon madness, I did not think that greater demonstrations were possible. I was profoundly mistaken, however, for the St. Petersburg public far surpassed anything I have seen before. On Adelina's nights extraordinary profits were made. Places for the gallery were sold for ten roubles each, while stalls were quickly disposed of for a hundred roubles each. The emperor and empress, with the whole court, took part in the brilliant reception accorded to Patti, and flowers to the amount of six thousand roubles were thrown at her."
That she has been literally worshipped from infancy upward is only a natural consequence of her unsurpassable gifts, and nowhere has this feeling manifested itself to such an extent as in Paris, and by none more so than by the four famous composers, Auber, Meyerbeer, Rossini, and Gounod. Auber, after hearing her sing Norina, in Donizetti's "Don Pasquale," offered her a bouquet of roses from (p. 381) Normandy, and in answer to her questions about her diamonds, said, "The diamonds you wear are beautiful indeed, but those you place in our ears are a thousand times better." Patti was the pet of the gifted composer of "Guillaume Tell," and no one was ever more welcome at Rossini's beautiful villa at Passy, well known as the centre of a great musical and artistic circle. The genial Italian died in November, 1868, and Patti paid her last tribute of respect to his memory by taking part in the performance of his immortal "Stabat Mater," which was given on the occasion of Rossini's burial service.
Gounod, always enthusiastic in his remarks upon her, said, "that until he heard Patti, all the Marguerites were Northern maidens, but Patti was the only Southern Gretchen, and that from her all future singers could learn what to do and avoid."
Although it is not the custom to bestow titles or honorific distinctions upon artists of the fair sex, yet, in lieu of these, to such an extent have presents been showered upon Adelina Patti, that the jewels which she has been presented with from time to time are said to be of the enormous value of £100,000. In the year 1885, when she appeared in New York as Violetta, the diamonds she wore on that occasion were estimated to be worth £60,000. One of the handsomest lockets in her possession is a present from Her Majesty, Queen Victoria, and a splendid solitaire ring which she is in the habit of wearing was given to her by the Baroness Burdett-Coutts. Of no less than twenty-three valuable bracelets, one of the most costly is that presented by the committee of the Birmingham festival. A magnificent comb, set with twenty-three large diamonds, is the gift of the Empress Eugénie. The emperors of Germany, Austria, and Russia have vied with each other in sending her jewels of the rarest value.
When singing in Italy, King Victor Emmanuel each night visited the opera for the purpose of hearing her; and at Florence, where the enthusiastic Italians applauded to the very echo, Mario, prince of Italian tenors, leaned from his box to crown her with a laurel wreath. A similar honor was bestowed upon her by the Duke of Alba at Madrid, who presented her with a laurel crown. At the opera house in that city numbers of bouquets and poems were to be seen whirling through the air attached to the necks of birds. Queen Isabella of Spain, gave a large amethyst brooch surrounded by forty enormous pearls, and the Jockey Club of Paris presented her with twelve laurel crowns. The citizens of San Francisco, upon the occasion of her last visit, presented her with a five-pointed star formed of thirty large brilliants, and from the Queen of Portugal she received a massive locket containing Her Majesty's portrait, enriched by an enormous oriental pearl encrusted in brilliants; and even at the present time scarcely a day passes without the "Diva" receiving some acknowledgment in recognition of her transcendent powers.
Adelina Patti's first husband was Henri, Marquis de Caux, an equerry to the Empress Eugénie, from whom she was separated and subsequently divorced; and, on June 10, 1886, she married Ernesto Nicolini, the famous tenor singer.
In appearance, Patti is still youthful, and really seems destined to rival the (p. 382) celebrated French beauty, Ninon de l'Enclos, who was so beautiful at sixty that the grandsons of the men who loved her in her youth adored her with equal ardor. Patti's figure is still slim and rounded, and not a wrinkle as yet is to be seen on her cheeks, or a line about her eyes, which are as clear and bright as ever, and which, when she speaks to you, look you straight in the face with her old winning smile.
During her career Patti has earned upward of half a million sterling, and the enormous sums paid to her at the present time more than double the amounts which Jenny Lind received, and which in that day were regarded as fabulous.
On a natural plateau, surrounded by picturesque vales, and situated in the heart of the very wildest and most romantic part of South Wales, between Brecon and Swansea, and at the base of the Rock of the Night, stands the Castle of Craig-y-nos. This is the nightingale's nest. The princely fortune which Patti has accumulated has enabled her so to beautify and enlarge her home, that it now contains all the luxuries which Science and Art have enabled Fortune's favorites to enjoy; and so crowded is it with curios and valuables that it may best be described as "the home of all Art yields or Nature can decree."
Here, in picturesque seclusion, surrounded by a unique splendor created by her own exertions, lives this gifted and beautiful songstress. She is the "Lady Bountiful" of the entire district, extending many miles around the castle, over which she presides with such hospitable grace. The number of grateful hearts she has won in the Welsh country by her active benevolence is almost as great as is the legion of enthusiastic admirers she has enlisted by the wonderful beauty of her voice and the series of artistic triumphs, which have been absolutely without parallel during the present century.[Back to Contents]
A little girl, as Sarcey relates, once presented herself at the Paris Conservatoire in order to pass the examination for admission. All she knew was the fable of the "Two Pigeons," but she had no sooner recited the lines—
"Deux pigeons s'aimaient d'amour tendre,
L'un d'eux, s'ennuyant au logis"—
than Auber stopped her with a gesture. "Enough," he said. "Come here, my child." The little girl, who was pale and thin, but whose eyes gleamed with intelligence, approached him with an air of assurance. "Your name is Sarah?" he said.
(p. 383) "Yes, sir." was the reply.
"You are a Jewess?"
"Yes, sir, by birth; but I have been baptized."
"She has been baptized," said Auber, turning to his colleagues. "It would have been a pity if such a pretty child had not. She said her fable of the 'Two Pigeons' very well. She must be admitted."

Thus Sarah Bernhardt, for it was she, entered the Conservatoire. She was a Jewess of French and Dutch parentage, and was born at Paris in 1844. Her father, after having her baptized, had placed her in a convent; but she had already secretly determined to become an actress. In her course of study at the Conservatoire she so distinguished herself that she received a prize which entitled her to a début at the Théâtre Français. She selected the part of Iphigénie, in which she appeared on August 11, 1862; and at least one newspaper drew special attention to her performance, describing her as "pretty and elegant," and particularly praising her perfect enunciation. She afterward played other parts at the Théâtre Français, but soon transferred herself from that house to the Gymnase, though not until she had made herself notorious by having, as was alleged, slapped the face of a sister-actress in a fit of temper.
The director of the Gymnase did not take too serious a view of his new actress, who turned up late at rehearsals, and sometimes did not turn up at all. Nor did her acting make any great impression at the Gymnase, where, it is true, she was only permitted to appear on Sundays. At this theatre she lost no time in exhibiting that independence and caprice to which, as much as to her talent, she owes her celebrity. The day after the first representation of a piece by Labiche, "Un Mari qui Lance sa Femme," in which she had undertaken an important part, she stealthily quitted Paris, addressing to the author a letter in which she begged him to forgive her.
After a tour in Spain, Sarah returned to Paris, and appeared at the Odéon. Here she created a certain number of characters, in such plays as "Les Arrêts," "Le Drame de la Rue de la Paix," and "Le Bâtard," but chiefly distinguished herself in "Ruy Blas," and in a translation of "King Lear." Already she had riveted the attention of the public and the press, who saw that a brilliant future lay before her.
At the end of 1872 she appeared at the Comédie Française, and with such distinction that she was retained, first as a pensionnaire, at a salary of six thousand francs, and afterward as a sociétaire. Her successes were rapid and dazzling, and whether she appeared in modern comedy, in classic tragedy, or as the creator of characters in entirely new plays, the theatre was always crowded. Her melodious voice and pure enunciation, her singularly varied accents, her pathos, her ardent (p. 384) bursts of passion, were such that her audience, as they hung upon her lips, forgot the caprices and eccentricities by which she was already characterized in private life. It seemed, however, that Sarah's ambition was to gain personal notoriety even more than theatrical fame; and by her performances of one kind or another outside the theatre make herself the talk of society. She affected to paint, to chisel, and to write; sent pictures to the Salon, published eccentric books, and exhibited busts. She would receive her friends palette in hand, and in the dress of a male artist. She had a luxurious coffin made for her, covered with velvet, in which she loved to recline; and she more than once went up in a balloon.
Her caprice, whether in private or public, was altogether unrestrained. In 1880 Émile Augier's admirable comedy, "L'Aventurière," was revived at the Comédie Française, and the author confided the part of Clorinde to Sarah Bernhardt. After the first representation, however, she was so enraged by an uncomplimentary newspaper criticism that she sent in her resignation to M. Émile Perrin, director of the theatre, quitted Paris, and went to England, where she gave a series of representations, and, appearing there for the first time, caused a veritable sensation in London society. Meanwhile, M. Perrin instituted against her, in the name of the Comédie Française, a lawsuit for breach of contract, with damages laid at three hundred thousand francs. It was at this juncture that Sarah accepted the offers of an enterprising manager for a tour in America, where she achieved no less phenomenal successes than in Europe.
A sensational account of this American tour was afterward published by one of her associates, Mlle. Marie Colombier, under the title of "Sarah Bernhardt en Amérique." This was followed by a second volume from the same pen, entitled "Sarah Barnum." The latter book, as its title suggests, was not intended as a compliment; and Sarah Bernhardt brought an action against the writer, by which she was compelled to expunge from her scandalous volume all that was offensive.
The rest of Sarah's career is too recent to be traced in detail. Nor can the life of an actress of our own time be dealt with so freely as that of a Sophie Arnould or an Adrienne Lecouvreur.
From America Sarah returned to Paris, where she revived all her old successes, and where, in 1888, at the Odéon, she produced a one-act comedy from her own pen, entitled "L'Aveu," which met with a somewhat frigid reception. She has appeared in several of Shakespeare's plays with great success, but her most ambitious and perhaps most admirable productions of late years have been her Cleopatra, first produced in Paris in 1890, and her Joan of Arc.
Among her numerous eccentricities, Mlle. Bernhardt once got married; London, by reason of the facilities it affords for this species of recreation, being chosen as the scene of the espousals. The hero of the matrimonial comedy, which was soon followed by a separation, to which, after many adventures on the part of both husband and wife, a reconciliation succeeded, was M. Damala, a Greek gentleman, possessed of considerable histrionic talent, who died in 1880.[Back to Contents]

TERMS OF PUBLICATION.
The work, "Great Men and Famous Women," will be published in sixty-eight parts, at twenty-five cents each; it will be printed on paper made expressly for it: each part will contain three full-page engravings, making a total of more than two hundred in the entire work, of which sixty-eight will be photogravures by Messrs. Goupil & Co., of Paris, and other eminent makers. There will be twenty-four pages of letterpress in each part.
No subscriber's name is received for less than the entire set. And no order can be cancelled after acceptance. The Publisher guarantees to complete the work in sixty-eight parts.
The parts are payable only as delivered, the carrier not being permitted to receive money in advance nor to leave parts on credit.
Subscribers who remove, or who are not regularly supplied, will please address the Publisher by mail.[Back to Contents]
Footnote 1: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 2: Giorgio Vasari, a contemporary of Titian, and himself a painter of no mean rank, wrote a series of lives of the Italian artists, from which the following is extracted. There are several slight inaccuracies in his work Titian was born, not in 1480, but in 1477, and died in 1576. He was in coloring the greatest artist who ever lived.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 3: Copyright, 1894, by Helmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 4: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 5: Reprinted by permission, from the Magazine of American History.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 6: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 7: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 8: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 9: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 10: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 11: Reprinted by permission, from the "Nation."[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 12: Our illustration represents him at Wahnfried in company with his wife Cosima, her father Franz Liszt, who was his lifelong friend, and Herr von Wolzogen.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 13: Reprinted by permission of The Cassell Publishing Company, from "Actors and Actresses of Great Britain and the United States."[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 14: Of Forrest's performance of Metamora, in the play of that name, W. R. Alger says, "Never did an actor more thoroughly identify and merge himself with his part than Forrest did in 'Metamora.' He was completely transformed from what he appeared in other characters, and seemed Indian in every particular, all through and all over, from the crown of his head to the sole of his foot."[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 15: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
Footnote 16: Copyright, 1894, by Selmar Hess.[Back to Main Text]
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Great Men and Famous Women, Vol. 8 (of
8), by Various
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK GREAT MEN AND FAMOUS WOMEN ***
***** This file should be named 29352-h.htm or 29352-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/2/9/3/5/29352/
Produced by Sigal Alon, Christine P. Travers and the Online
Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This
file was produced from images generously made available
by The Internet Archive/Canadian Libraries)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
[email protected]. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
[email protected]
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.